Method for verifying the tightness of a tank system in a motor vehicle
a technology for tightness testing and motor vehicles, applied in the direction of fluid tightness measurement, combustion air/fuel air treatment, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to reliably decide in this manner, and failure to achieve fault outpu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
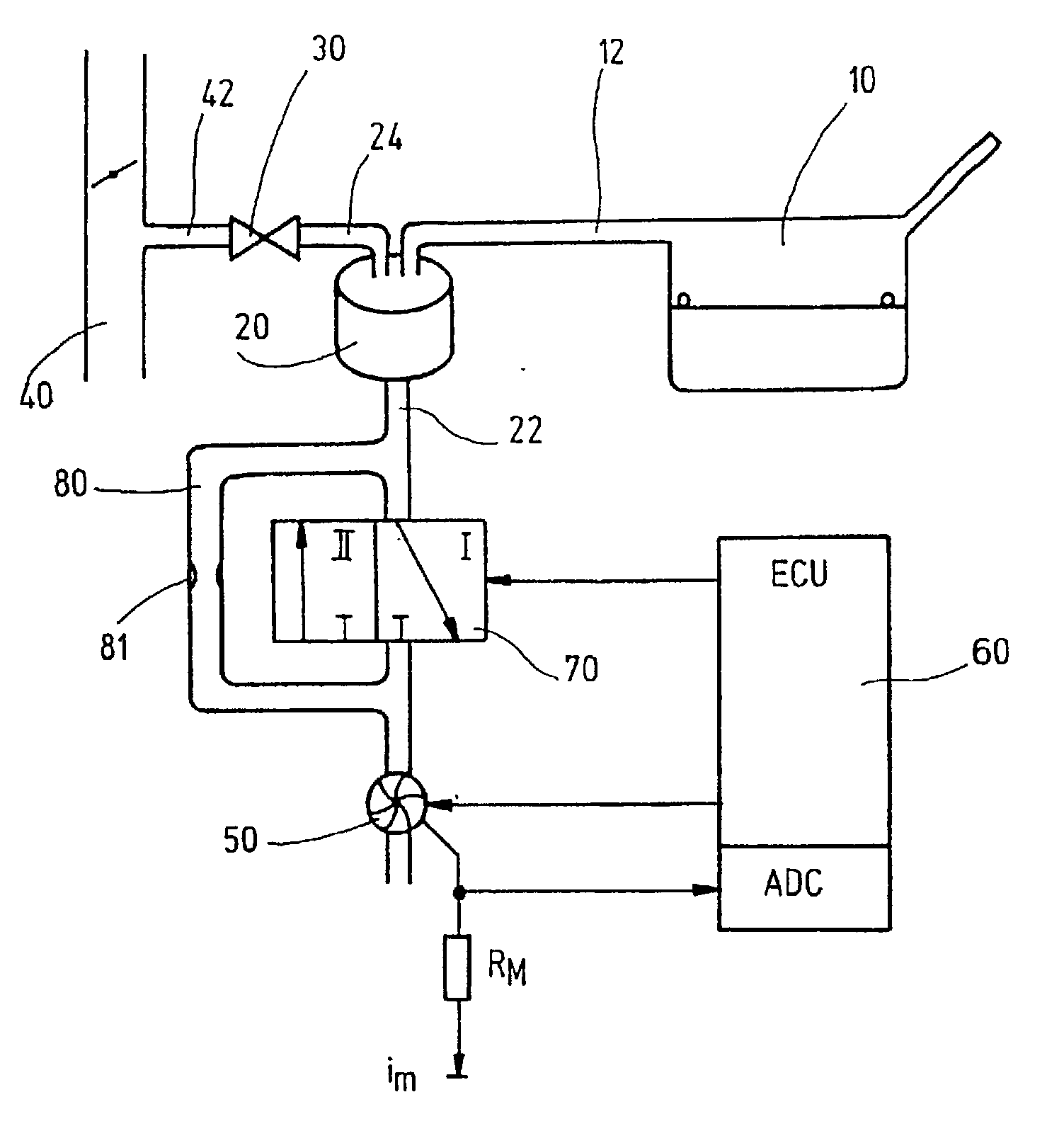
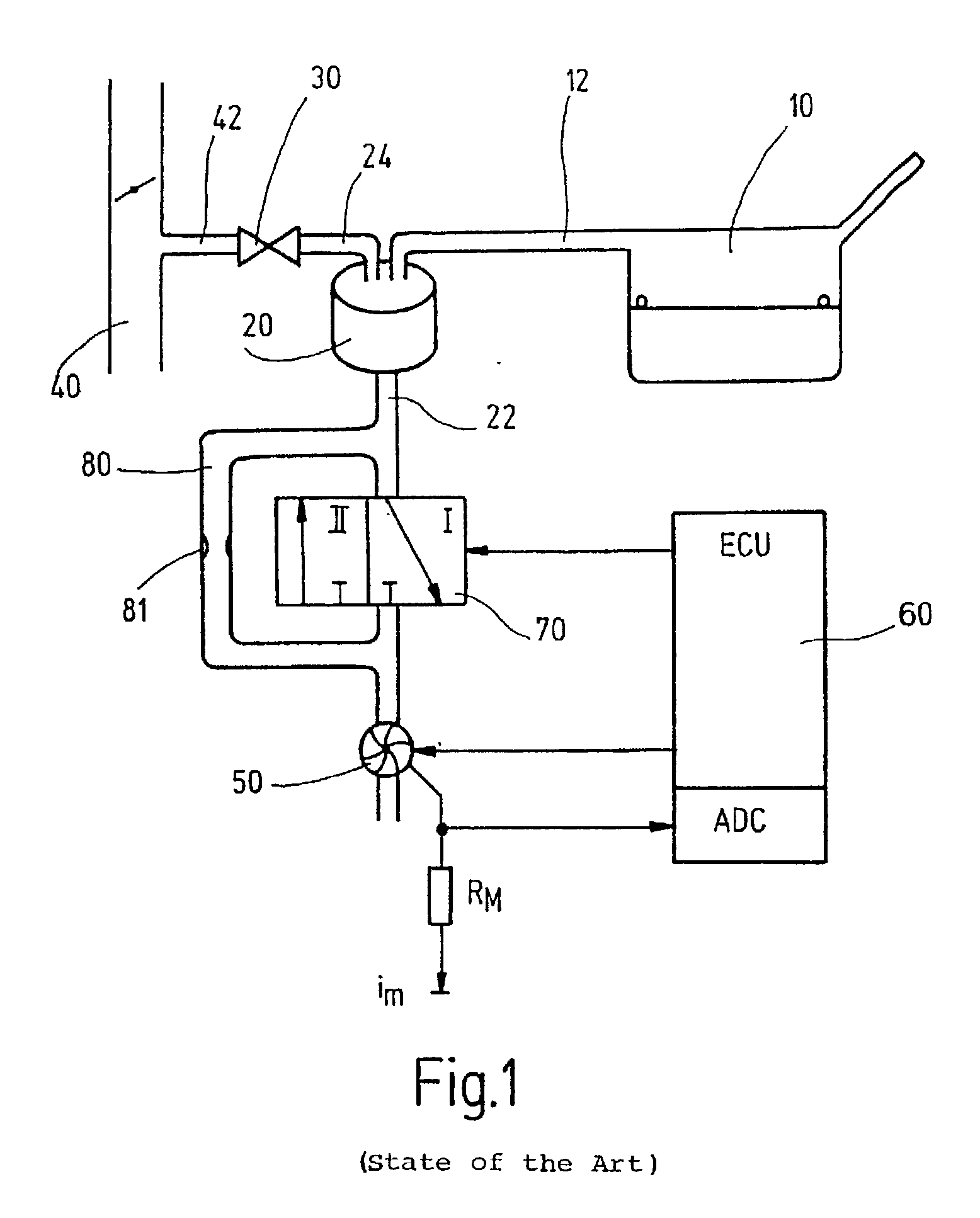
[0021] The invention is described in the following with respect to an example of a tank-venting system of a motor vehicle. It is, however, understood that the method of the invention can be used not only for a tank-venting system but for any desired tank system.
[0022] A tank-venting system of a motor vehicle tank system is shown in FIG. 1 and includes a tank 10, an adsorption filter 20 (for example, an active charcoal filter), a venting line 22 connectable to the ambient and a tank-venting valve 30. The adsorption filter 20 is connected to the tank 10 via a tank connecting line 12. The tank-venting valve 30 is connected, on the one hand, to the adsorption filter 20 via a valve line 24 and, on the other hand, to an intake manifold 40 of an internal combustion engine (not shown) via a valve line 42.
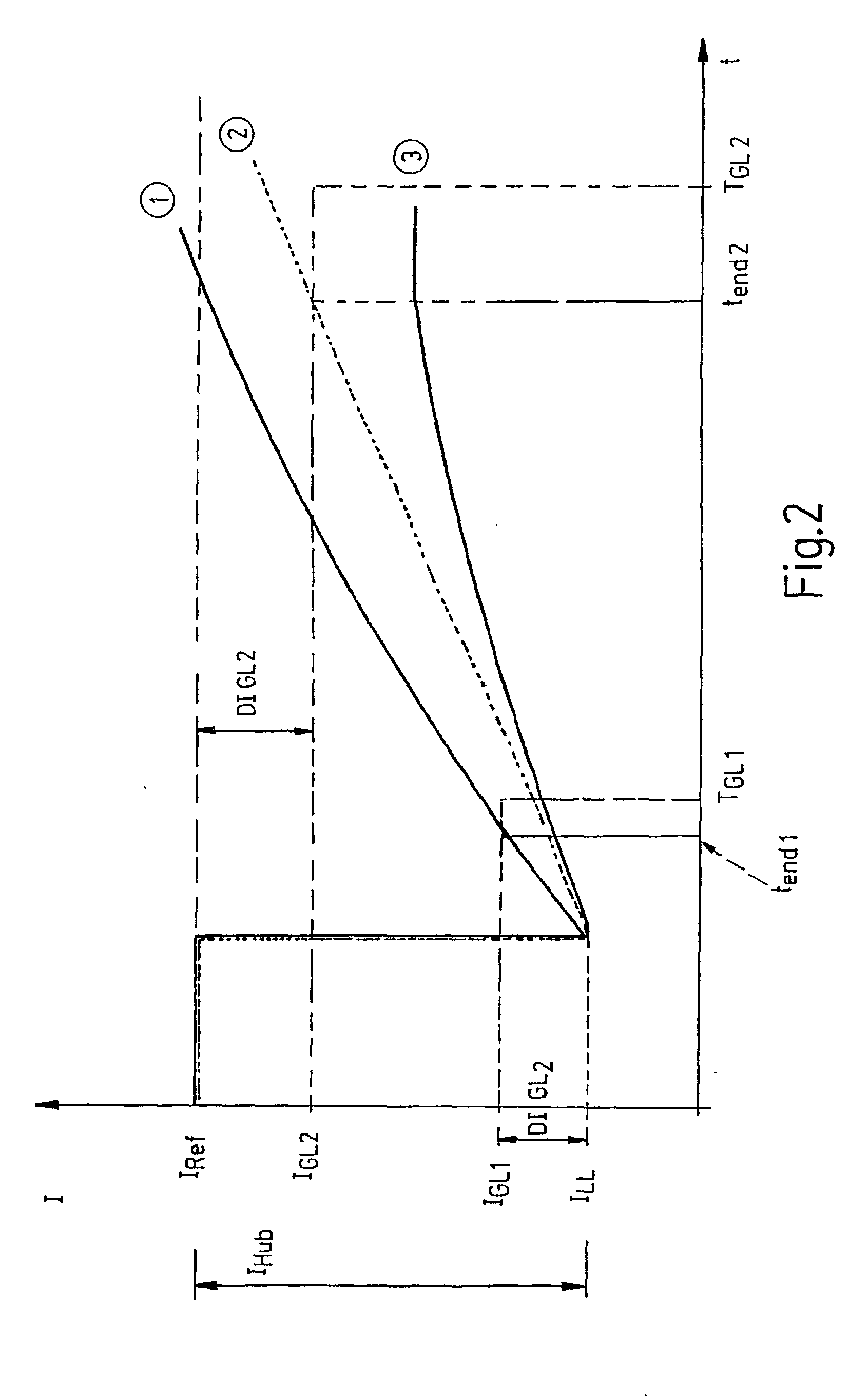
[0023] Hydrocarbons develop in the tank 10 because of vaporization and these hydrocarbons deposit on the adsorption filter 20. To regenerate the adsorption filter 20, the tank-venting valve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com