Optimized method of controlling yaw for rotary-wing aircraft, and a system for implementing it
A rotorcraft and yaw control technology, applied in control/adjustment systems, aircraft, rotorcraft, etc., can solve problems such as crosswind control restrictions, uncomfortable driving positions, and static mode offsets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] According to one aspect of the invention, the collective pitch and yaw maps are optimized by imposing a varying bias control thereon which is a function of flight type and pilot control position.
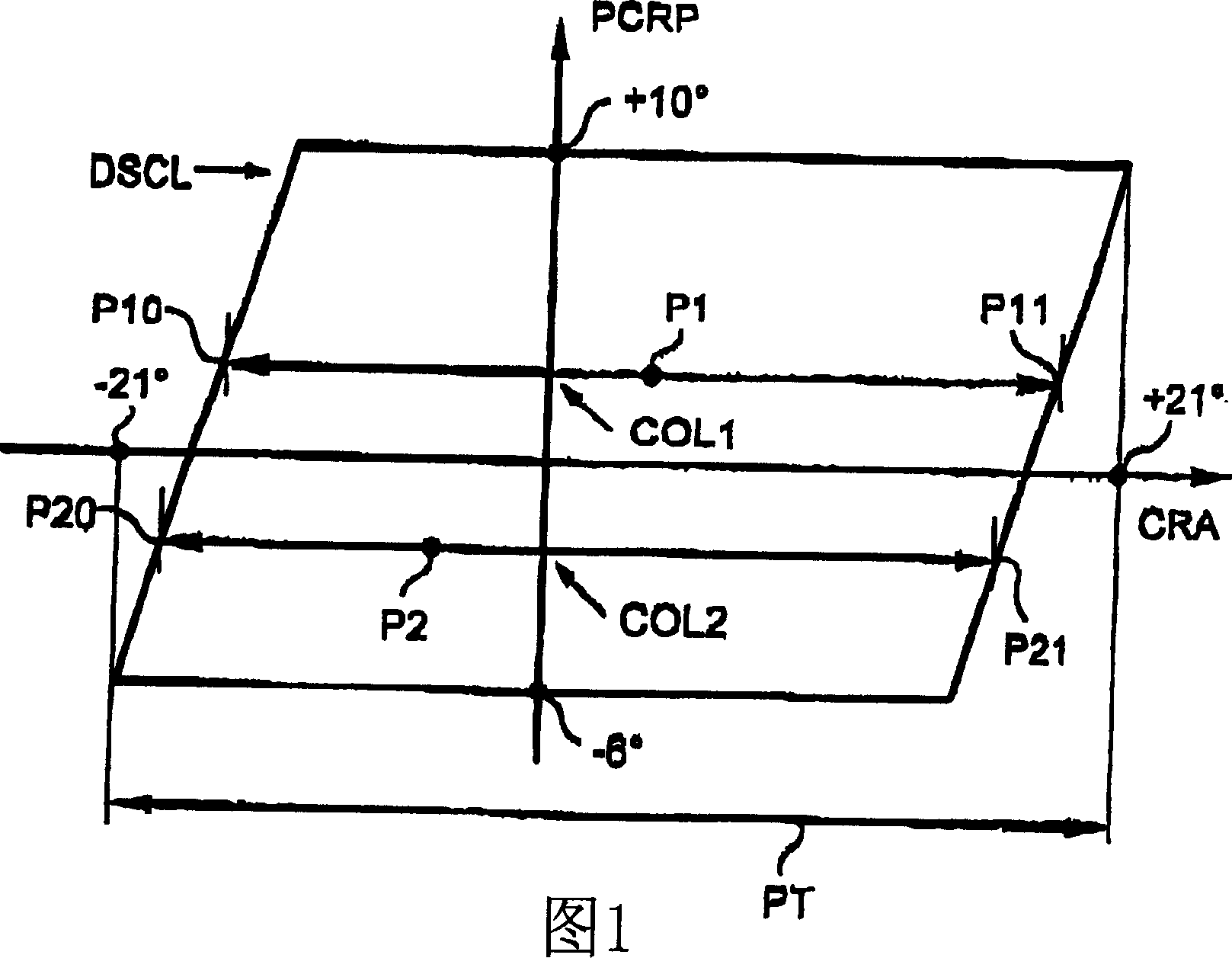
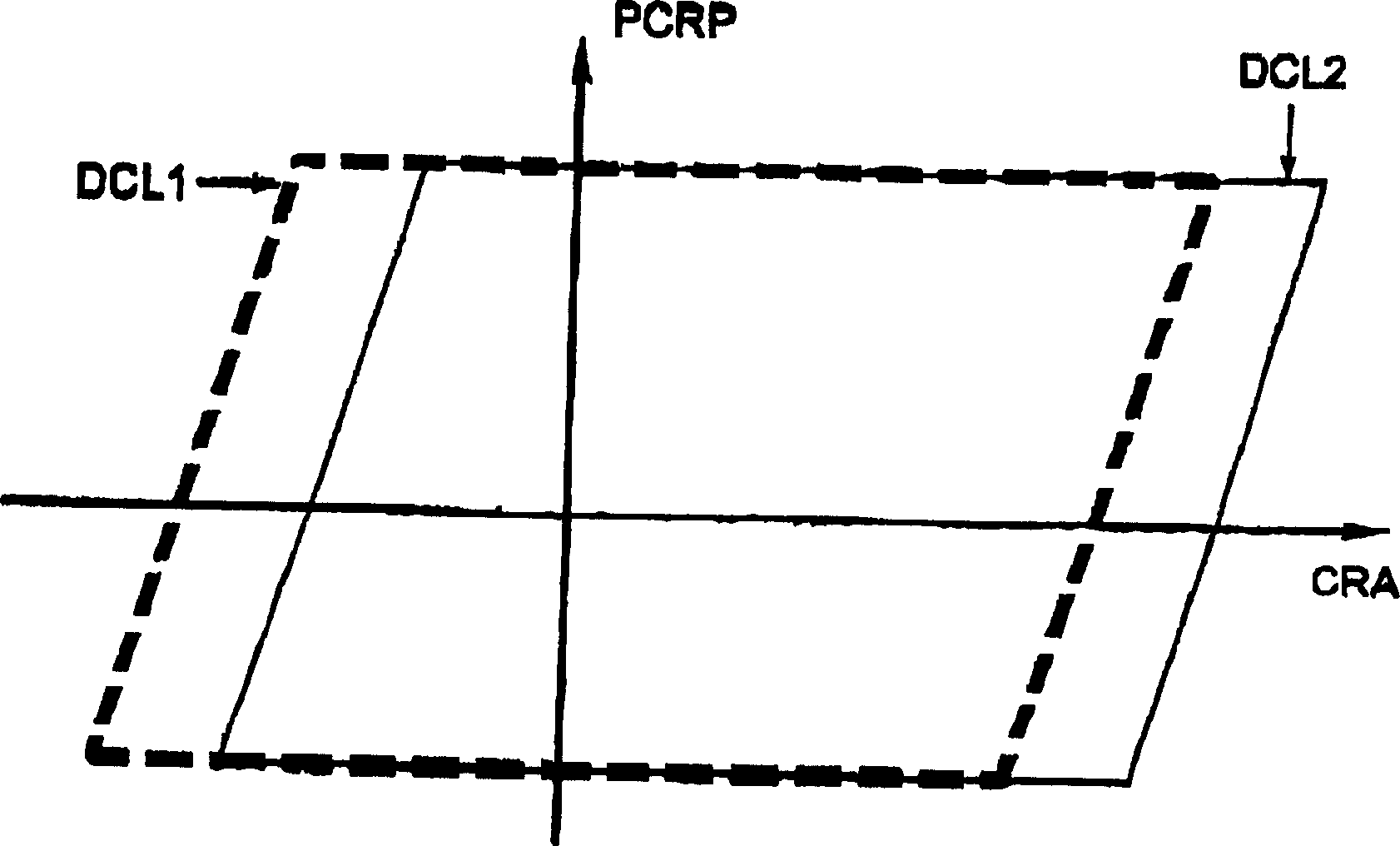
[0047] Referring to Figures 1, 2, 7 and 8, the axis of abscissa represents the magnitude of the helicopter tail rotor controlling CRA, and the axis of ordinate represents the magnitude of the main rotor collective pitch PCRP.
[0048] In the graph of FIG. 1 , the tail rotor control range P1 available to the pilot (and flight control system) for a particular collective position COL1 extends between a minimum control position P10 and a maximum control position P11 . In another collective position COL2, the tail rotor control range accessible to the pilot is a range P2 extending between a minimum control position P20 and a maximum control position P21. The switchover from P1 to P2 due to the collective pitch change from COL1 to COL2 is along the hypotenuse of the parallelogram. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com