Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
一种非挥发性存储、非挥发性的技术,应用在半导体存储装置领域,能够解决无法稳定读出、输入电流偏差等问题,达到容易设计可靠性、缓和需求规格、改善阈值恶化的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
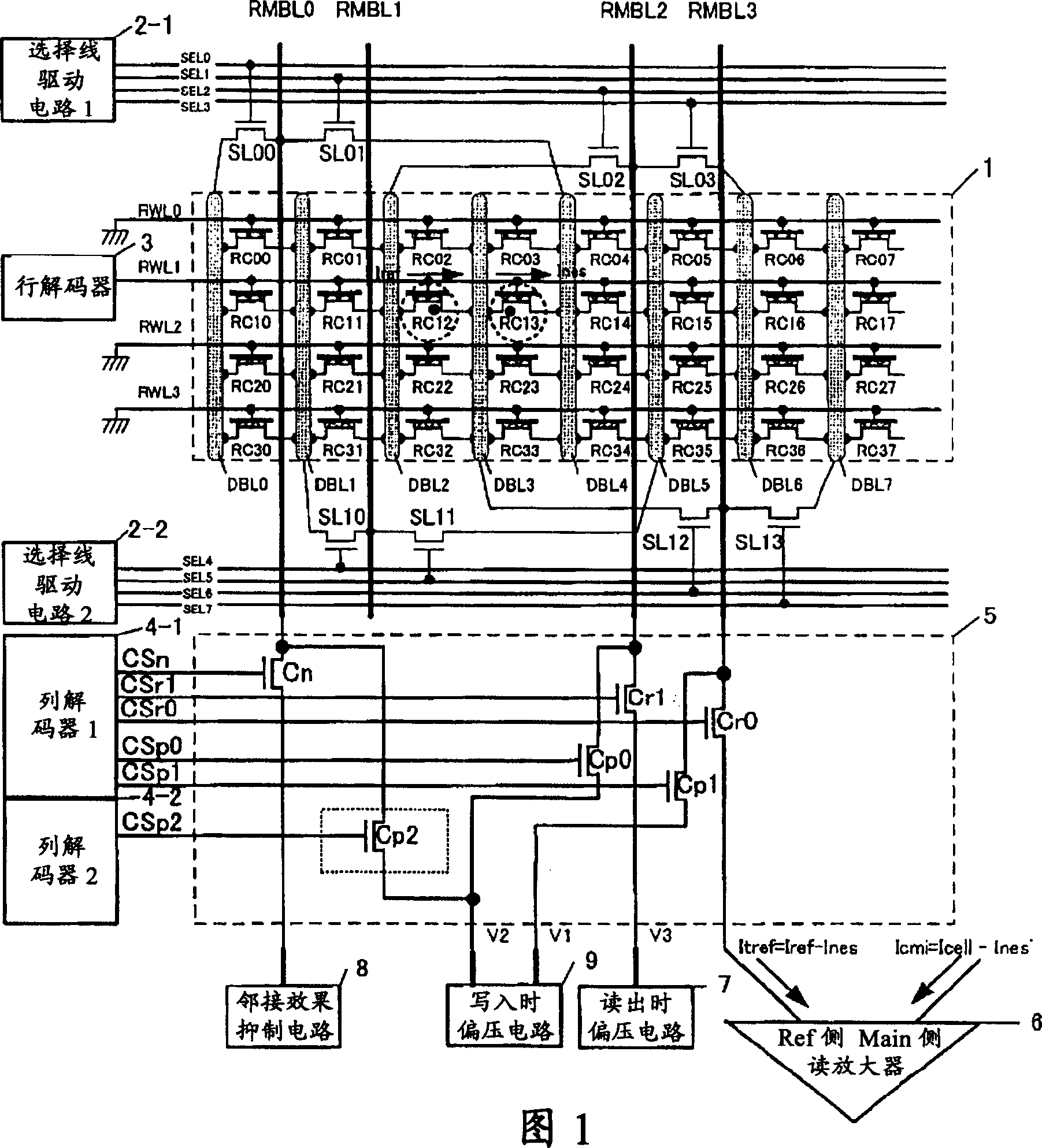
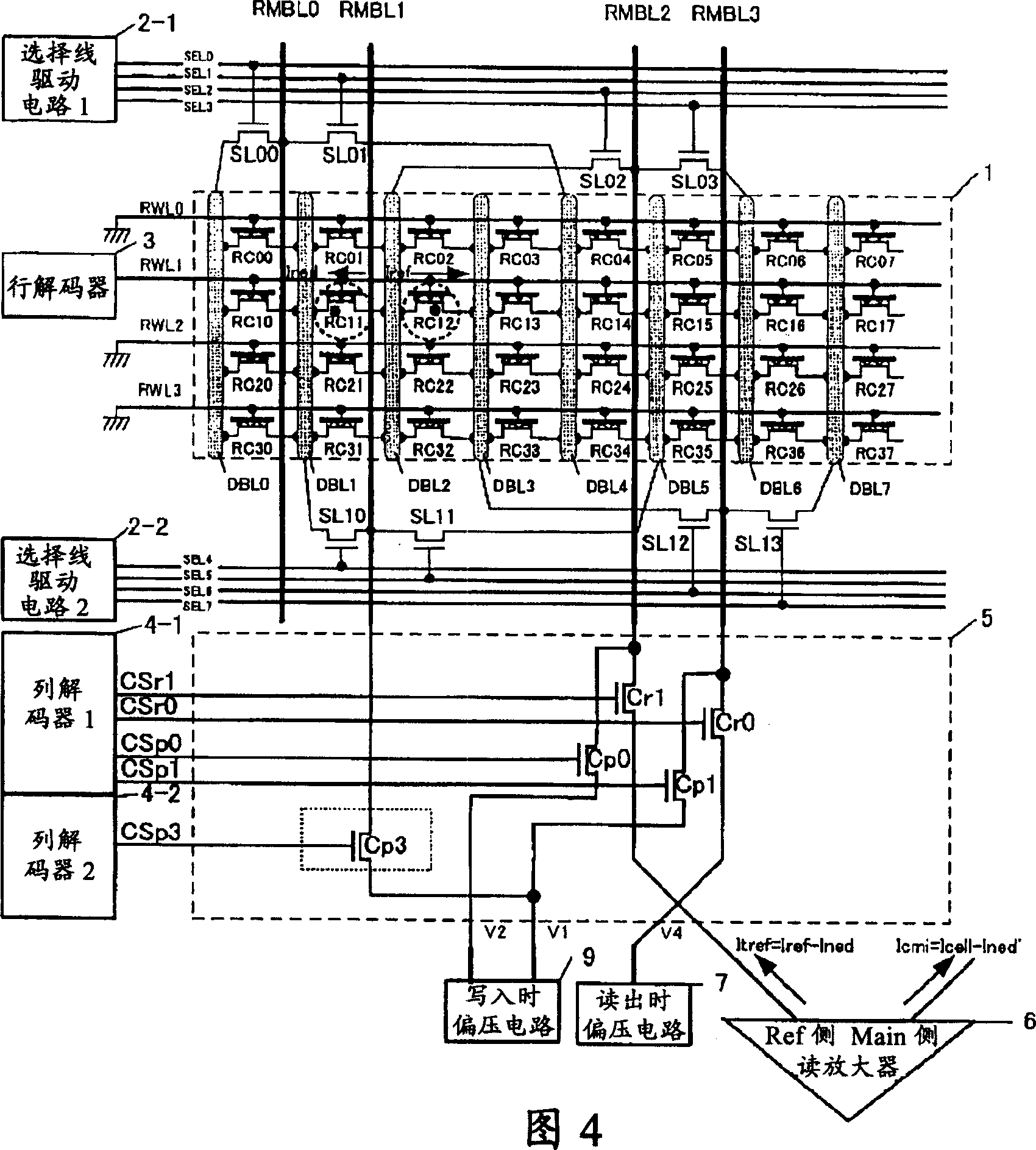
[0059] Hereinafter, the outline of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of this embodiment can reduce the variation of the adjacent effect in the source side read method.
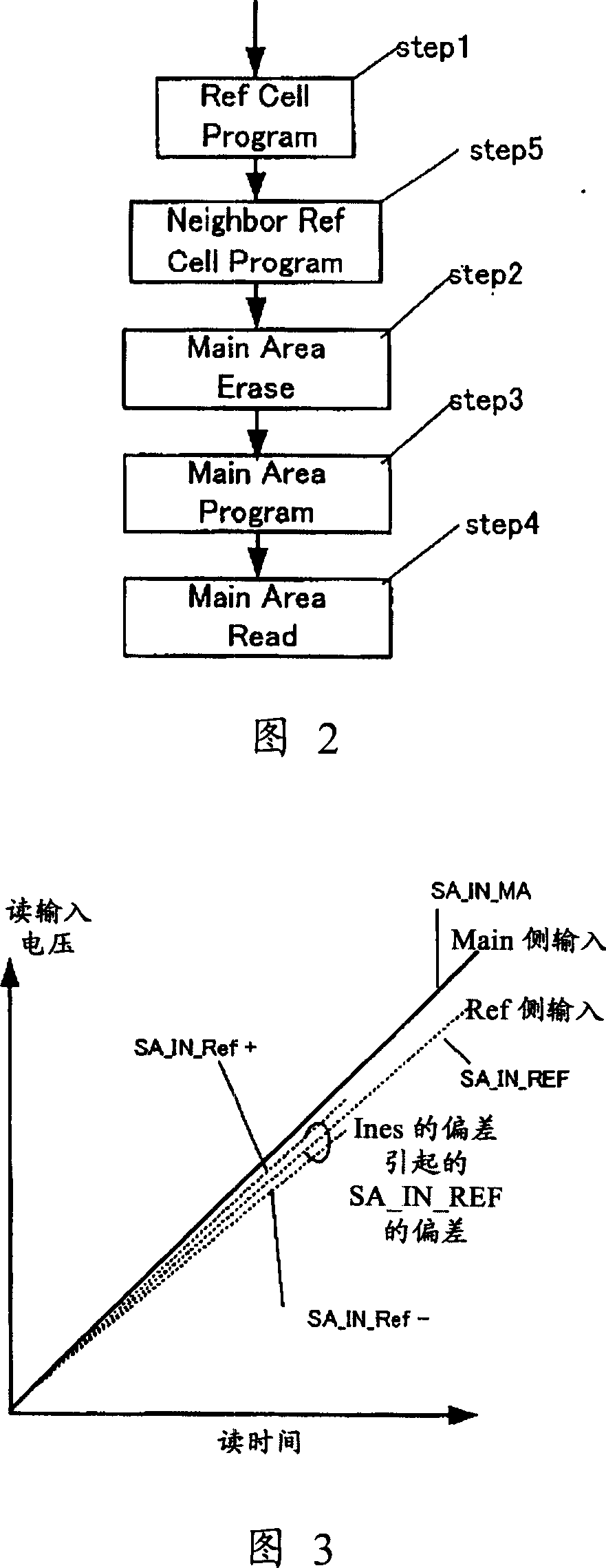
[0060] FIG. 2 is an example of an algorithm for rewriting and reading operations in the first embodiment of the present invention. First, it is set in step1, and a predetermined reference current is made to flow by writing into the reference cell, and then, in step5, writing is performed in a cell adjacent to the reference cell. Afterwards, in the rewriting operation during actual use, step 2 of erasing, step 3 of writing, and step 4 of reading are performed on the main body area.
[0061] In addition, in step1, step2, and step3, it is also possible to include a case where a check action for adjusting the level (level) is included.
[0062] In addi...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0068] Hereinafter, an outline of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. The nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of this embodiment can reduce the variation of the adjacent effect in the drain side read method.
[0069] FIG. 2 is an example of an algorithm for rewriting and reading operations in the second embodiment of the present invention. First, it is set in step1, and a predetermined reference current is made to flow by writing into the reference cell, and then, in step5, writing is performed in a cell adjacent to the reference cell. Afterwards, in the rewriting operation during actual use, step 2 of erasing, step 3 of writing, and step 4 of reading are performed on the main body area.
[0070] In addition, step1, step2, and step3 can also include the case of including a verification action for level adjustment.
[0071] In addition, for the position of ste...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0078] Hereinafter, an outline of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of this embodiment, the variation of the adjacent effect in the source side read method is reduced, and the access time is improved by speeding up the charge on the drain side.
[0079] FIG. 2 is an example of an algorithm for rewriting and reading operations in the third embodiment of the present invention. First, it is set in step1, and a predetermined reference current is made to flow by writing into the reference cell, and then, in step5, writing is performed in a cell adjacent to the reference cell. Afterwards, in the rewriting operation during actual use, step 2 of erasing, step 3 of writing, and step 4 of reading are performed on the main body area.
[0080] In addition, step1, step2, and step3 can also include the case of including a verifica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com