Electro-optical device, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic apparatus using electro-optical device
An electro-optic device and manufacturing method technology, applied in optics, nonlinear optics, static indicators, etc., can solve problems such as defective products, difficulty in drawing spacers, and difficulty in homogenizing products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
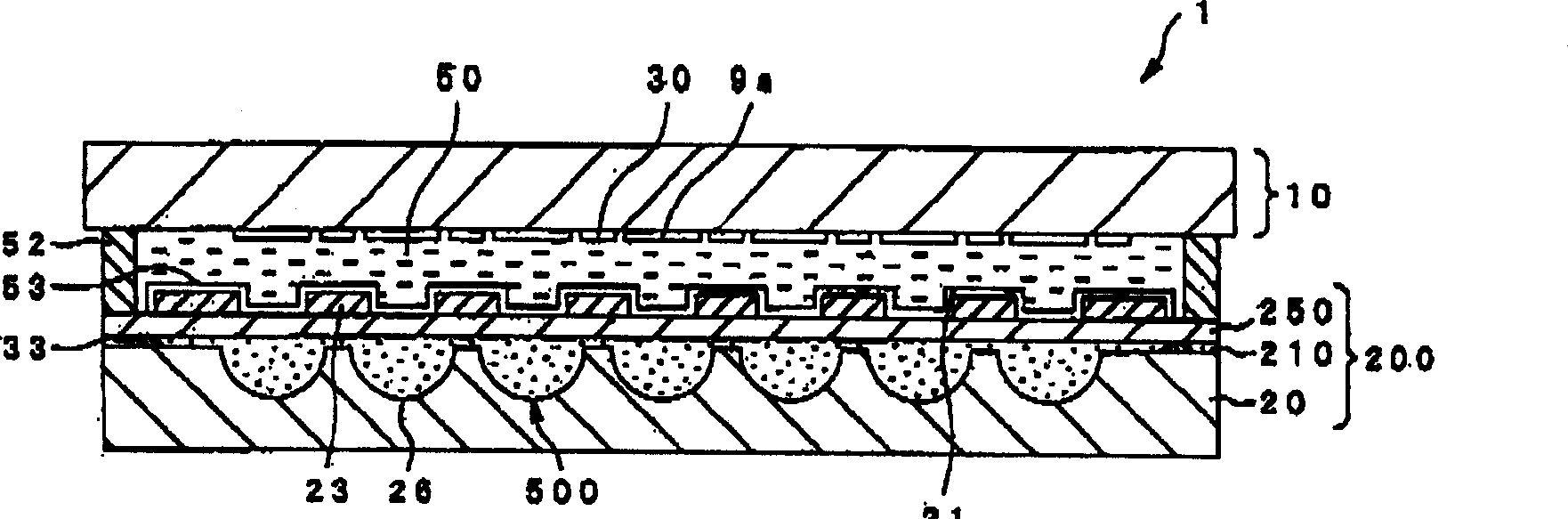
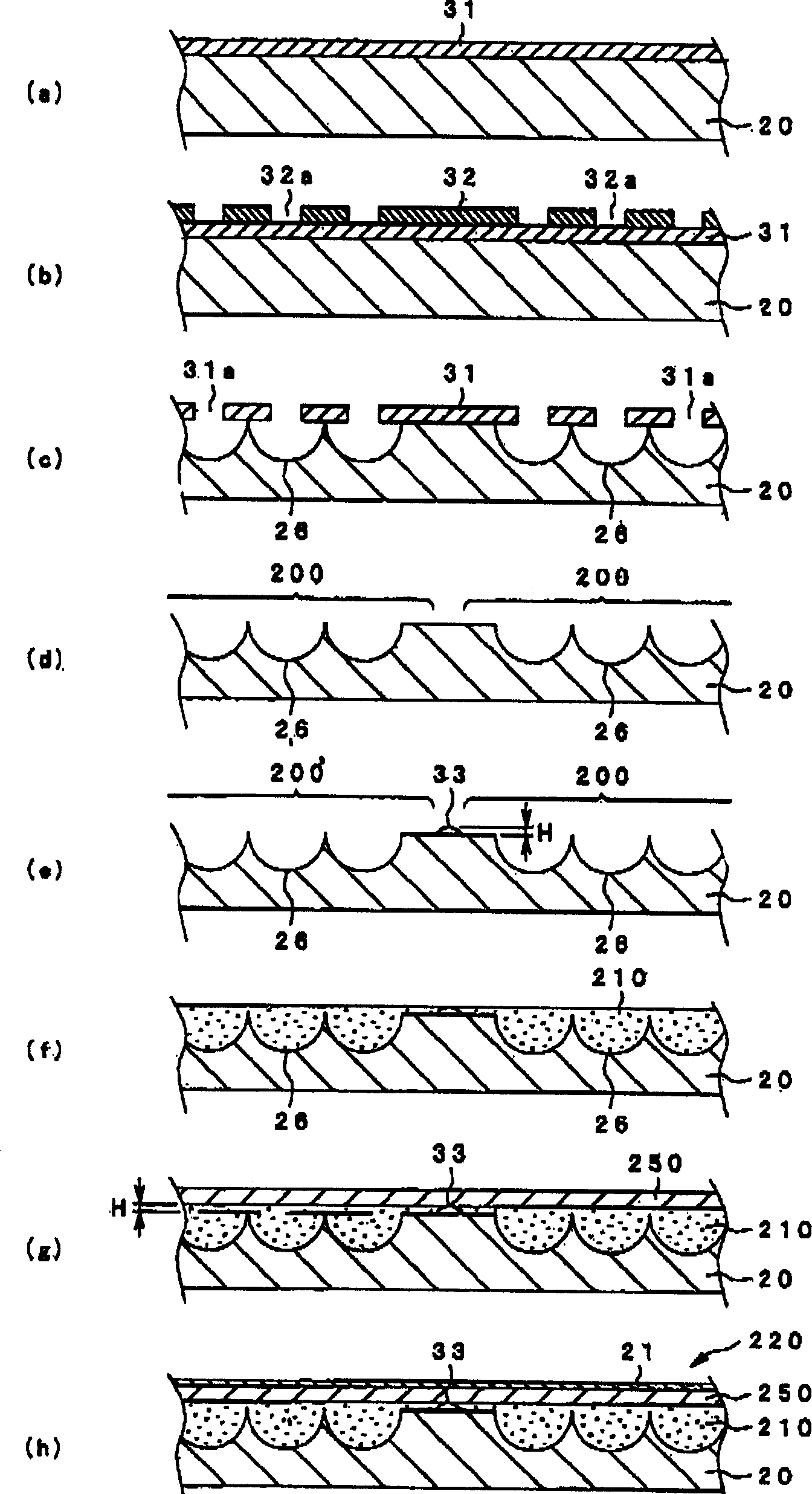
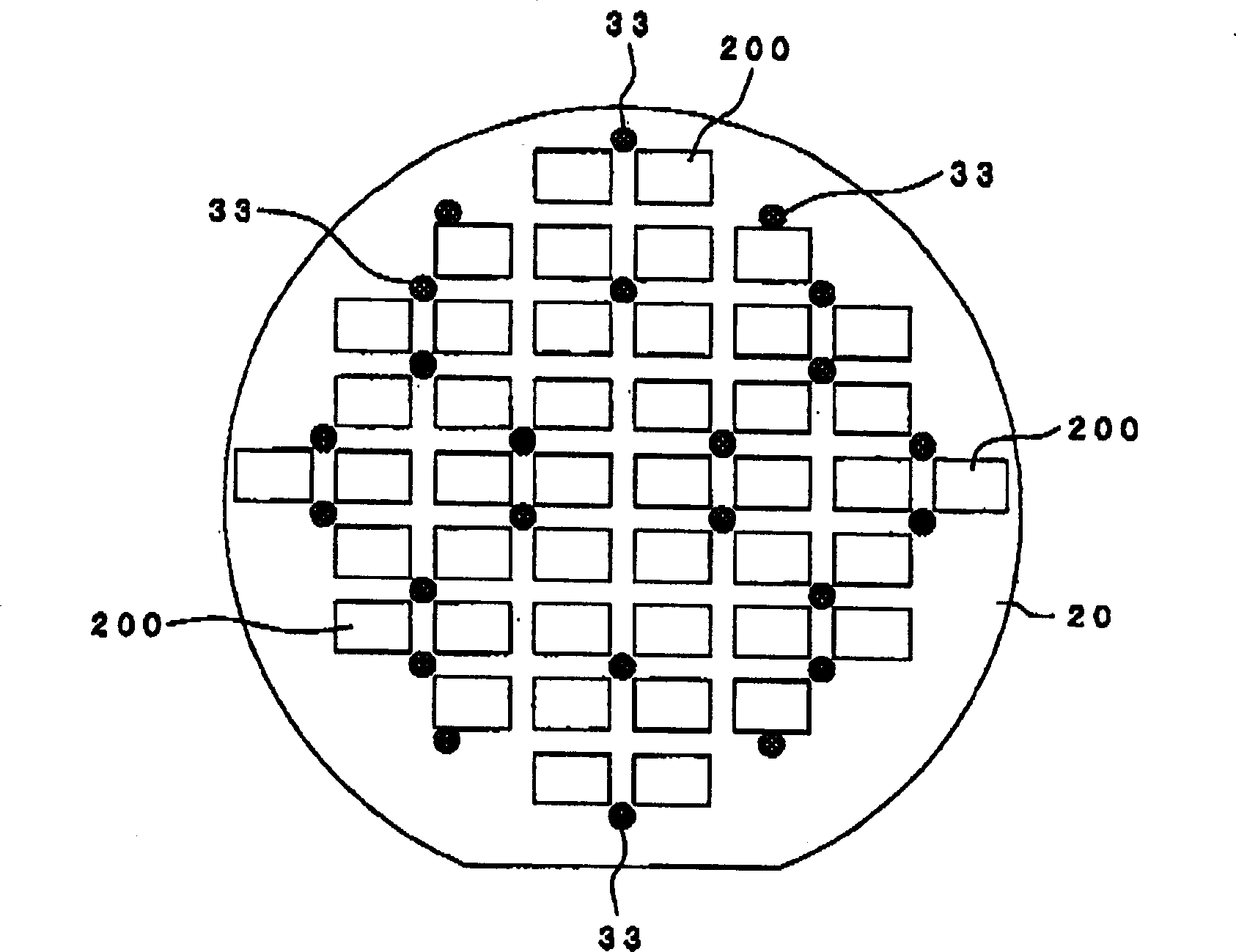
[0101] based on Figure 4 , Embodiment 1 of the method of dot-drawing the support body 33 on the lens glass substrate 20 will be specifically described. Figure 4 It is an enlarged cross-sectional view of a main part showing the drawing state of the support according to this embodiment.
[0102] In this embodiment, the curable material used as the molding material of the support body 33 is discharged from the droplet ejection device main body 300 to the surface of the lens glass substrate 20 in a predetermined amount, and when the curable material adheres to the lens glass substrate 20 Surface tension forms the support body 33 of height H.
[0103] Here, the configuration of the droplet discharge device main body 300 will be briefly described. The droplet discharge device main body 300 corresponds to a head body of an inkjet printer, and includes a piezoelectric element 301 constituting an ultrasonic wave generating unit. Electrodes (not shown) are provided on both surfaces...
Embodiment 2
[0116] based on Figure 5 , Embodiment 2 of the method of dot-drawing the support body 33 on the lens glass substrate 20 will be specifically described.
[0117]Although in the above-mentioned Embodiment 1, the height H of the support body 33 is set using the surface tension of the curable material, in this embodiment, the cured liquid mixed with the spacer 34 is discharged from the droplet discharge device main body 300 in a predetermined amount. The support body 33 is formed by drawing dots on the lens glass substrate 20 using a non-reactive material.
[0118] The curable material diluted with the solvent and the spacer 34 are supplied to the liquid agent storage portion 304 of the droplet discharge device main body 300 . The spacer 34 is made of glass fiber, glass beads, etc., and is a sphere with a particle diameter of 5 to 20 μm. In actual use, the particle diameter is determined according to the height H of the support body 33 .
[0119] Furthermore, in addition to the...
Embodiment 3
[0126] based on Figure 6 , Embodiment 3 of the method of dot-drawing the support body 33 on the lens glass substrate 20 will be specifically described.
[0127] Although in the above-mentioned second embodiment, the liquid solution mixed with the spacer 34 in the curable material is discharged from the droplet discharge device main body 300, and the support body 33 is formed on the lens glass substrate 20, but in this embodiment, the The spacer 34 is scattered on the lens glass substrate 20 , and then the support body 33 is dot-drawn on the lens glass substrate 20 with the curable material discharged from the droplet discharge device main body 300 . Therefore, only the curable material diluted with the solvent is discharged from the droplet discharge device main body 300 .
[0128] In this composition, first, if Figure 6 As shown in (a), spacers 34 are scattered throughout the lens glass substrate 20 . The particle size of the spacer 34 is determined by the height H of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com