Therapeutic delivery of carbon monoxide
A carbonate and carbonate compound technology, applied in the direction of organic active ingredients, non-central analgesics, active ingredients of boron compounds, etc., can solve problems such as unsuitable for commercial radiopharmaceutical use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to 8
[0063] Reagent
[0064] Chloro(glycinato)ruthenium(II) tricarbonyl ([Ru(CO) 3 Cl (glycine ester)] or CORM-3) 24 . Borane carbonate disodium salt (Na 2 [H 3 BCO 2 ], here indicated as "CORM-A1") 31 . Sodium borohydride (NaBH 4 ) and all other reagents were from Sigma Chemicals (Poole, Dorset).
[0065] Preparation of blunt CORM-A1 and its use as a negative control
[0066] The chemistry of borane carbonate in aqueous solution has been described previously 31 . This compound is relatively stable in distilled water at basic pH. When the pH approaches more physiological conditions (pH = 7.4), the compound starts to release CO, and the rate of CO release is very fast at acidic pH. Based on this fact, we generated the inactive form of CORM-A1 (iCORM-A1) by reacting the compound with acid. Specifically, a small aliquot (10 μl) of concentrated hydrochloric acid (10 M) was added to 1 ml of CORM-A1 in water (100 mM final concentration). The reaction caused a rapid evolutio...
Embodiment 1
[0071] Example 1. Conversion of myoglobin (Mb) to carbon monoxide myoglobin by CO gas
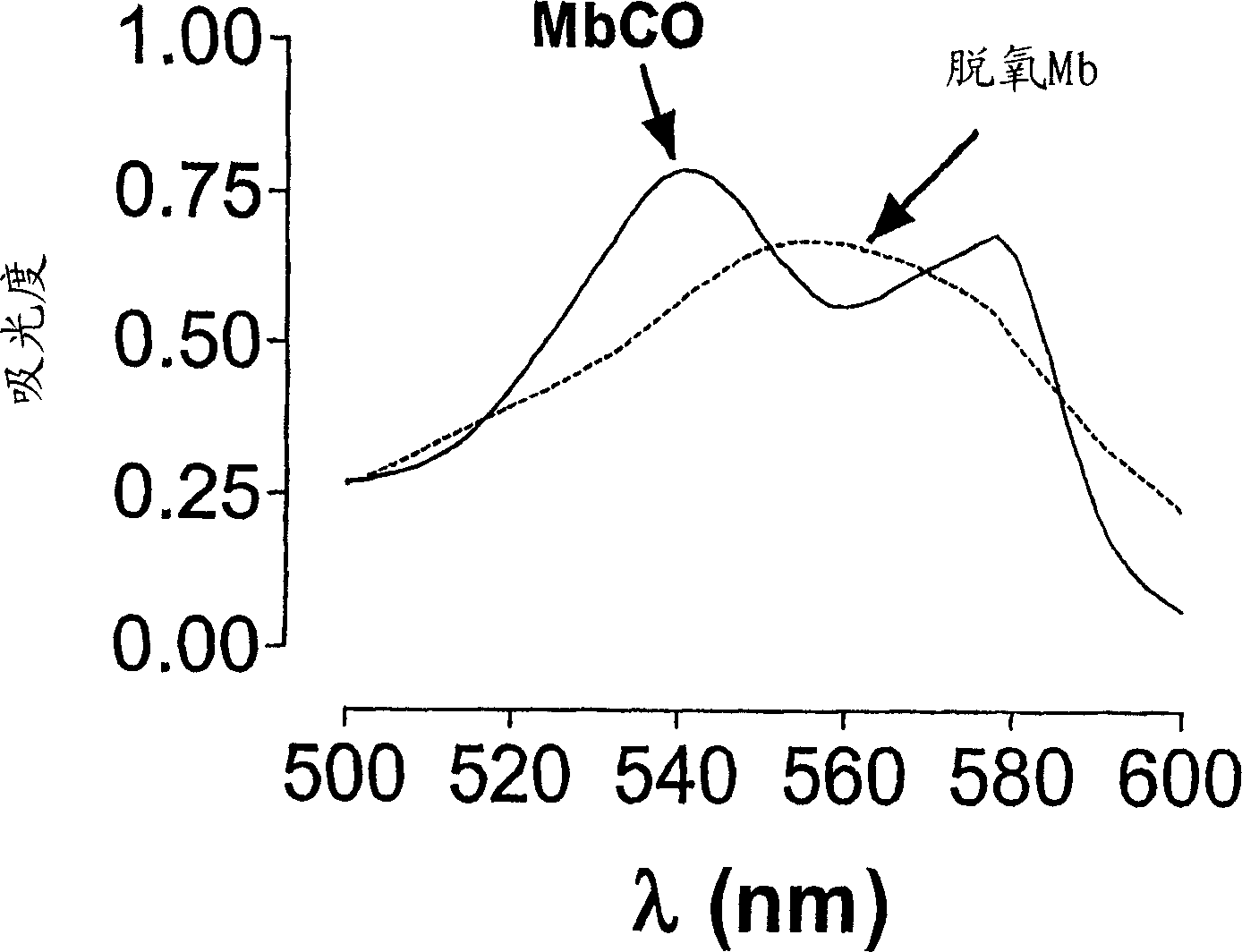
[0072] Myoglobin (Mb) in its reduced state exhibits a characteristic spectrum with a maximum absorption peak at 555 nm (see figure 1 ,dotted line). Rapid conversion of carbon monoxide myoglobin (MbCO) was observed when Mb solution (50 μΜ) was bubbled with CO gas (1%) for 1 min. Such as figure 1 As shown, MbCO displays a characteristic spectrum (solid line) with two maximum absorption peaks at 540 and 576 nm, respectively. This method has been studied previously to monitor and detect CO release from CO-RMs 23 , and can be used to examine how various conditions such as different pH and temperature affect the kinetics of CO release (see Example 4).
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2. Conversion of myoglobin (Mb) to carbon monoxide myoglobin by CORM-A1
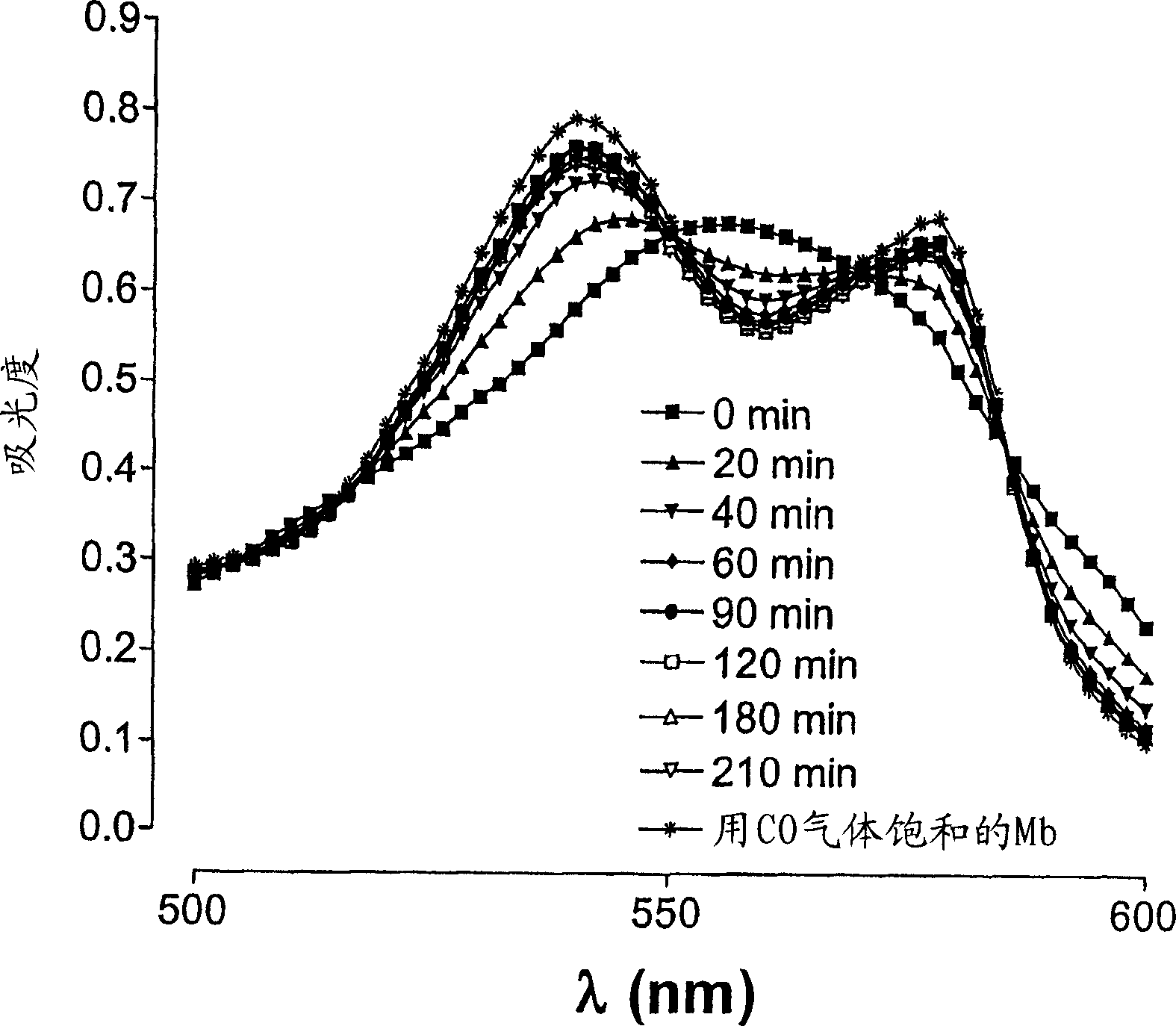
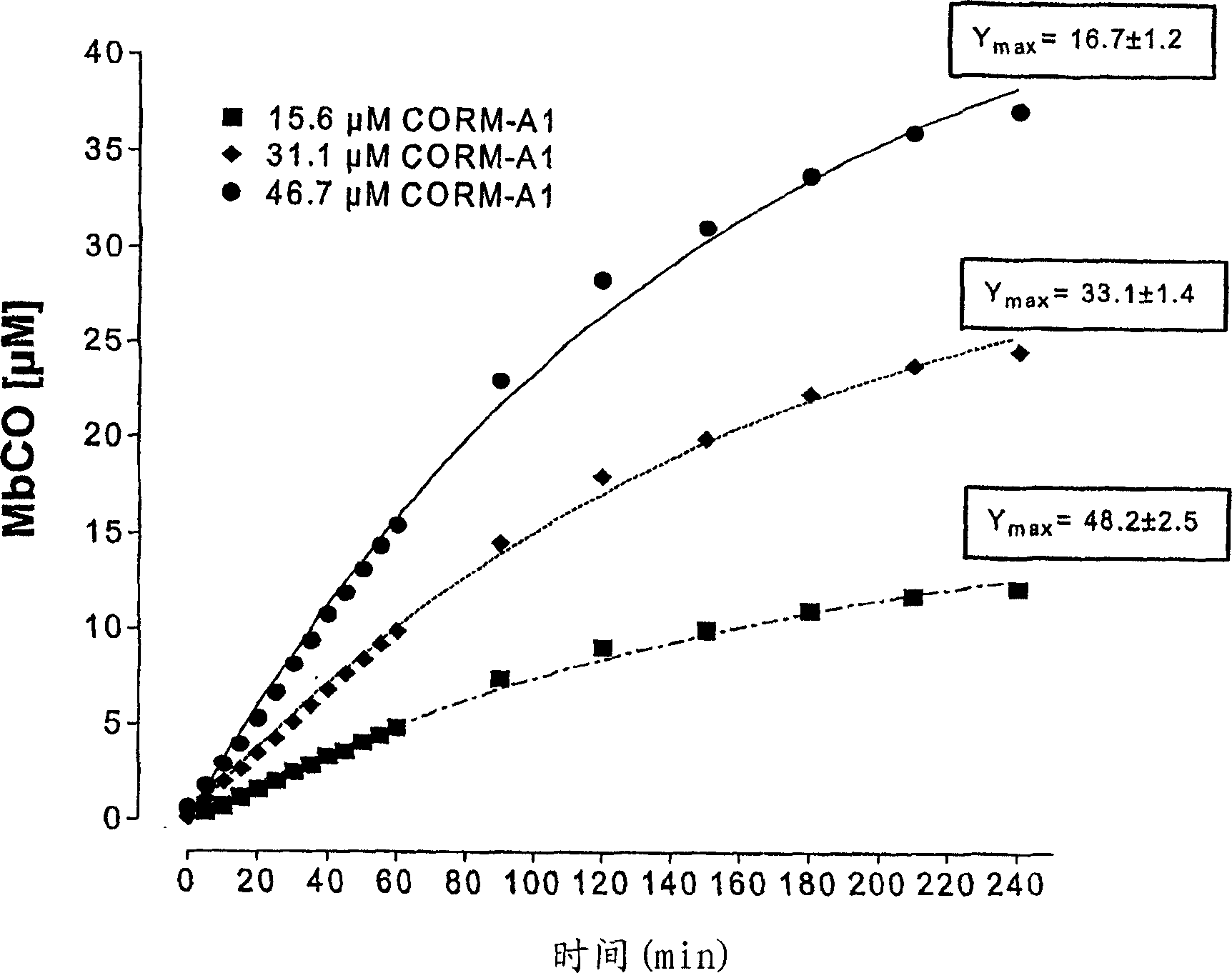
[0074] Addition of CORM-A1 (60 μΜ) to a solution containing reduced Mb (pH = 7.4, temperature = 37°C) resulted in the gradual generation of MbCO over time. Such as figure 2 As shown, after 210 min of incubation, the standard spectrum of reduced Mb (solid squares) was transformed into a characteristic spectrum (empty inverted triangles). Traces containing asterisks represent MbCO spectra when Mb was saturated with CO gas (positive control) as described in Materials and Methods.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com