Use of hif alpha stabilizers for enhancing erythropoiesis
A technology of erythropoietin and red blood cells, which is applied in the application field of HIFα stabilizers that enhance red blood cell production, and can solve the problems of weakened iron utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
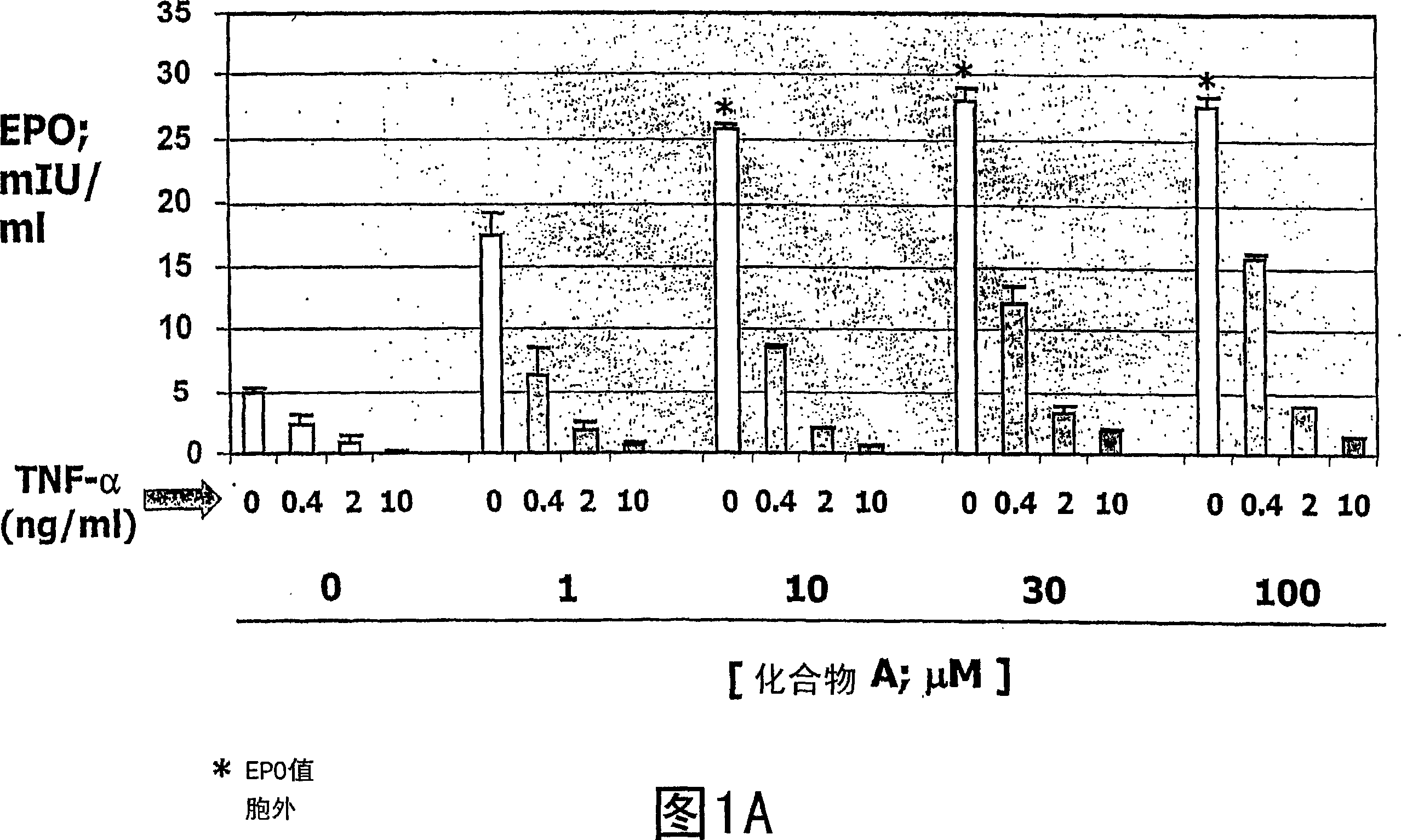
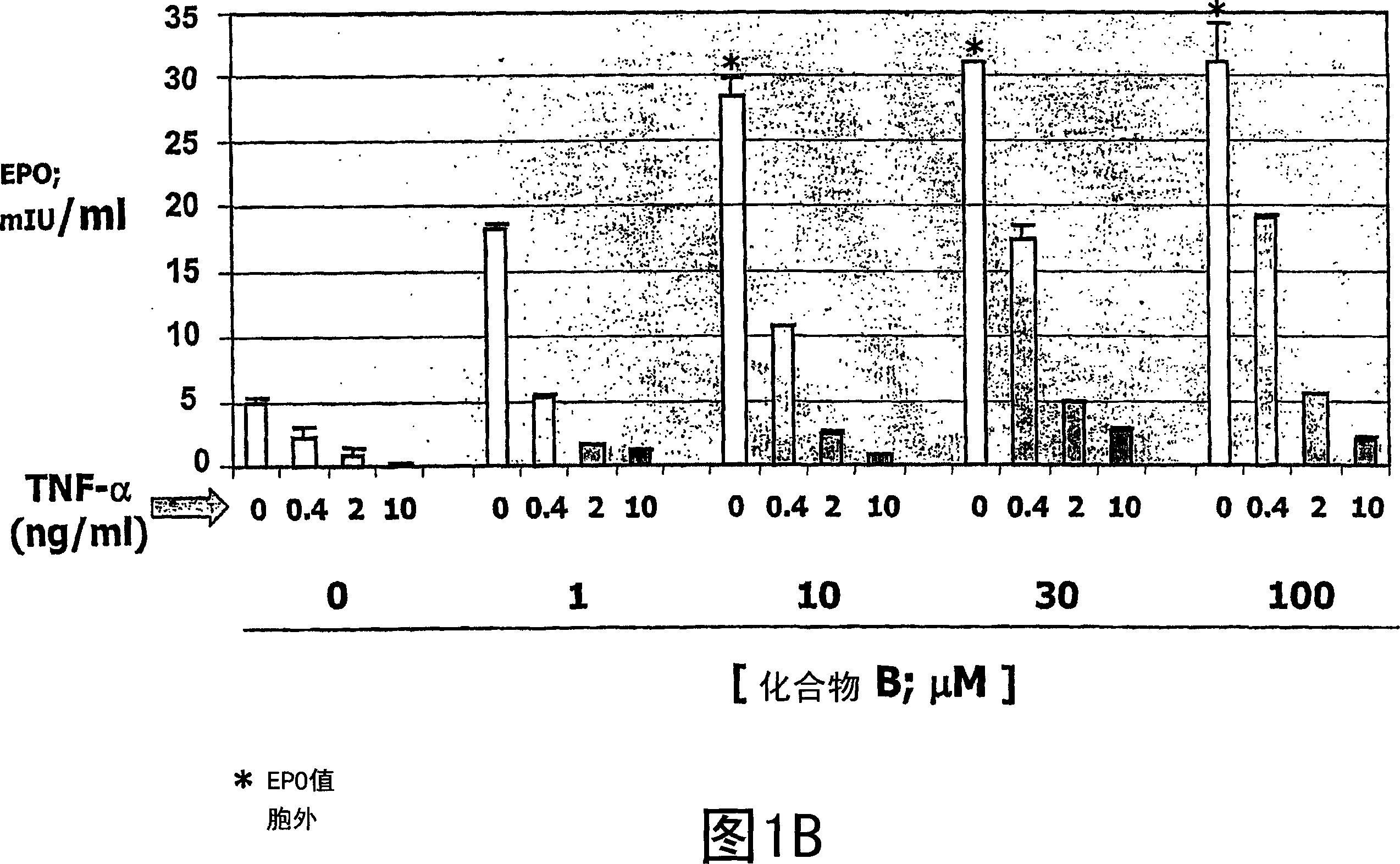
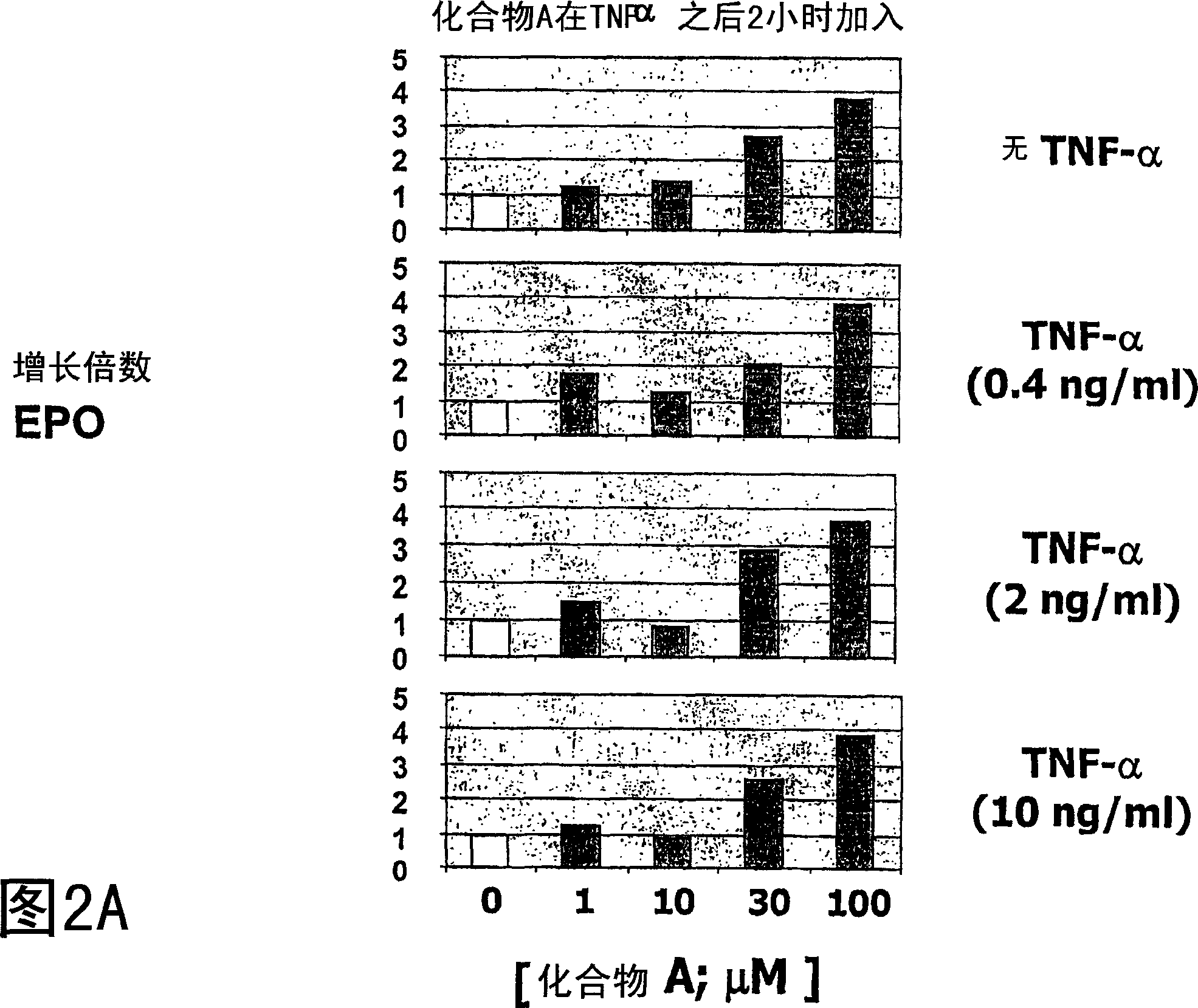
[0263] Embodiment 1: Overcoming the inhibitory effect of TNF-α on EPO generation
[0264] Hep3B cells were treated with various concentrations (0, 0.4, 2, 10 ng / ml) of TNF-α in the absence or presence of compound A or compound B for three days. Secreted EPO levels were determined using a commercially available ELISA kit (R&D Systems, catalog number DEP00). In the absence of compound, treatment of Hep3B cells with TNF-[alpha] decreased EPO production in a dose-dependent manner. Hep3B cells treated with various concentrations of Compound A (Fig. IA) or Compound B (Fig. IB) in the absence of TNF-[alpha] showed a dose-dependent increase in EPO production. Addition of either of these compounds in the presence of TNF-[alpha] significantly reduced the inhibitory effect of TNF-[alpha] on EPO production. Overcoming of the inhibitory effect of TNF-[alpha] on EPO production by prolyl hydroxylase inhibition was observed in the presence of low (eg 0.4 ng / ml) and high (eg 10 ng / ml) concen...
Embodiment 2
[0268] Example 2: Overcoming the inhibitory effect of IL-1β on EPO production
[0269] Hep3B cells were treated with various concentrations (0, 0.4, 2, 10 ng / ml) of IL-1β in the absence or presence of compound A or compound B for 3 days. Secreted EPO levels were determined using a commercially available ELISA kit (R&D Systems, catalog number DEP00). Treatment of Hep3B cells with IL-1β decreased EPO production in a dose-dependent manner in the absence of compound. In the absence of IL-1β with various concentrations of compound A ( Figure 3A ) or compound B ( Figure 3B ) treated Hep3B cells showed a dose-dependent increase in EPO production. Addition of either compound in the presence of IL-1[beta] significantly reduced the inhibitory effect of IL-1[beta] on EPO production. Overcoming of IL-1β inhibition of EPO production by prolyl hydroxylase inhibition was observed in the presence of low (eg 0.4 ng / ml) and high (eg 10 ng / ml) concentrations of IL-1β. Thus, the inhibitory ...
Embodiment 3
[0273] Example 3: Inhibition of TNF-alpha-induced VCAM-1 expression
[0274] Adhesion of endothelial cells to lymphocytes occurs in part through expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1 by endothelial cells. VCAM-1 expression in endothelial cells is induced by various inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α. To study the effect of HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibition on TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 expression, HUVEC (human umbilical vein endothelial cells) were treated with TNF in the absence or presence of various concentrations of compound B or compound C - Alpha stimulation for 1 day. VCAM expression was then measured.
[0275] like Figure 5As shown, TNF-α (1 ng / ml) induced VCAM-1 expression in HUVEC cells. However, addition of Compound B or Compound C to TNF-α-stimulated cells resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 expression. This data demonstrates that the methods and compounds of the invention are effective at reducing VCAM-1 expression as...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com