Compound, composition and method for preventing neurodegeneration in acute and chronic injury of central nervous system
A technology of compounds and compositions, applied in the field of neurological diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 5
[0057]
[0058] Reagent (a) N,N-methylformamide (DMF), triethylamine, room temperature, 4 hours.
[0059] The specific compounds of interest in formula (I) are as follows:
[0060] 5-benzylaminosalicylic acid
[0061] 5-(4-Nitrobenzyl)aminosalicylic acid (NBAS)
[0062] 5-(4-Chlorobenzyl)aminosalicylic acid (CBAS)
[0063] 5-(4-Trifluoromethyl)aminosalicylic acid (TBAS)
[0064] 5-(4-fluorobenzyl)aminosalicylic acid (FBAS)
[0065] 5-(4-Methoxybenzyl)aminosalicylic acid (MBAS)
[0066] 5-(Pentafluorobenzyl)aminosalicylic acid (PBAS)
[0067] Ethyl 5-(4-nitrobenzyl)amino-2-hydroxybenzoate (NAHE)
[0068] 5-(4-Nitrobenzyl)-N-acetamido-2-hydroxybenzoic acid ethyl ester (NNAHE)
[0069] 5-(4-Nitrobenzyl)-N-acetamido-2-acetoxy-benzoic acid ethyl ester (NNAAE)
[0070] 5-(4-Nitrobenzoyl)aminosalicylic acid (NBAA)
[0071] 5-(4-Nitrobenzenesulfonyl)aminosalicylic acid (NBSAA)
[0072] 5-[2-(4-nitrophenyl)-ethyl]aminosalicylic acid (NPAA)
[0073] 5-[3-(4-nitrophenyl)n-propyl]aminosalic...
experiment Embodiment 1
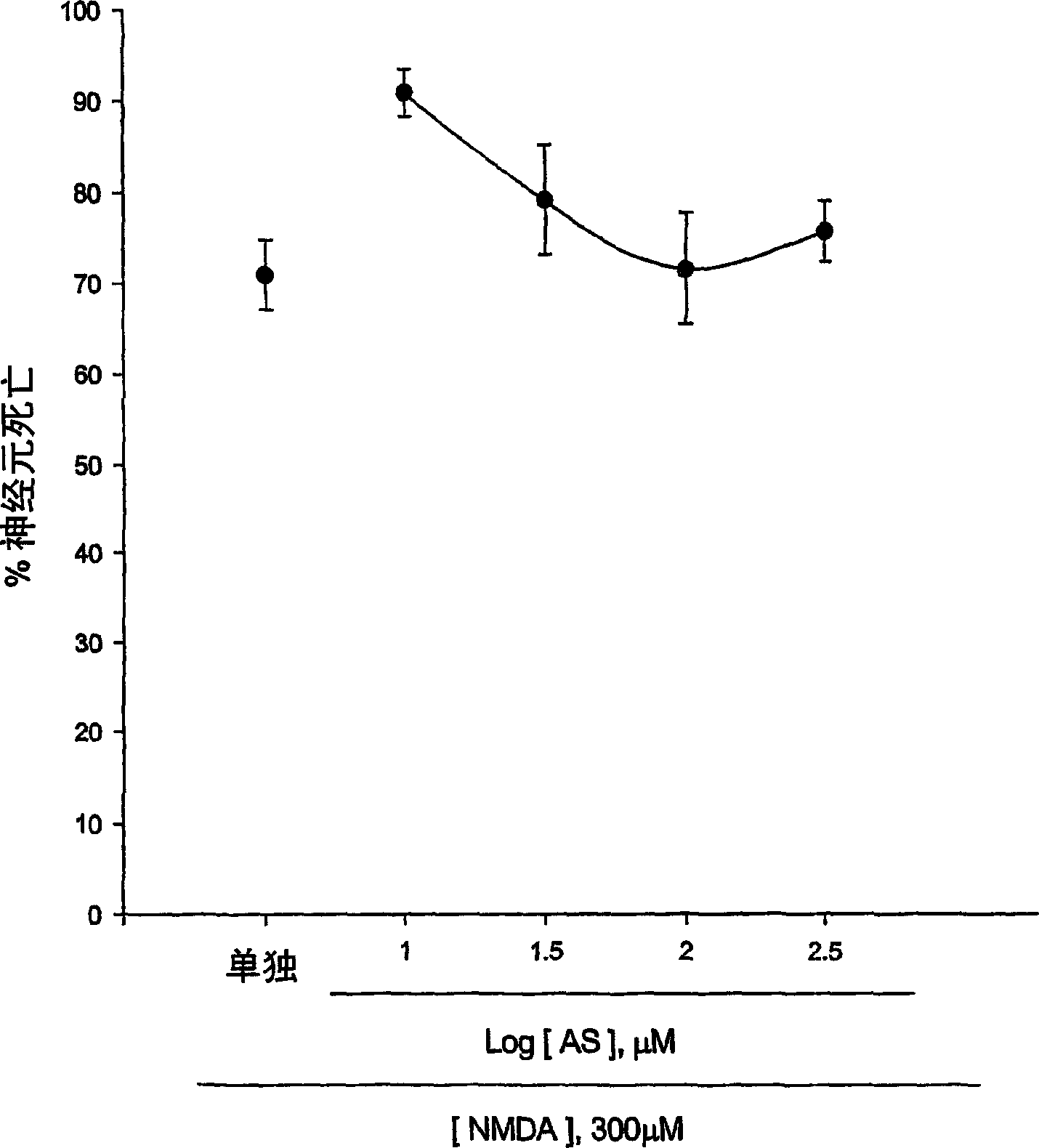
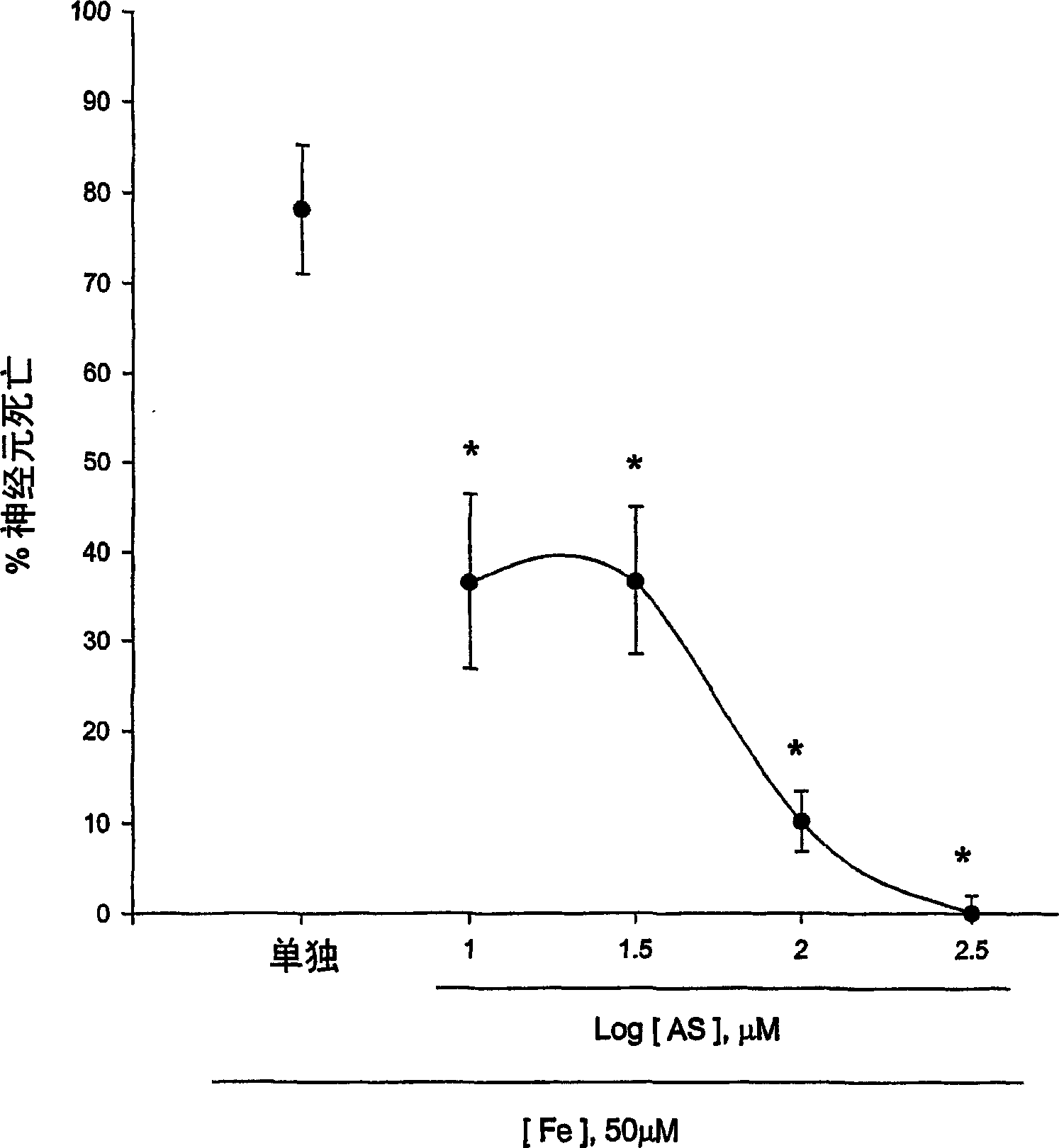
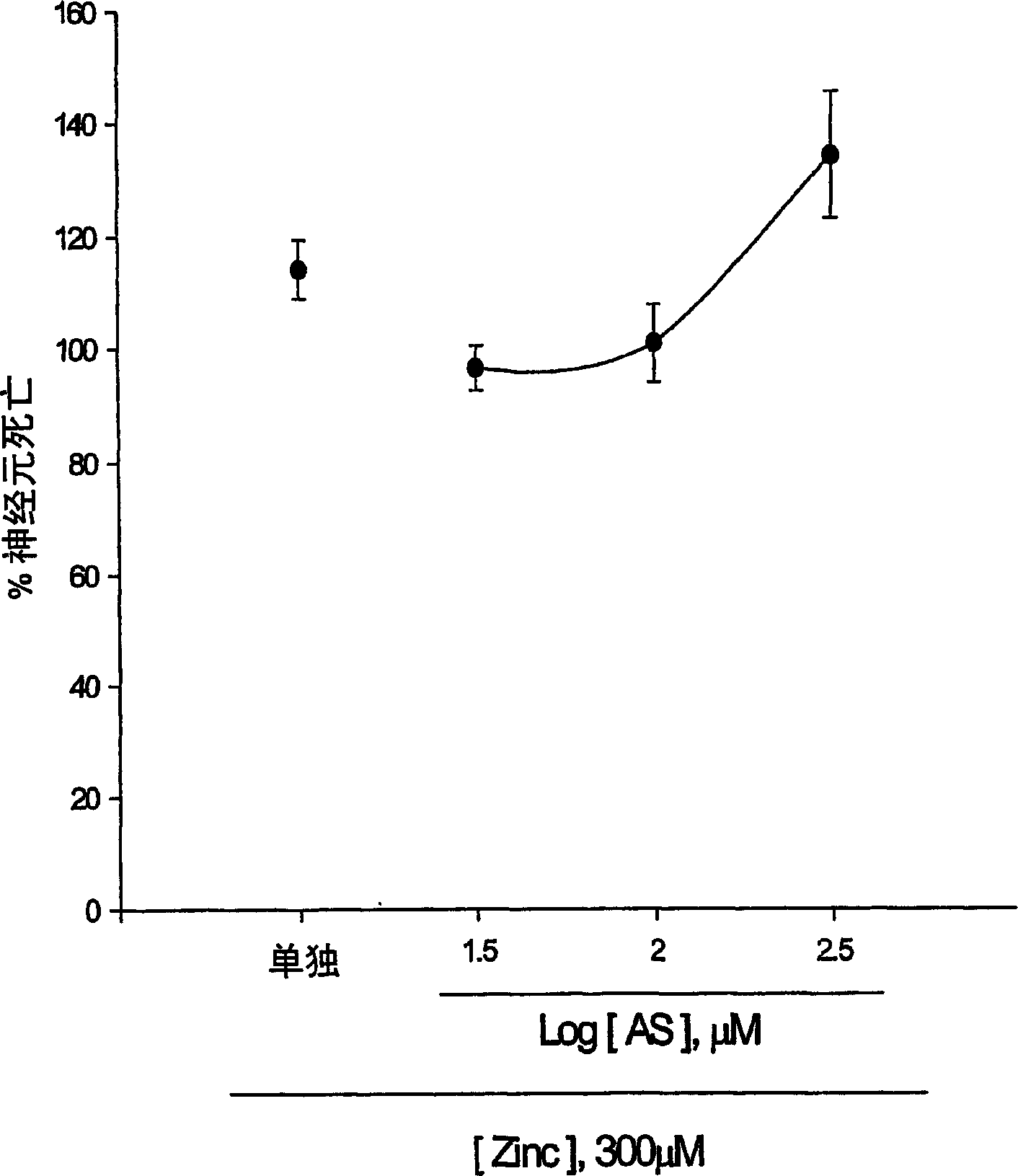
[0123] Experimental Example 1: Antioxidant effect of 5-aminosalicylic acid
[0124] The neuroprotective effect of 5-aminosalicylic acid (AS) was tested in primary cortical cell cultures. Within 24 hours, AS containing 10-300 micromolar did not reduce neuronal death caused by exposure to 300 micromolar NMDA for 10 minutes (Fig. 1.a). Interestingly, increasing AS by 10-100 micromolar dose-dependently prevented the neurotoxicity of free radicals caused by exposure to ferrous ions for 24 hours (Fig. 1b). During and after zinc ion treatment, continuous addition of AS did not reduce neuronal death after 24 hours. These neurons were exposed to 300 micromole zinc ions for 30 minutes. The neuroprotective effect of AS against free radical neurotoxicity is attributed to the direct antioxidant properties of compound AS which reduces the level of DPPH (a stable free radical). Compared with trolox (a membrane-permeable vitamin E), AS is a weak oxidant.
[0125] Reactant
Concentr...
experiment Embodiment 2
[0128] Experimental Example 2: Neuroprotective effects of 5-benzylaminosalicylic acid and its derivatives
[0129] Neuroprotective effects of 1.5-benzylaminosalicylic acid
[0130] Synthesize BAS and test its ability to resist nerve damage, which is induced in cortical cell culture. At the same time, the addition of 300 micromoles of 5-benzylaminosalicylic acid (BAS) approximately reduced NMDA-induced neuronal death by 50% (Figure 2a). In the presence of 1 micromole of BAS, contact with 50 micromole of ferrous ions (Figure. 2b) or 10 millimole of BSO (Figure. 2c) caused a considerable reduction in neuronal death. Add 3 micromole With Moore BAS, neuronal death is basically completely blocked. Adding 30-300 micromolar BAS will dose-dependently reduce neuronal death caused by contact with 300 micromole zinc ions for 30 minutes in 24 hours. Like AS or trolox, BAS is a direct antioxidant (Table 2). The antioxidant properties of BAS can be observed at a dose as low as 1 micromolar.
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mp | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mp | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mp | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com