Bispecific antibodies that bind to CD38 and CD3
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
“Triple F” Bispecific Antibody
[0346]The present invention describes novel immunoglobulin compositions that co-engage a first and second antigen. One heavy chain of the antibody contains a single chain Fv (“scFv”, as defined herein) and the other heavy chain is a “regular” Fab format, comprising a variable heavy chain and a light chain (see FIG. 1). This structure is sometimes referred to herein as “triple F” format (scFv-Fab-Fc). The two chains are brought together by the dimeric Fc region (see FIG. 2). The Fc region can be modified by amino acid substitution to allow for efficient purification of the “triple F” heterodimer. Further, the Fc region can be modified by amino acid substitution to promote the formation of the “triple F” heterodimer. Examples of Fc substitutions are described more fully below.
[0347]Fc substitutions can be included in the “triple F” format to allow for efficient purification of the desired “triple F” heterodimer over the undesired dual scFv-Fc and mAb homo...
example 2
cific Antibodies Derived from the “Triple F” Format
[0350]Multi-specific antibodies can be constructed by attaching additional scFv or Fab domains that bind a third antigen to the C-terminus of one of the “triple F” heavy chains. See FIG. 5 for examples. Alternatively, the C-terminal scFv or Fab may bind the first or second antigen, thus conferring bivalency and an increase in overall binding affinity for that antigen.
[0351]Multi-specific antibodies can also be constructed by coupling the scFv-Fc heavy chain of the “triple F” format may with rearranged antibody heavy chains as depicted in FIG. 6. Such rearranged heavy chains may include an additional Fv region that binds a third antigen or an additional Fv region that binds the first antigen or second antigen, thus conferring bivalency and an increase in overall binding affinity for that antigen.
example 3
Fab×Anti-CD3 scFv “Triple F” Bispecific
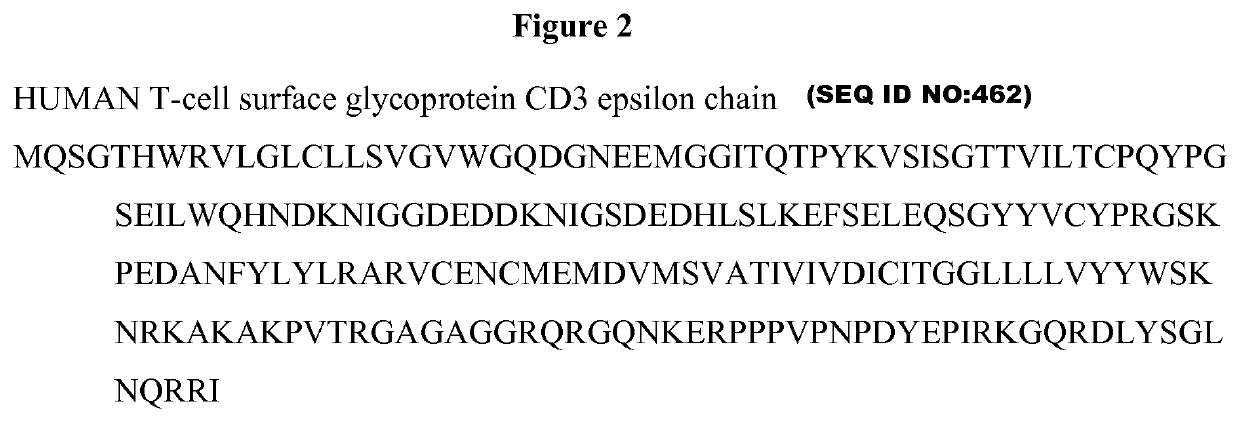
[0352]Amino acid sequences for anti-CD19 Fab×anti-CD3 scFv “triple F” bispecifics are listed in the figures. Amino acid substitutions made to allow for efficient purification of the desired “triple F” heterodimer over the undesired dual scFv-Fc and mAb homodimers are underlined. Amino acid sequences for preferred humanized anti-CD3 variable regions are listed in FIGS. 2 and 6 (with CDRs underlined). Some examples of expression and purification of the desired “triple F” species and its bioactivity are given below.
[0353]The production of XENP11874, a “triple F” bispecific with an anti-CD 19 Fab and anti-CD3 scFv, is outlined in FIG. 9. In FIG. 9A, the ion exchange purification of the desired “triple F” heterodimer from the undesired dual scFv-Fc and mAb homodimers is shown. The purity of the “triple F” fraction was checked by IEF gel, (data shown in FIG. 9B of U.S. Ser. No. 61 / 818,410, all figures and legends of which are expressly incorporated b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com