Oxygen electrodes
An oxygen electrode and electrode technology, applied in the field of oxygen electrodes, can solve the problems of bacteria diffusion, printing peeling, high cost, etc., and achieve the effects of improving measurement accuracy, good adhesion, and reducing pinholes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
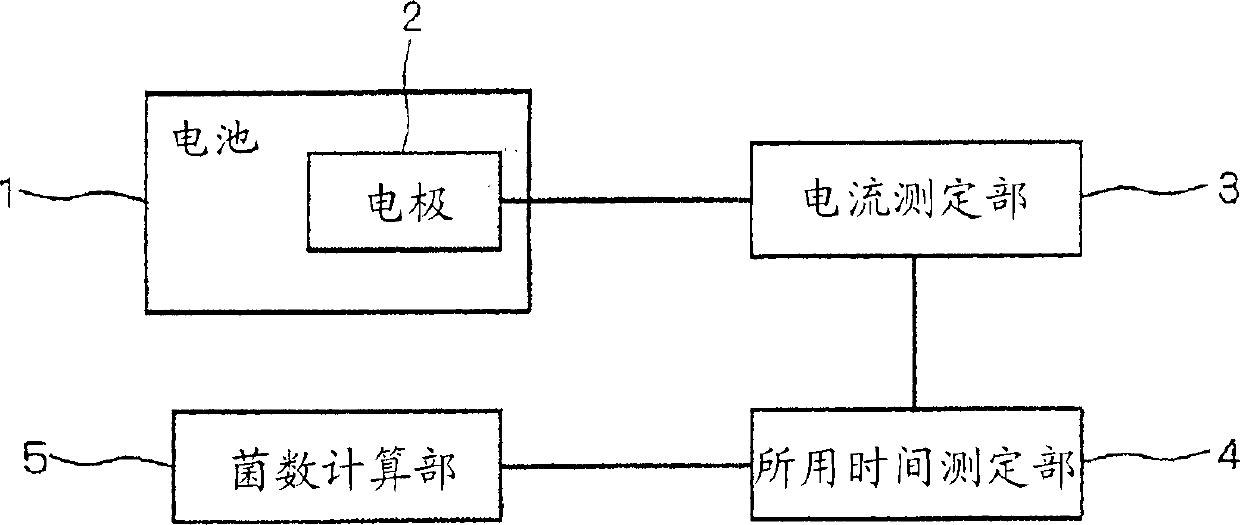
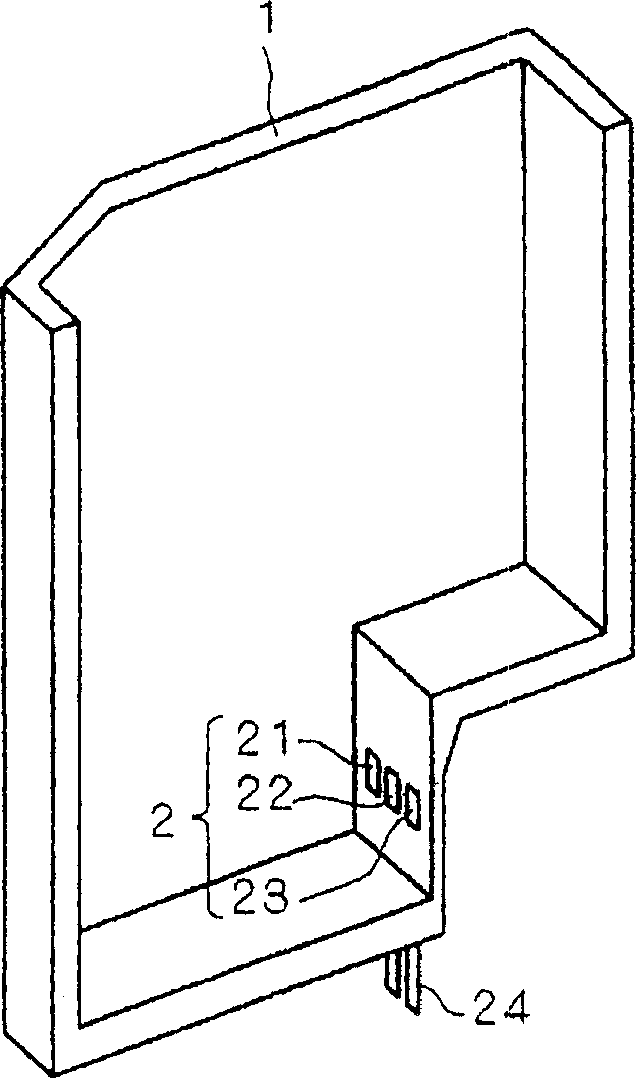
[0040] FIG. 1 shows a block diagram of a bacteria count measuring device using an oxygen electrode according to the present embodiment. A battery 1 is provided in this bacterial count measuring device, and a culture medium to which a sample is added is stored in the battery 1 . Furthermore, an oxygen electrode 2 used in the oxygen electrode method is provided in the battery 1 . FIG. 2 shows a cross-sectional perspective view of the battery 1 . Three electrodes constituting the oxygen electrode 2 are provided on the side wall near the bottom of the battery 1 , namely the counter electrode 21 , the working electrode 22 and the reference electrode 23 . Furthermore, the battery 1 is provided with an output terminal 24 electrically connected to the counter electrode 21 , the working electrode 22 , and the reference electrode 23 , and the oxygen electrode 2 is connected to the current measuring unit 3 through the output terminal 24 .
[0041] In the current measuring unit 3 in FIG...
Embodiment approach 2
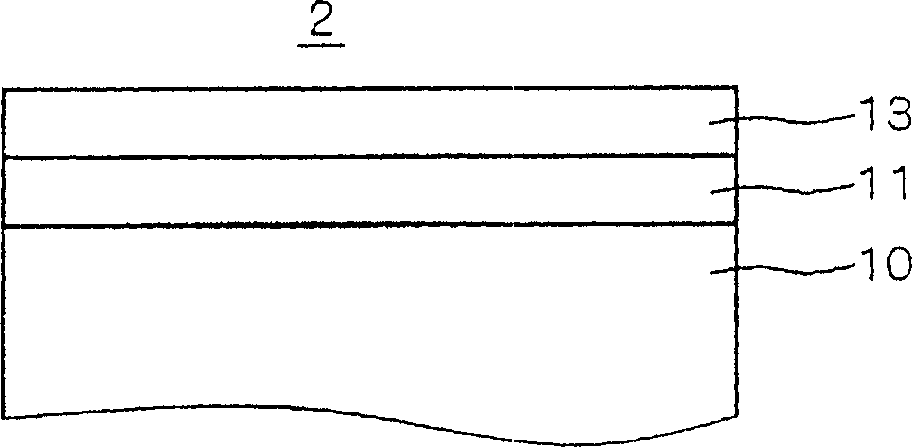
[0056] Since the oxygen electrode 2 according to the first embodiment is composed of the copper electrode base material 10 - the nickel layer 11 - the Au layer 13, the oxygen electrode can be formed at low cost. However, when the nickel layer 11 is deposited on the surface of the electrode base material 10 under general plating conditions, there is a problem that pinholes are likely to be formed on the nickel layer 11 . If pinholes are formed on the nickel layer 11, the Au layer 13 laminated thereon will also be affected by the nickel layer 11 to cause pinholes. If a large number of pinholes are formed in the Au layer, the surface of the electrode base material 10 will be exposed, and when measuring the amount of dissolved oxygen in a liquid medium, there will be a difference between the current value at the initial stage of measurement and the predetermined threshold value due to the influence of the electrode base material 10 The problem of getting smaller.
[0057] The dif...
Embodiment approach 3
[0070] In Embodiment 2, copper is used for the electrode base material 10 , but the present invention is not limited thereto, and other materials may be used for the electrode base material 10 as long as it is suitable for measuring the amount of dissolved oxygen. For example, in this embodiment, stainless steel is used for the electrode base material 10 . In addition, the bacterial count measuring device using the oxygen electrode according to the present embodiment is the same as the block diagram of the bacterial count measuring device shown in FIG. 1 . Furthermore, the battery 1 used in this embodiment is also the same as the cross-sectional perspective view of the battery 1 shown in FIG. 2 . Therefore, detailed descriptions of the bacterial count measuring device and the battery 1 are omitted.
[0071] Next, the cross-sectional view of the oxygen electrode 2 according to this embodiment is basically the same as the cross-sectional view shown in FIG. 6 , except that the e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com