Synchronous switch boost transducer of light emitting diode driver
A boost converter and converter technology, applied in output power conversion devices, conversion equipment and instruments without intermediate conversion to AC, can solve problems such as lack of protection mechanism, circuit danger, and burnout of boost converters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The details related to the present invention will be further described below with reference to the drawings. The same numbers or labels in the drawings represent the same components or concepts. In addition, it is emphasized again that the so-called "turn off" (turn off) switching component in this article refers to controlling the switching component to a non-conductive state.
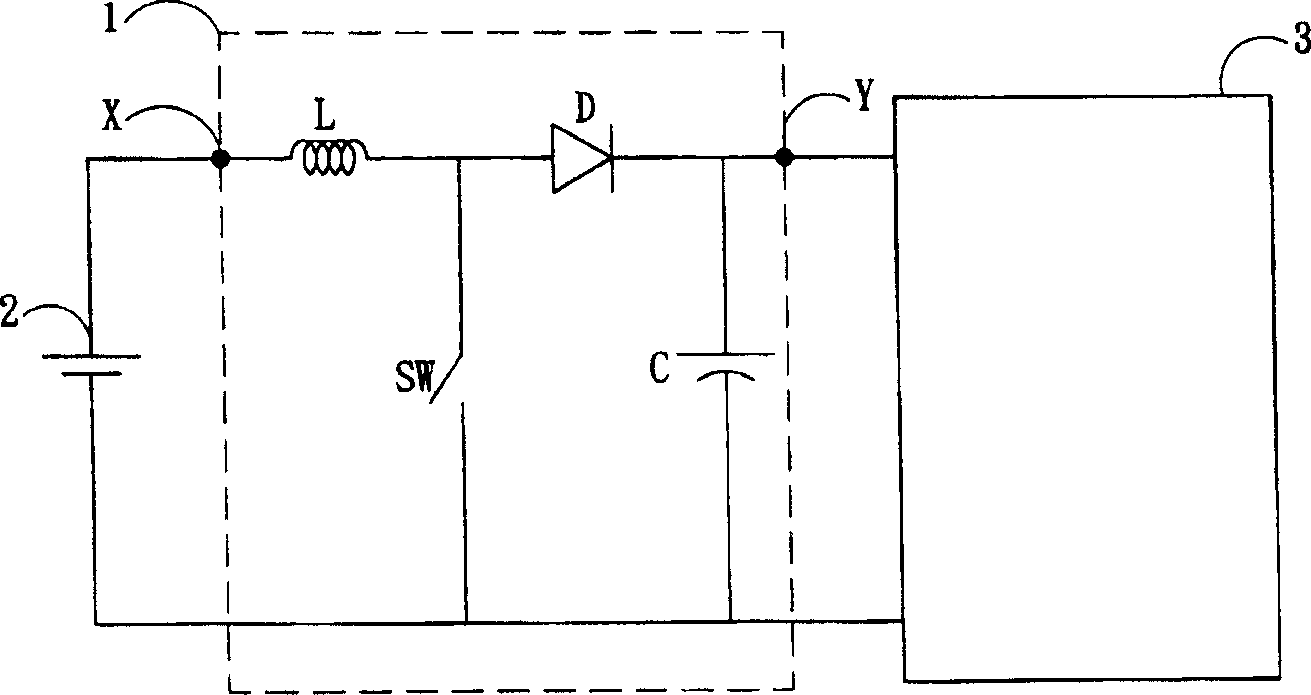
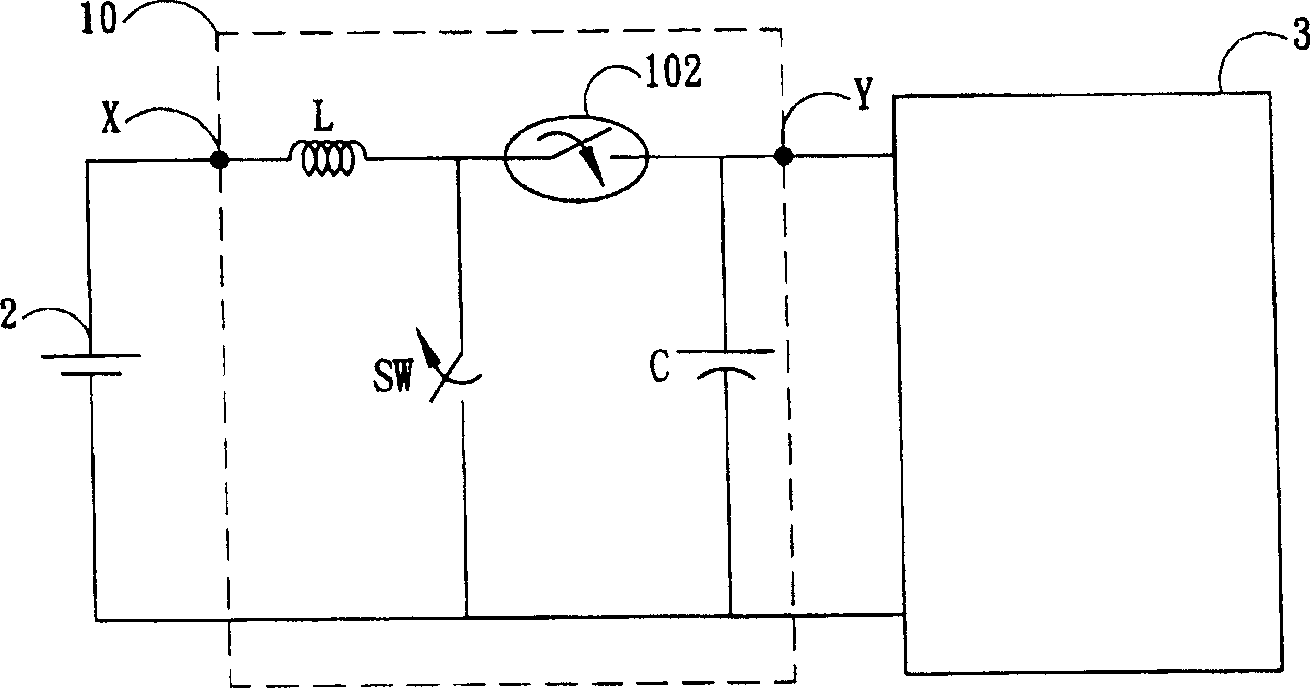
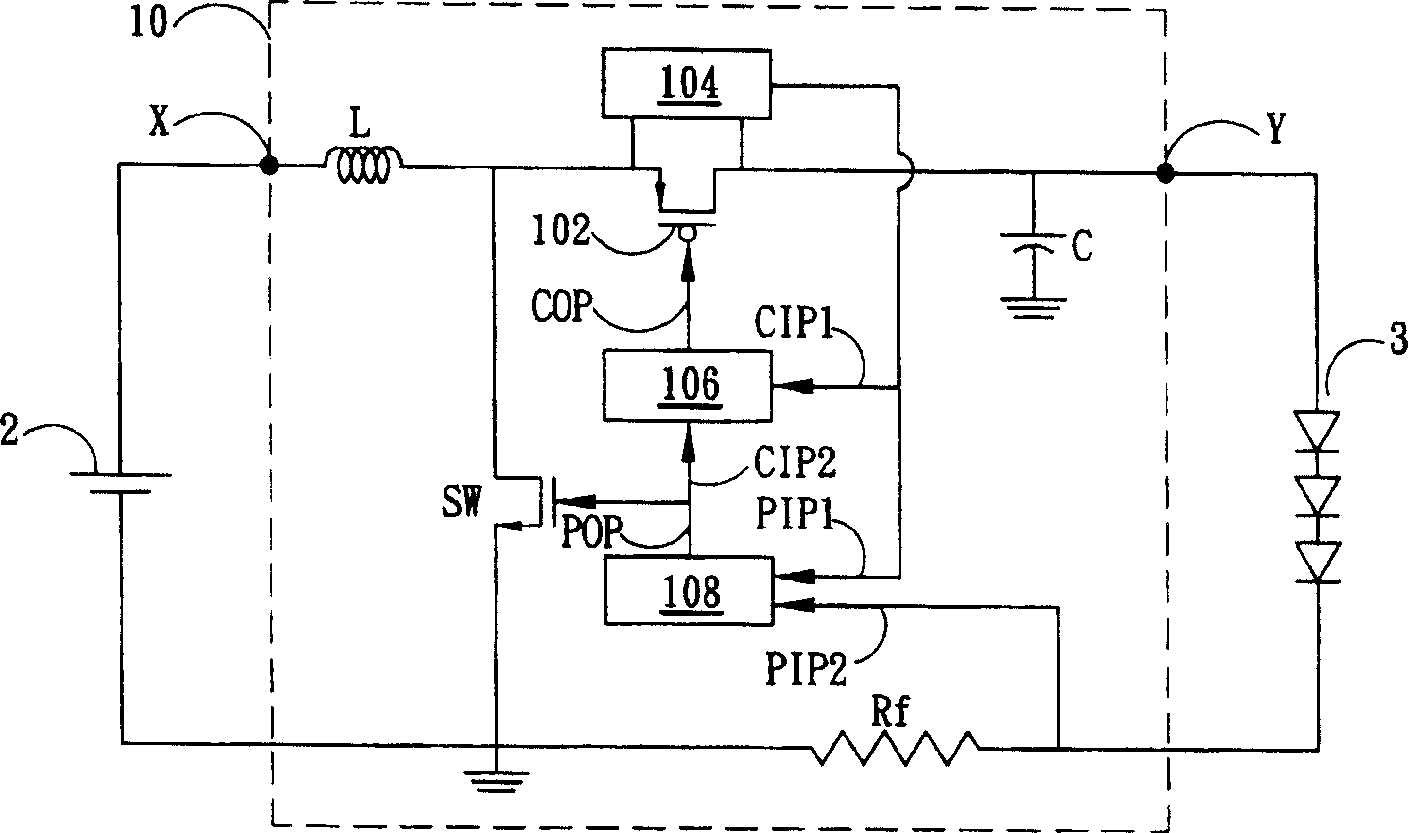
[0044] figure 2 is a schematic circuit diagram for driving a semiconductor light emitting device such as a light emitting diode according to the present invention. and figure 1 similar, figure 2 The schematic circuit diagram includes a boost converter 10, a DC power supply 2, and a light emitting diode module 3. The boost converter 10 includes a power supply terminal X, an inductor L, a synchronous switching component 102 , a switching component SW, a capacitor C, and a driving output terminal Y. and figure 1 Compared with the conventional boost converter, it is obvious that the main di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com