Variable transconductance circuit
A circuit, variable technology, applied in differential amplifiers, DC-coupled DC amplifiers, head configuration/installation, etc., which can solve problems such as increased current consumption, current consumption installation circuit area, difficulty in achieving low power supply voltage operation, etc. Achieve the effect of high gm and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
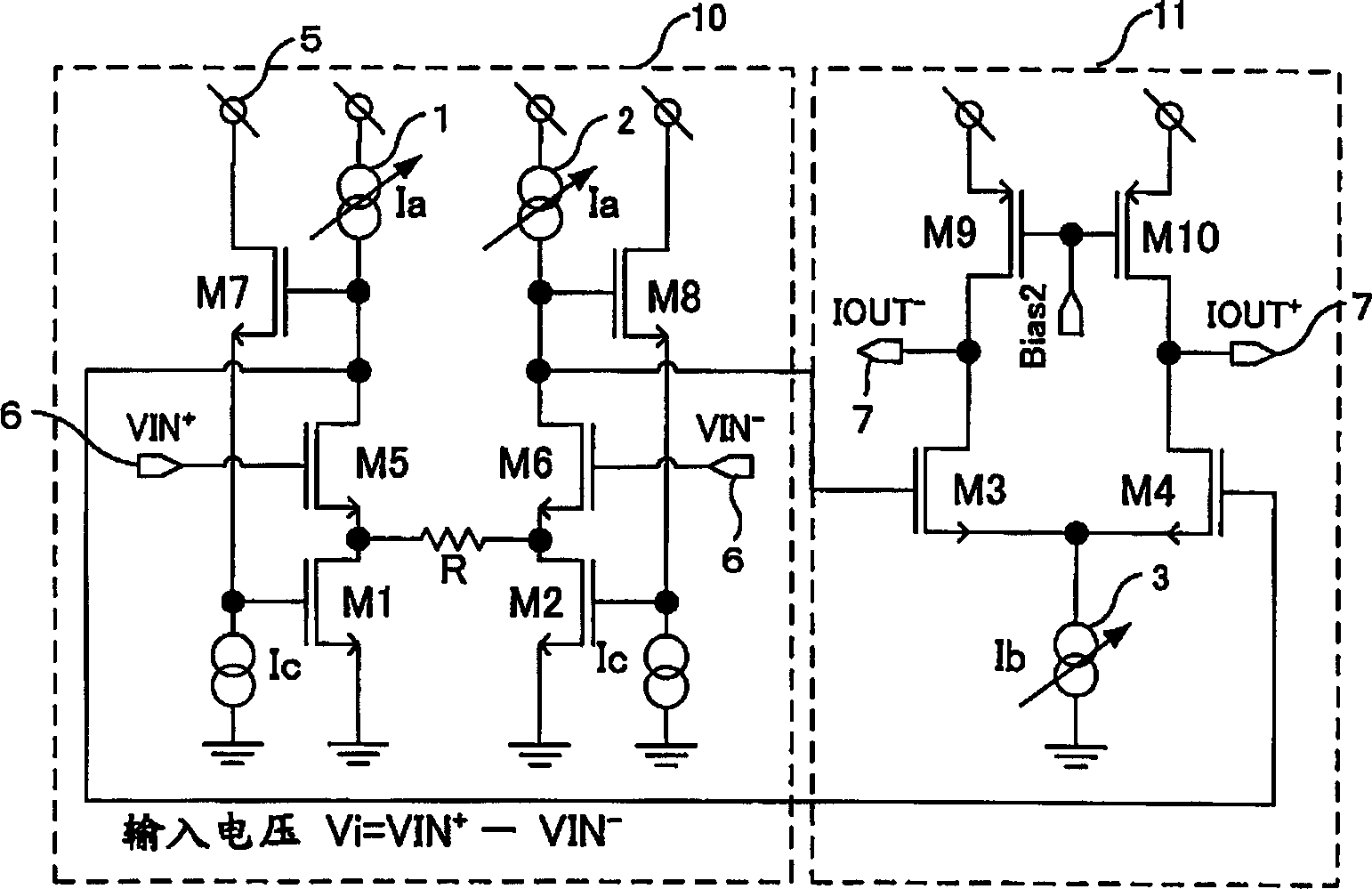
[0052] figure 1 It is the variable transconductance circuit of the first embodiment. The linear voltage-current conversion unit is a voltage-current conversion unit described in the prior art. The input voltage signal Vi is converted into a current by the resistor R between the sources of the MOS transistors M5 and M6, and becomes the respective drains of the MOS transistors M1 and M2. current. At this time, the gate voltage difference between the MOS transistors M1 and M2 is shown in Equation 4.
[0053] ΔVg = ( Ia + Vi R k 1 · β - Ia - Vi R ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
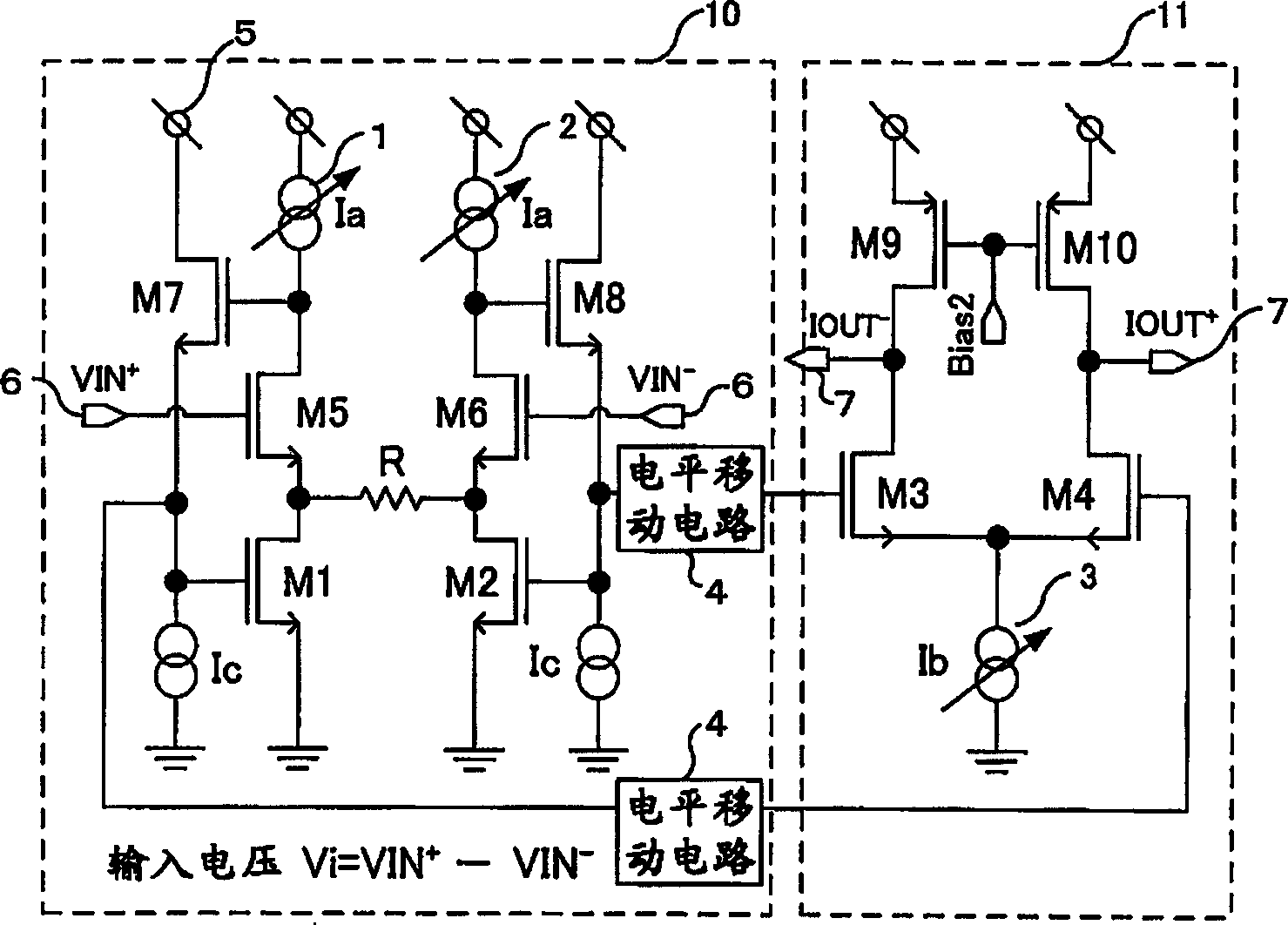
[0065] figure 2 It is the variable transconductance circuit of the second embodiment. exist figure 1 In the variable transconductance circuit, since the gate voltages of the MOS transistors M4 and M3 are automatically determined by the gate-source voltages of the MOS transistors M1 and M7, and the MOS transistors M2 and M8, respectively, in order to make the MOS Transistors M3 and M4 work in the saturation region to automatically determine the output dynamic range, and the design freedom is restricted. To solve this problem, in figure 2 Among them, the gate of the MOS transistor M1 and the gate of the MOS transistor M4, and the gate of the MOS transistor M2 and the gate of the MOS transistor M3 are each connected through a level shift circuit 4. . By appropriately setting the DC level shift amount of the level shift circuit 4, the design freedom of the output dynamic range is improved. As long as the input impedance is high enough, the level shifting circuit 4 can also...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0067] exist figure 1 , figure 2 In the structure, MOS transistors M1, M5, M7 or MOS transistors M2, M6, M8 form a negative feedback loop, and its unity gain frequency f0 and Ia are in the relationship of formula 8, and the frequency characteristics of the circuit change with the change of gm.
[0068] f 0 ∝ Ia - - - ( 8 )
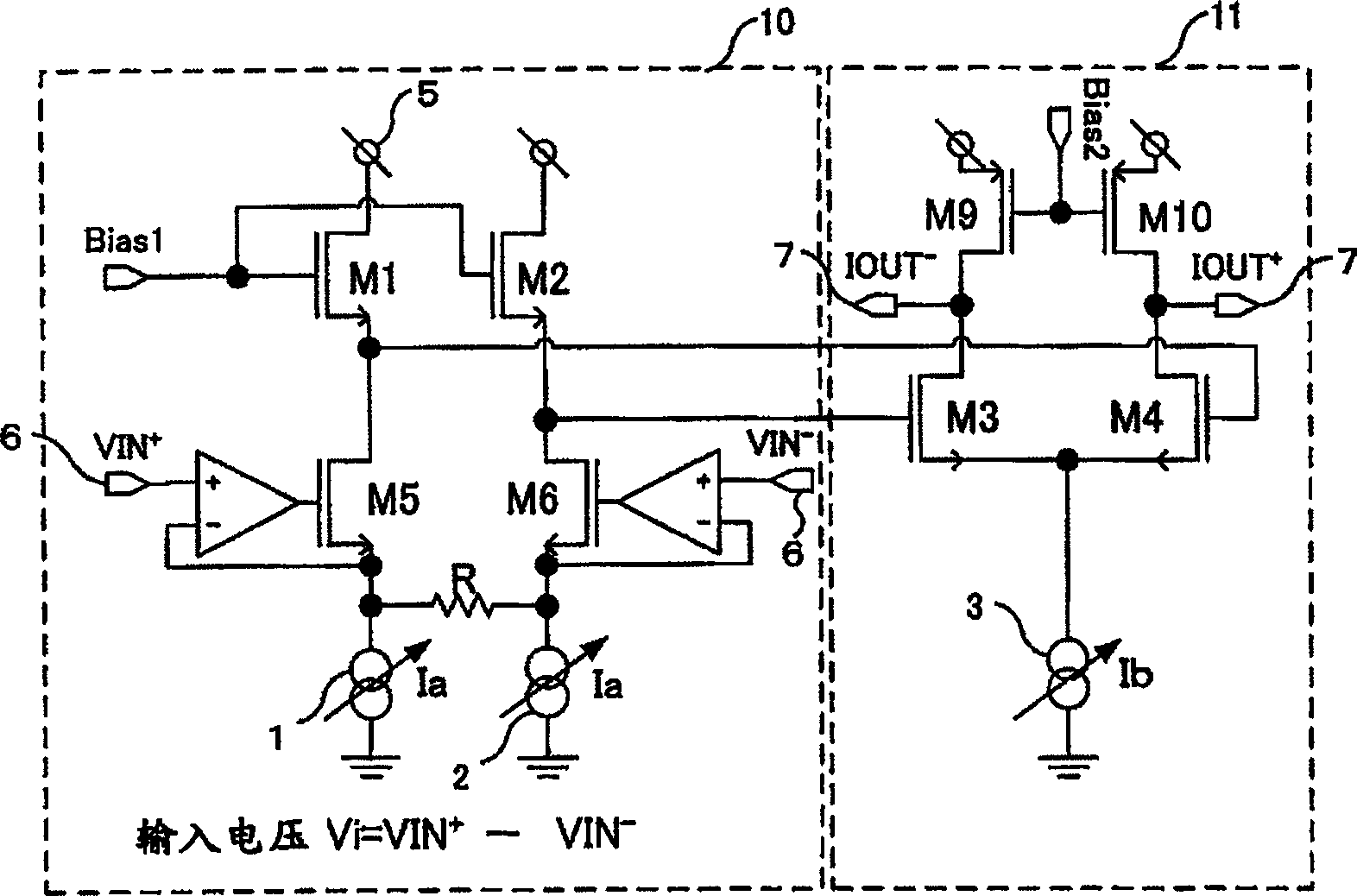
[0069] image 3 This is the variable transconductance circuit of the third embodiment, which is designed to solve the above-mentioned problems. The MOS transistor M5 and the current source 1, the MOS transistor M6 and the current source 2 respectively form an output source follower of the operational amplifier, and a resistor R is connected between the respective outputs. When a voltage signal Vi is input, a potential difference Vi also occurs across the resistor R, and a signal current Vi / R flows. This signal c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com