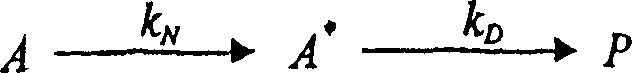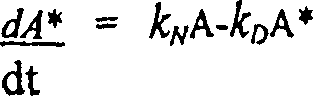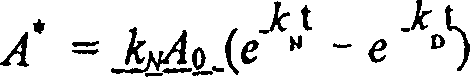Microspheres comprising therapeutic and diagnostic radioactive isotopes
A radioisotope, radioactivity technology, applied in the directions of radioactive carrier, radioactive physical shape, radioactive preparations in vivo, etc., can solve the problems of measuring the biodistribution of microspheres, unable to directly measure the biodistribution, complicated development of microspheres, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0139] Calculation contains 89 Y The glass microspheres required for optimal 197 Au quantity
[0140] experimental design
[0141] In this example, we want to use a sufficient amount of 198 Au labeled radioactive 90 Y glass microspheres so that the microspheres can be detected by a gamma camera. In this example, in addition to containing gold compounds, the microspheres have the same composition as commercially available Theraspheres (40% Y 2 o 3 (weight) or 31% Y) the same composition. Activation by neutrons containing stable isotope Y 89 and Au 197 The glass microspheres were used for this method. In this example, if the sample is removed from the neutron flux, the radioactivity required per 50 mg of glass microspheres is 100 mCi Y 90 and 1 μCi Au 198 , we wish to calculate the required initial Au 197 quantity. Y 89 and Au 197 The neutron capture cross-sections are 1.3 target and 98.8 target respectively, and Y 90 and Au 198 The decay constants are 3.0...
Embodiment 2
[0152] In this example, we assume that the glass composition contains 13% Y 2 o 3 (weight) (or 10% Y), and the radioactive Y required per 50 mg of glass microspheres 90 100mCi, Au 198 10μCi. Other amounts are with embodiment 1. Similar calculations show that the glass should contain 291ppb gold and require a neutron activation time of 6.10×10 5 s. Similar calculations can be made for other proportions of these elements, or other elements combined in any proportion.
Embodiment 3
[0154] Preparation of glass beads
[0155] There have been previous reports on the preparation of glass microspheres. See US Patent 5,302,369. In these preparations, Si, Al, K, Mg, Al, Pb, and P 2 o 5 of different compositions of glass. 50 g of glass obtained in batches was melted in a platinum crucible using an electric furnace at close temperature. A typical melt cycle requires 3 hours per charge at 1000°C and 3 to 4 hours to purify the melt at the approximate melting temperature.
[0156] The crucible containing the melt was quenched with 25°C water, and then the glass feedstock obtained in the crucible was crushed and ground to -100 mesh. The -100 mesh glass powder was then slowly fed with a vibrating doctor blade to an oxygen / propane flame where surface tension pulled the molten particles into balls. The flow rates of oxygen and propane for each glass composition were adjusted to produce spherical particles of the highest particle size fraction. After spheroidizati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com