Method and device for performing submicroliter reactions with nucleic acids or proteins
A nucleic acid, reaction technique used in the field of preparing and conducting small-scale reactions using nucleic acids or proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0262] Reaction Mixture Preparation Example 1: Reagents are pipetted and mixed on a substrate using a capillary cartridge
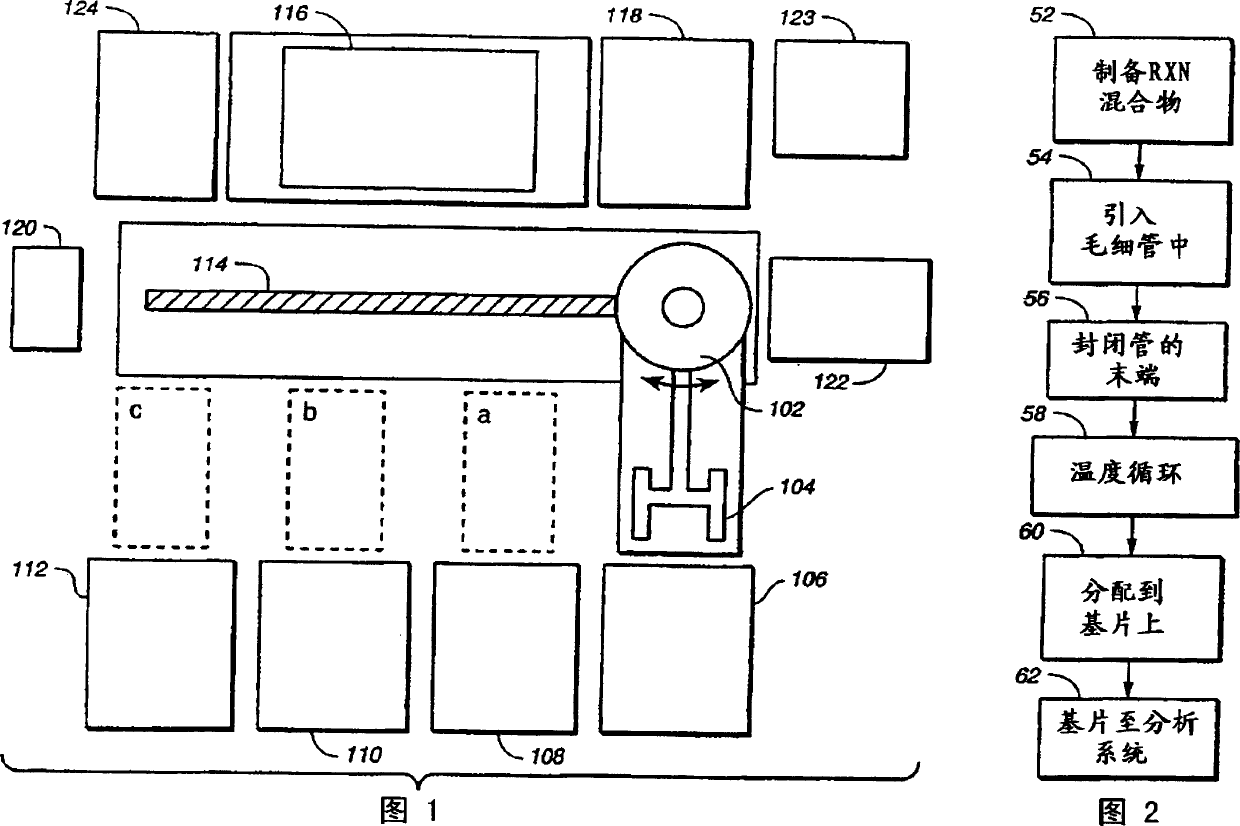
[0263] One way to prepare the reaction mixture is to use a pipette to measure the components of the reaction mixture separately. For example, when preparing a PCR mix, the nucleic acid sample and the PCR reagents will be measured separately and then dispensed into the same container where they are brought together. When using the automated system of FIG. 1 , an automated robot 102 moves a transfer head 104 containing capillary cassettes to the position where the sample plate is located. Dip the capillary end of the capillary cartridge into the well. The capillary is primed by capillary action to measure precise amounts of sample. The wells of the sample plate contain PCR-amplified nucleic acid samples. DNA samples should be diluted sufficiently so that each capillary in the capillary cartridge contains 5-20 ng of DNA in a volume of 10-10,000 nL.
[02...
Embodiment 2
[0273] Example 2 of Capillary Cartridge Sampling: Gas Replacement
[0274] A second method of dividing the liquid contained in the capillary tubes of the capillary cartridge is to use a gas displacement device. As shown in FIG. 1 , the microplates from the microplate residence chamber are transferred by the transfer head 104 to the sample dispensing device position 122 . A gas sample divider is installed here, such as the sample divider depicted in Figures 4A-C. The transfer head 104 then lifts one more capillary cartridge and primes it with the sample from the multiwell plate or with the reagents. The capillary cartridge moves to the sample dispensing device position 122 and contacts the gas displacing device head. The substrate of the capillary cartridge is placed on the receiving platform on the head of the gas displacement device. In addition, the gas displacement device head can be connected to the automated robot 102 .
[0275]As shown in FIG. 4A , a gas displacement...
Embodiment 3
[0284] Reaction Mixture Assembly Example 3: Solid Phase Capture
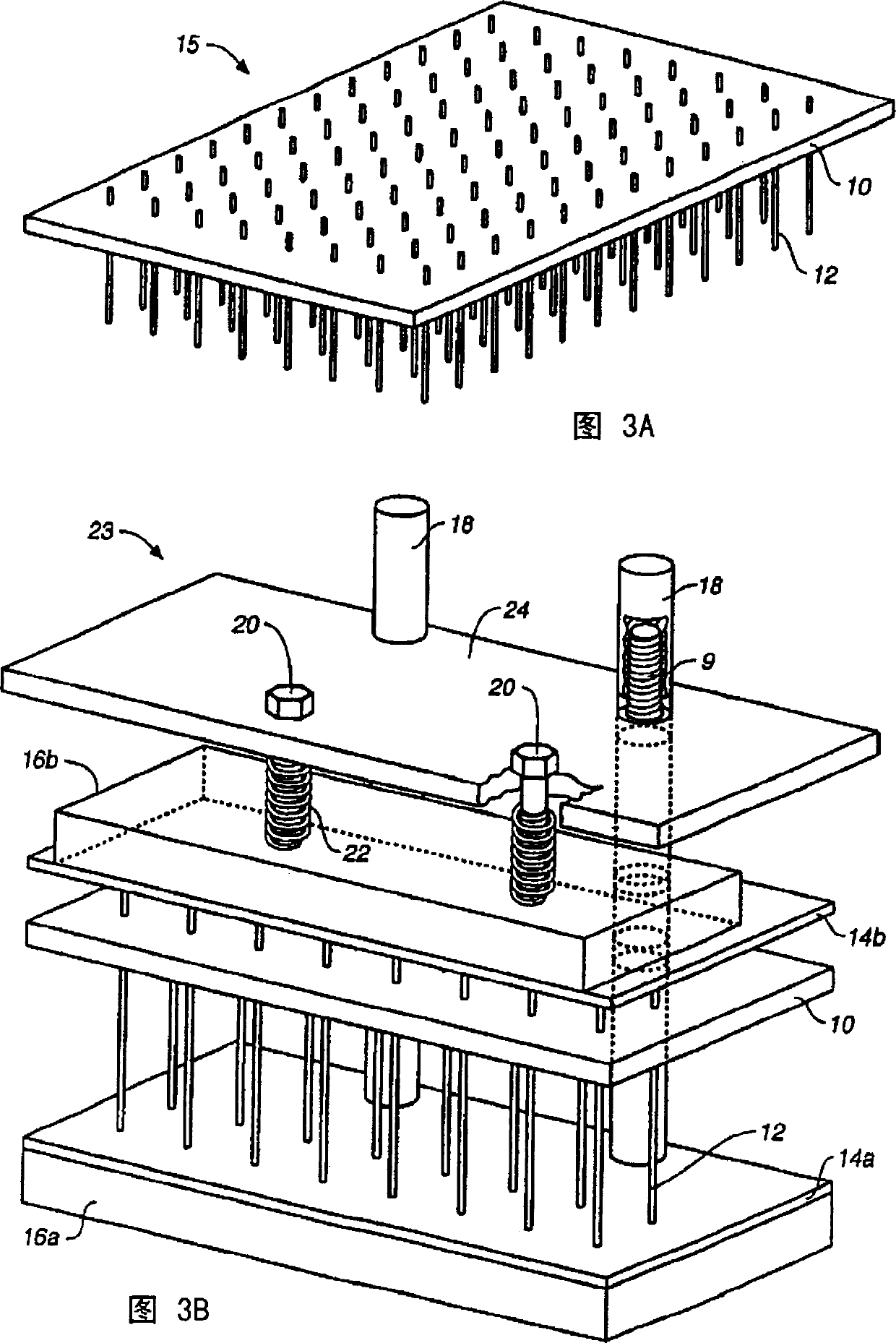
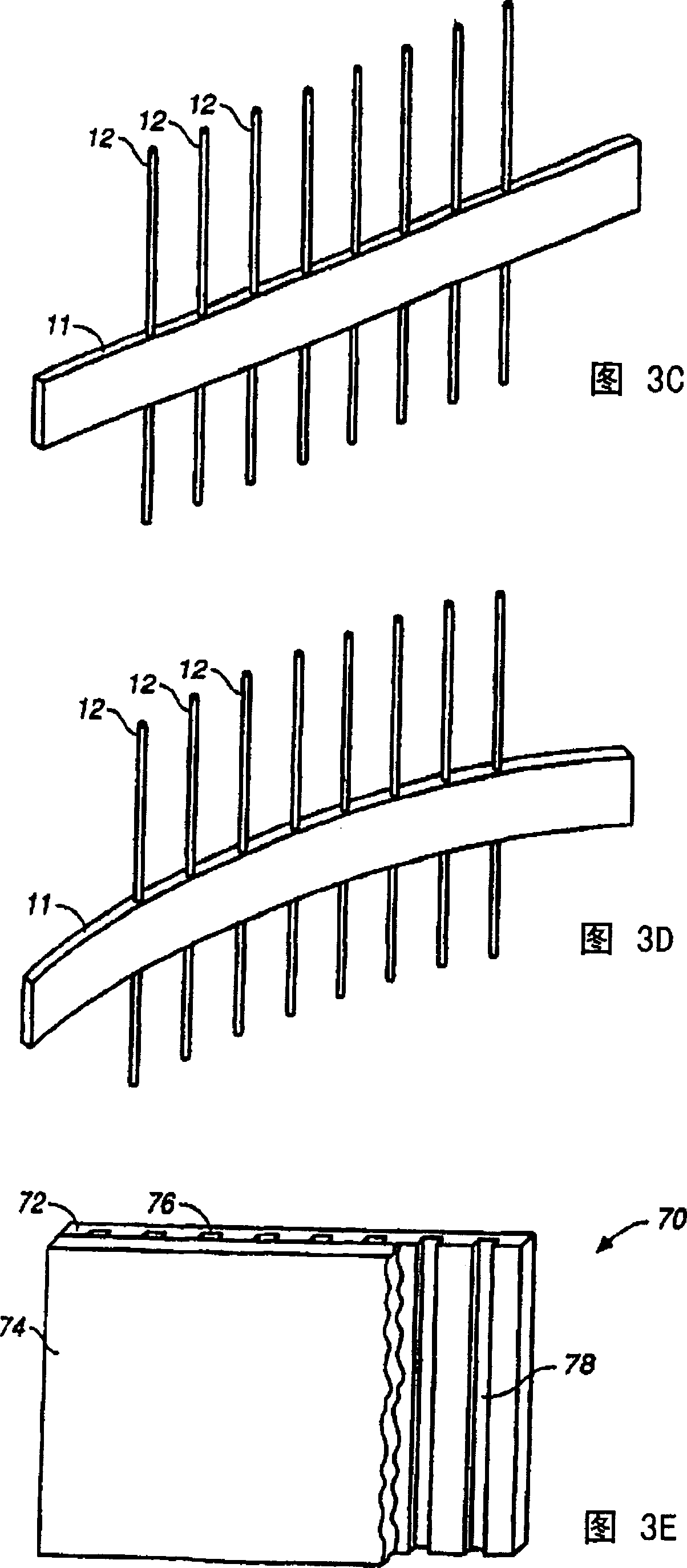
[0285] A third method of assembling the reaction mixture is to capture species from the sample on the substrate surface, such as the inner surface of a capillary segment. The captured species can be nucleic acids, enzymes, other biopolymers or chemicals. Desired species captured from a sample can be attached to surfaces in a variety of ways. These methods include covalent binding, antibody binding, DNA hybridization, hydrophobic interactions, electric fields, magnetic fields or other chemical or physical forces. After the sample is bound, the liquid remaining in the suspended sample can be drained from the capillary or microchip by chemical reaction or physical force. The capillary can be used for gas displacement or centrifugation, vacuum method can also be used. Sample material will remain on the surface of the substrate. In this single step, the sample material is also substantially purified. The reactio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com