Methods for treating post-surgical pain by admisnistering a nerve growth factor antagonist and compositions containing the same
A technology of nerve growth factor and postoperative pain, which is applied in the field of prevention, improvement or treatment of postoperative pain, and can solve the problems of not very effective pain, limited therapeutic use, sedation tolerance and addiction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0191] Anti-NGF monoclonal antibody is effective in treating postoperative pain
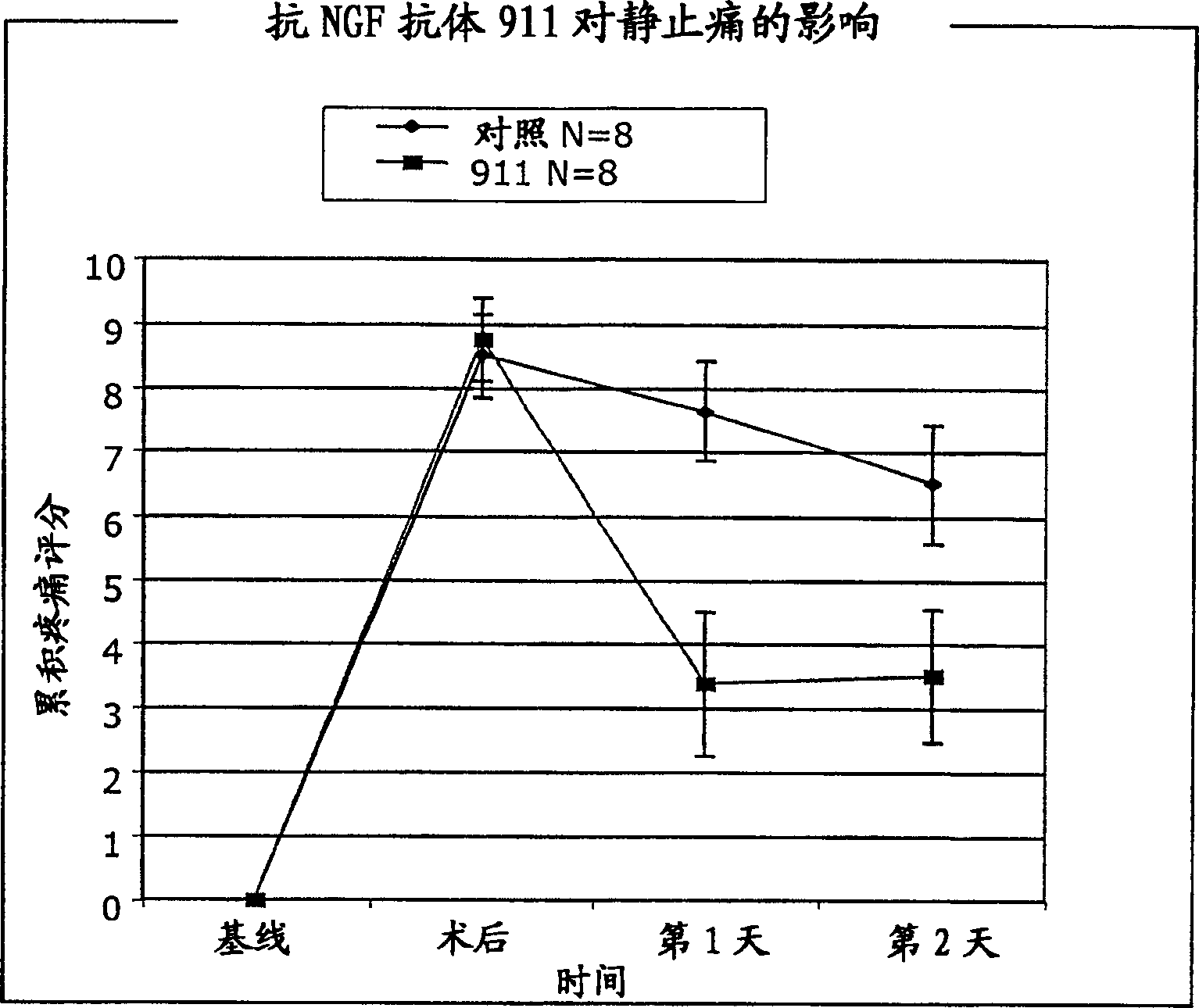
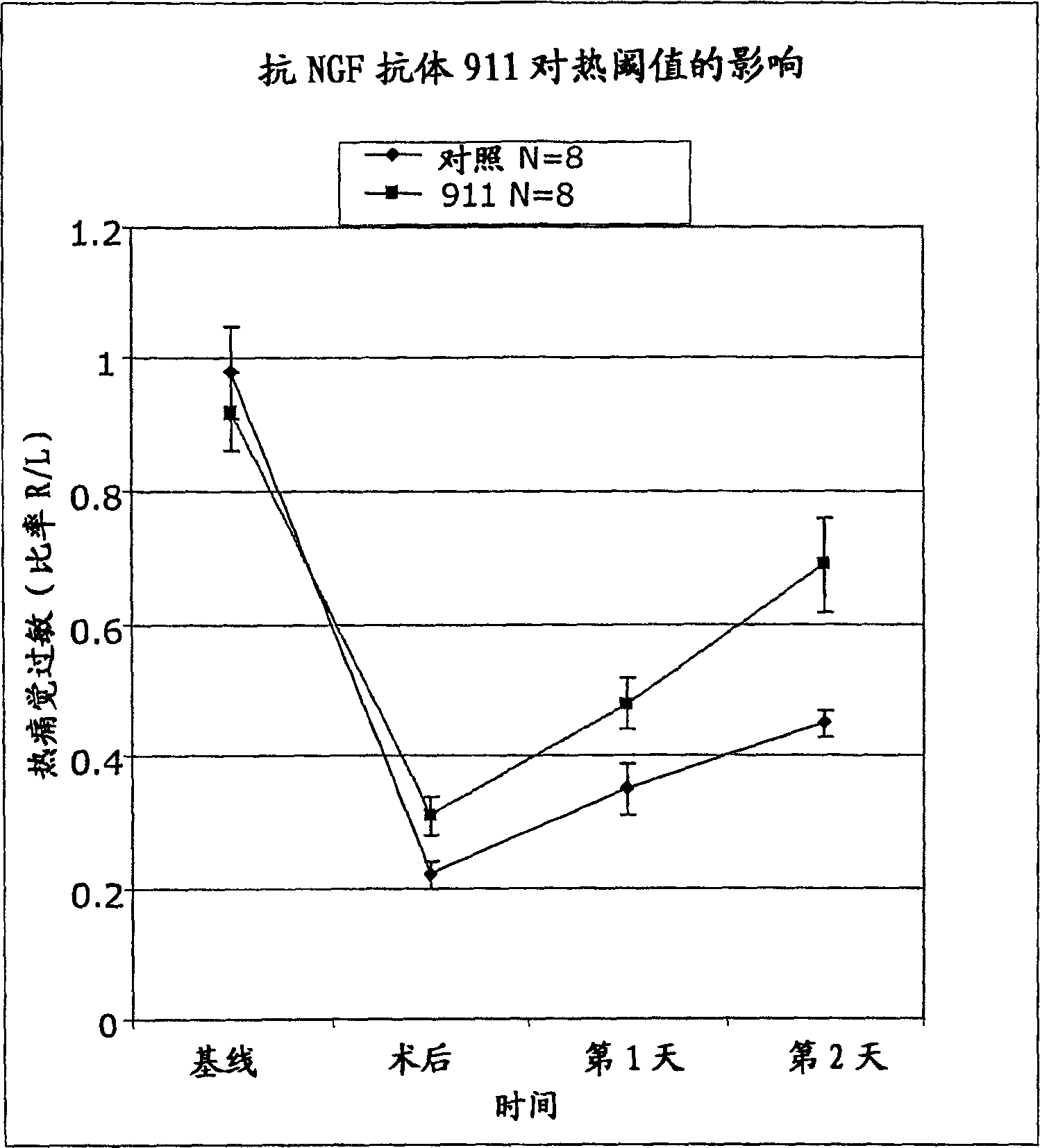
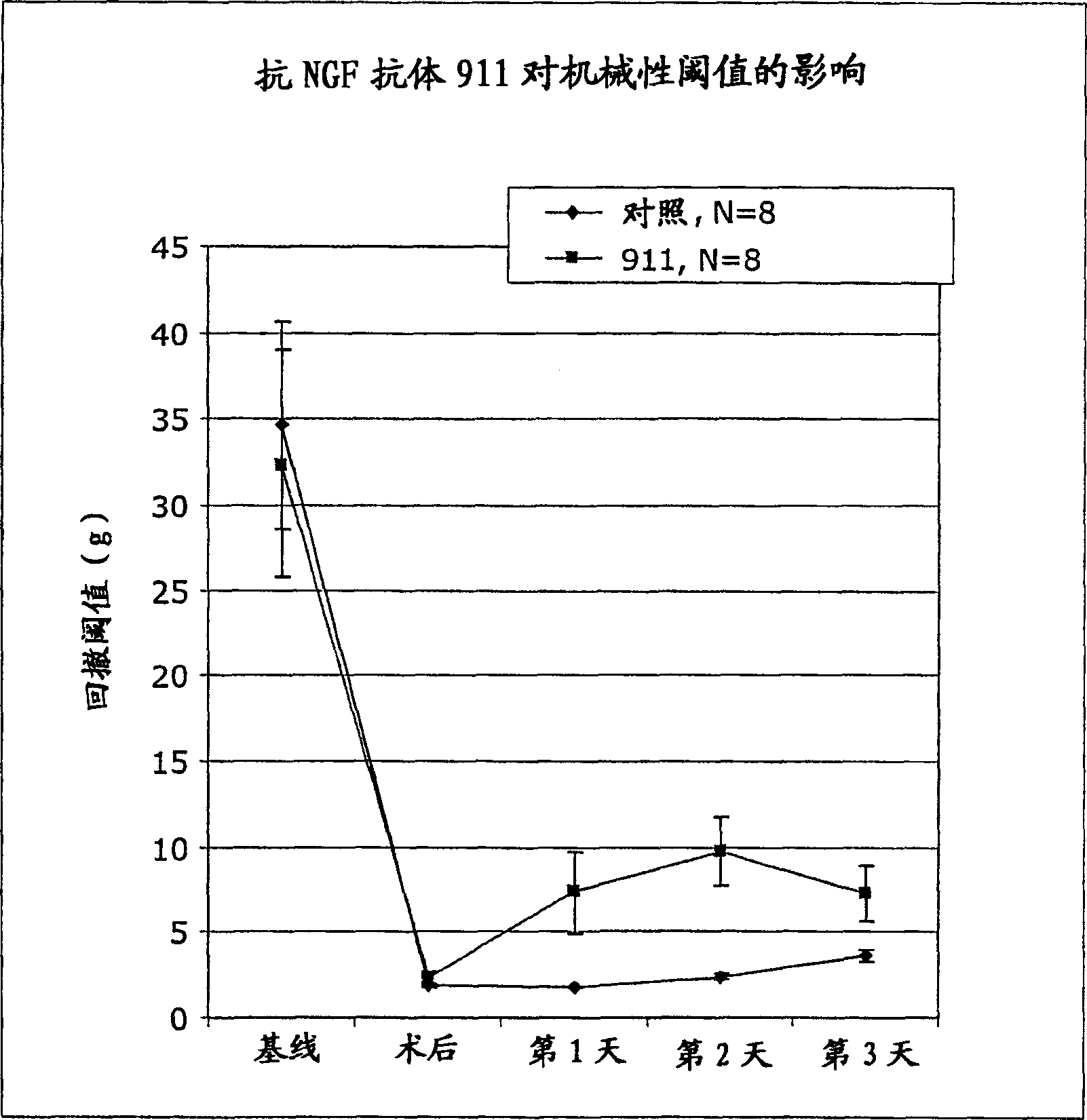
[0192] We evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of anti-NGF antibody 911 (mouse monoclonal antibody; see Hongo et al., Hybridoma 19:215-227 (2000)) using a pain model simulating postoperative pain. Each experiment included 16 animals (n=8 15 hours before cutting, the anti-NGF antibody was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.), for each test, the concentration of the antibody was different (35 or 7 mg / kg). The control group did not receive the antibody, but the intraperitoneal Saline solution is injected.
[0193] animal. Male Sprague Dawley rats weighing 220-240 grams were purchased from Harlan (San Diego) and allowed to acclimatize in the animal house for one week prior to surgery.
[0194] Operation. Surgery was performed according to the procedure disclosed by Brennan, et al., Pain 64:493-501 (1996). Animals were anesthetized with 2% isoflurane in air mixture and maintained via nose co...
Embodiment 2
[0200] Treatment of postoperative pain with humanized anti-NGF antibody and opioid therapy for postoperative pain
[0201] treatment comparison
[0202] The effect of a humanized anti-NGF antibody designated E3 on postoperative pain was examined in the animal model for postoperative pain as described in Example 1. The E3 antibody includes a human heavy chain IgG2a constant region (which contains the following mutations: A330P331 to S330S331 (amino acid numbering refers to the wild-type IgG2a sequence; see Eur. J. Immunol. (1999) 29:2613-2624)); human light chain kappa constant region; and heavy and light chain variable regions, as shown in Tables 1 and 2.
[0203] Anti-NGF antibodies were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) at various antibody concentrations (0.004, 0.01, 0.02, 0.1, 0.6 and 1 mg / kg animal body weight) 15 hours before incision. The negative control group received no antibody and was injected intraperitoneally with saline solution. Twenty-...
Embodiment 3
[0206] Preoperative and postoperative treatment of postoperative pain with anti-NGF antibodies
[0207] The efficacy of anti-NGF antibodies in reducing postoperative pain was tested in the animal model of postoperative pain described in Example 1 using male Sprague Dawley rats purchased from Harlan (Wisconsin), when administered after incision. Two hours after making the incision, humanized anti-NGF antibody E3 (0.5 mg / kg) was injected intravenously (i.v.). A control group received no antibody and received saline solution intravenously. Surgery was performed as described in Example 1, and rest pain was assessed as cumulative pain scores 24 hours after surgery. Such as Figure 5 As shown, treatment with anti-NGF antibody significantly reduced rest pain 24 hours after incision when the antibody was administered 2 hours after incision (p<0.05). These results demonstrate that anti-NGF is effective in improving postoperative pain when administered postoperatively.
[0208...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com