Alloy material for semiconductor, semiconductor chip using such alloy material, and method for manufacturing same
A technology of alloy materials and semiconductors, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, metal material coating processes, etc., can solve the problems of uneven alloy layer, reduced stability of alloy layer composition, and complicated methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1: the preparation of alloy material
[0055] Au ingots and Ag ingots were weighed so that Au and Ag had different ratios, and after melting these ingots by high-frequency melting, Au and Ag were poured into a mold to prepare an AuAg alloy material. Au and Ag with a purity of 4N were used as raw materials.
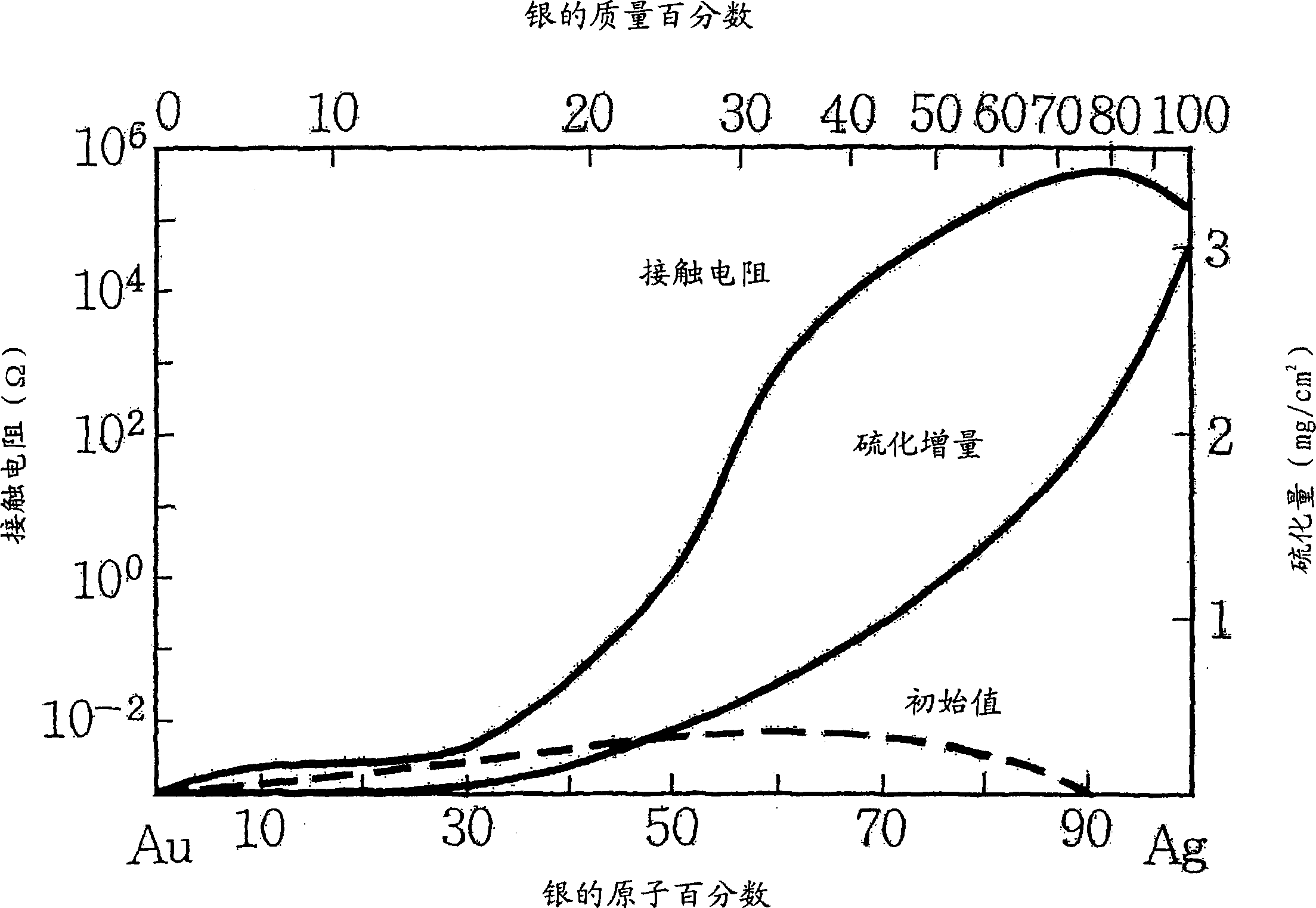
[0056] The obtained alloy materials with different compositions were made into samples with respective dimensions of about 50×20×1, and the samples were kept at 60°C, 90mmHg, H 2 S atmosphere for 10 days. The samples were then measured separately to obtain the relationship between the composition of the sample and the amount of vulcanization, and the relationship between the composition of the sample and the contact resistance. The contact resistance before and after the vulcanization test was measured by a four-terminal method. The vulcanization increment was determined from the weight of the sample before and after the vulcanization test using a prec...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2: the preparation of alloy material
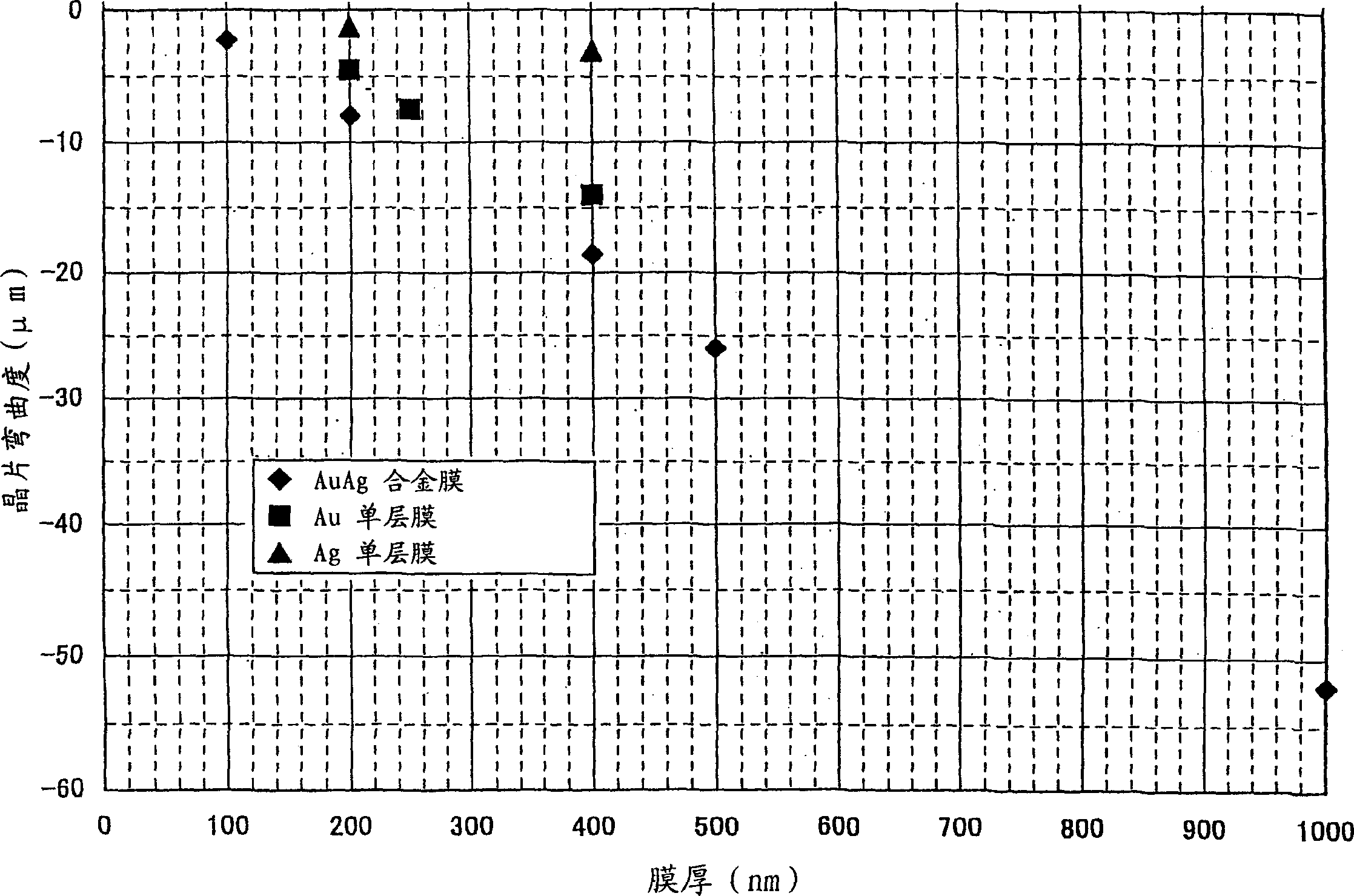
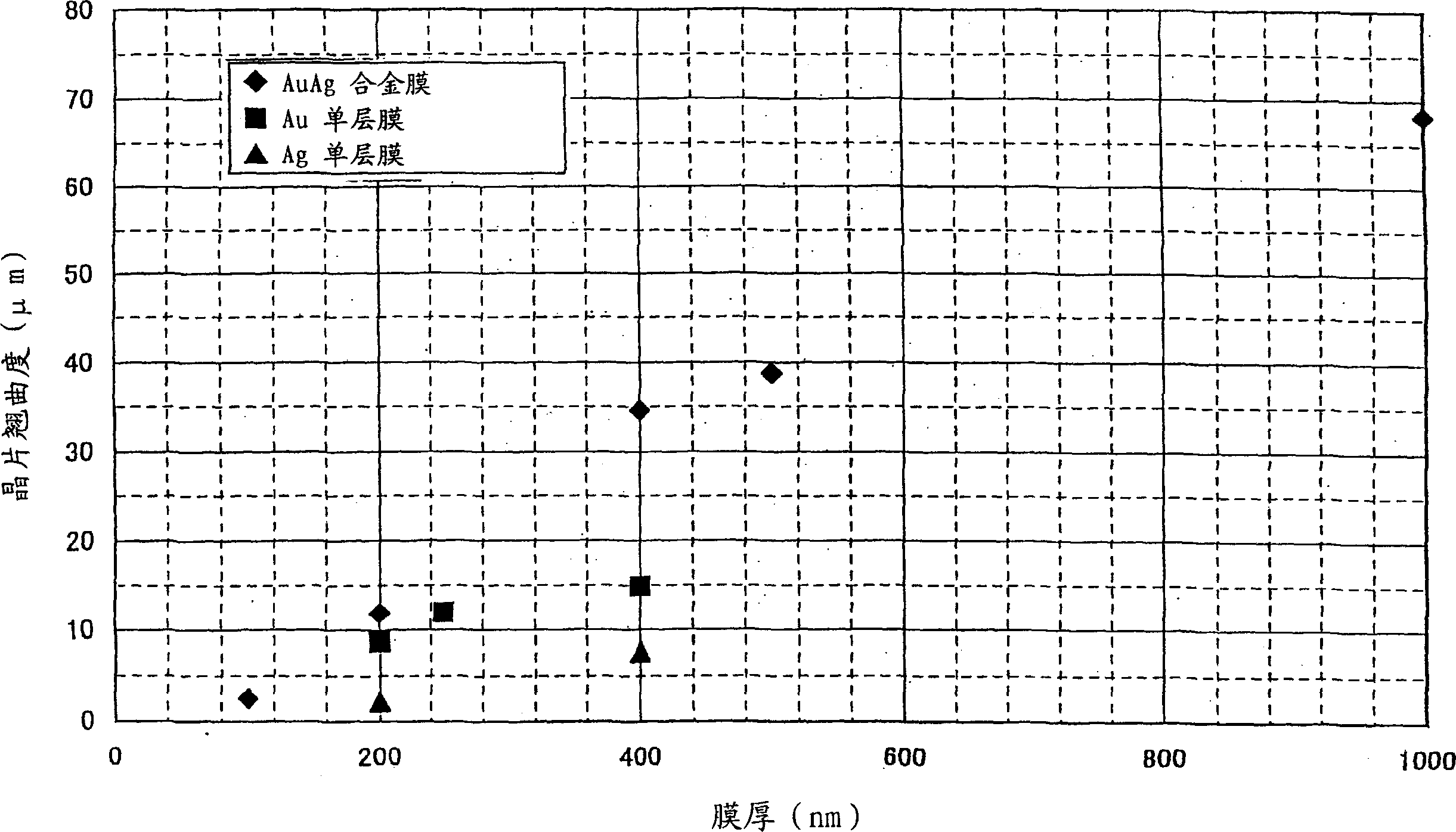
[0061] 7.5 kg of an Au ingot with a purity of 4N and 2.5 kg of an Ag ingot with a purity of 4N were put into a crucible and melted by a high-frequency melting method. Au and Ag are then poured into a mold to prepare an alloy ingot with an Au-Ag ratio of 75%-25%. The thus obtained AuAg alloy material has the machinability of Au and the ductility of Ag.
[0062] The resulting alloy ingots were rolled to form 8 mm thick plates. The plate was formed into a 250 mm diameter disk on a lathe and bonded to a backing plate made of Cu to prepare an AuAg alloy target. For comparison, Au targets and Ag targets were prepared in the same manner as AuAg alloy targets.
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3: the preparation of alloy material
[0064] AuAg alloy targets were prepared in the same manner as in Example 2, except that the proportion of Ag was set to 3 wt%, 10 wt%, and 40 wt%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com