Listeria attenuated for entry into non-phagocytic cells, vaccines comprising the listeria, and methods of use thereof
A non-Listeria and Listeria technology, applied in the direction of bacteria, bacterial antigen components, applications, etc., can solve the problems of poor reliability of infectious agents or cancer cells, and inability to respond successfully
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0235] Example 1. Construction of Mutant Listeria Strains
[0236] A. Preparation of Mutant Listeria Strains
[0237] The Listeria strain was from 10403S (Bishop et al., J. Immunol. 139:2005 (1987)). The established methods of SOE-PCR and allelic exchange (Camilli et al., Mol. Microbiol. 8: 143 (1993)) were used to generate Lisi with in-frame deletions of the indicated genes. Terrier strains. Mutant strain LLO L461T (DP-L4017) is described in Glomski et al. J. Cell. Biol. 156: 1029 (2002), incorporated herein by reference. The ΔactA mutant (DP-L4029) is the DP-L3078 strain described in Skoble et al., J. of Cell Biology, 150: 527-537 (2000), incorporated herein by reference, which was depleted of prophage. (Prophage curing is described in (Lauer et al., J. Bacteriol. 184:4177 (2002), US Patent Application Publication No. 2003 / 0203472)). LLO has also previously been reported - mutant (DP-L4027) (Lauer et al., J. of Bacteriology, 184:4177-4186 (2002)), and LLOΔ26 (DP-L4042...
Embodiment 2
[0303] Example 2. Pathogenicity study of Listeria
[0304] The median lethal dose (LD) of certain mutant Listeria strains was determined by IV infection of mice 50 ). Three to five female C57BL / 6 mice were infected IV with triplicate 5-fold dilutions of the strain. Mice were observed daily for 10 consecutive days and sacrificed when they showed signs of distress. Calculate the median lethal dose. The data are shown in Table 1 below. The results indicated that mutant Listeria strains deficient in internalin B (ΔinlB, ΔactAΔinlB and ΔactAΔinlAB) were less virulent when combined with actA deletion. Only the ΔinlB strain showed similar virulence to wild Listeria.
[0305] strain
Embodiment 3
[0306] Example 3. Evaluation of in vivo cytotoxic activity in mice inoculated with Listeria monocytogenes
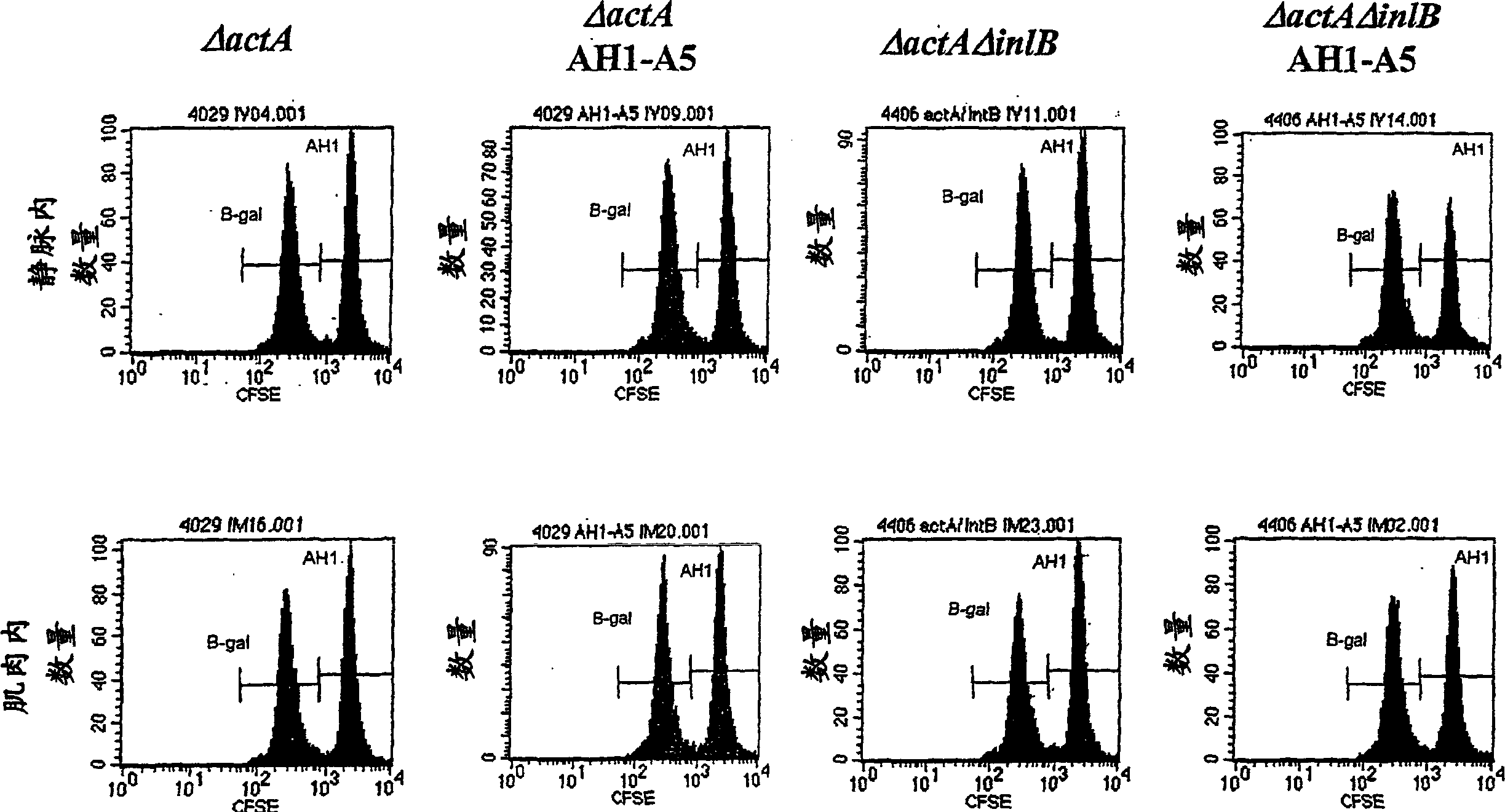
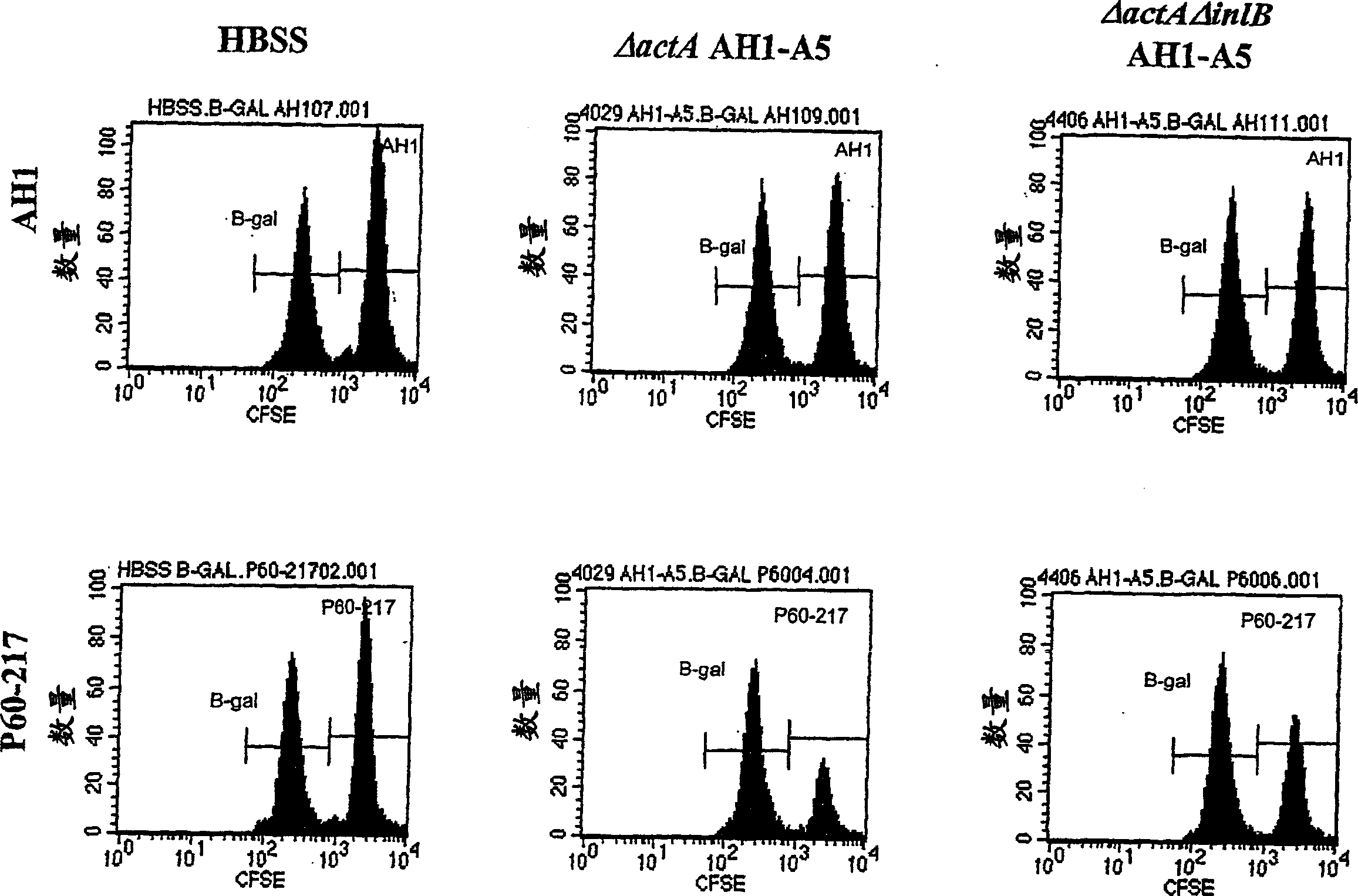
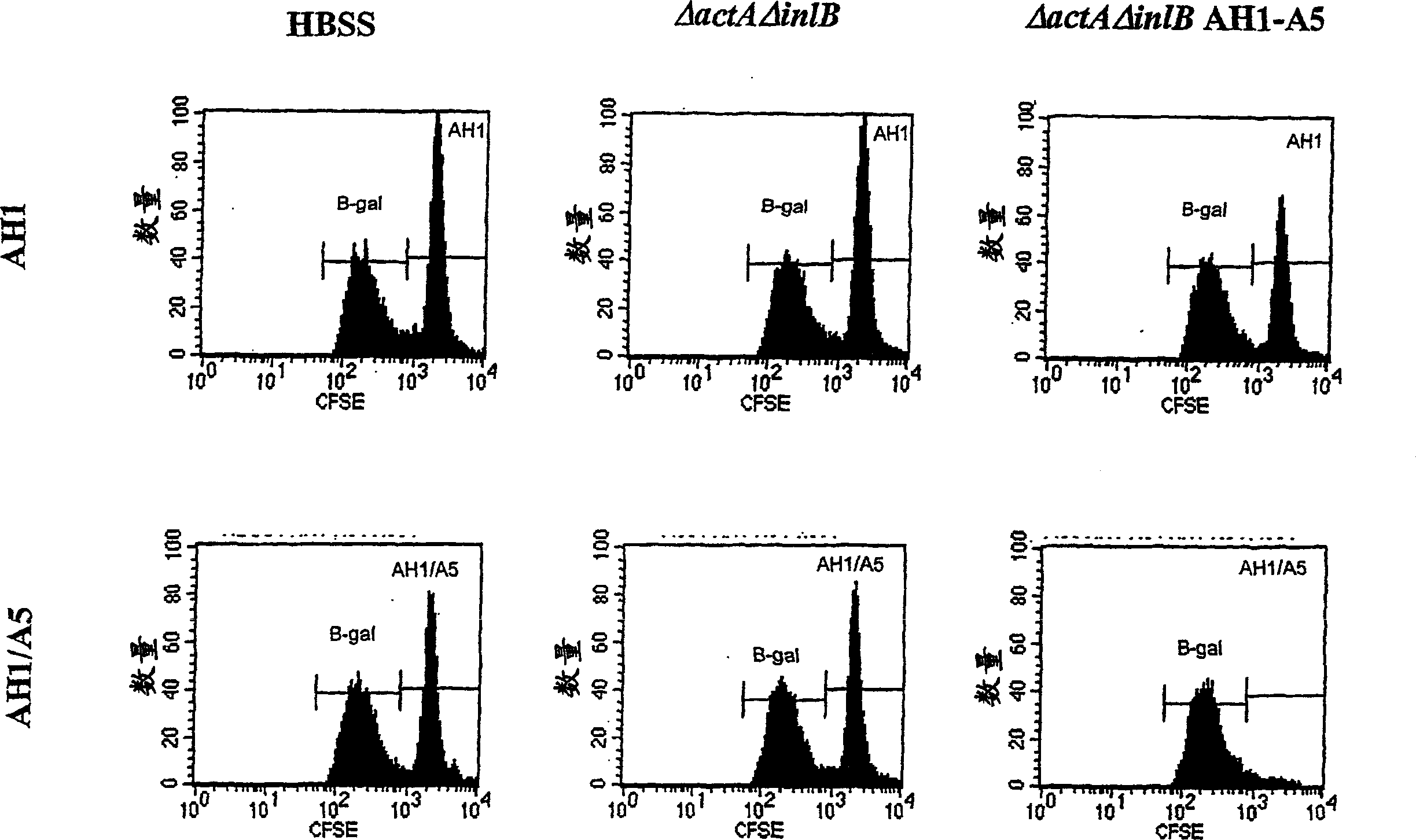
[0307] The ability to lyse antigen-specific target cells in vaccinated mice was evaluated in a series of experiments. In the first experiment, as shown in Table 2, Listeria monocytogenes strains DP-L4029 (ΔactA), DP-L4029ΔinlB (ΔactAΔinlB) and The same strain engineered to express AH1-A5 was inoculated into Balb / c mice. Listeria constructs expressing AH1-A5 also expressed hemolysin-deleted LLO and truncated OVA (see Example 1.C above). The inoculation dose is 0.1LD 50 . The spleens of 10 naive Balb / c mice were harvested in RPMI1640 medium to prepare the target cell population. The cells are isolated and the red blood cells are lysed. White blood cells were counted and divided into two equal portions. Using 0.5 μg / ml of target (AH1, SPSYVYHQF (SEQ ID NO: 8), purchased from SynPep, Dublin, CA) or control (β-gal, TPHPARIGL (SEQ ID NO: 19)) specific peptide at 37°C ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com