Patents
Literature
1269results about "Condensed fuel collection/return" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
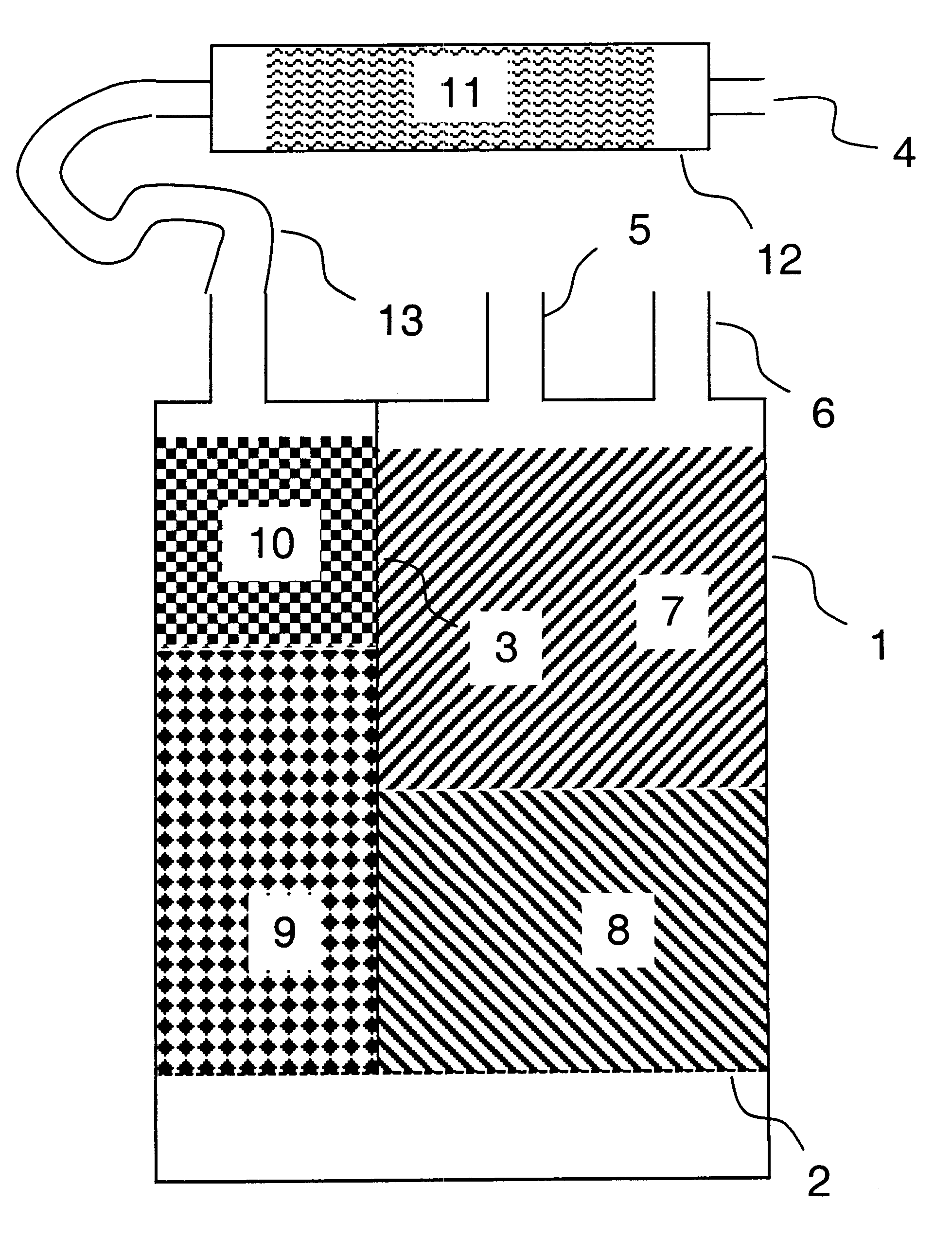
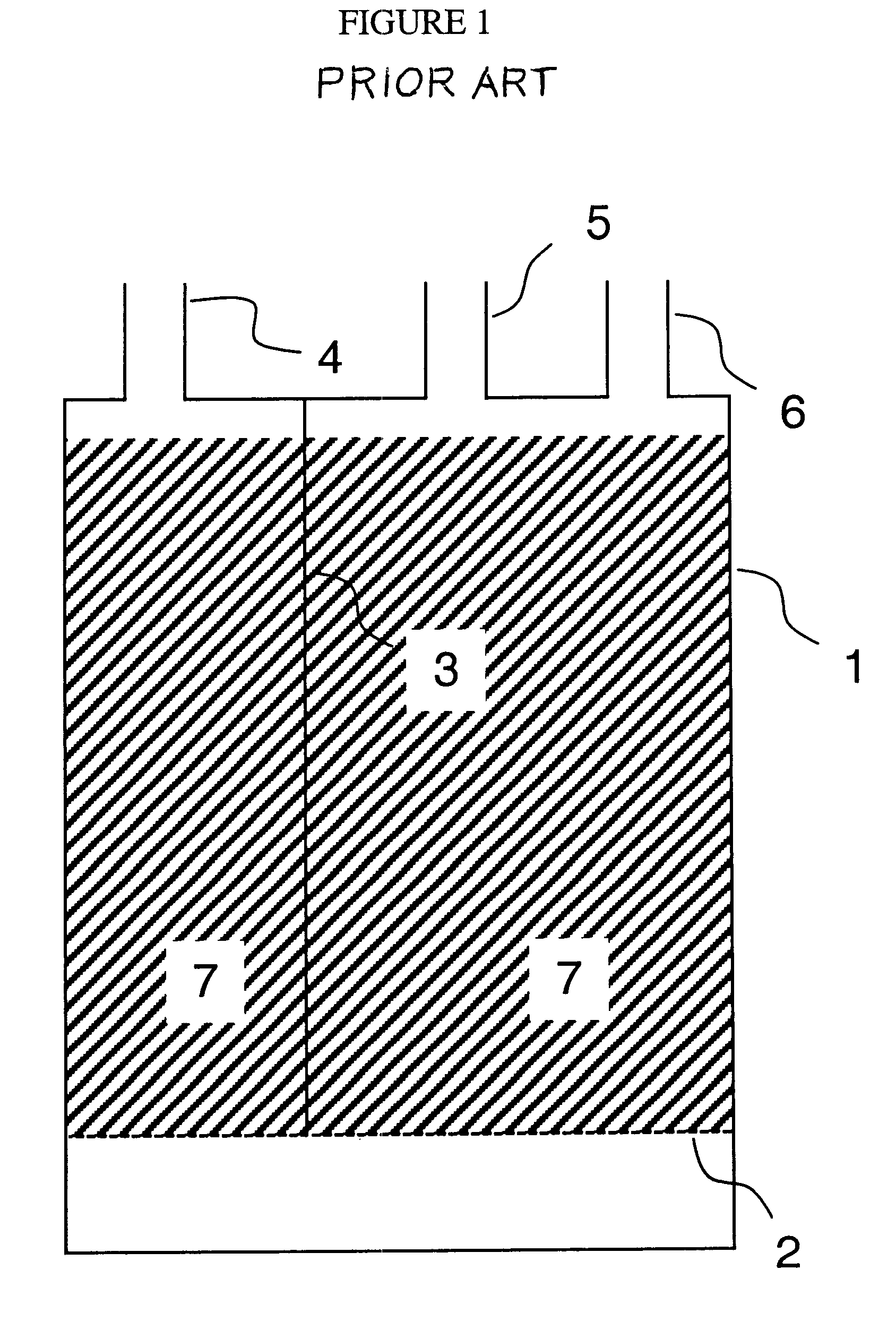
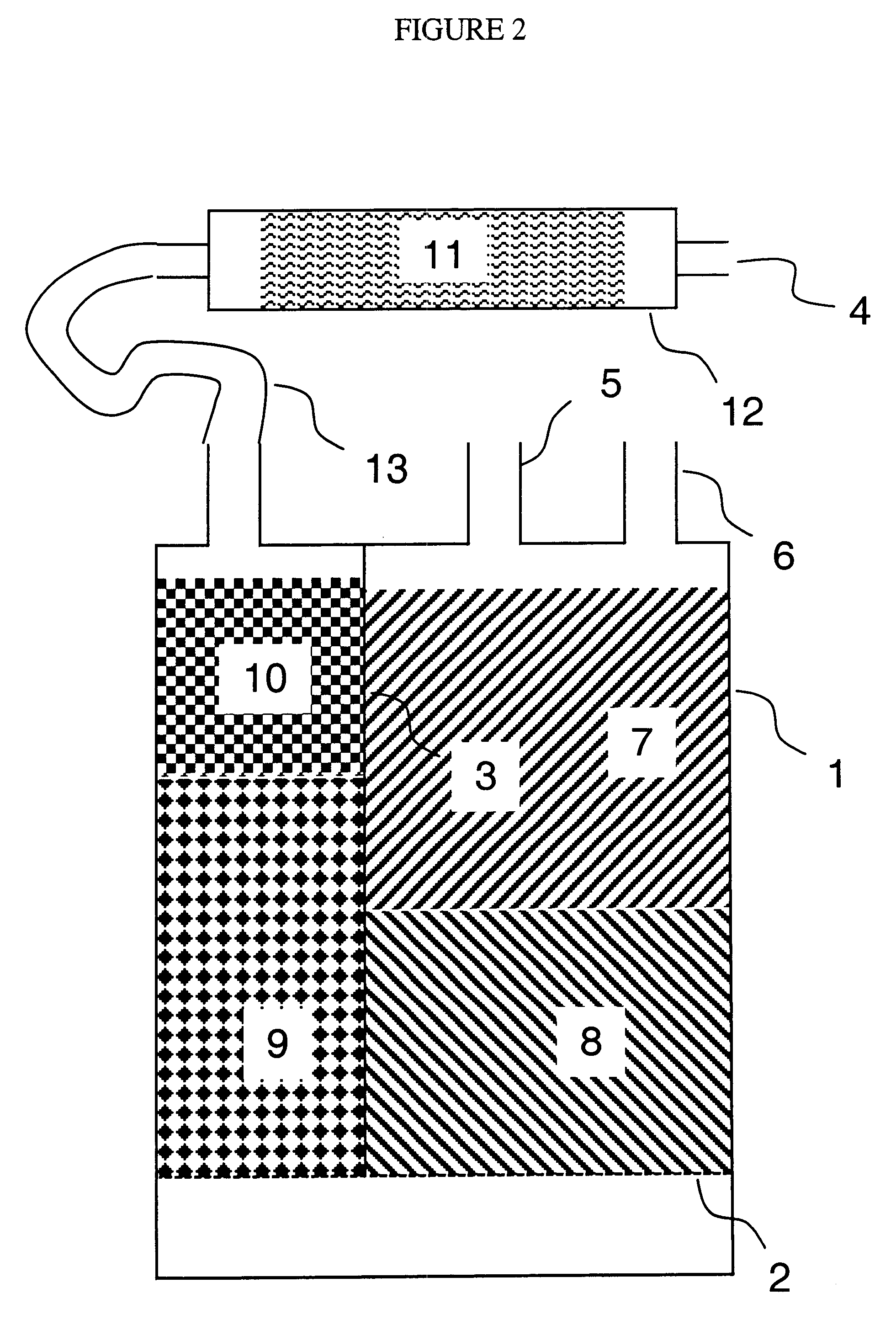
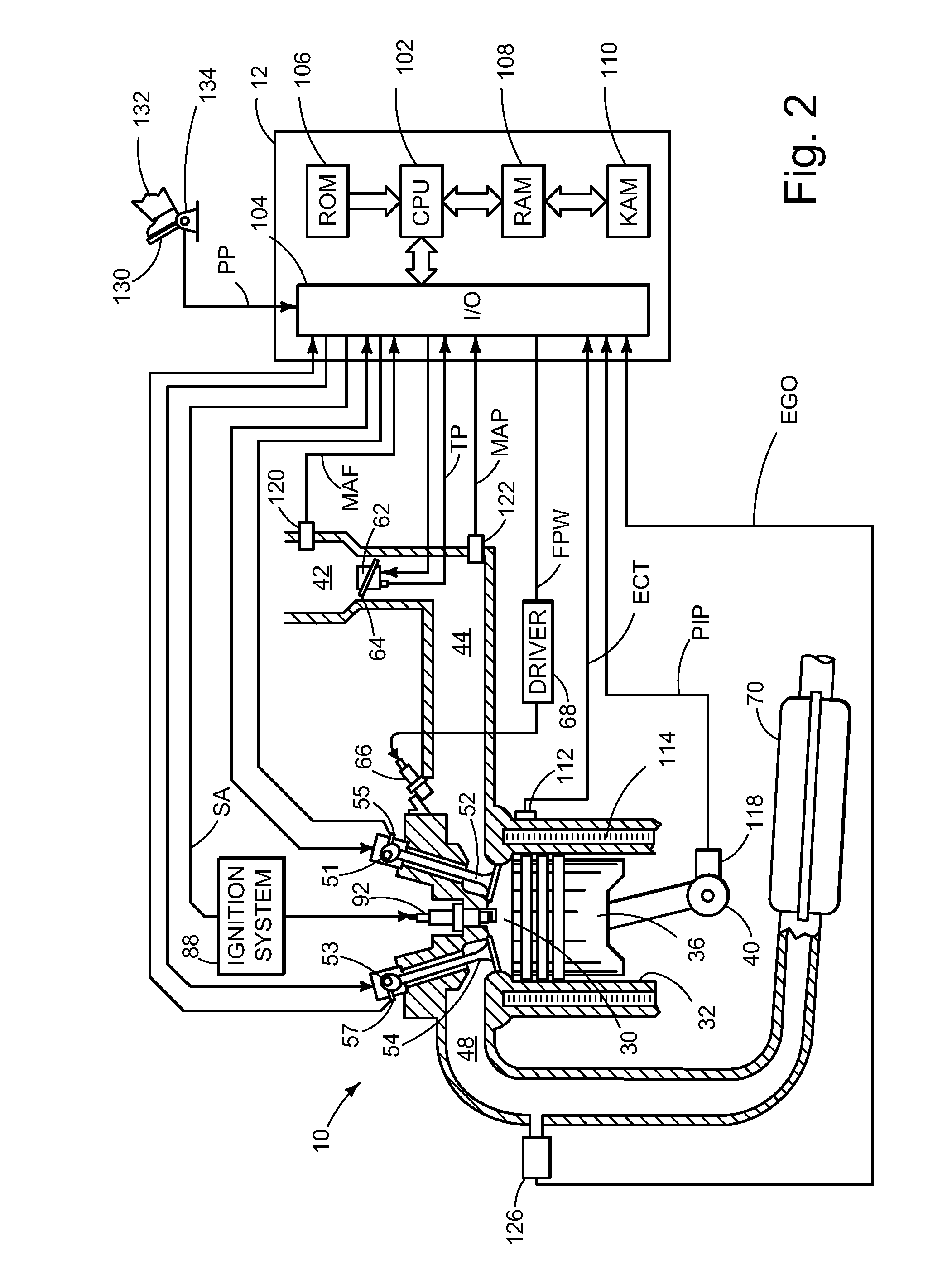
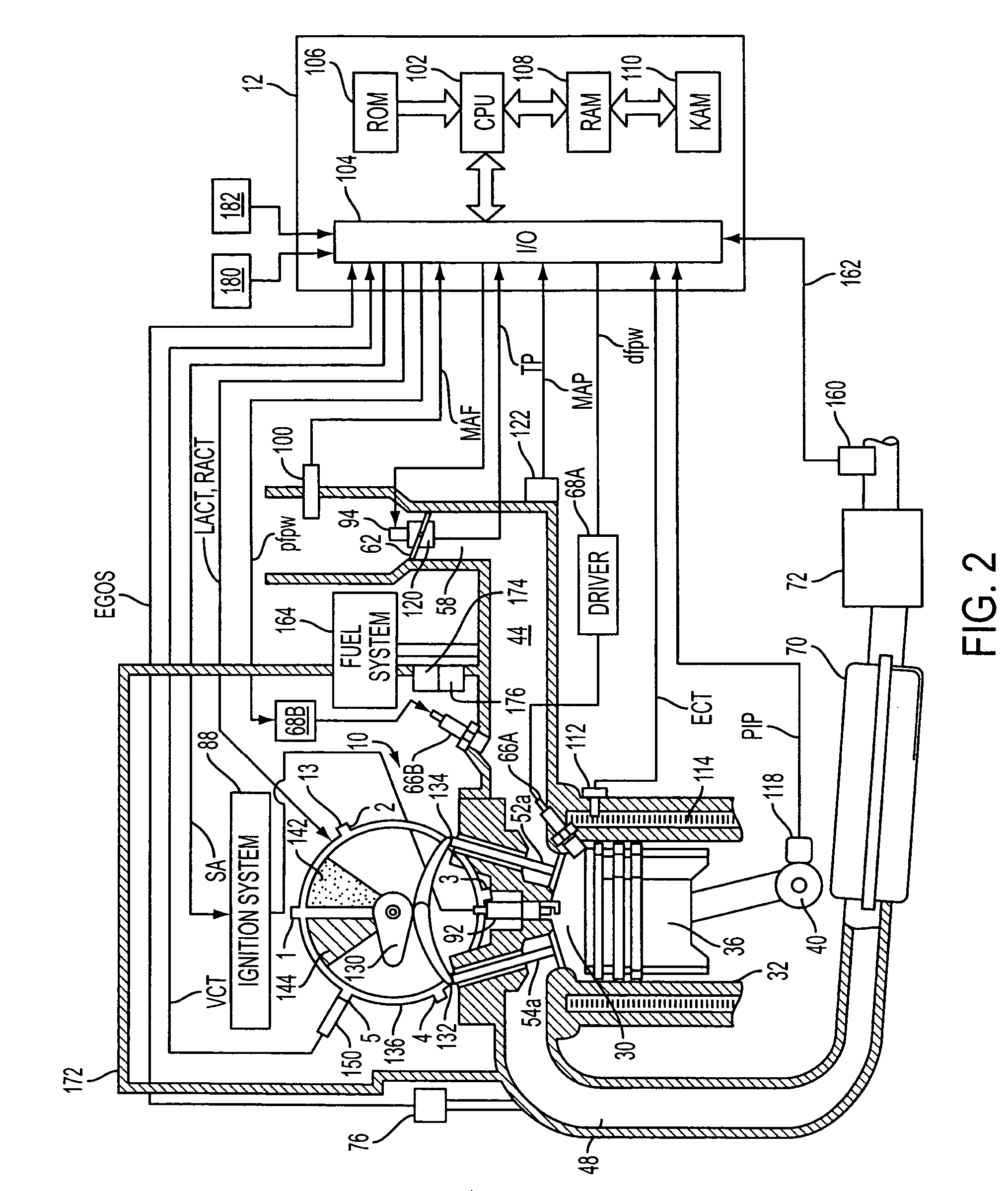
Method for reducing emissions from evaporative emissions control systems
InactiveUS6540815B1Loss in working capacityEmission reductionGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHigh concentrationSorbent
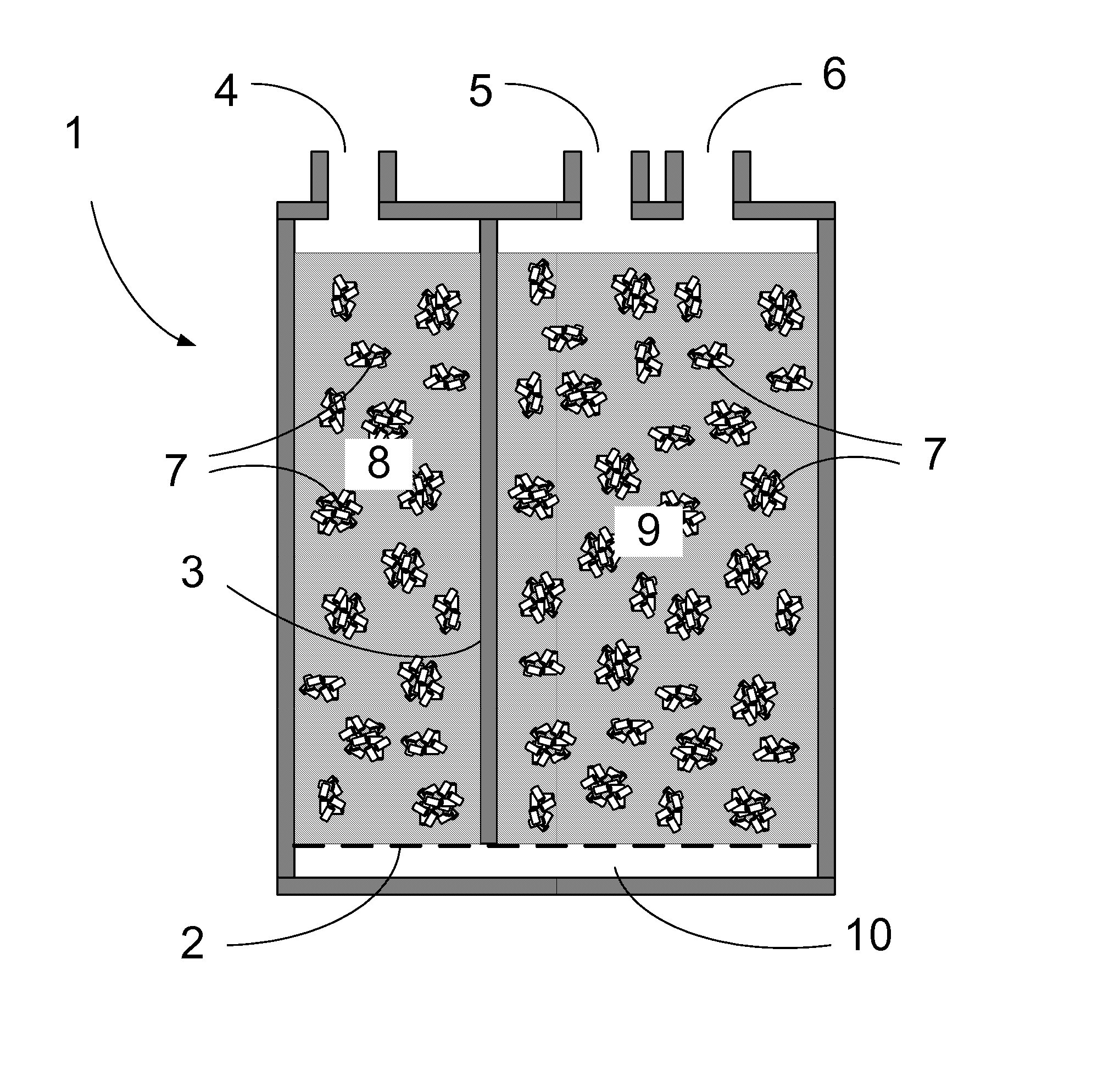
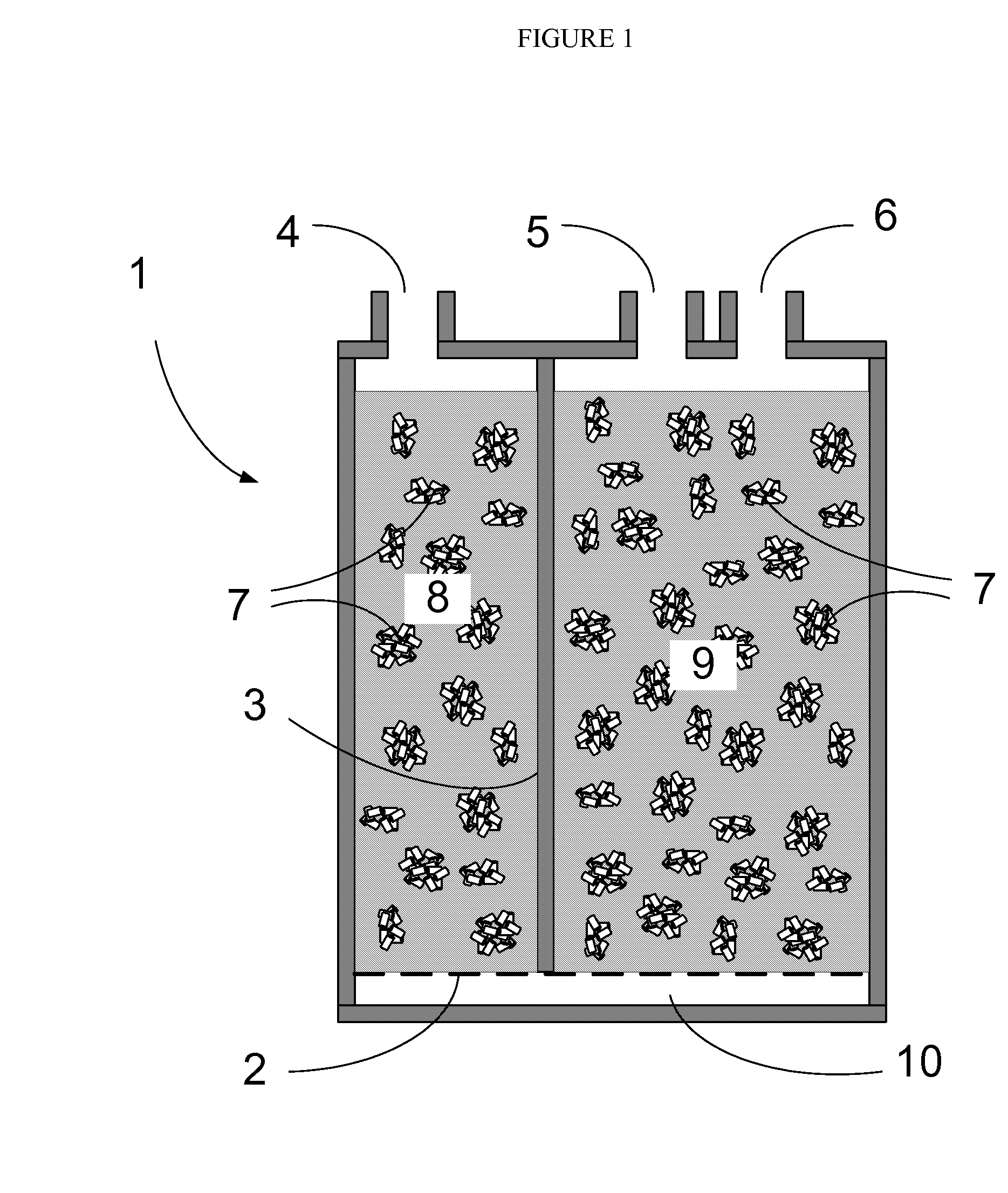
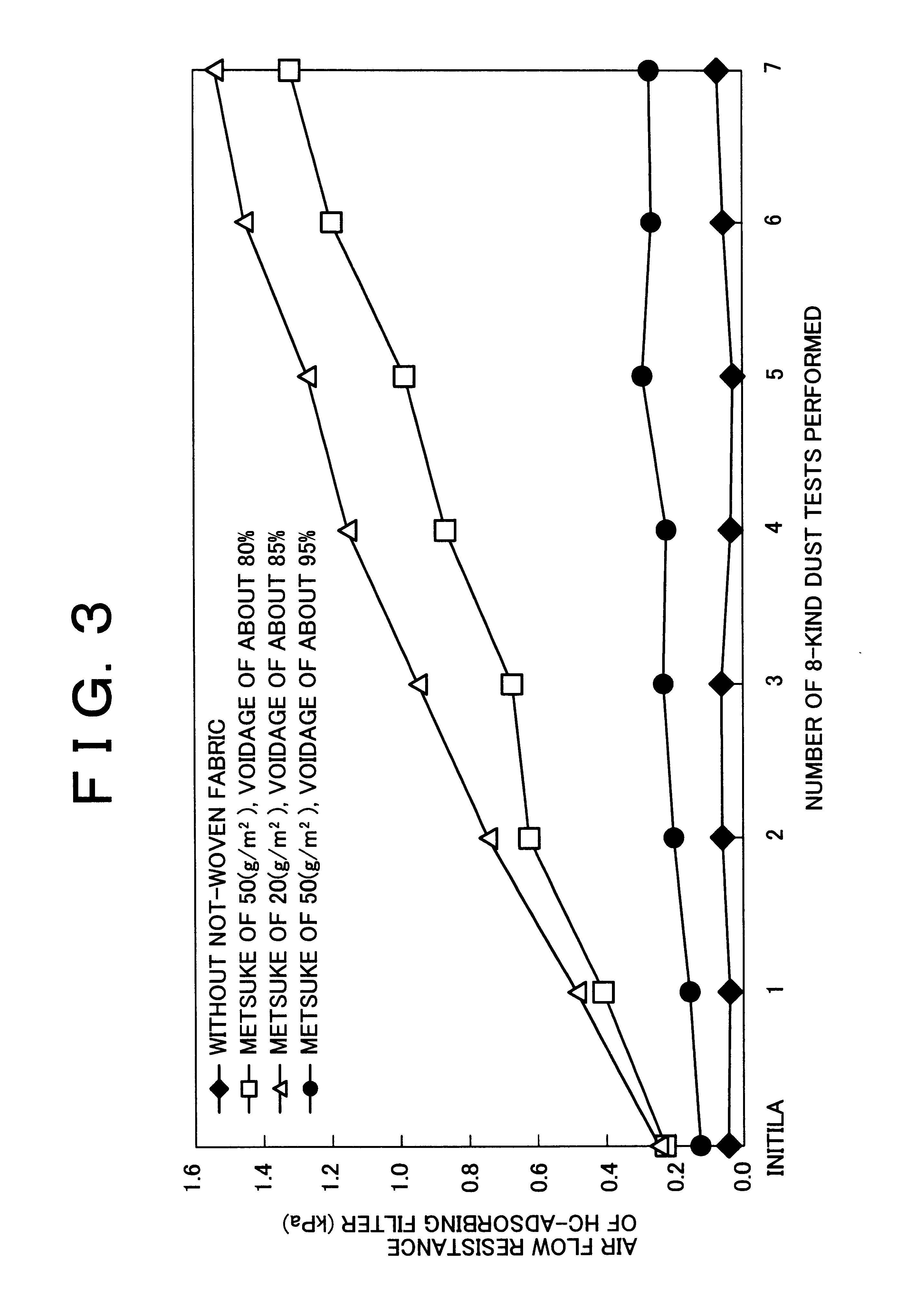
Disclosed is a method for sharply reducing diurnal breathing loss emissions from automotive evaporative emissions control systems by providing multiple layers, or stages, of adsorbents. On the fuel source-side of an emissions control system canister, high working capacity carbons are preferred in a first canister (adsorb) region. In subsequent canister region(s) on the vent-side, the preferred adsorbent should exhibit a flat or flattened adsorption isotherm on a volumetric basis and relatively lower capacity for high concentration vapors as compared with the fuel source-side adsorbent. Multiple approaches are described for attaining the preferred properties for the vent-side canister region. One approach is to use a filler and / or voidages as a volumetric diluent for flattening an adsorption isotherm. Another approach is to employ an adsorbent with the desired adsorption isotherm properties and to process it into an appropriate shape or form without necessarily requiring any special provision for dilution. The improved combination of high working capacity carbons on the fuel source-side and preferred lower working capacity adsorbent on the vent-side provides substantially lower diurnal breathing emissions without a significant loss in working capacity or increase in flow restriction compared with known adsorbents used in canister configurations for automotive emissions control systems.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
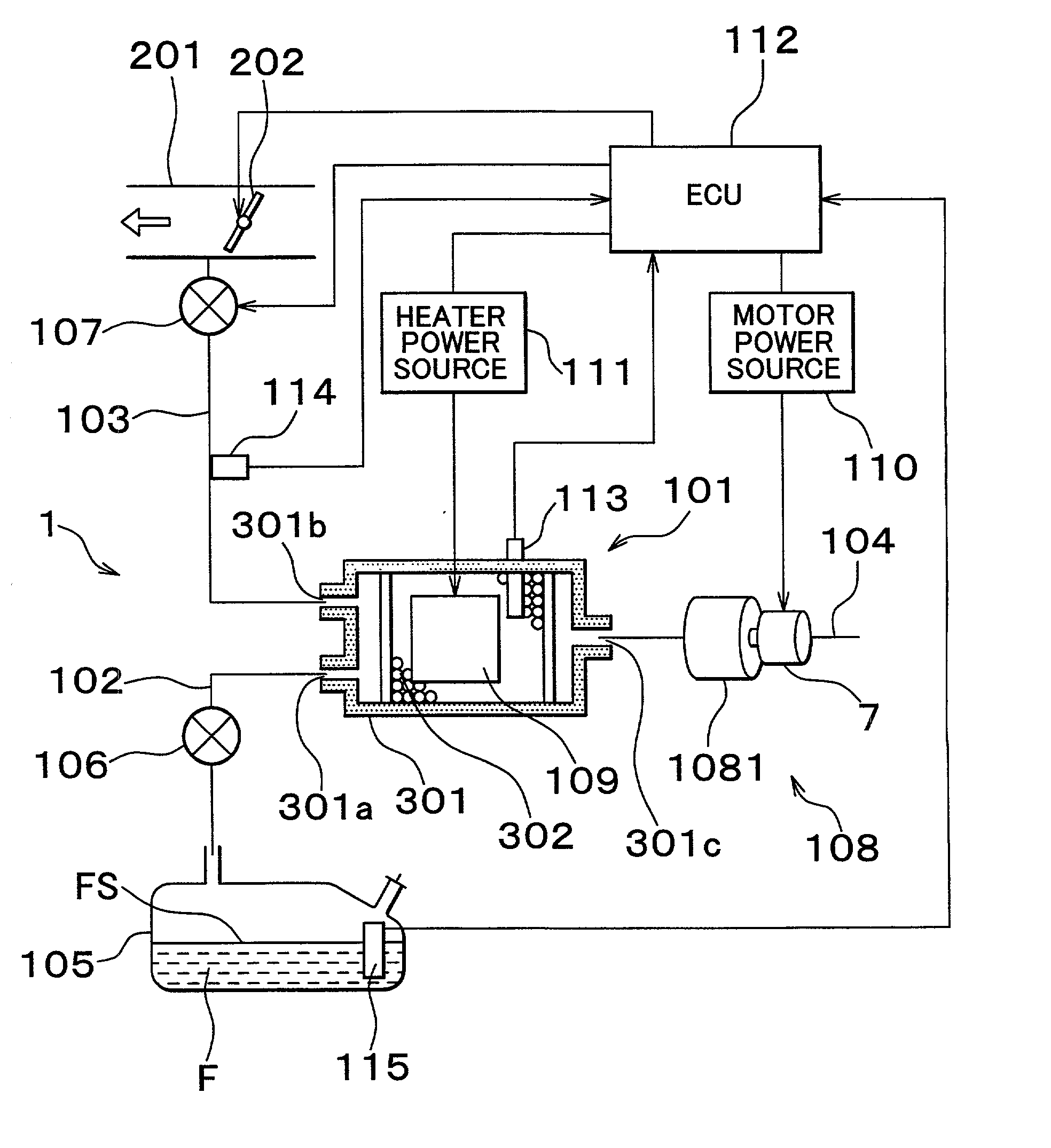
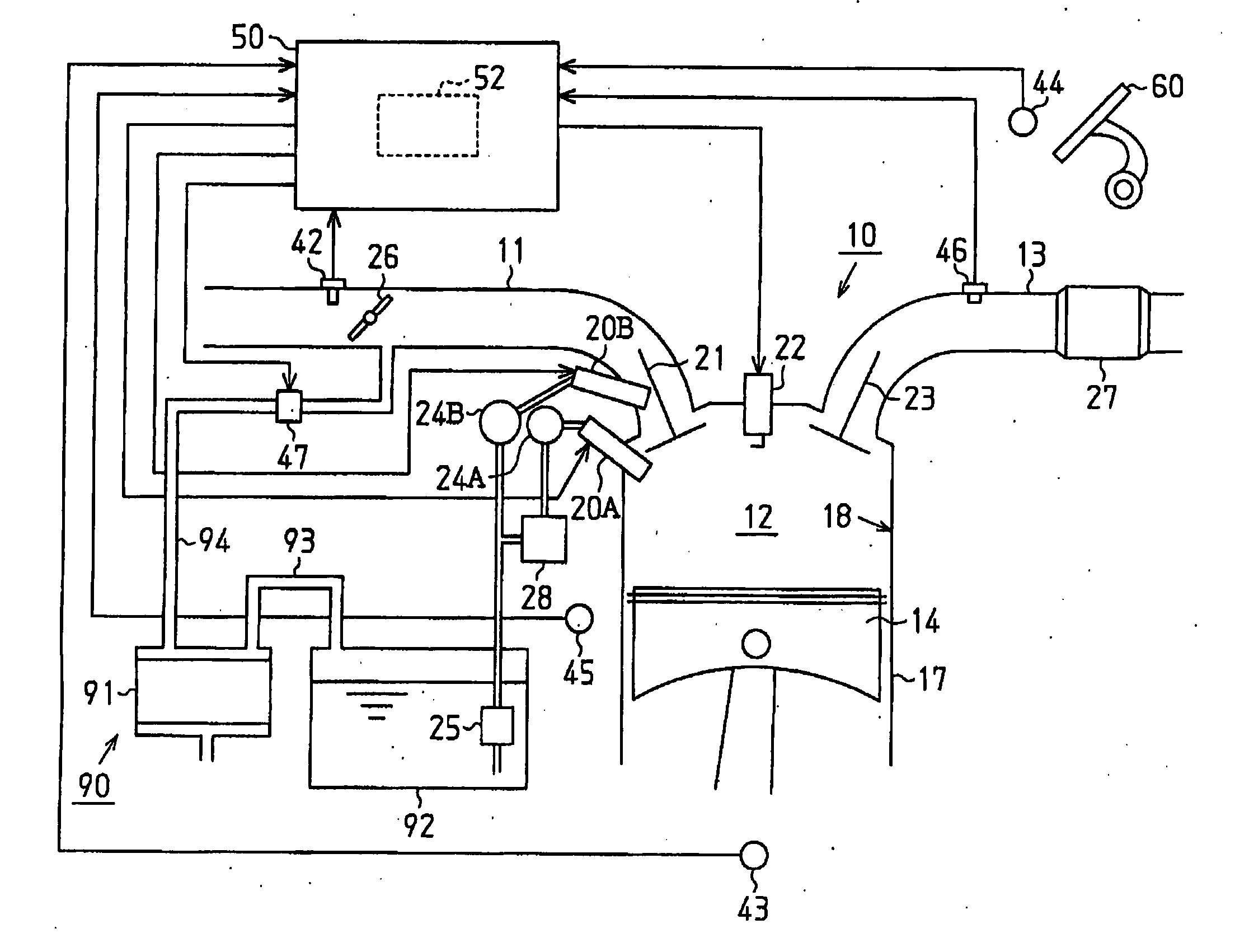
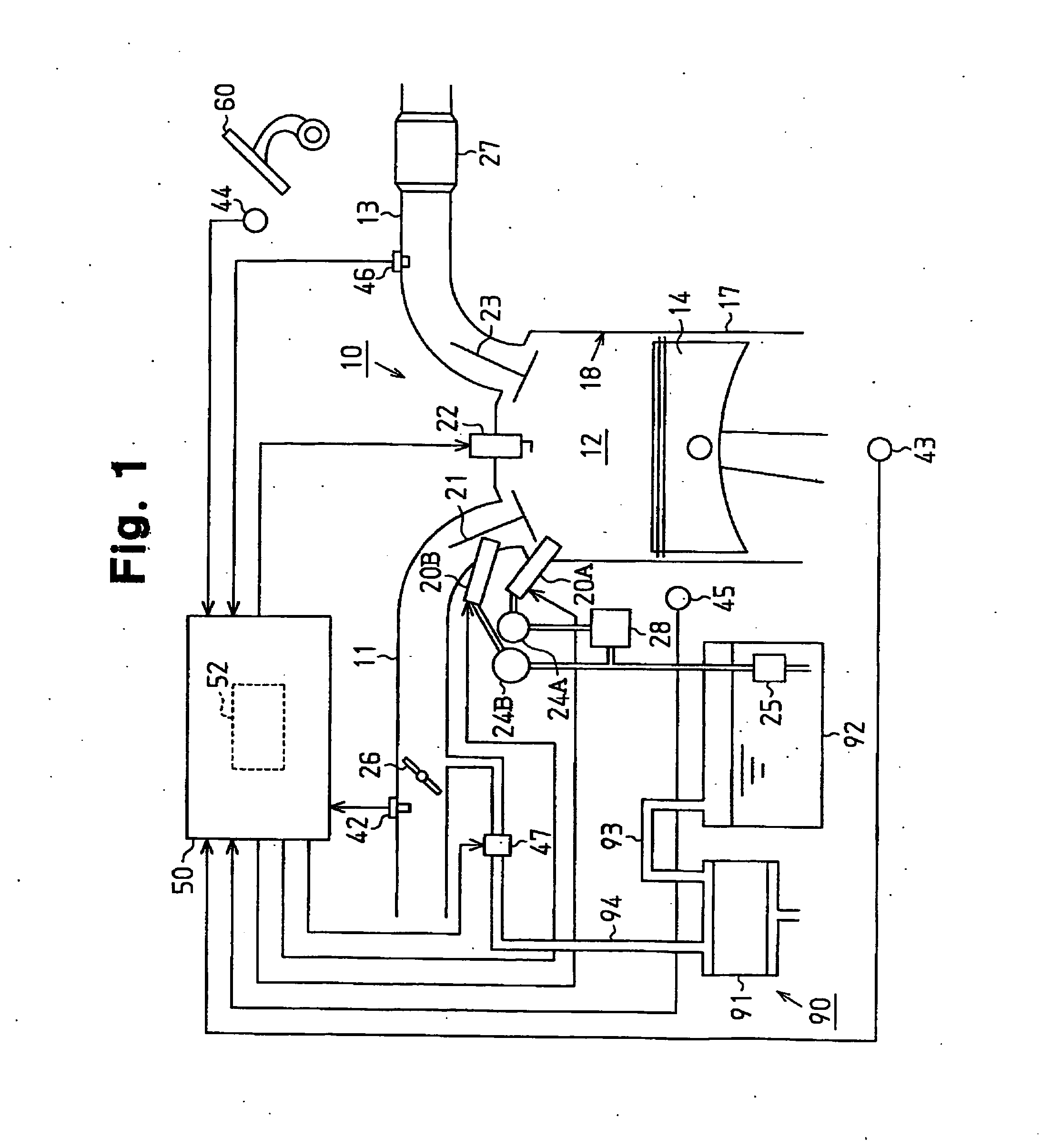
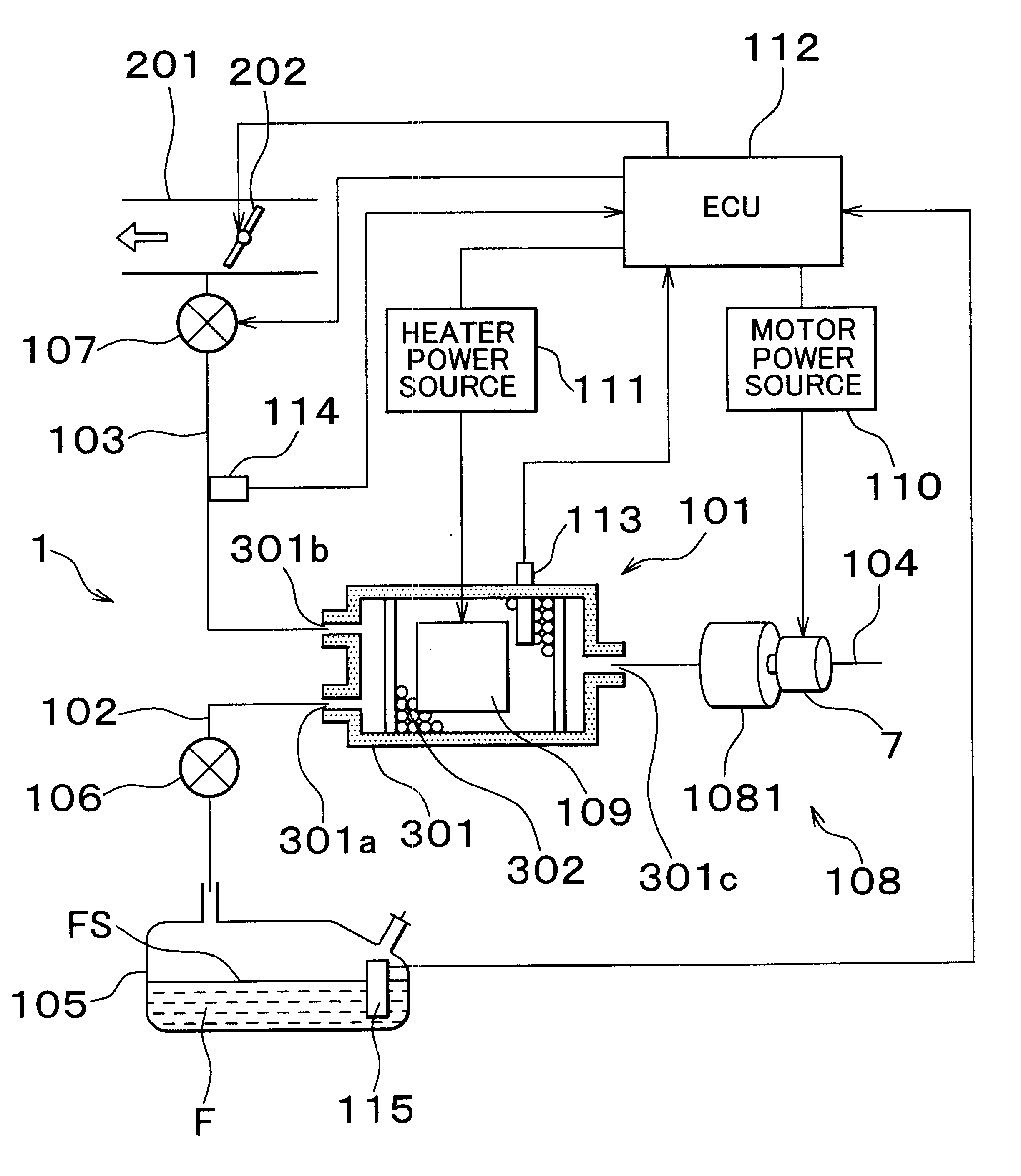
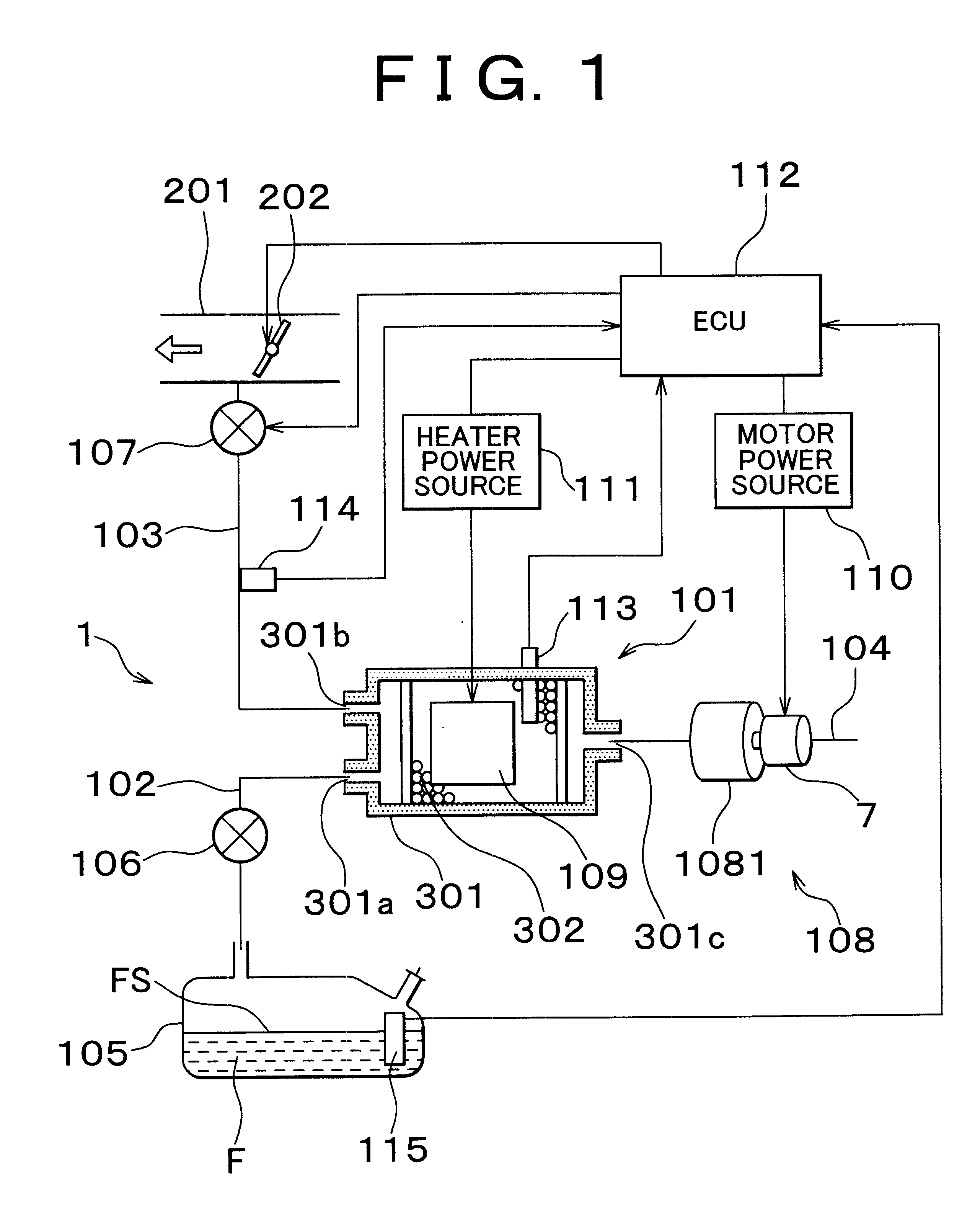
Fuel vapor handling apparatus and diagnostic apparatus thereof
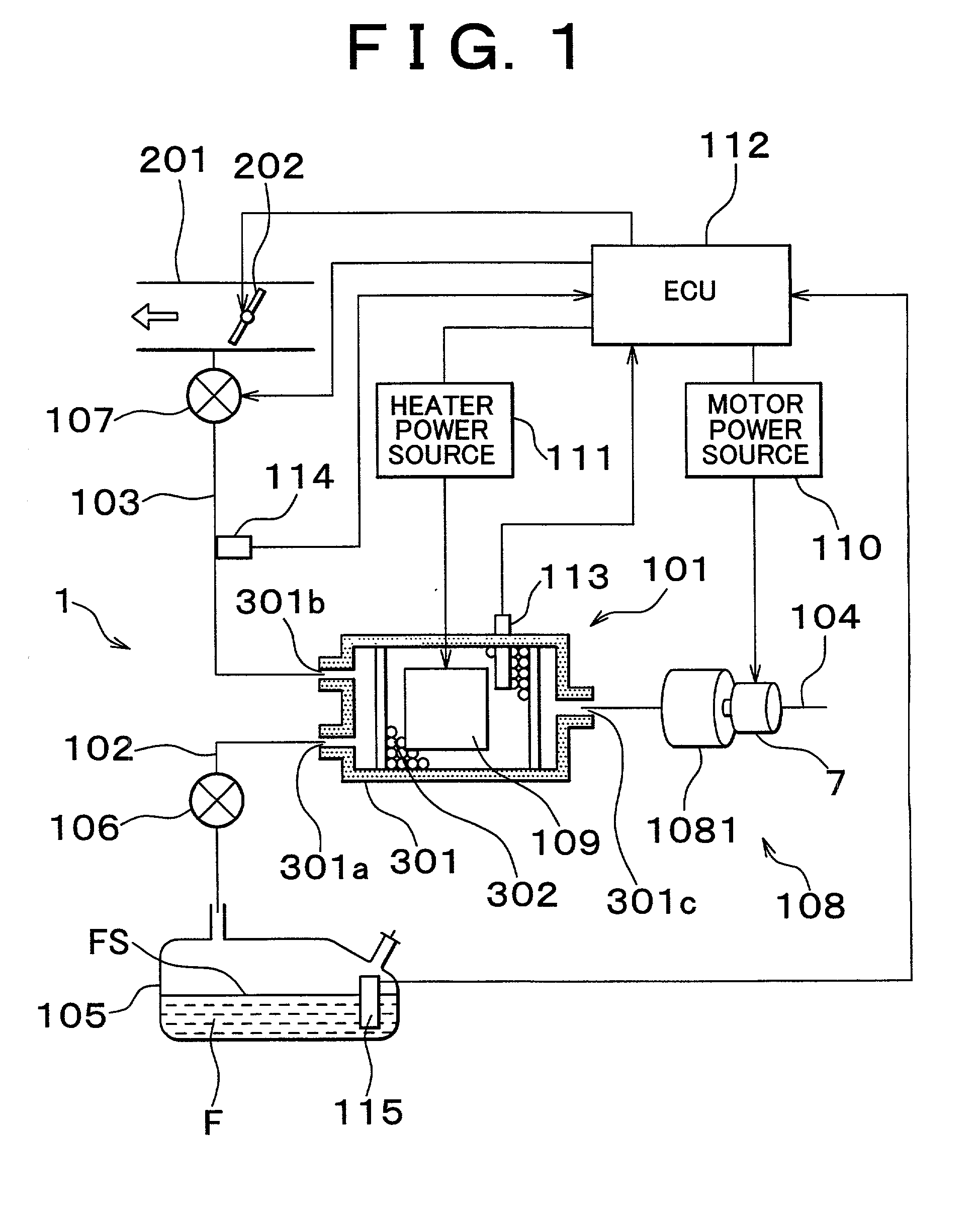
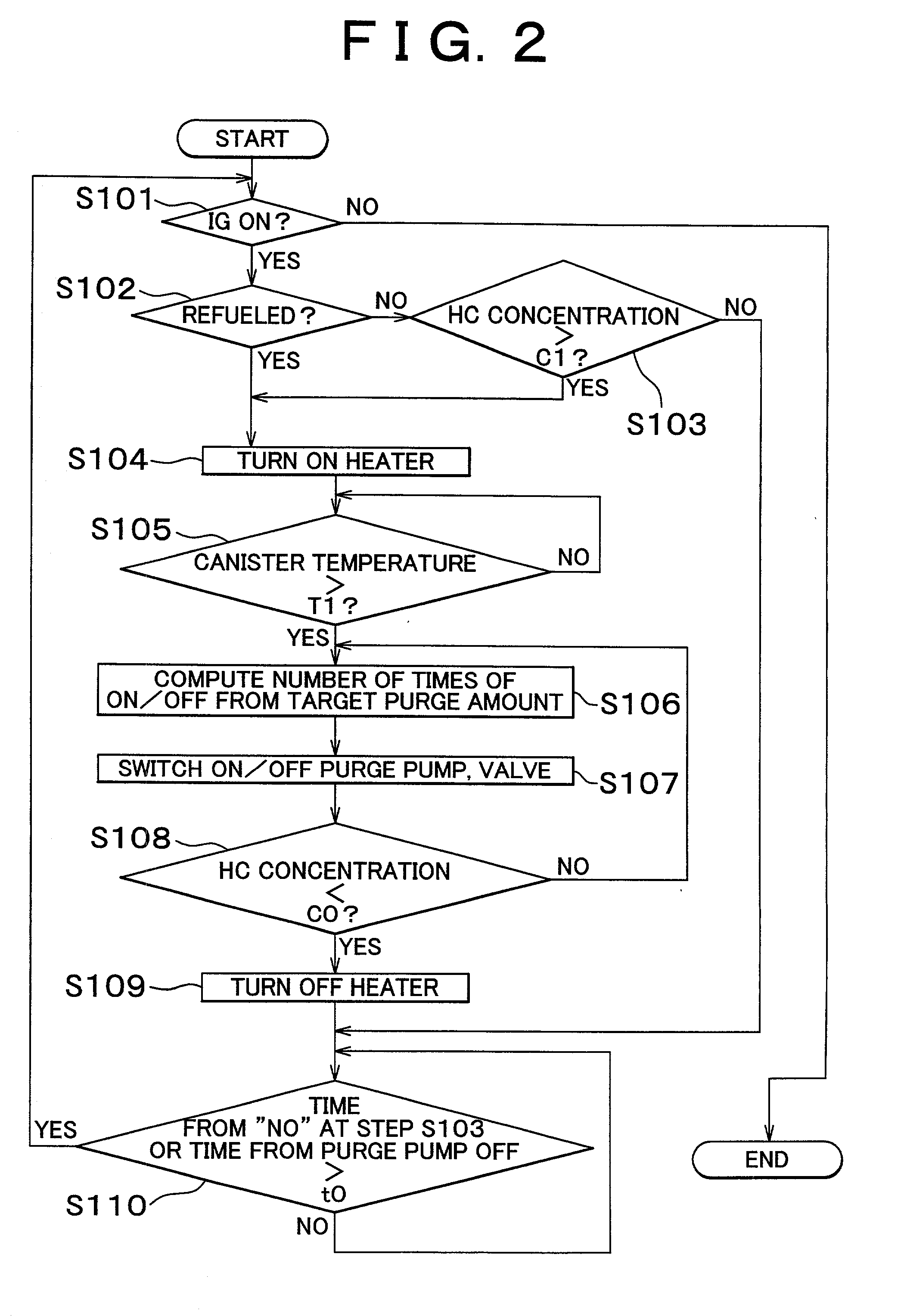
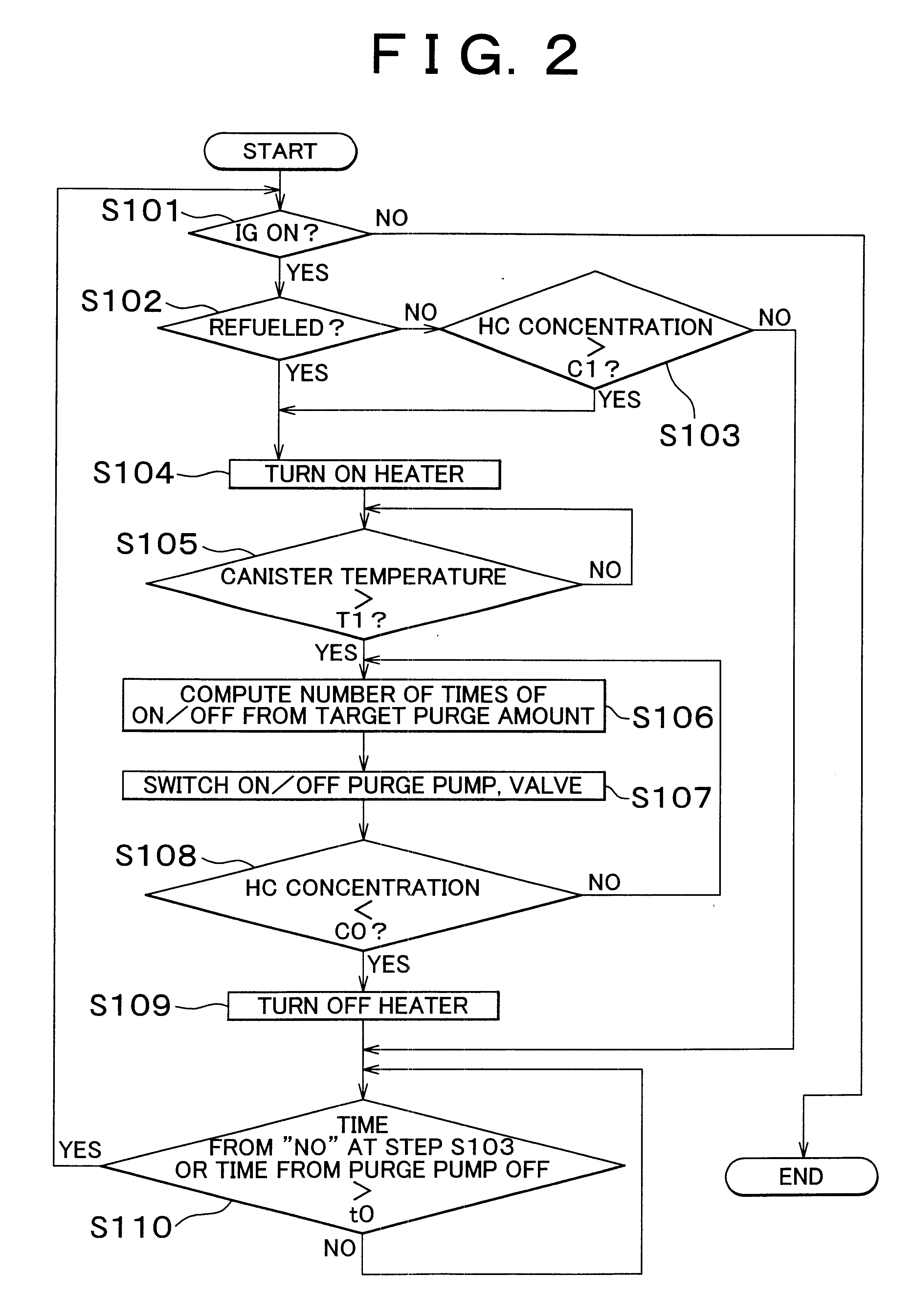
InactiveUS20020162457A1Desorption of fuel is facilitatedFuel can be purged efficientlyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFuel injection apparatusDesorptionVaporization
A fuel vapor handling apparatus supplies a purging air to a canister by using a purge pump and purges fuel desorbed from the canister into an intake pipe. A controller intermittently operates the purge so that the canister internal temperature recovers from a reduced level caused by the latent heat of vaporization of fuel during an operating period of the purge pump. Therefore, desorption of fuel from the canister during an operating period is facilitated. Since the actual operating time of the purge pump is reduced, the life of a motor that is a power unit of the purge pump becomes longer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Purge system for ethanol direct injection plus gas port fuel injection
ActiveUS7293552B2Low costElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesPort fuel injectionEngineering
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
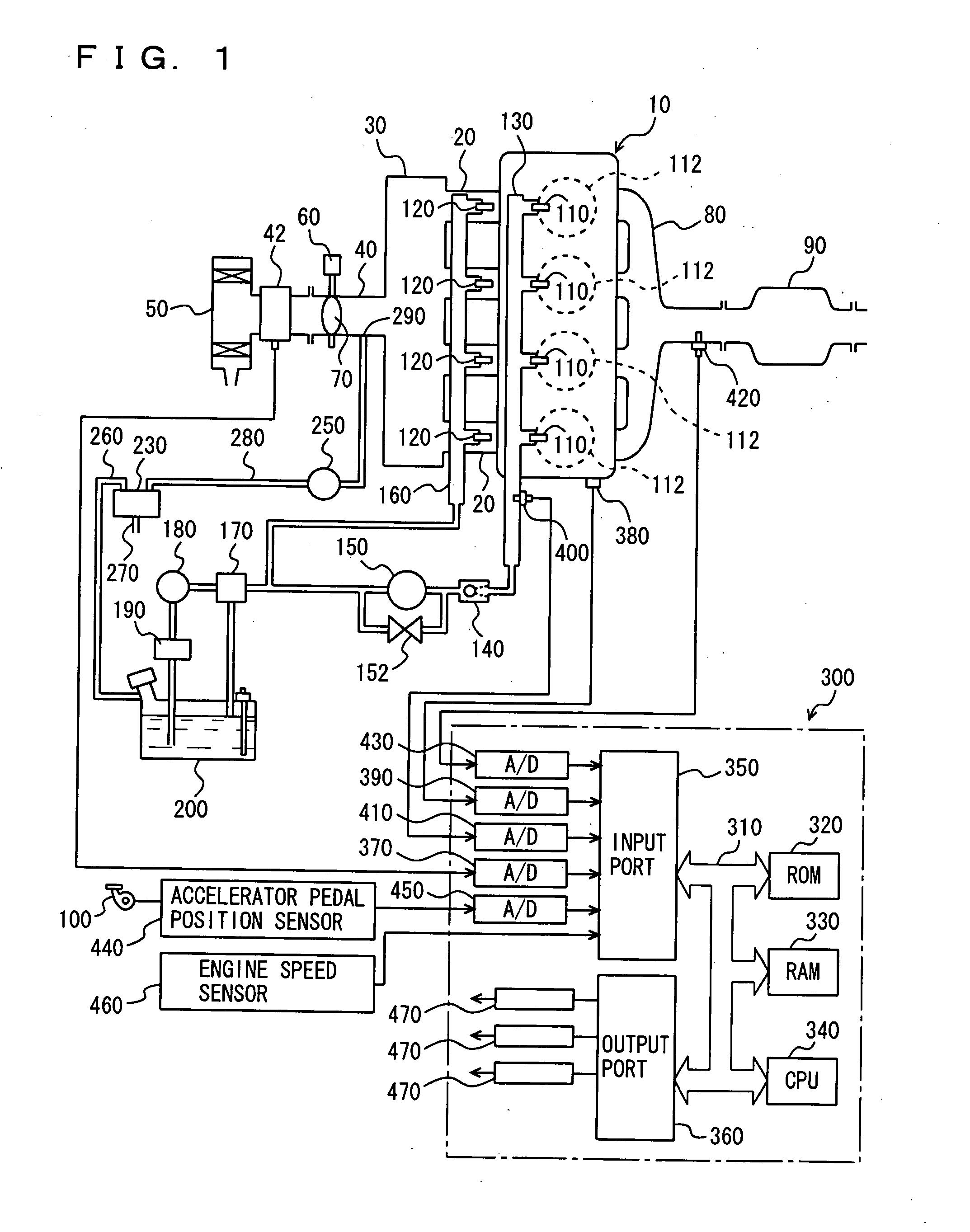
Control device of internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20050274353A1Avoid volatilityLowering of of emissionElectrical controlCombustion enginesInlet manifoldFuel injection
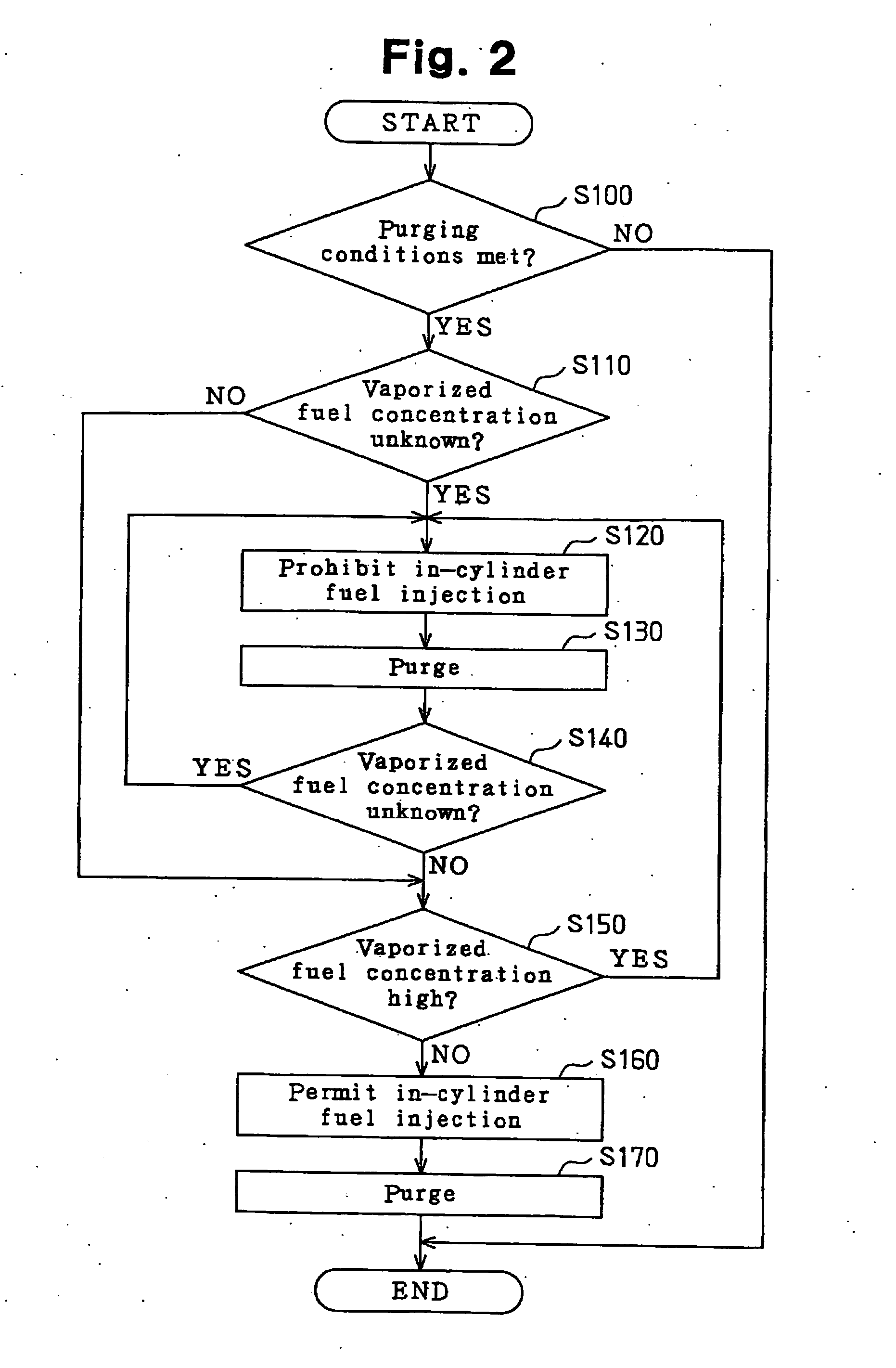
When an injection sharing ratio r is neither 0 nor 1, an engine ECU executes a program including a step of calculating a purge reduction amount of an in-cylinder injector as fpg×r and calculating a purge reduction amount of an intake manifold injector as fpg×(1-r) when performing purge processing according to a current fuel injection sharing ratio of the injectors, and a step of calculating a correction fuel injection amount of the in-cylinder injector by raising the fuel injection amount to a minimum fuel injection amount, and calculating a correction fuel injection amount of the intake manifold injector by subtracting the raised amount from the fuel injection amount of the intake manifold injector when the fuel injection amount of the in-cylinder injector calculated by using the purge reduction amount is lower than the minimum injection amount.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
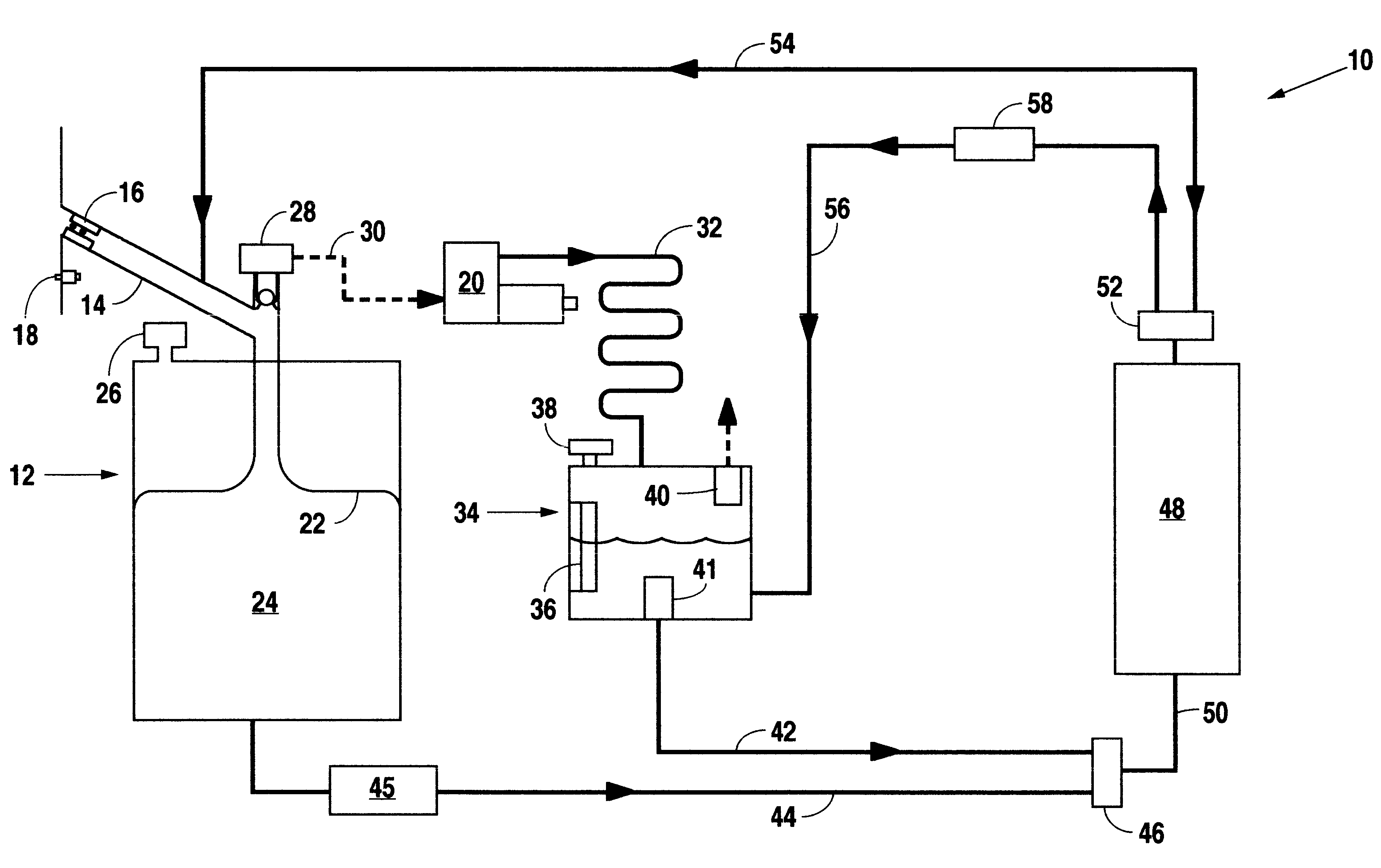
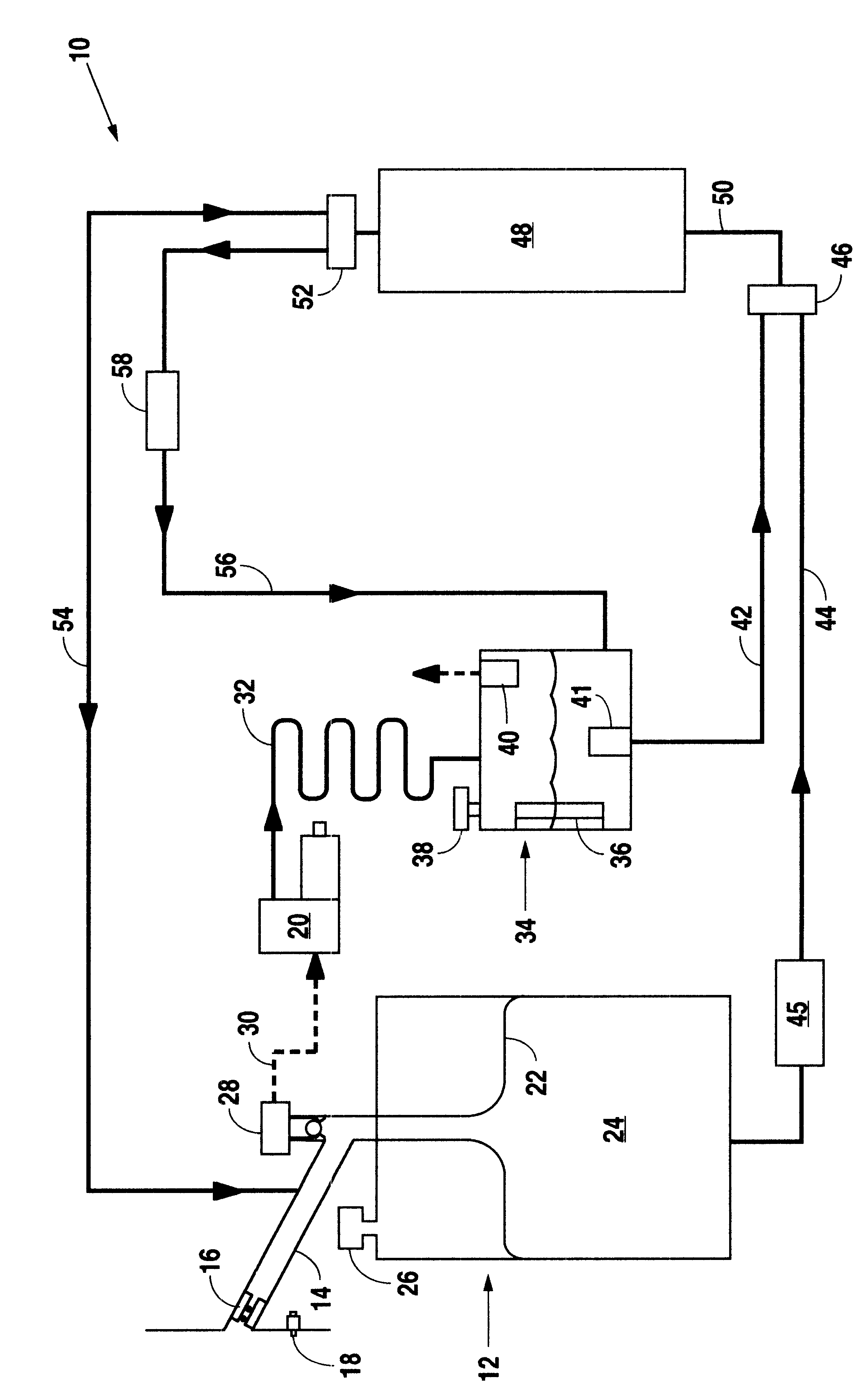
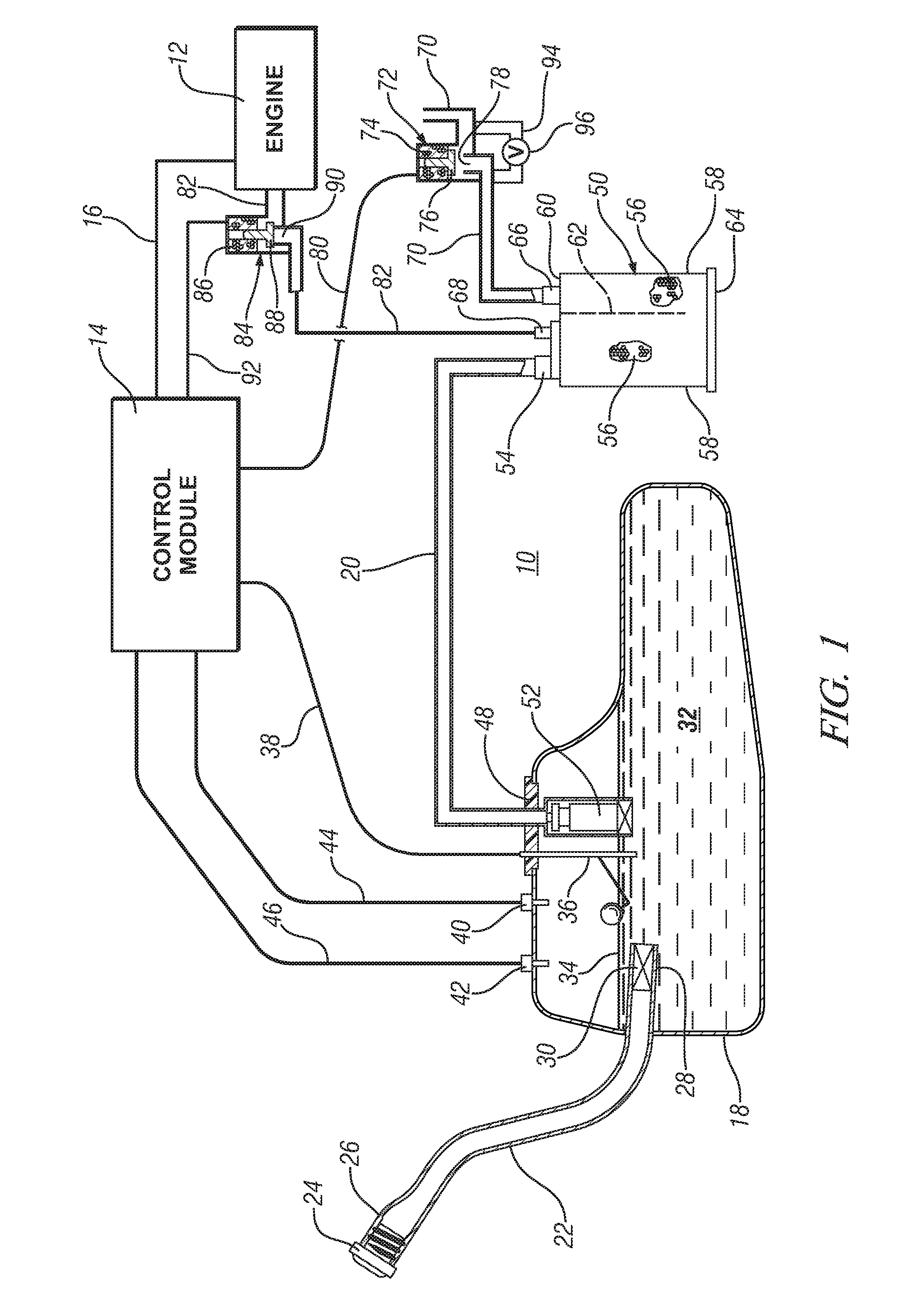
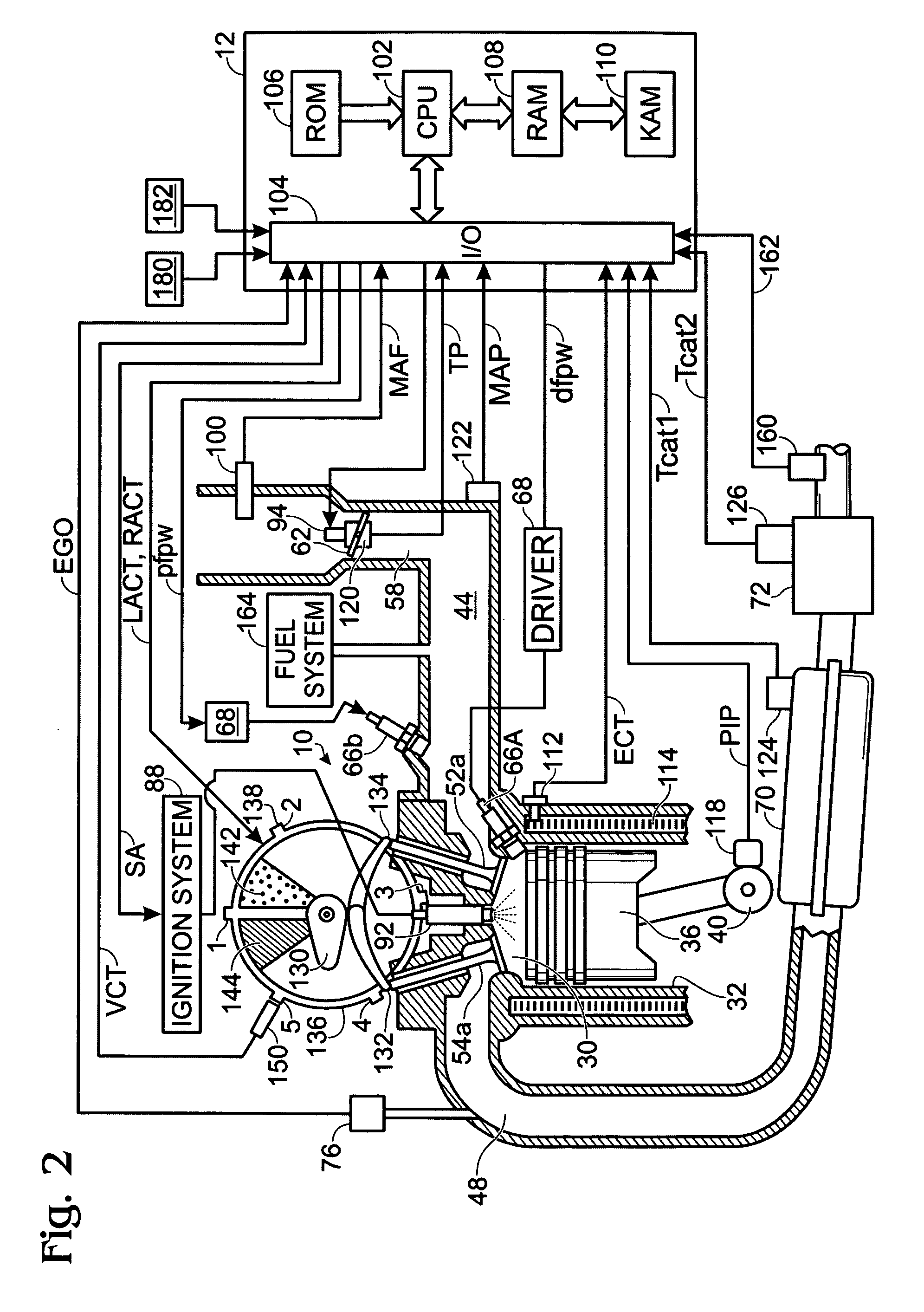
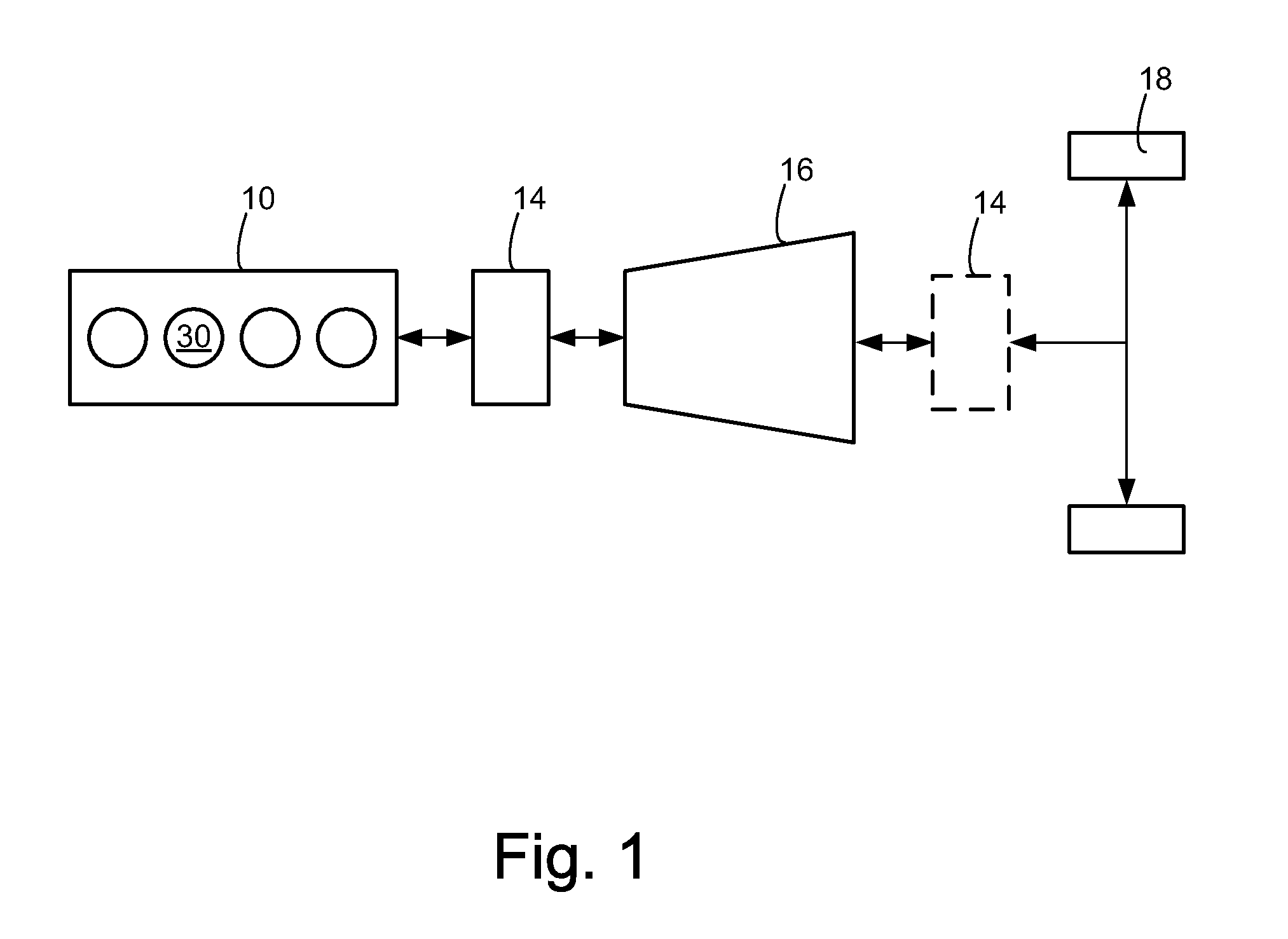
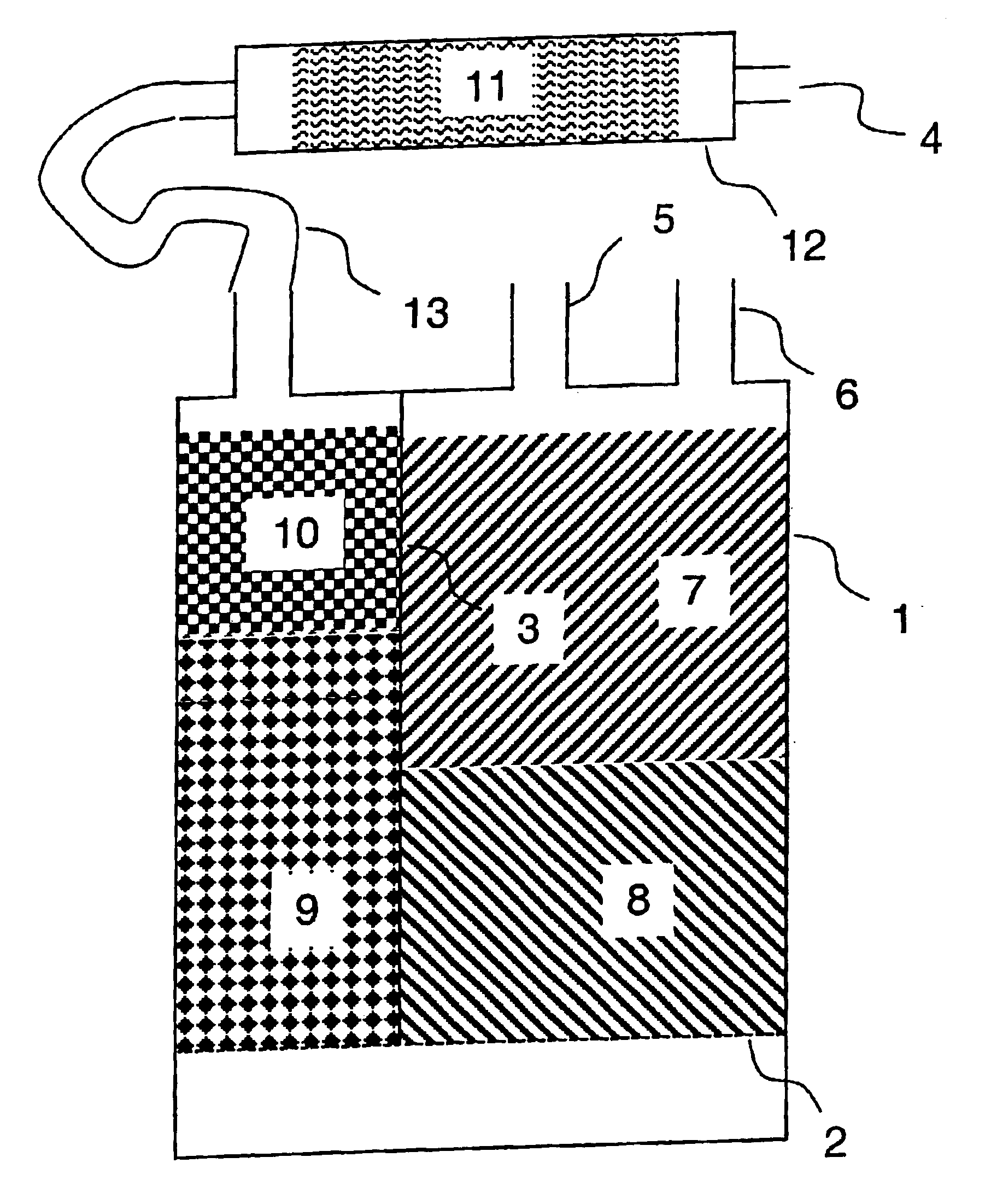
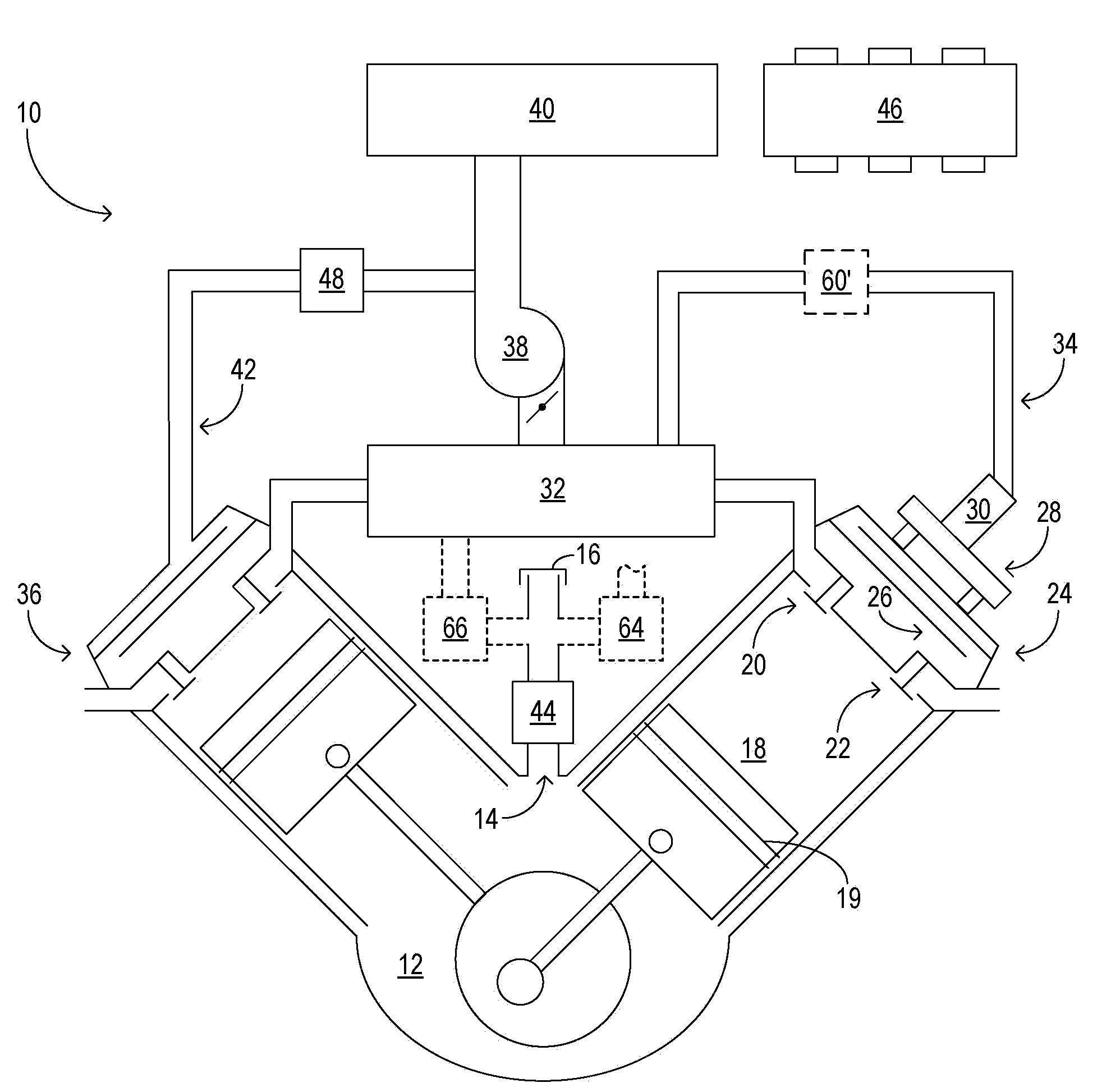
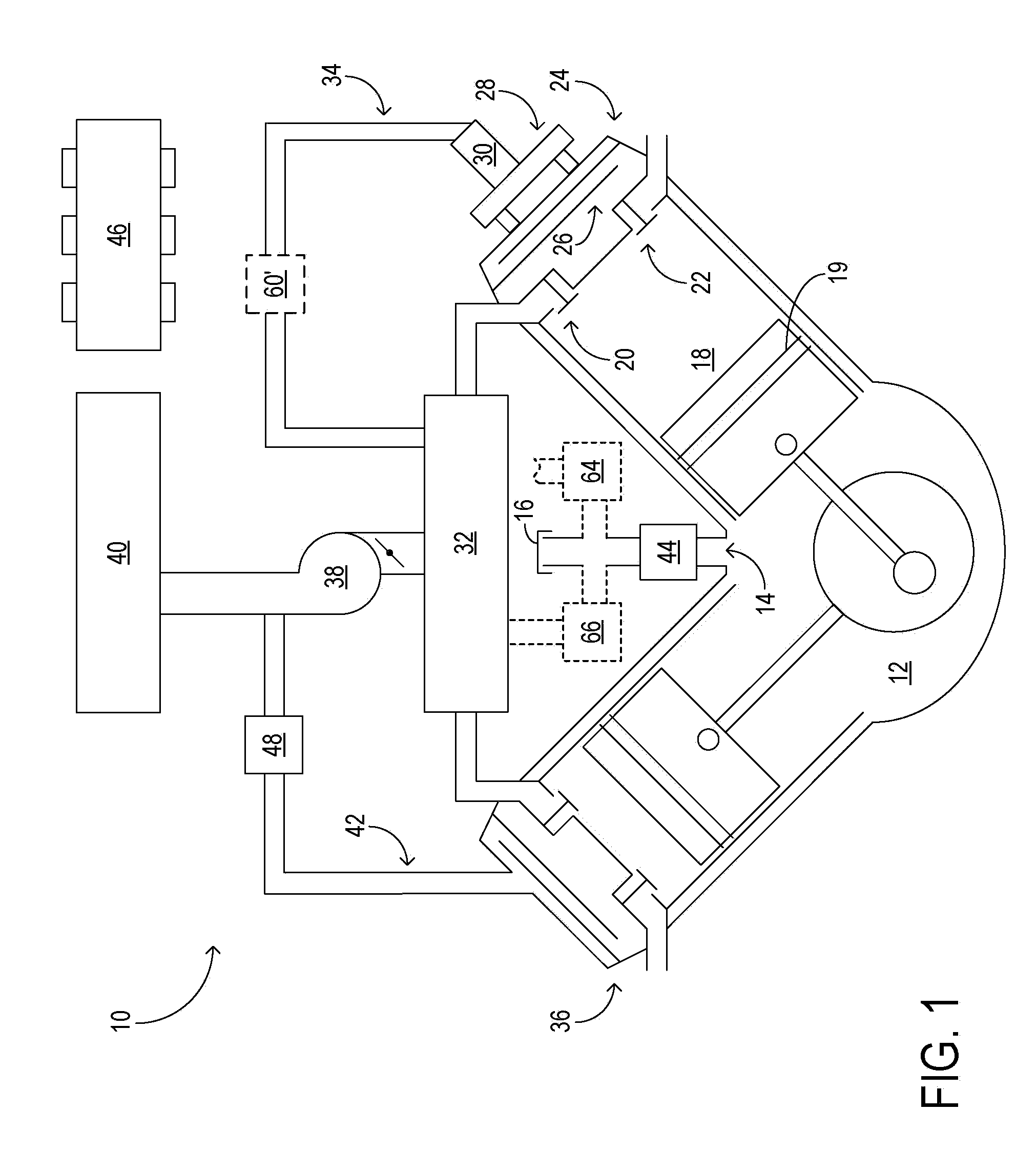
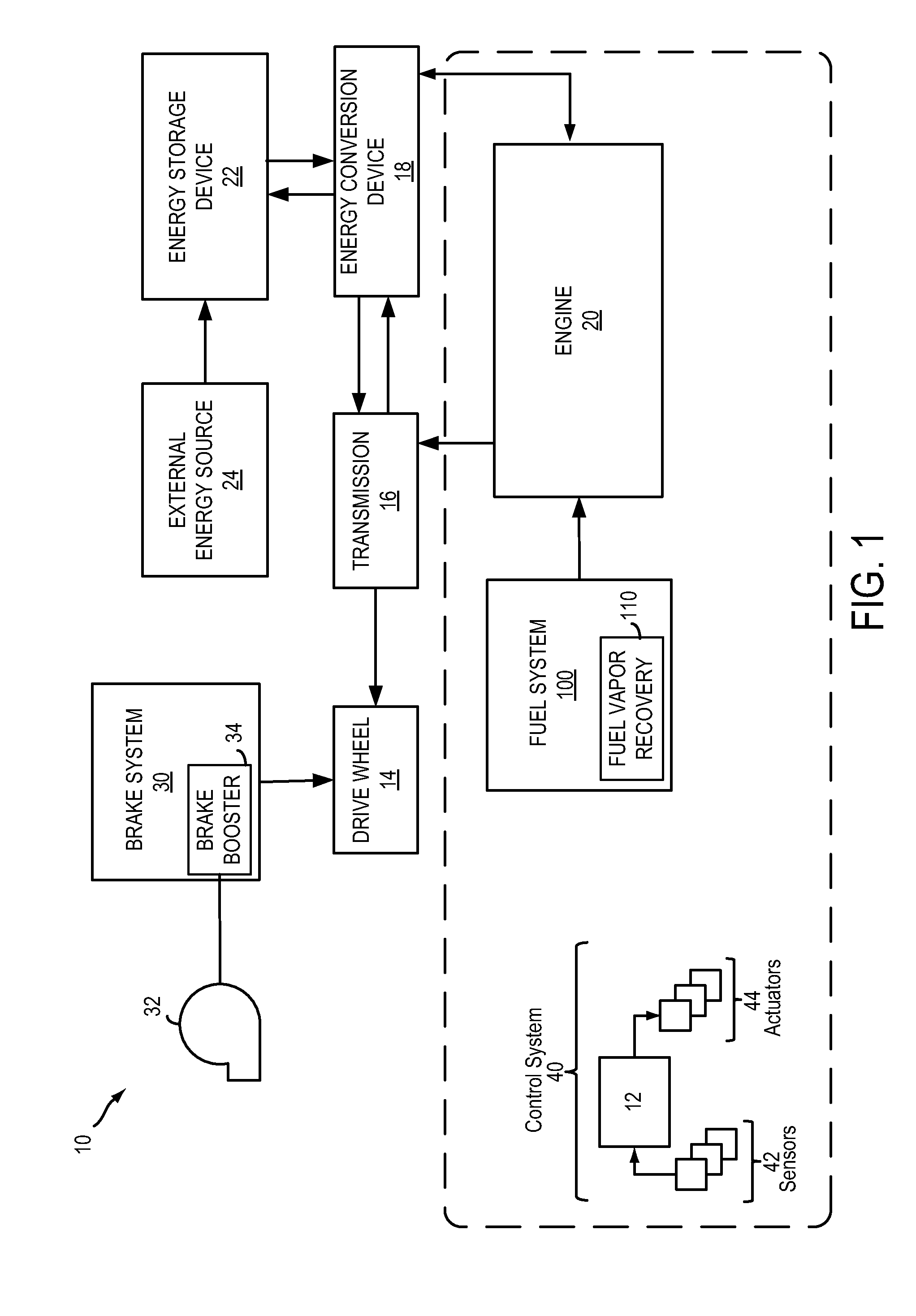
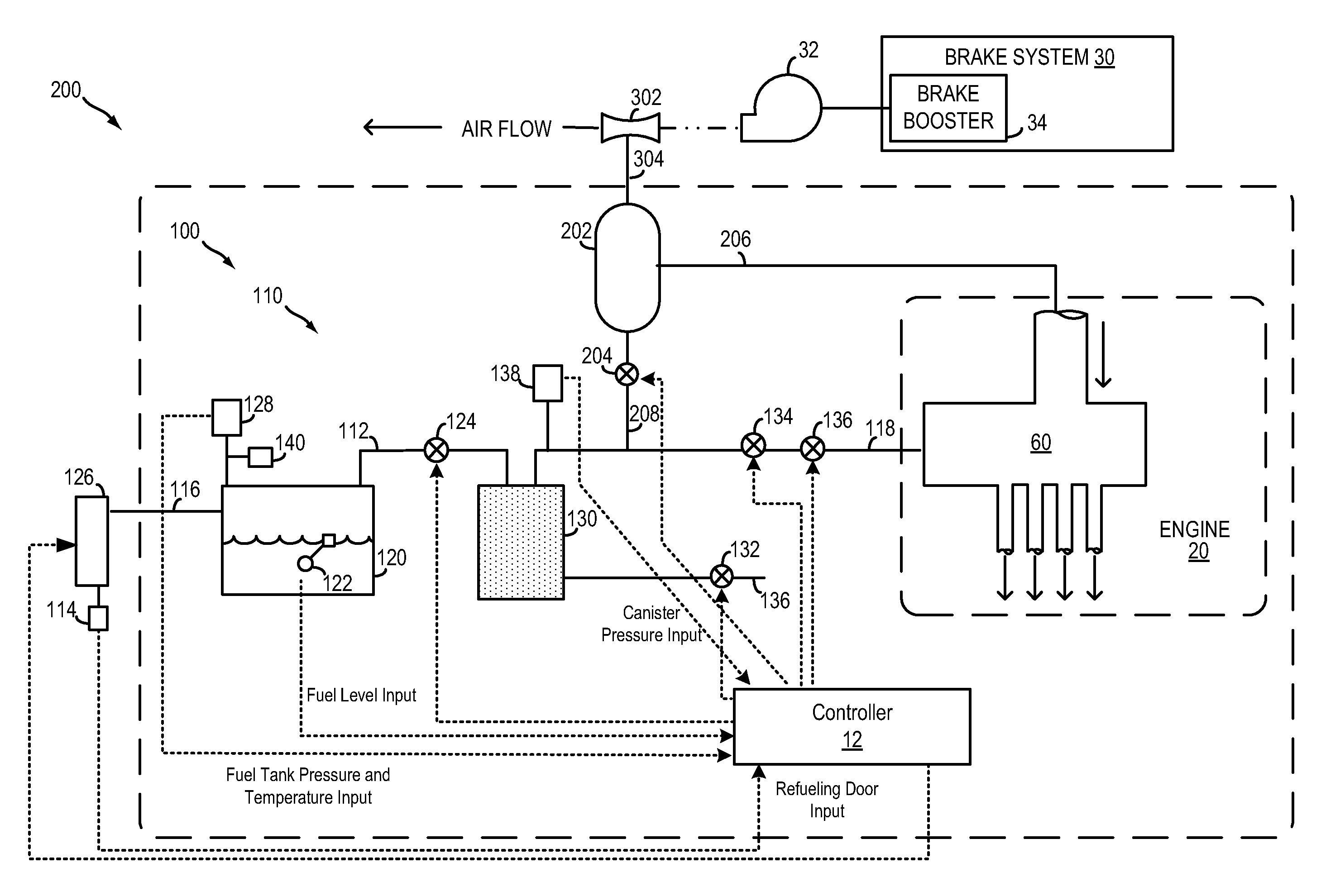
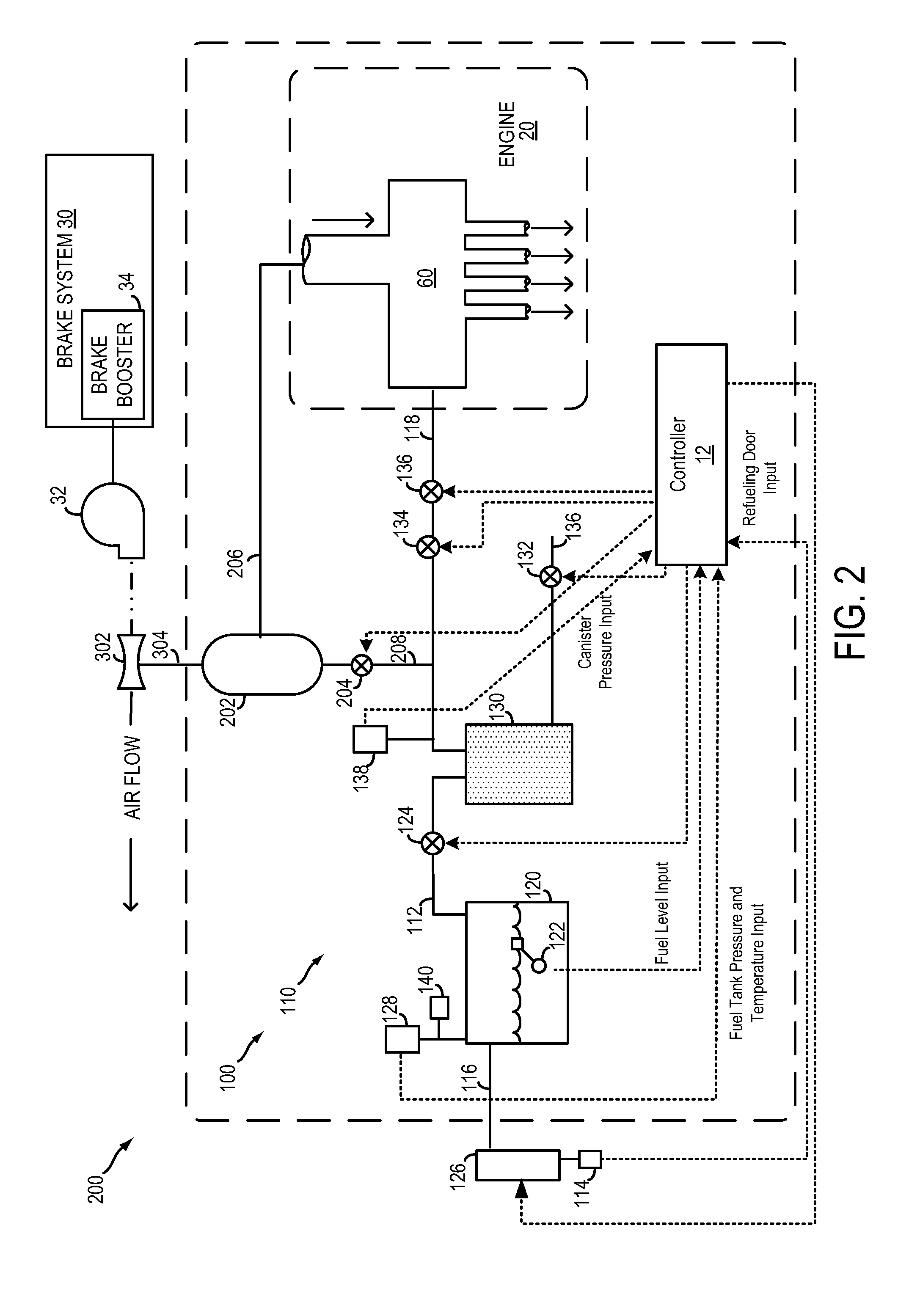
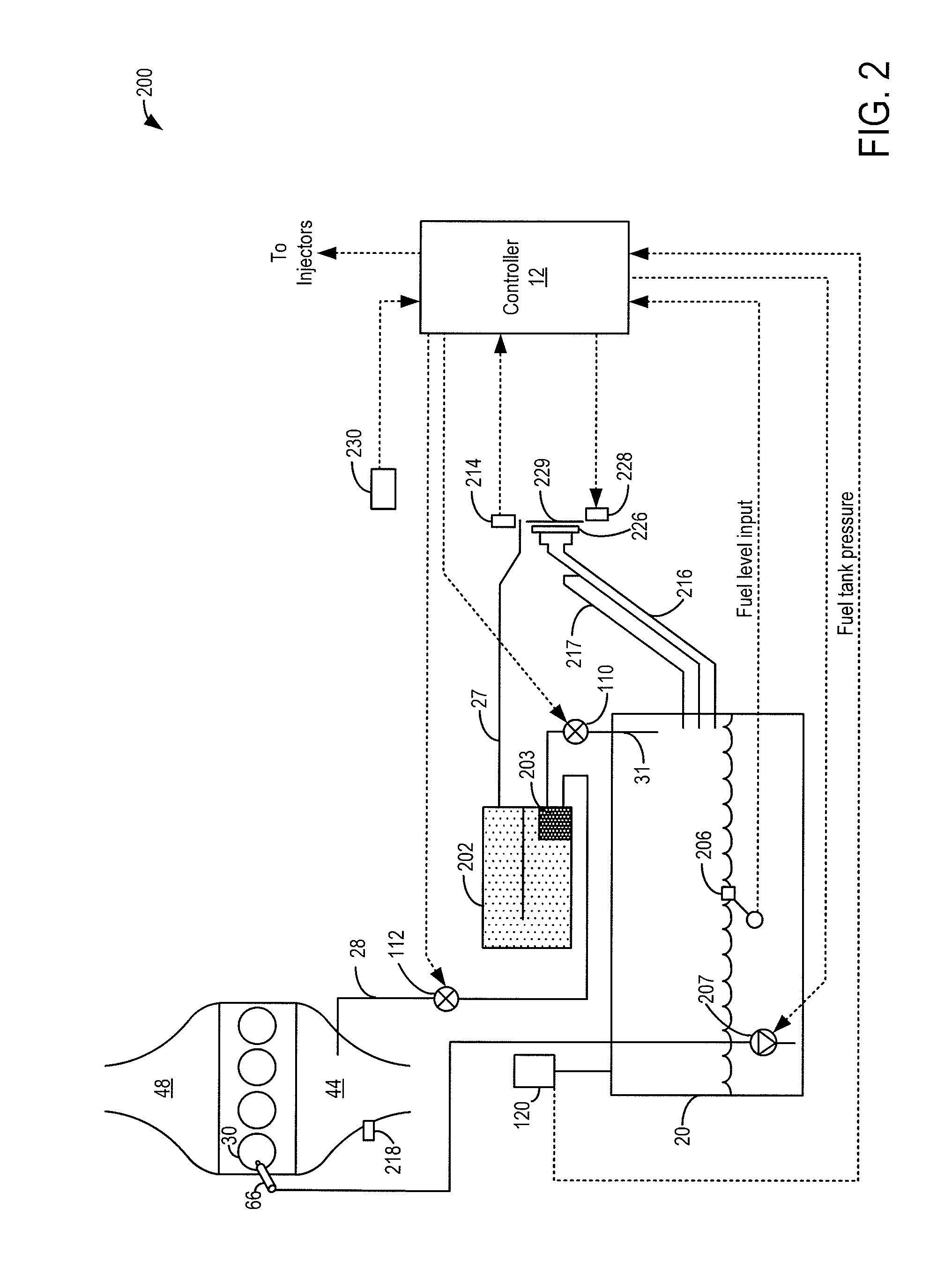
On-board fuel vapor collection, condensation, storage and distribution system for a vehicle
An on-board fuel vapor recovery system draws vapors from a fuel tank, compresses the vapors, and then cools the compressed vapors to form a condensate liquid fuel which is stored in an auxiliary condensate tank for introduction to an engine for enhanced cold start operation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
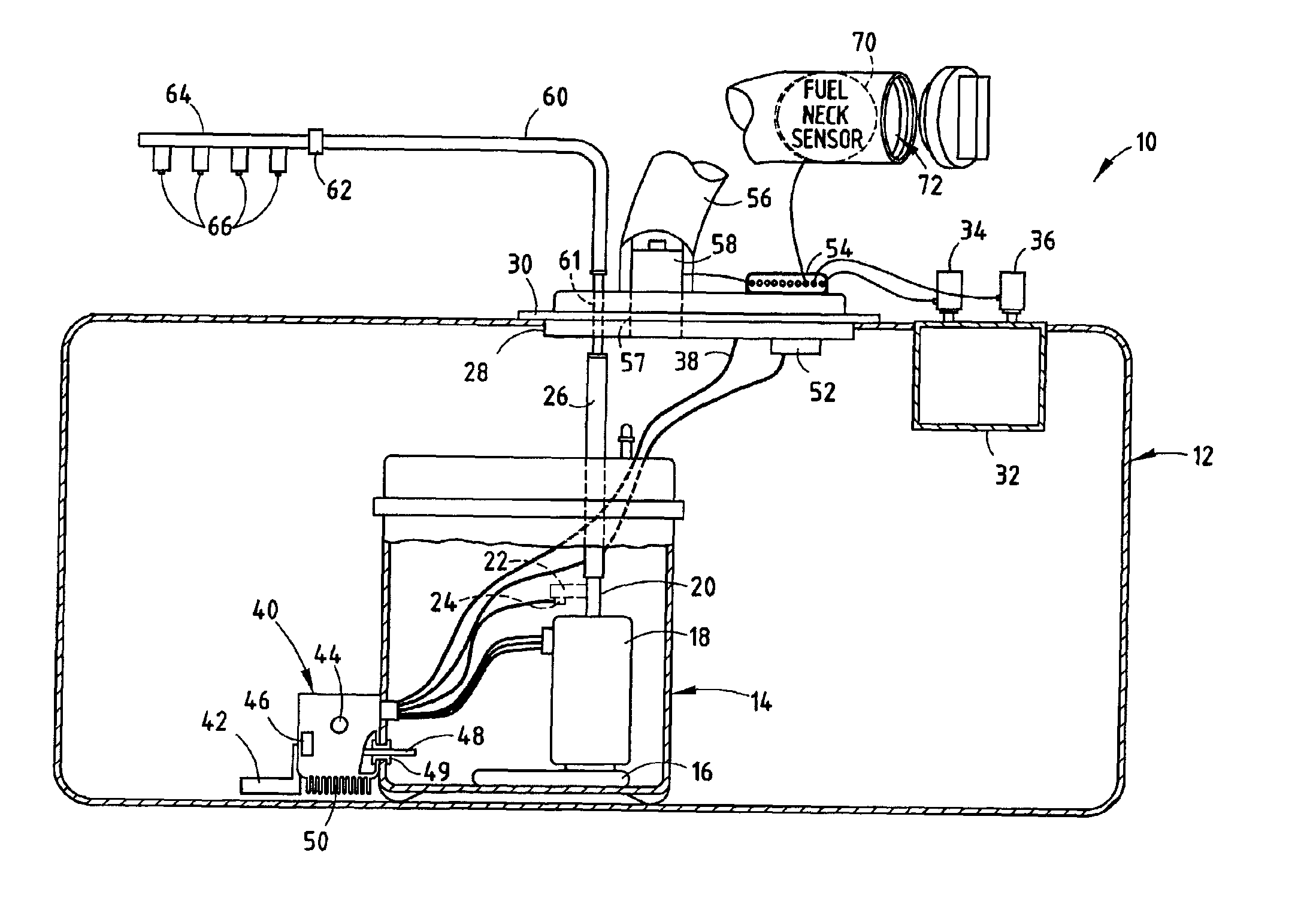
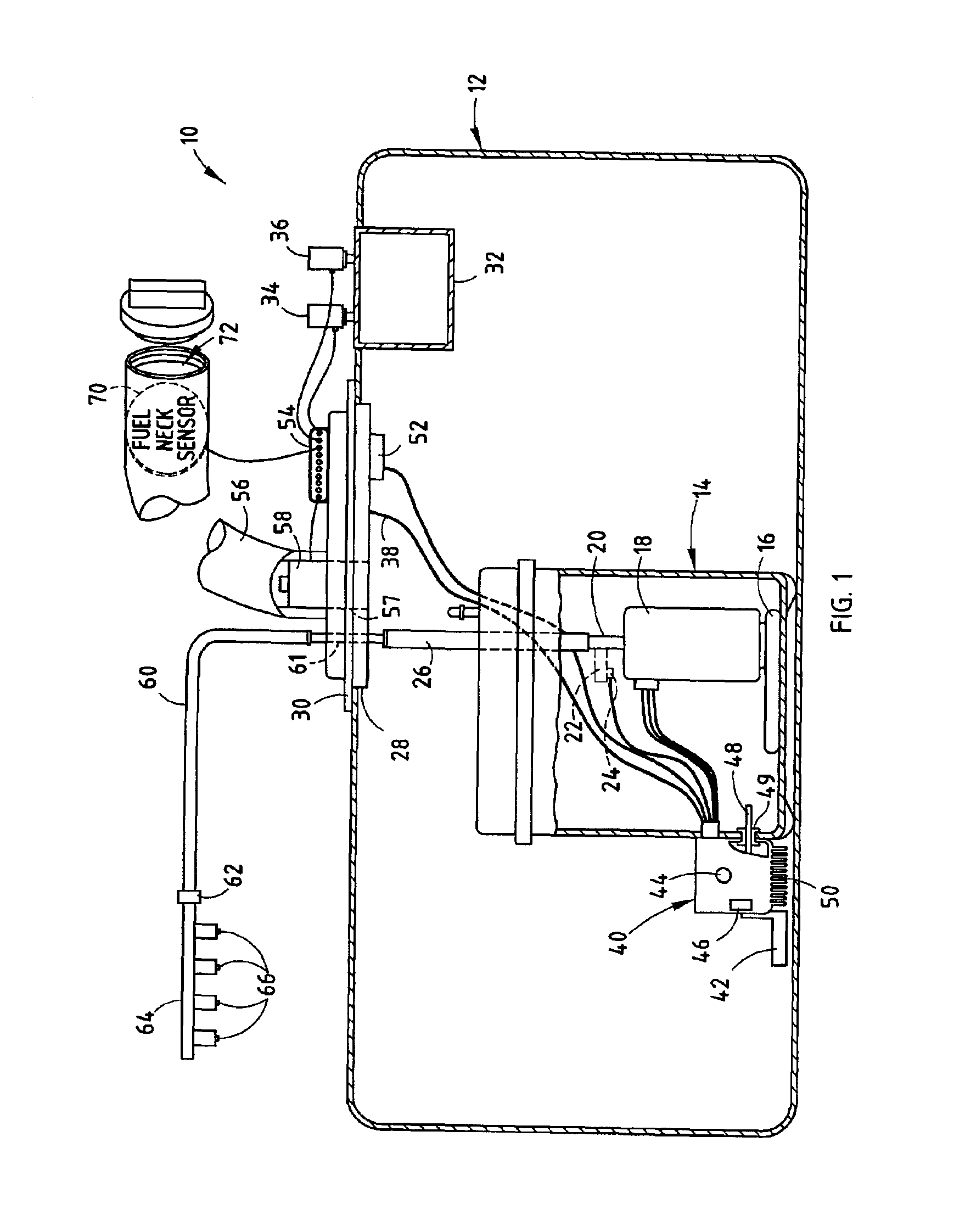
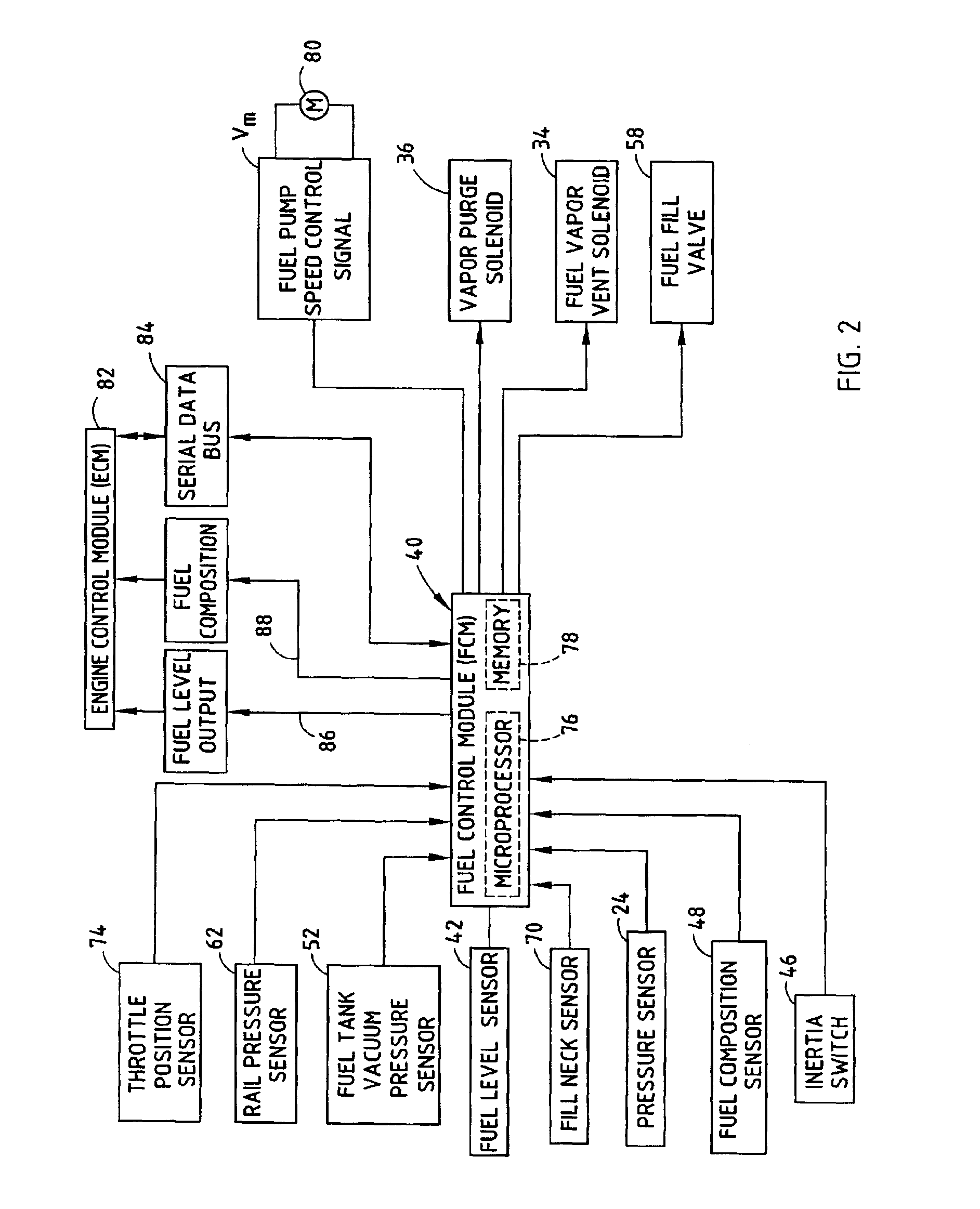
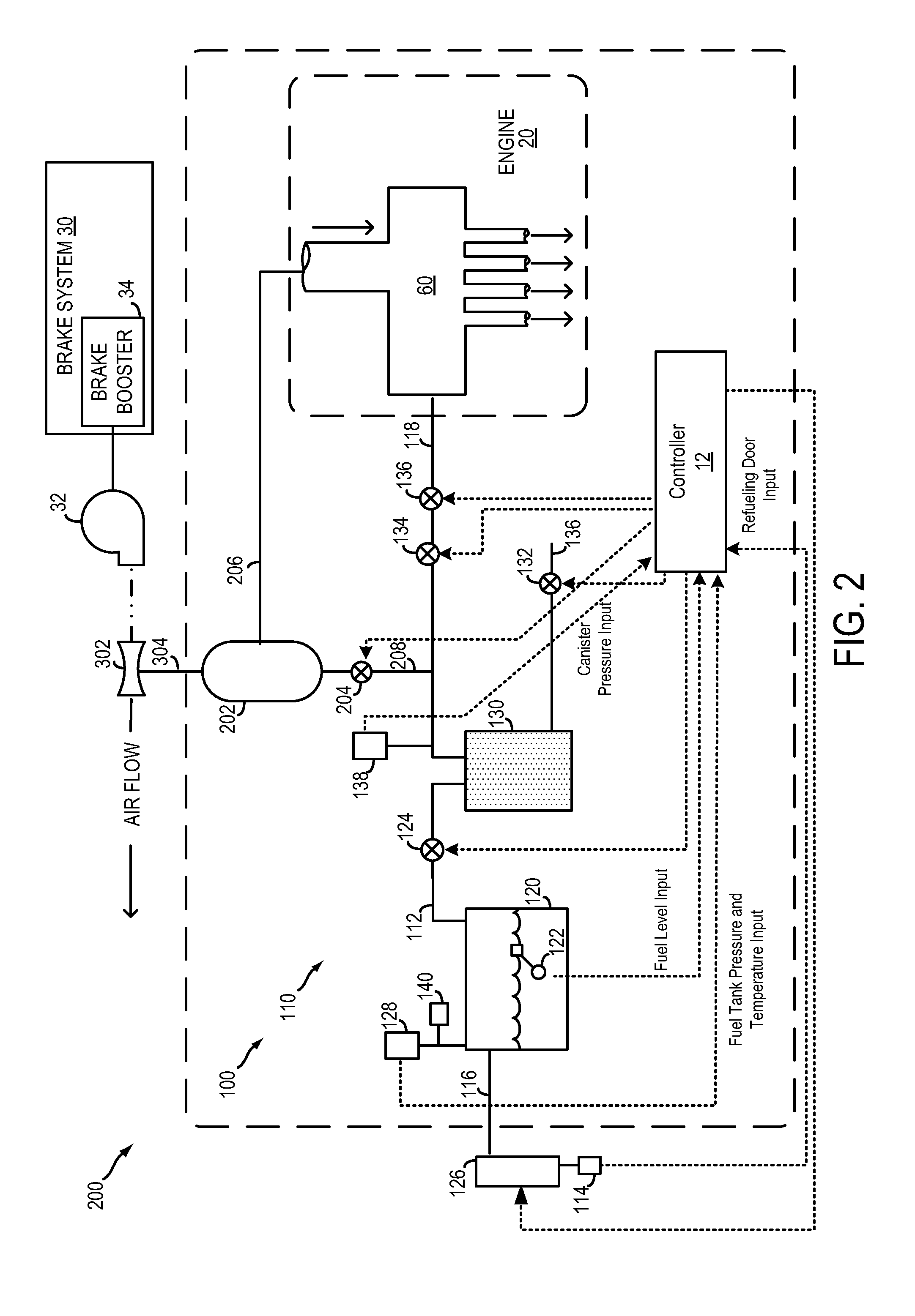
Vehicle fuel management system
InactiveUS6877488B2Affordable controlElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelActuatorFuel vapor
An integrated fuel management system and method for controlling the fuel storage and delivery in a vehicle. The fuel management system includes a fuel storage tank for storing fuel in a vehicle, a vapor collection canister located within the fuel storage tank, a vent actuator coupled to the vapor collection canister for venting gas from the canister during a vent operation, and a purge actuator coupled to the canister for purging fuel vapor from the canister during a purge operation. A variable speed fuel pump is disposed within the fuel storage tank for delivering fuel to a fuel delivery line for an engine. The fuel management system has a controller provided in a module disposed in communication with the fuel for controlling the amount of fuel pumped with the variable speed fuel pump to deliver fuel to the fuel delivery line and further control the purge and vent actuators.
Owner:UUSI
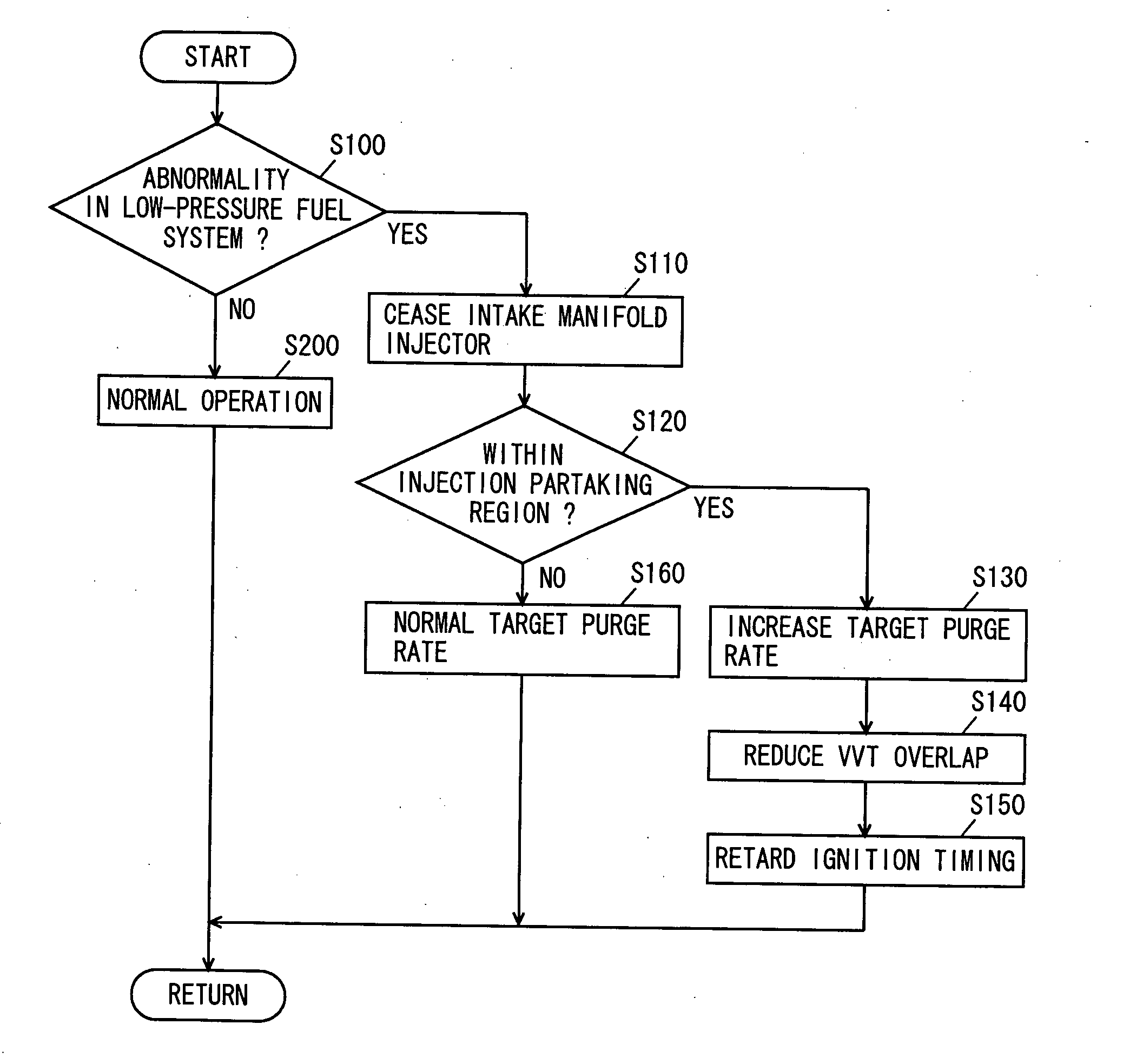
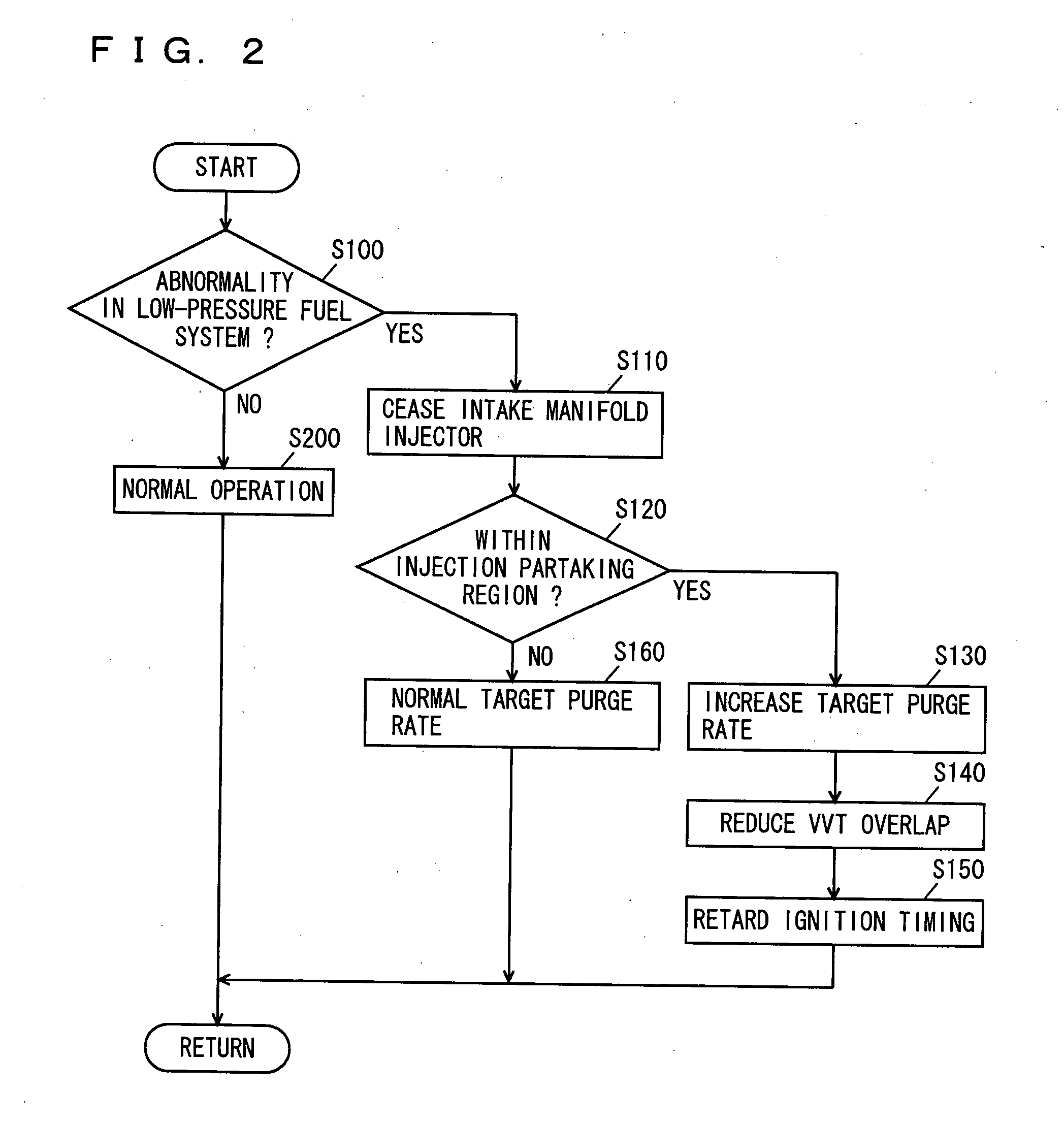
Control apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060090732A1Increasing purge rateVariation can be suppressedValve arrangementsElectrical controlIgnition timingInlet manifold
An engine ECU executes a program including the steps of: determining presence of abnormality in a low-pressure fuel system; ceasing an intake manifold injector when determination is made of abnormality in the low-pressure fuel system; increasing the target purge rate when the engine operation state attains an injection partaking state between an in-cylinder injector and an intake manifold injector; reducing the VVT overlap; and retarding the ignition timing.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
System and method for engine with fuel vapor purging
ActiveUS20070119411A1Improve engine performanceLow costElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringFirst relationship
A method for controlling engine operation of an engine having a cylinder receiving fuel from a first and a second fuel injector, the first injector having a first relationship between a first input signal and a first amount of injected fuel, and the second injector having a second relationship between a second input signal and a second amount of injected fuel; the method comprising of varying injection from the first injector into the cylinder, varying injection from the second injector into the cylinder, purging fuel vapors from a fuel system into the cylinder, and adaptively learning said first and second relationships based on sensed operating conditions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
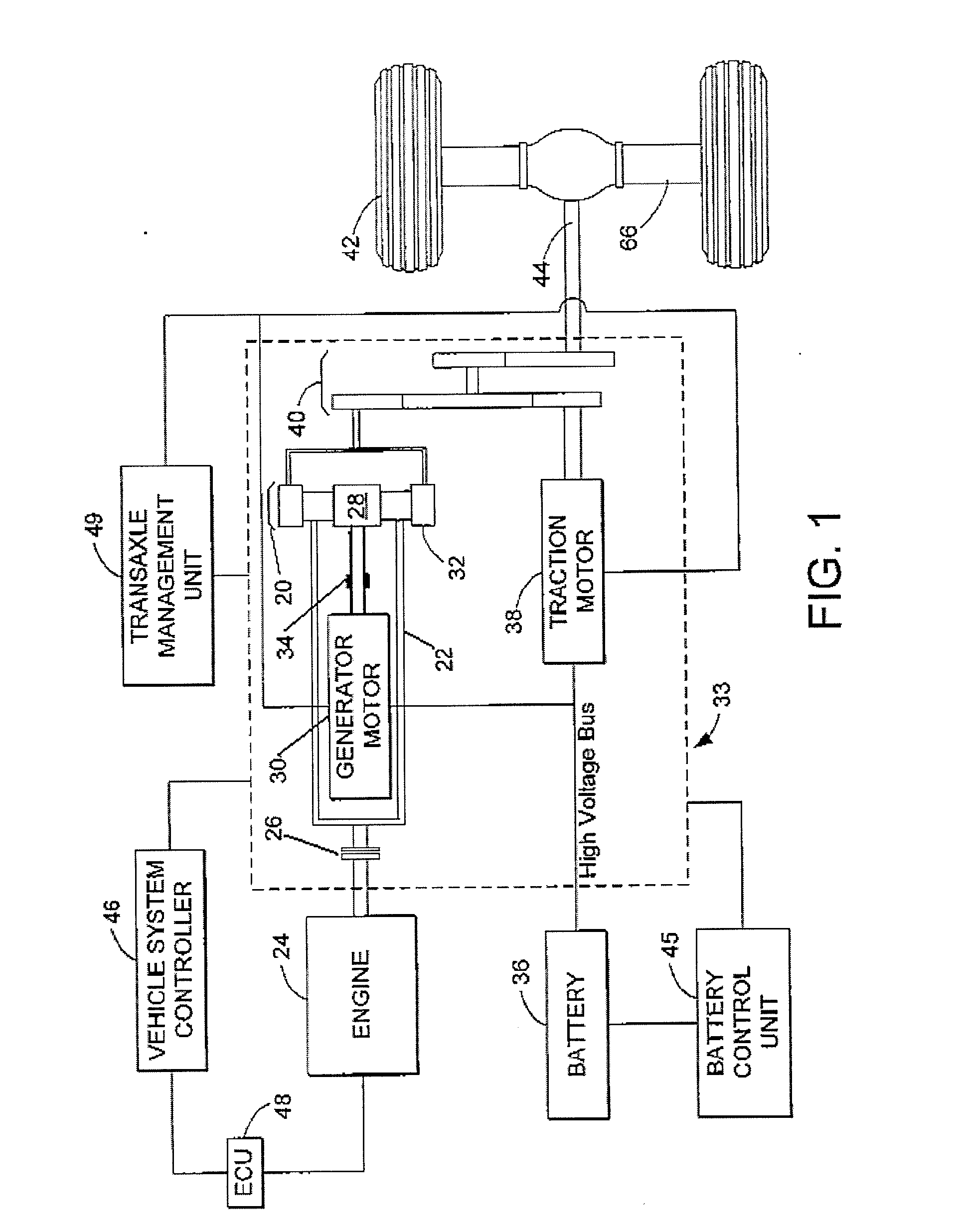
Evaporative emission control in battery powered vehicle with gasoline engine powered generator
InactiveUS7448367B1Preventing bleed emissionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelGasolineEngine power
A plug-in hybrid vehicle is driven by one or more electric motors powered by a battery system with supplemental electric power provided by a gasoline engine powered generator. A canister, connected by a fuel vapor vent passage, is used to admit and temporarily adsorb fuel vapor from a vehicle fuel tank during refueling. The canister also has a first fuel vapor and air flow passage for venting the canister and introducing ambient air (in the reverse flow direction) for removing vapor stored in the canister during tank refueling. The canister has a second passage for conducting air and purged vapor from the canister to the operating engine. The first and second passages are opened only during engine operation for purging of stored fuel vapor. The first flow passage is selectively opened when the tank is being refueled. The sealed fuel system eliminates diurnal fuel tank vapor generation and canister bleed emissions.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
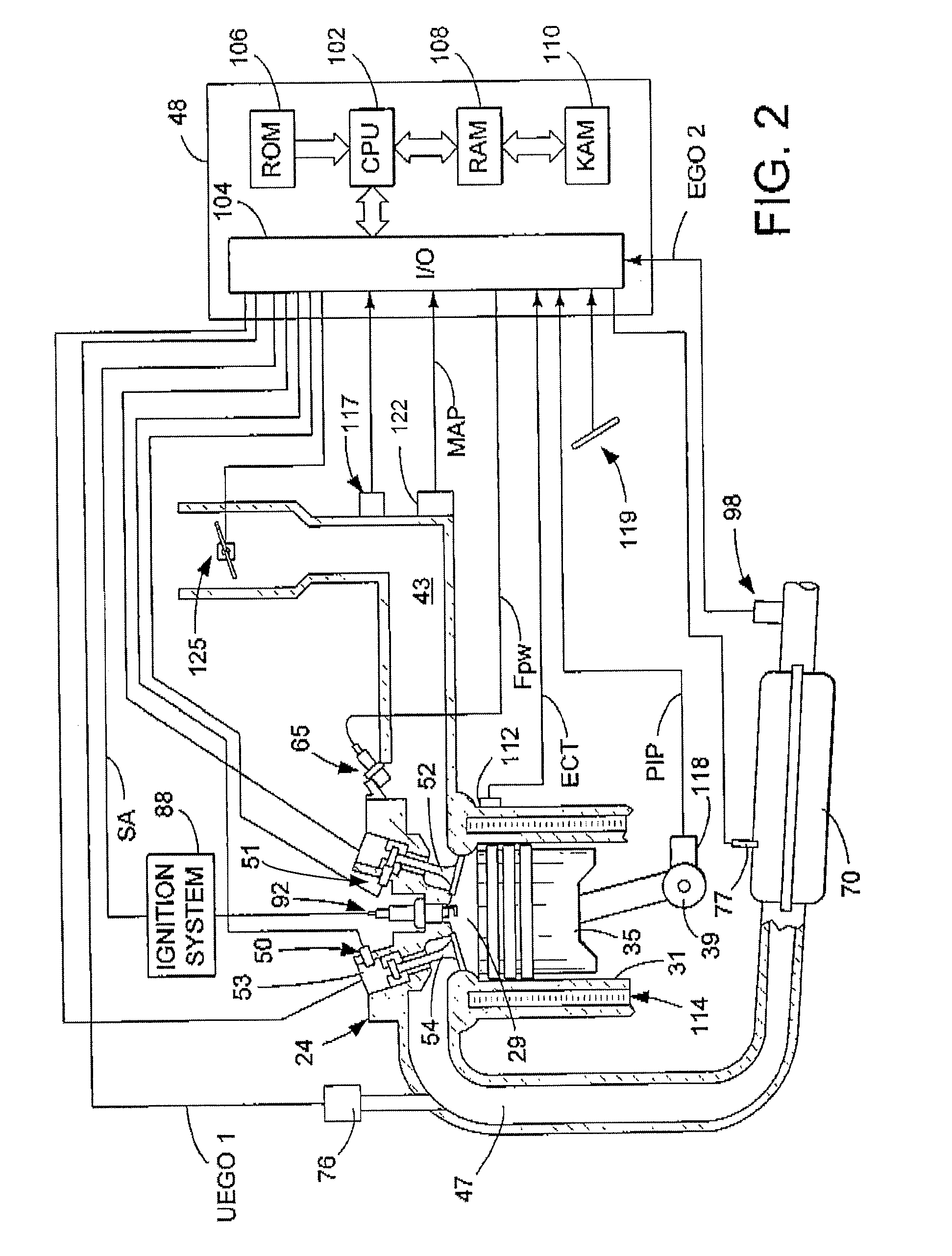
Fuel injection control apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20050183698A1Suppressing hampering of engine combustionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustionExternal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine includes a direct injector for injecting fuel directly into a combustion chamber of the engine, an intake passage injector for injecting fuel into an intake passage of the engine, and a vaporized fuel processing unit for purging purge gas containing a vaporized fuel into the intake passage. A fuel injection control apparatus includes a detecting section and an injection control section. The detecting section detects the amount of the vaporized fuel in the purge gas. The injection control section changes a fuel injection mode of at least one of the direct injector and the intake passage injector depending on the detected amount of the vaporized fuel. As a result, hampering of engine combustion due to purge gas is suppressed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel vapor treatment system for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS6971375B2Purge fuel vapor efficientlyLimit air-fuel ratioElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelAtmospheric airEngineering
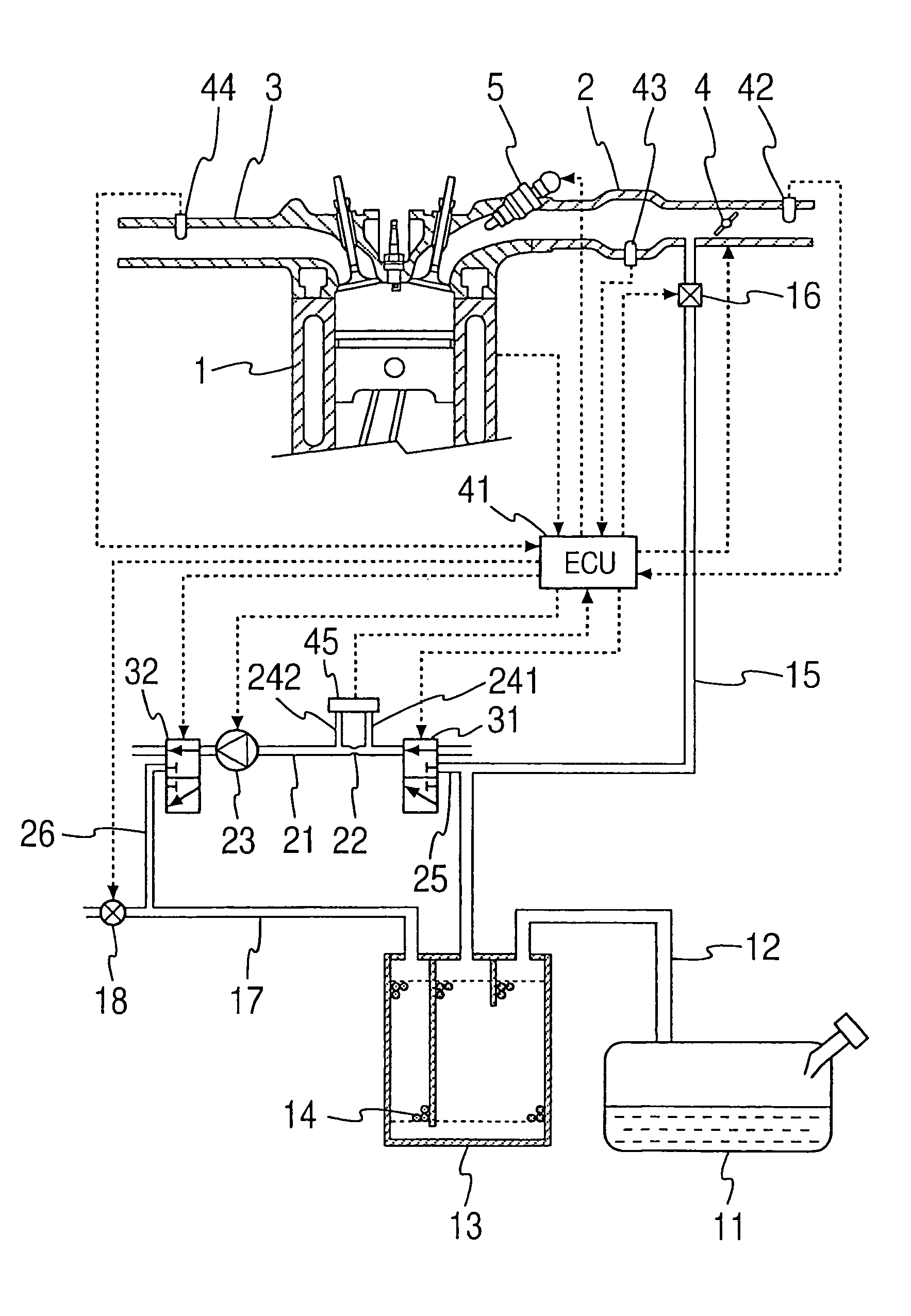
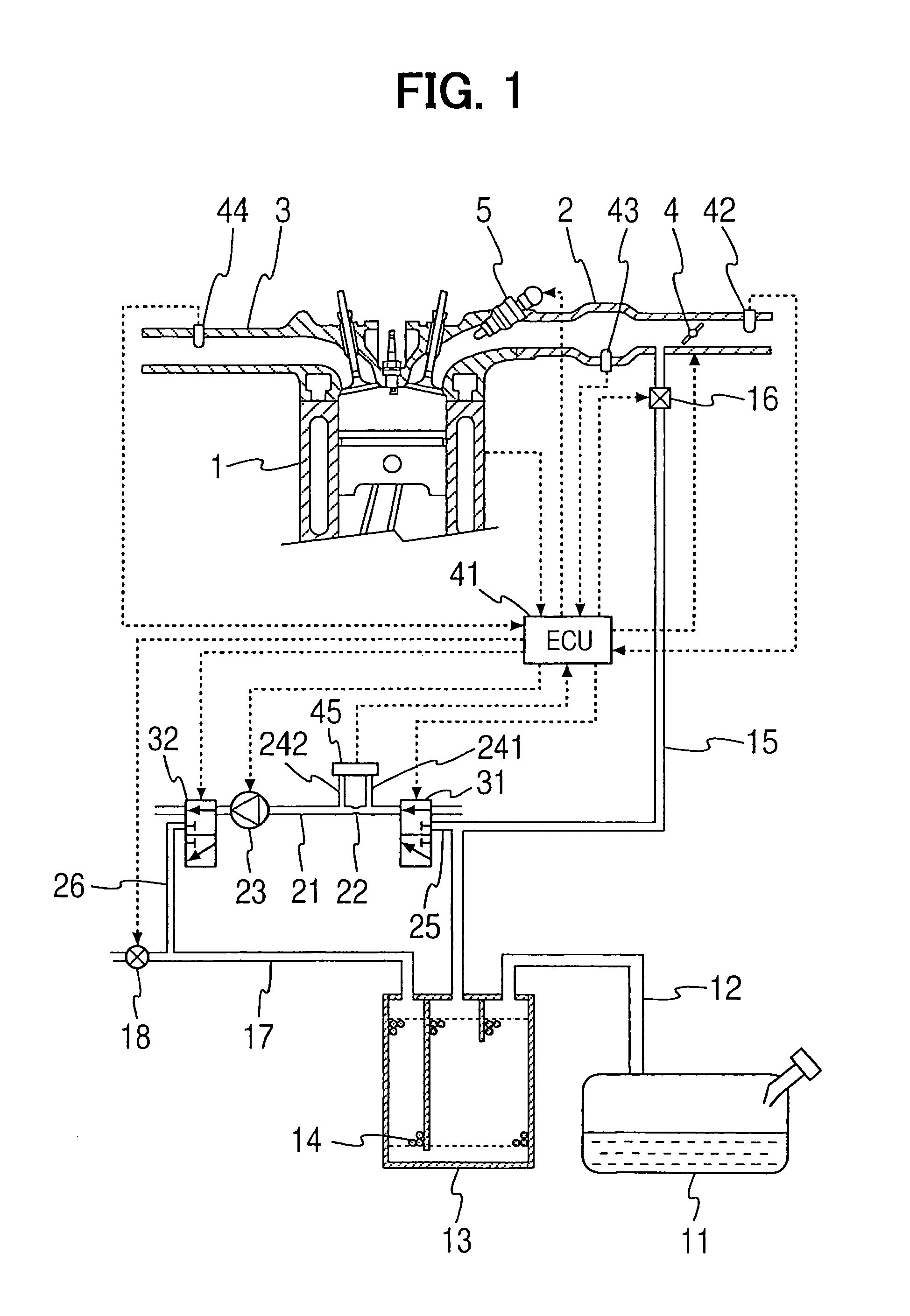
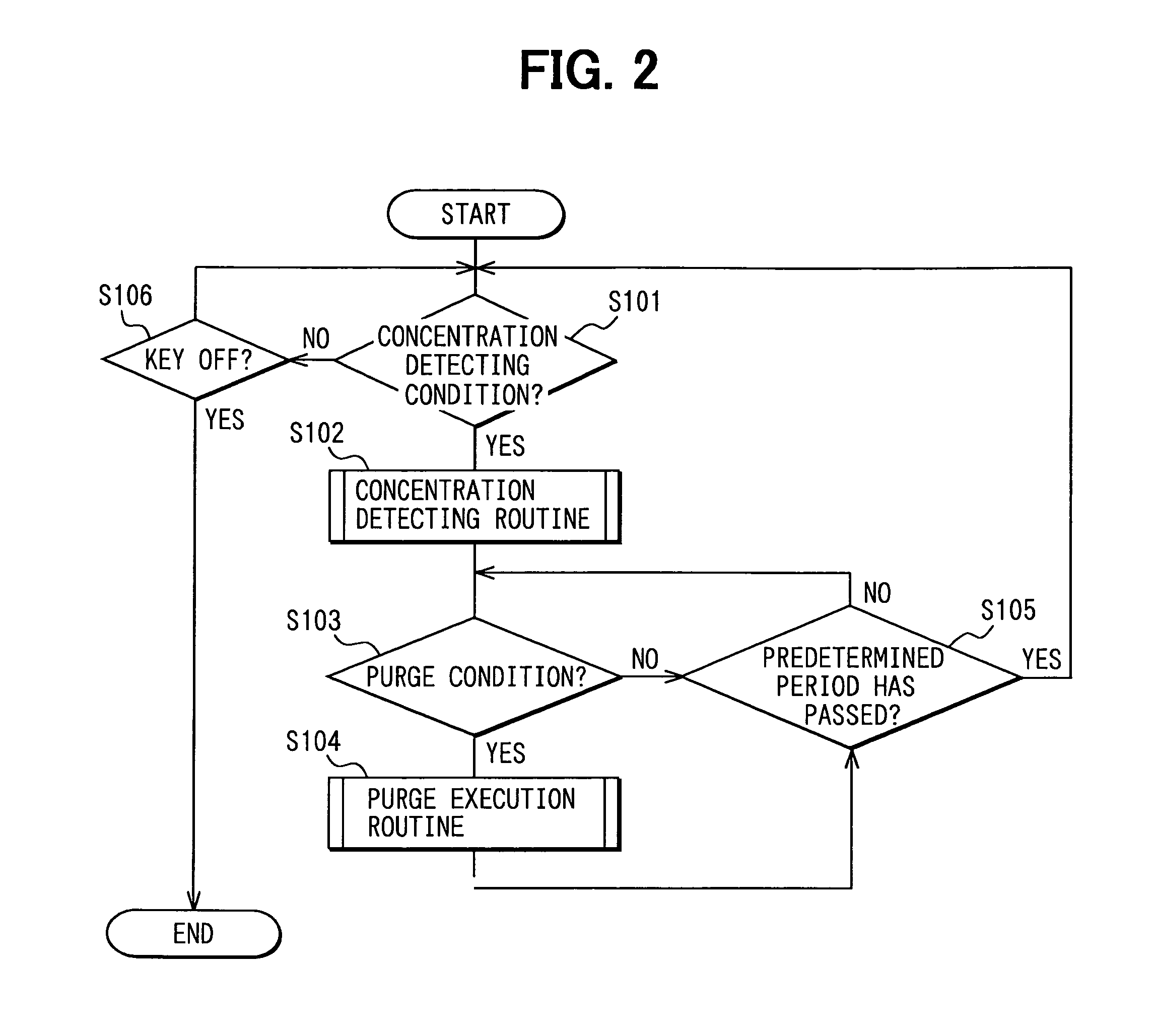
A pump generates a gas flow within a measurement passage having an orifice. A differential pressure sensor detects a pressure difference between both ends of the orifice. Switching valves are disposed in the measurement passage to create a first concentration measurement state in which the measurement passage is opened at both ends thereof and the gas flowing through the measurement passage is the atmosphere, and a second concentration measurement state in which the measurement passage is in communication at both ends thereof with a canister and the gas flowing through the measurement passage is a fuel vapor-containing air-fuel mixture provided from the canister. An ECU calculates a fuel vapor concentration by based on a pressure difference detected in the first concentration measurement state and a pressure difference detected in the second concentration measurement state.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
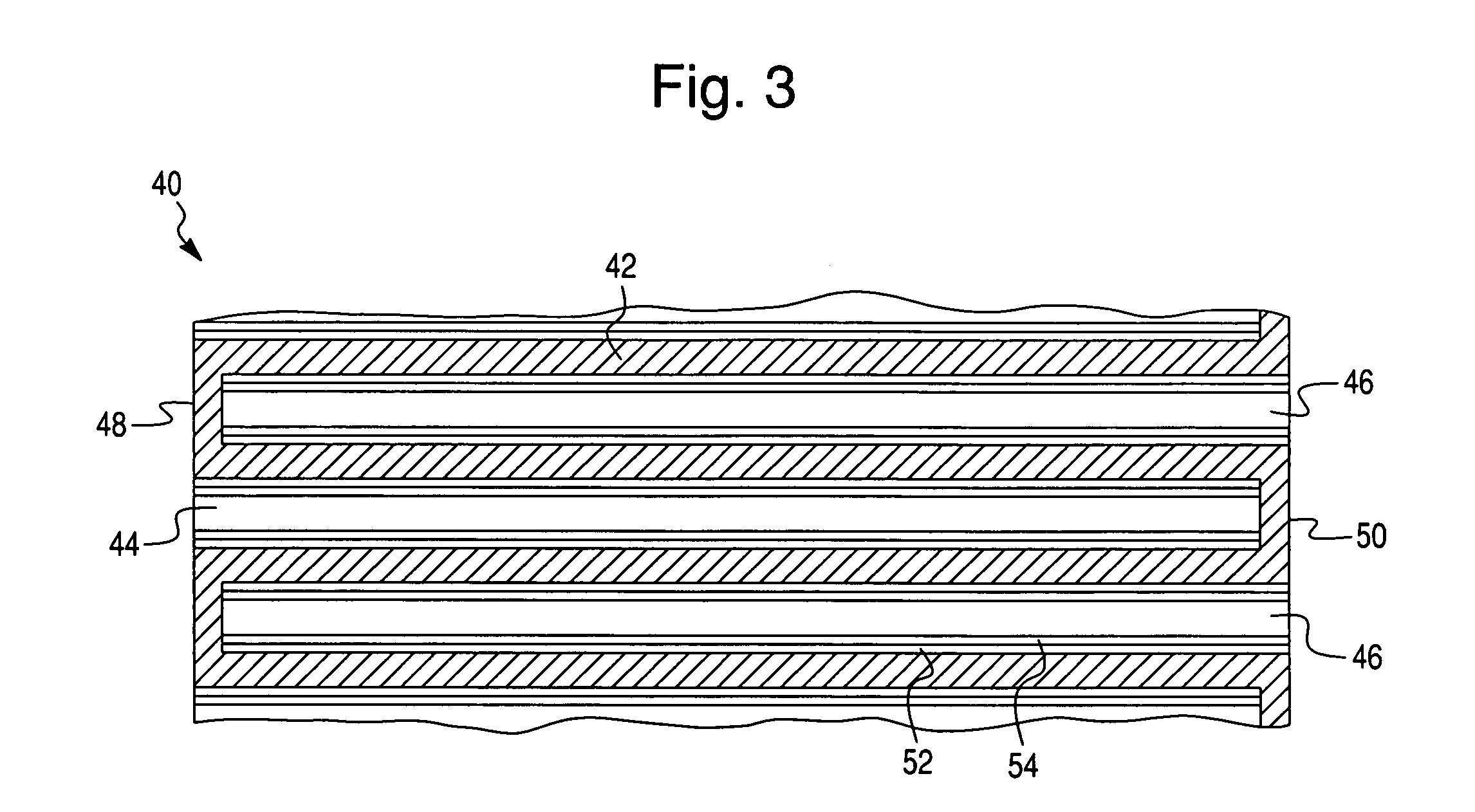
Evaporative emission control using selective heating in an adsorbent canister
InactiveUS20070266997A1Increase capacityProlong lifeGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelSorbentEngineering
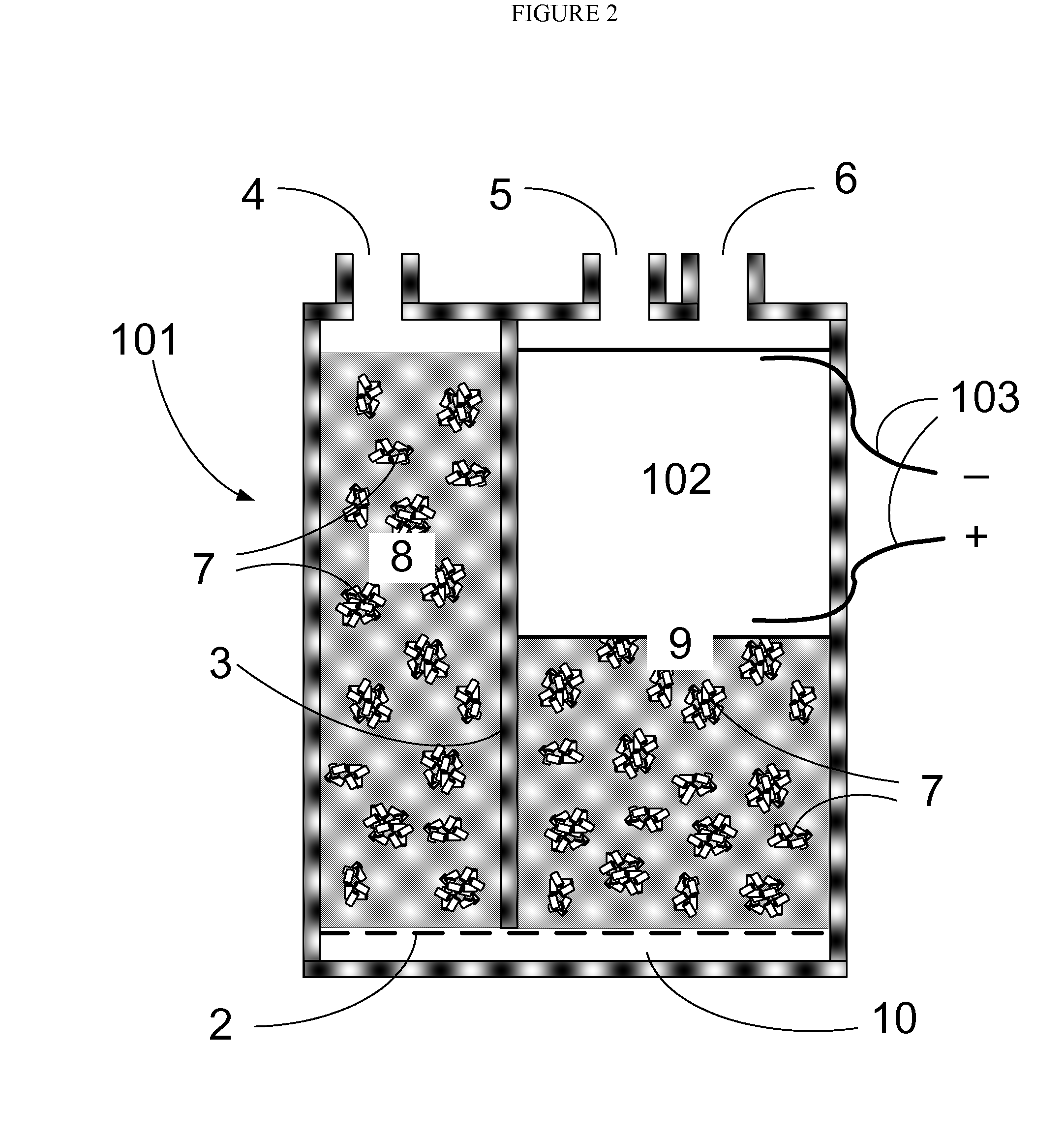
An invention is disclosed for efficiently improving the working capacity and useful service life of an evaporative emission control canister by selectively heating the adsorbent towards the purge outlet of the vapor path.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
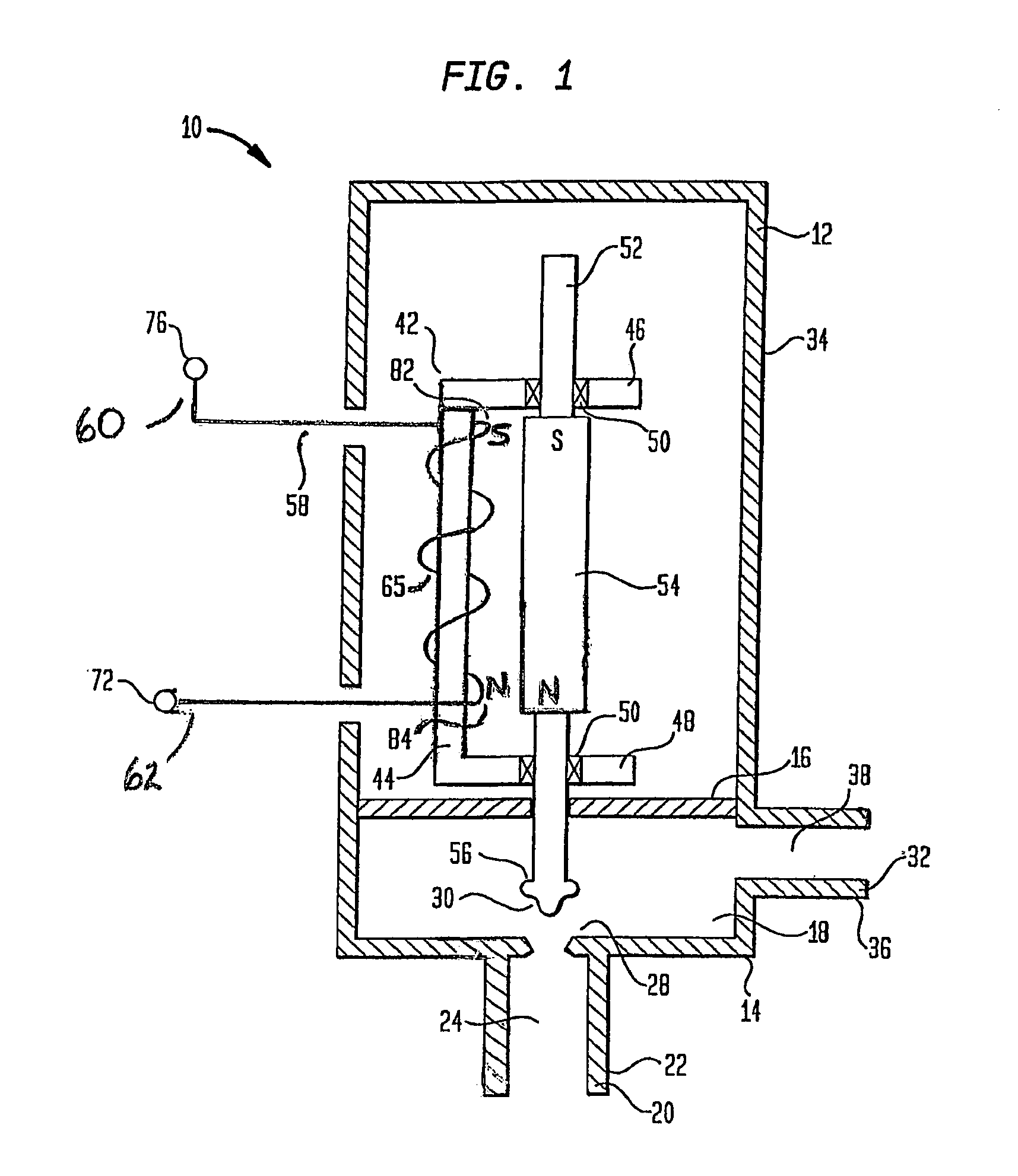
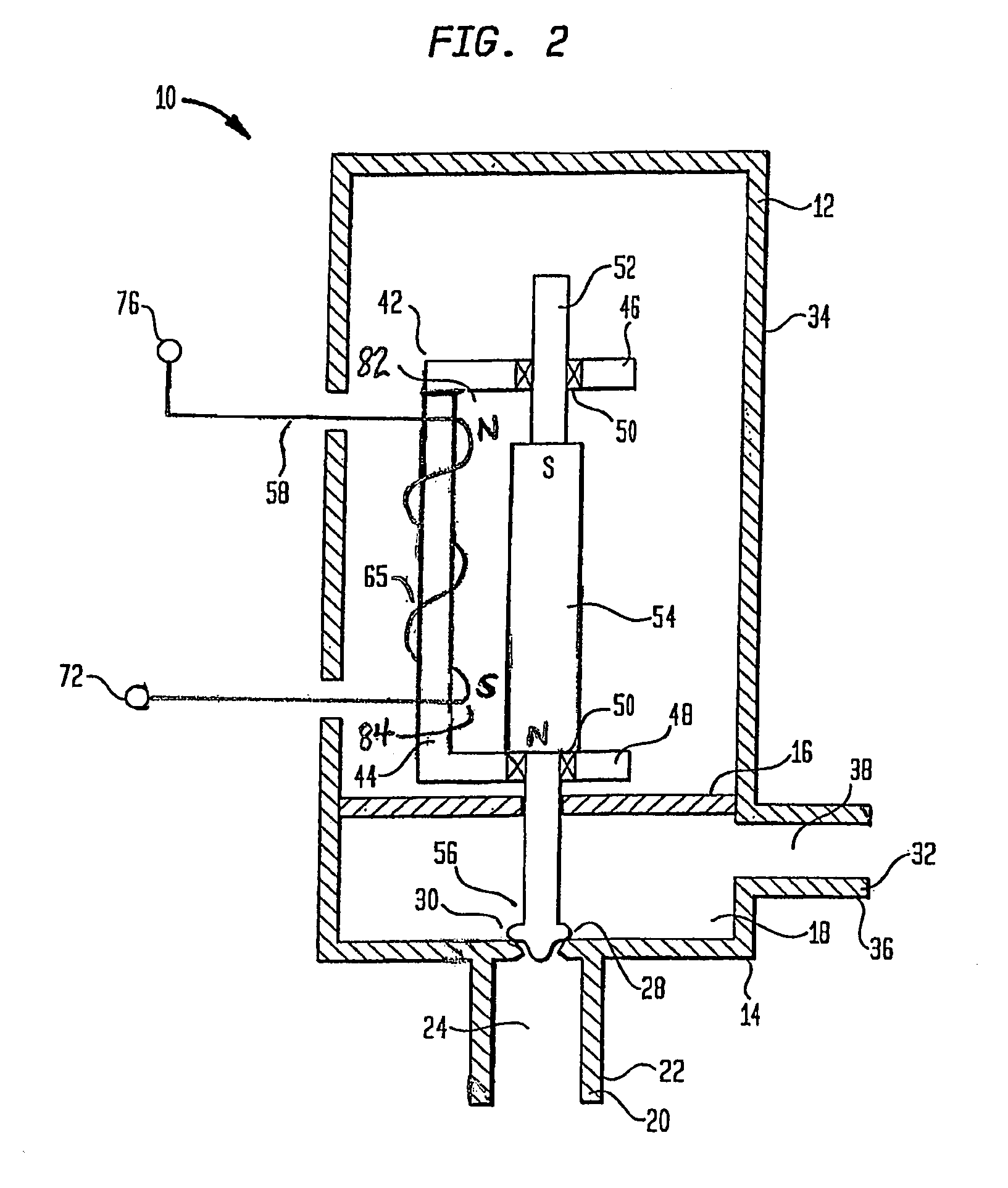
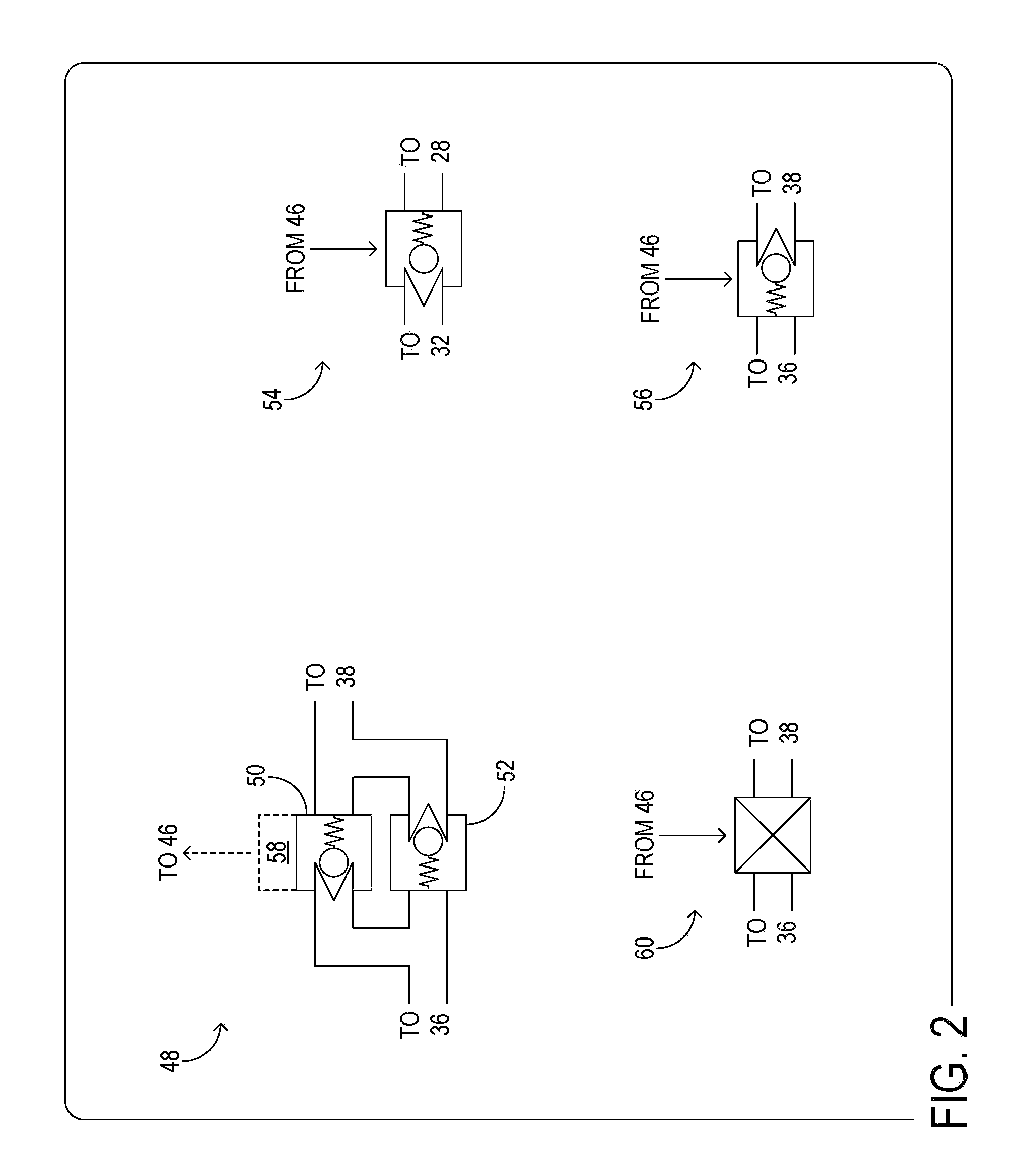
Bipolar valve having permanent magnet
ActiveUS7011076B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelBobbinSolenoid valve
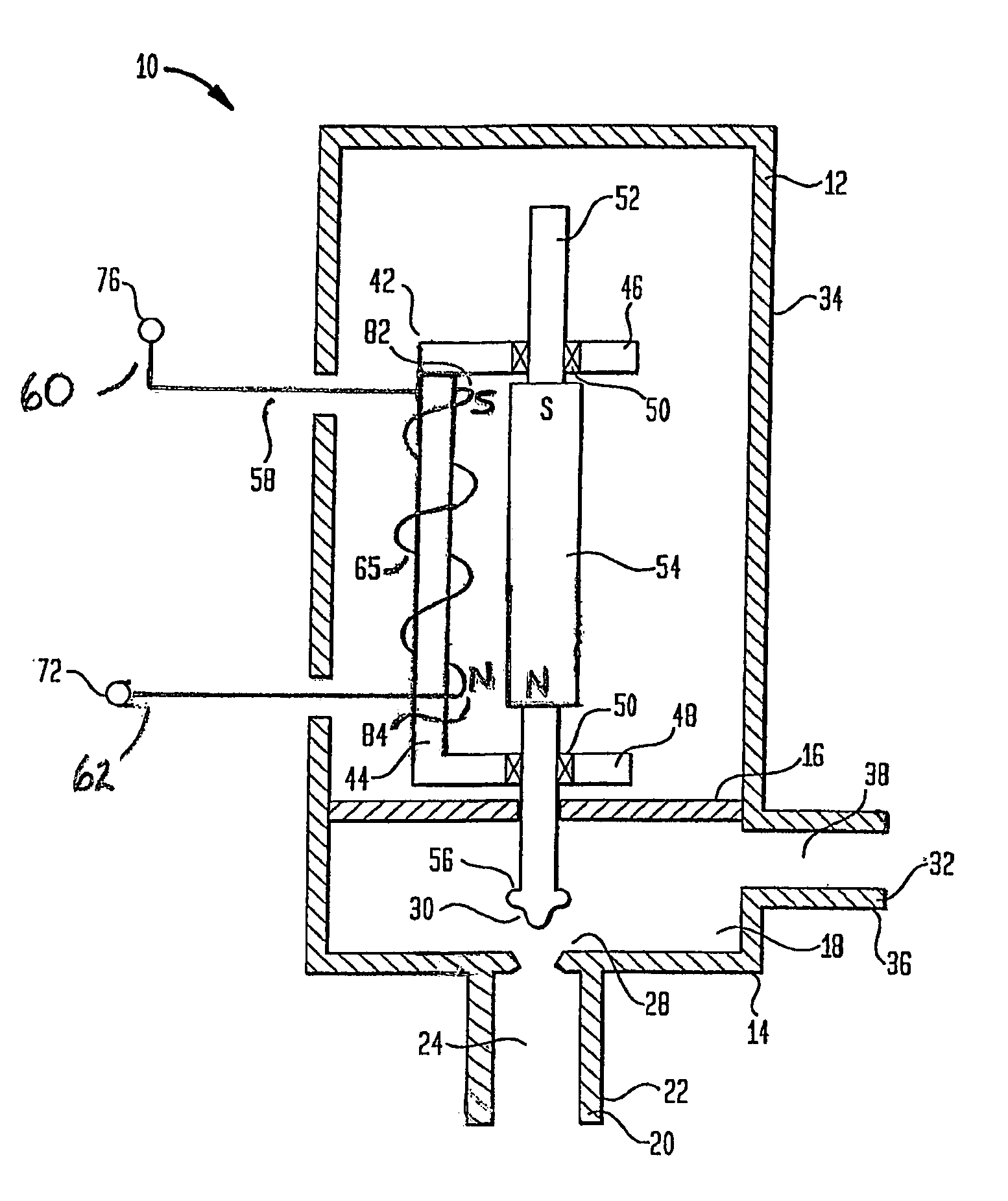
A solenoid for use in valves used in evaporative emission control systems, such as canister purge valves or vent solenoid valves. The solenoid includes a housing having an inlet port and an outlet port. The housing further includes a guide element having a bobbin section. A valve shaft is slidably mounted to the guide element, wherein the valve shaft includes a permanent magnet and a valve element. The valve element is movable between a closed position wherein the inlet port is closed and an open position wherein the inlet port is opened. A coil is formed on the bobbin adjacent the magnet. In use, the coil generates directional magnetic fields oriented to cause the magnet to be repelled to move the valve element to the open position and oriented to cause a magnetic attraction with the magnet to move the valve element to the closed position.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
System and method for engine with fuel vapor purging
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Catalytic reactive component reduction system and methods for the use thereof
ActiveUS7694916B2Minimizes ventingReduce riskOrganic chemistryIndirect heat exchangersGas phaseEngineering
Owner:PHYRE TECH
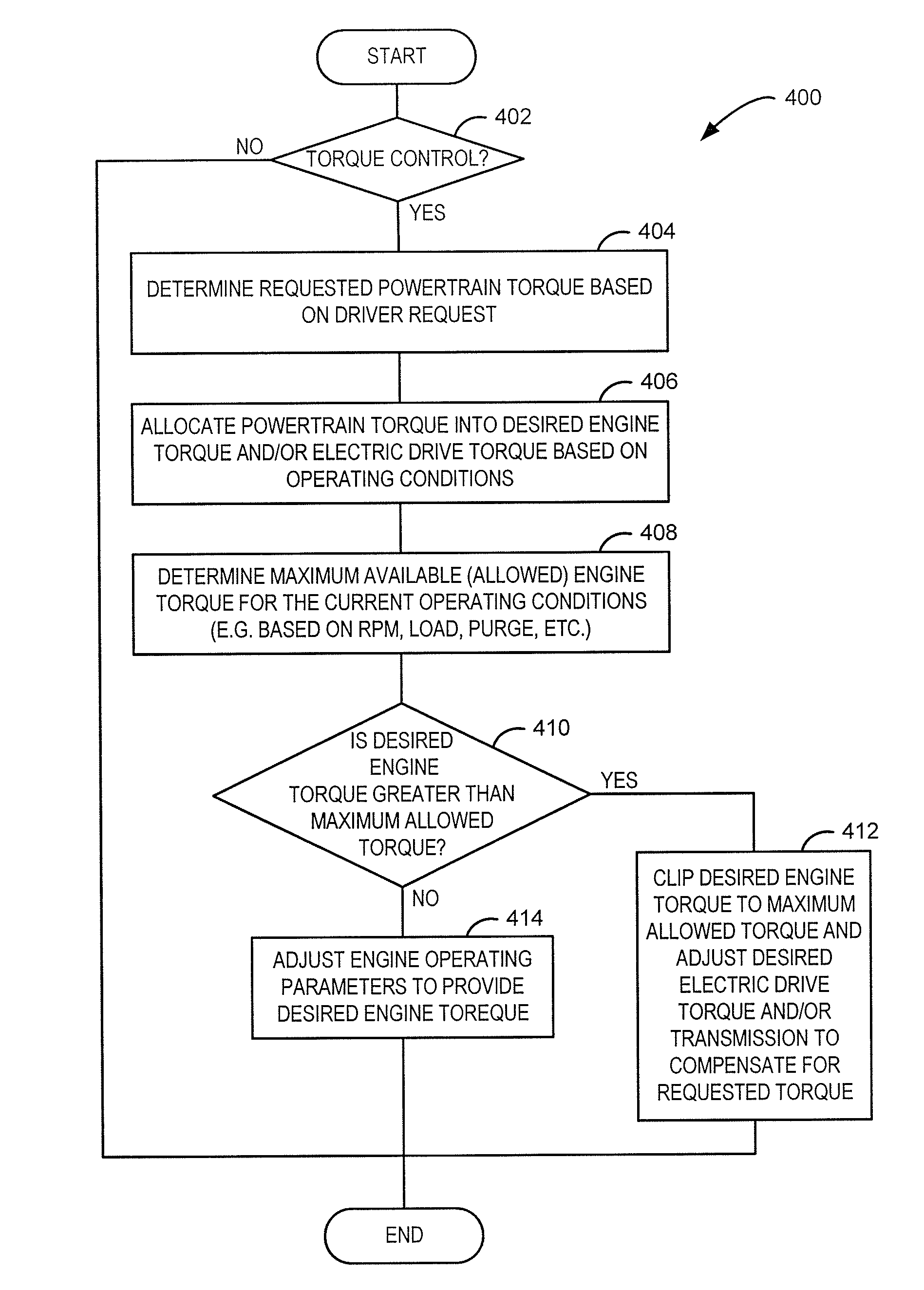
Dynamic Allocation of Drive Torque
ActiveUS20080308066A1Accurate estimateEnhance vehicle operationHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectricityExternal combustion engine
A method for operating a powertrain in a vehicle is provided. The powertrain includes an electric drive and an internal combustion engine. The method comprises providing torque to drive the vehicle from both the electric drive and the engine, where engine torque is varied within an allowable range; and when operating the engine at an edge of the range, adjusting the range based on whether a selected operating condition can be provided by the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for Fuel Vapor Canister Purging
ActiveUS20080271718A1Inhibition releaseAccelerate emissionsHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlLiquid fuelInternal combustion engine
A method of controlling fuel vapor purging in a hybrid electric vehicle capable of selectively operating an internal combustion engine is provided. The method includes, determining a fuel tank condition parameter based on an amount of liquid fuel residing in a fuel tank of the hybrid electric vehicle and a duration since the previous fuel tank filling event, in response to the fuel tank condition parameter exceeding a threshold limit, initiating operation of the internal combustion engine and purging fuel vapor from the fuel vapor canister for a predetermined duration, and in response to the fuel tank condition parameter being less than the threshold limit, selectively purging fuel vapor from the fuel vapor canister based on an engine operating condition.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
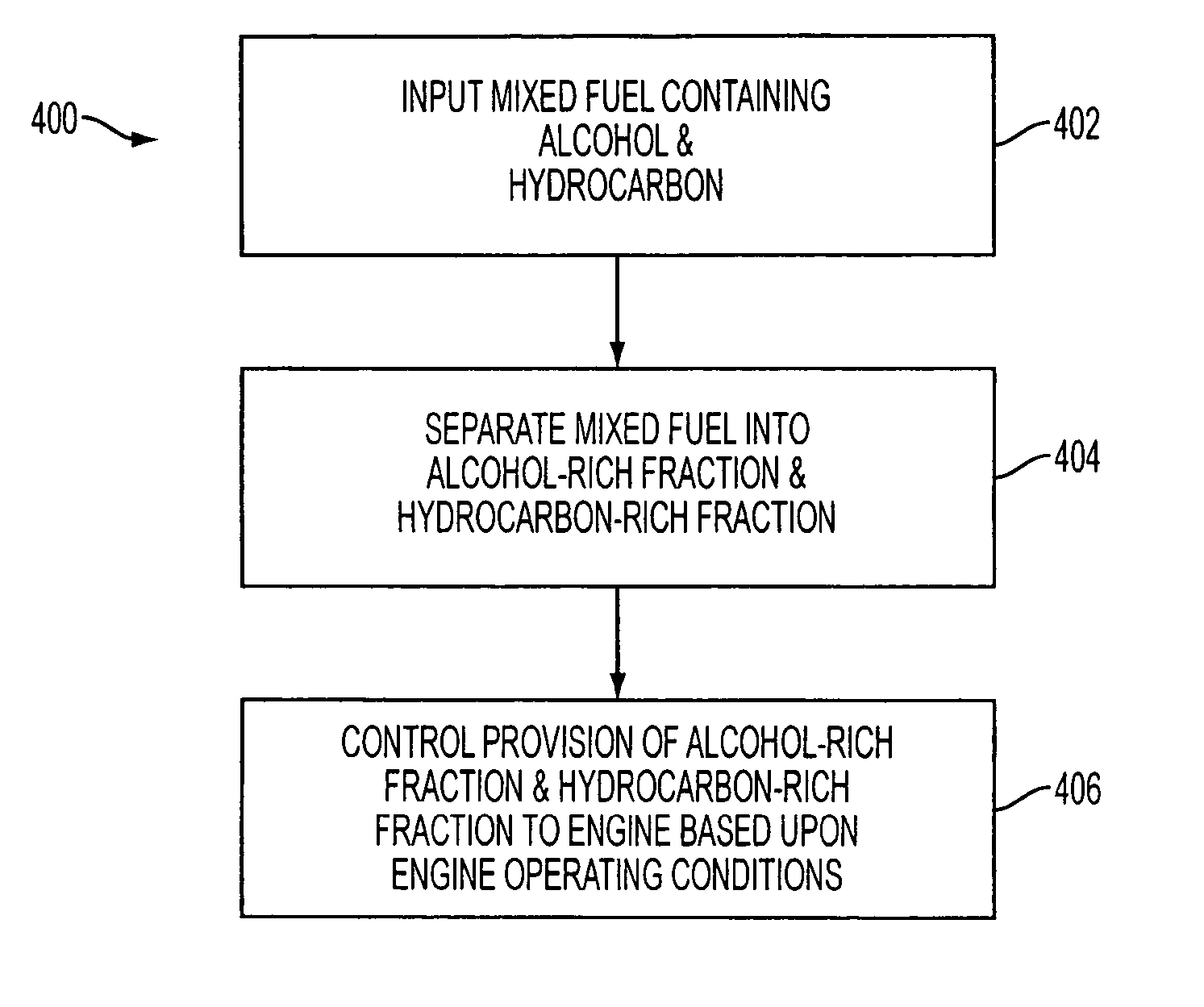
Apparatus with mixed fuel separator and method of separating a mixed fuel
InactiveUS20070215127A1Low costImprove charge cooling effectNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesHigh rateFuel tank
An apparatus comprising an internal combustion engine, a fuel tank, a fuel separator disposed fluidically between the fuel tank and the engine, wherein the fuel separator comprises first and second passageways separated at least partially by a selective barrier that selectively transports a first fuel in a fuel mixture at a higher rate than a second fuel in the fuel mixture, and wherein the first passageway is configured to receive an input of fuel from the fuel tank, and an extraction fluid source in fluid communication with the second passageway of the fuel separator.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
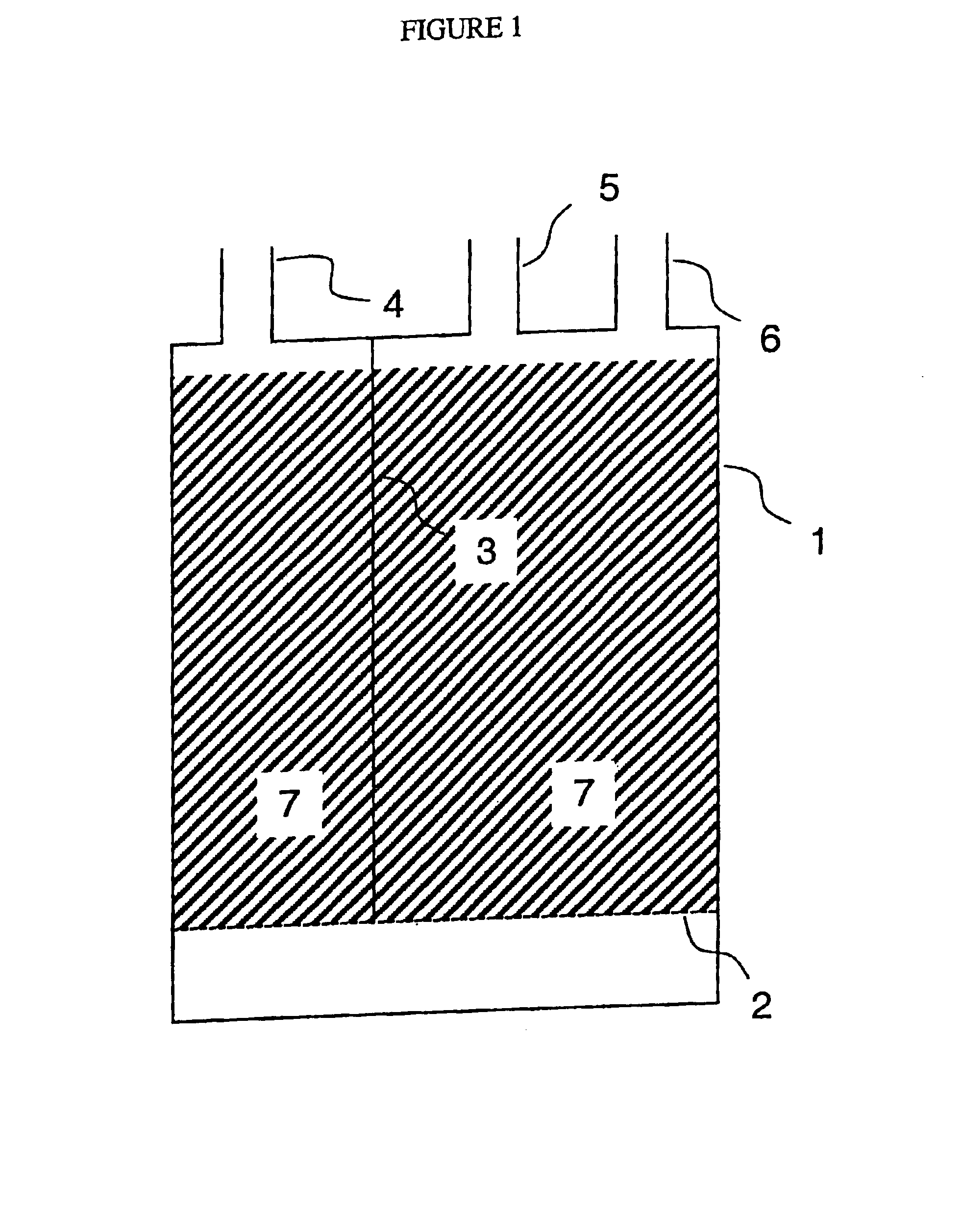
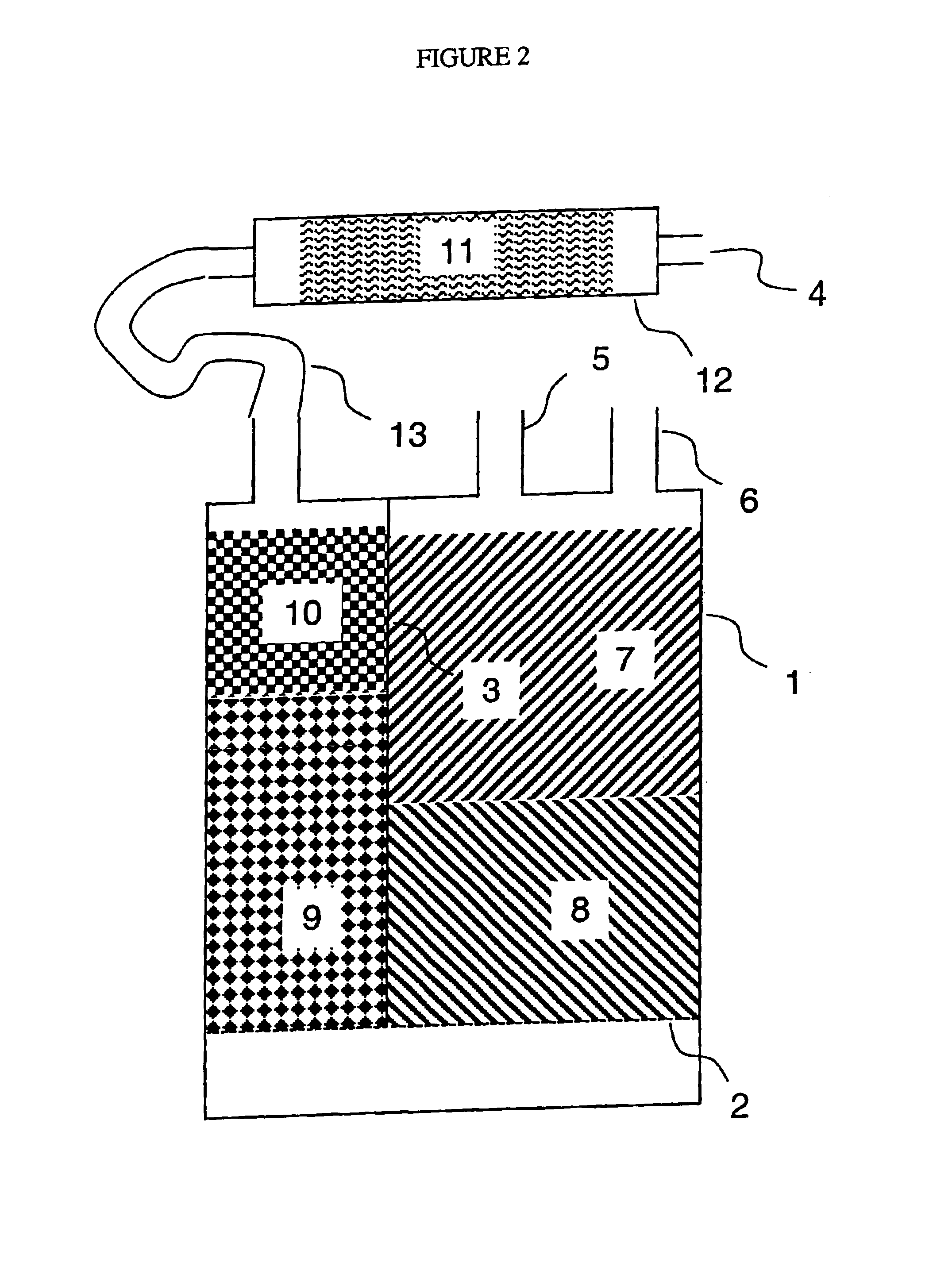
Method for reducing emissions from evaporative emissions control systems
InactiveUSRE38844E1Loss in working capacityEmission reductionGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHigh concentrationSorbent
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Crankcase breech detection for boosted engines
InactiveUS20100147270A1Prolonged duty cycleIncreased blow-byCombustion enginesLubrication pressure controlMobile vehicleAtmospheric air
Methods for indicating whether a crankcase of an engine is breeched are provided. One example method comprises restricting a communication of the crankcase with atmosphere, acting to increase or decrease a crankcase pressure, and indicating whether the crankcase is breeched based on the crankcase pressure. Another example method comprises sensing a crankcase pressure component, and indicating whether the crankcase is breeched based on the crankcase pressure component, the crankcase communicating with atmosphere via a conduit, a restrictedness of the conduit responsive to one or more of a crankcase pressure and a signal from an electronic control unit of the motor vehicle. Still other examples provide more particular methods for indicating whether the crankcase is breeched, and example configurations that enable the various methods.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
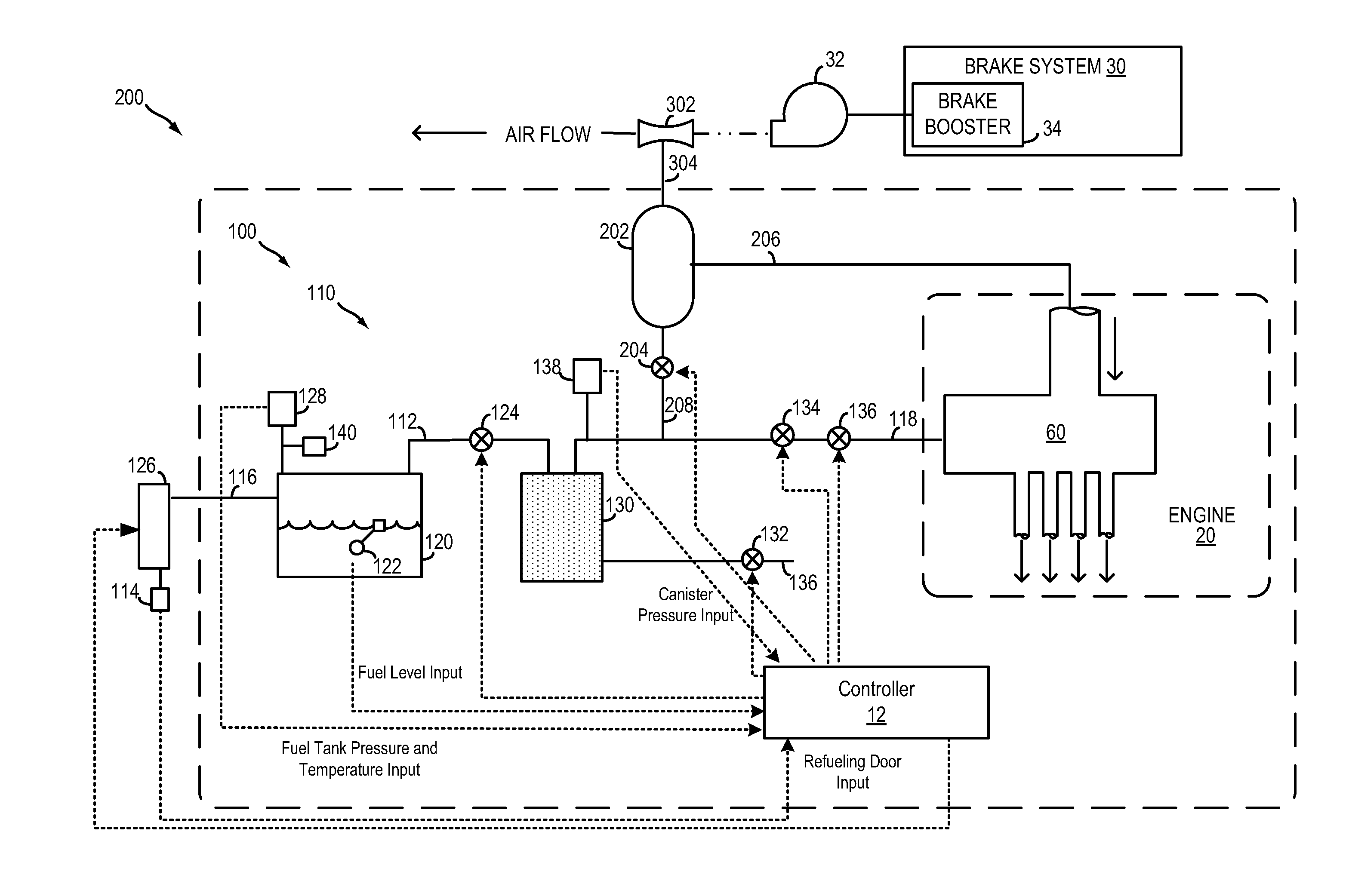
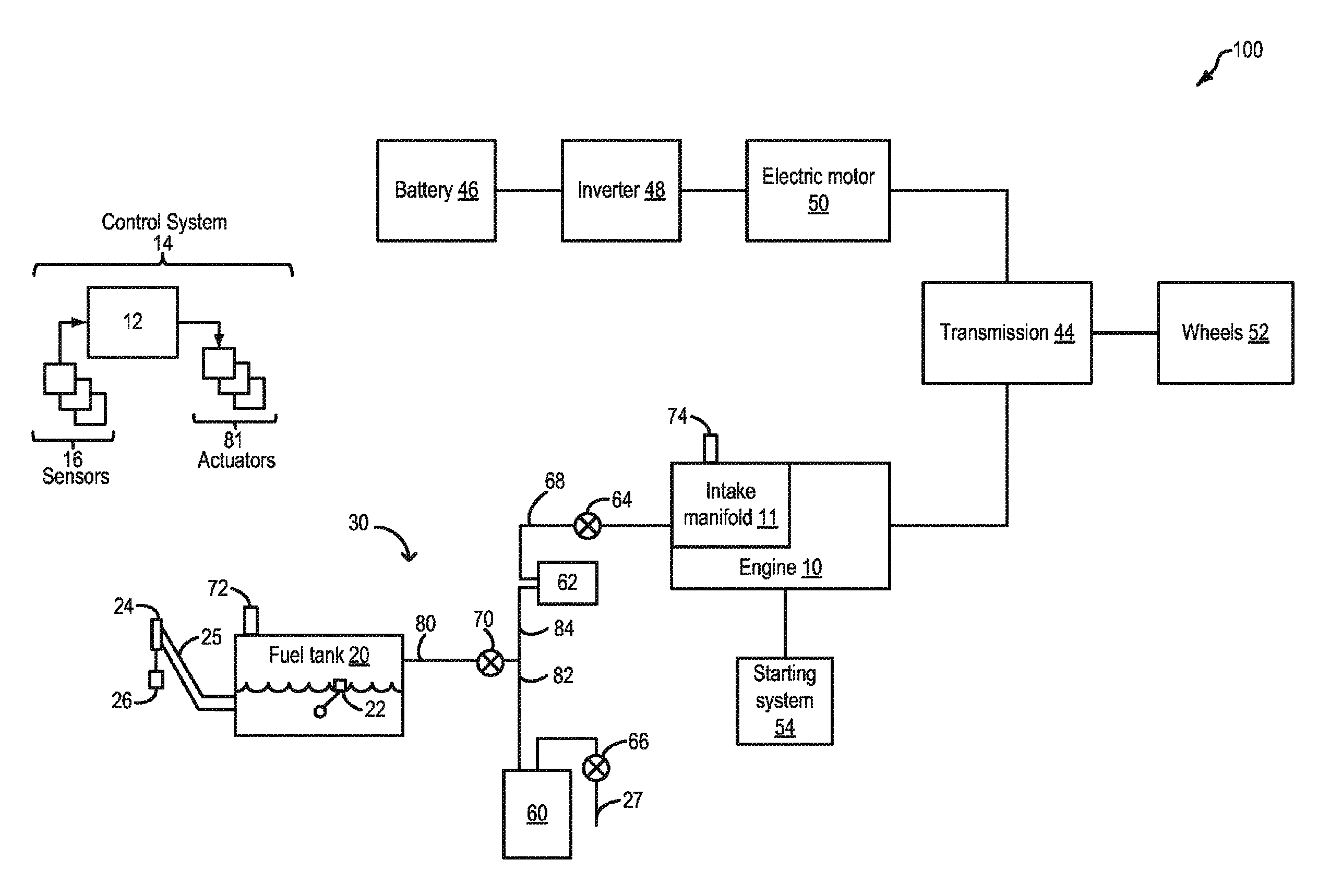
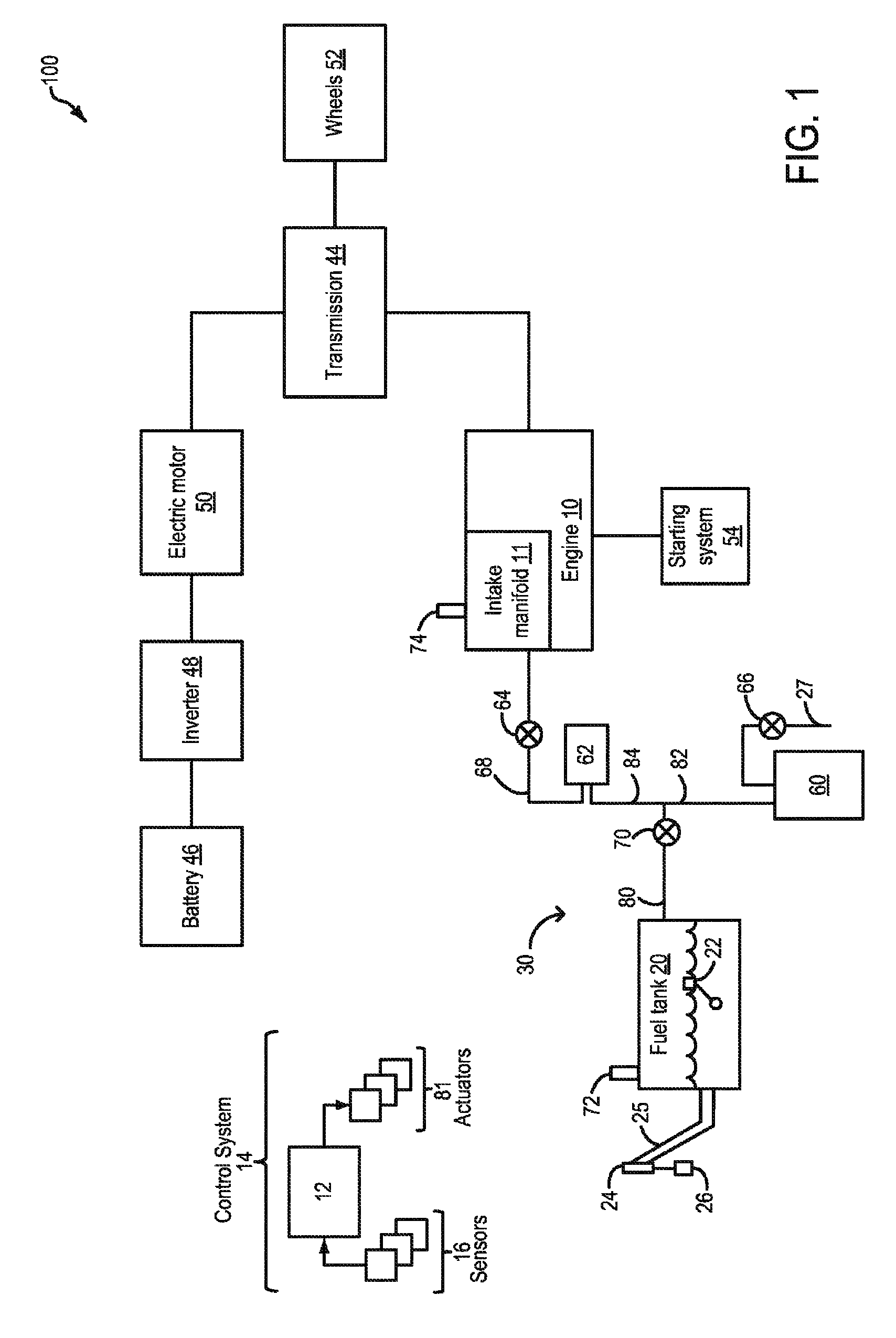
Method and system for fuel vapor control
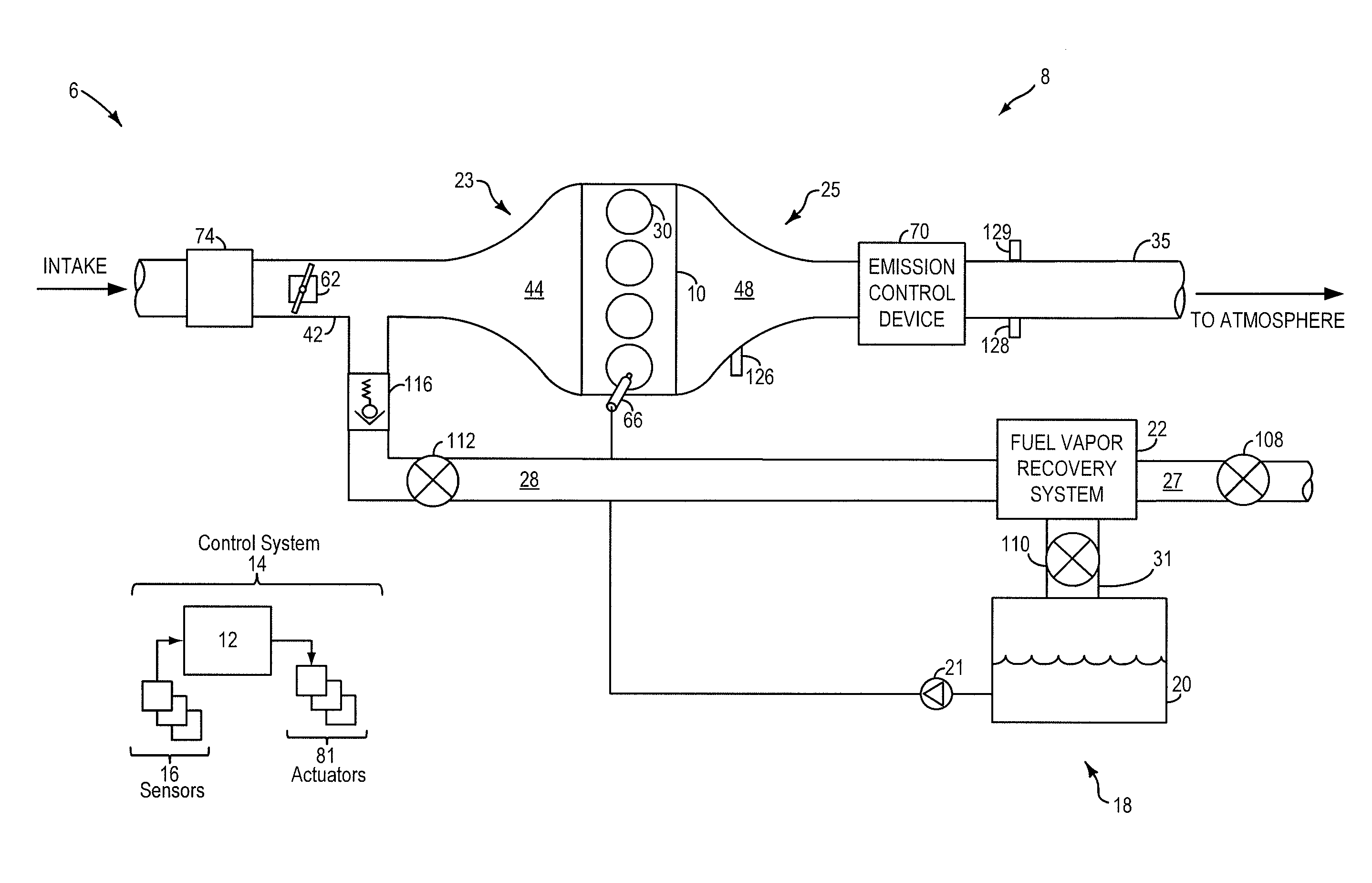
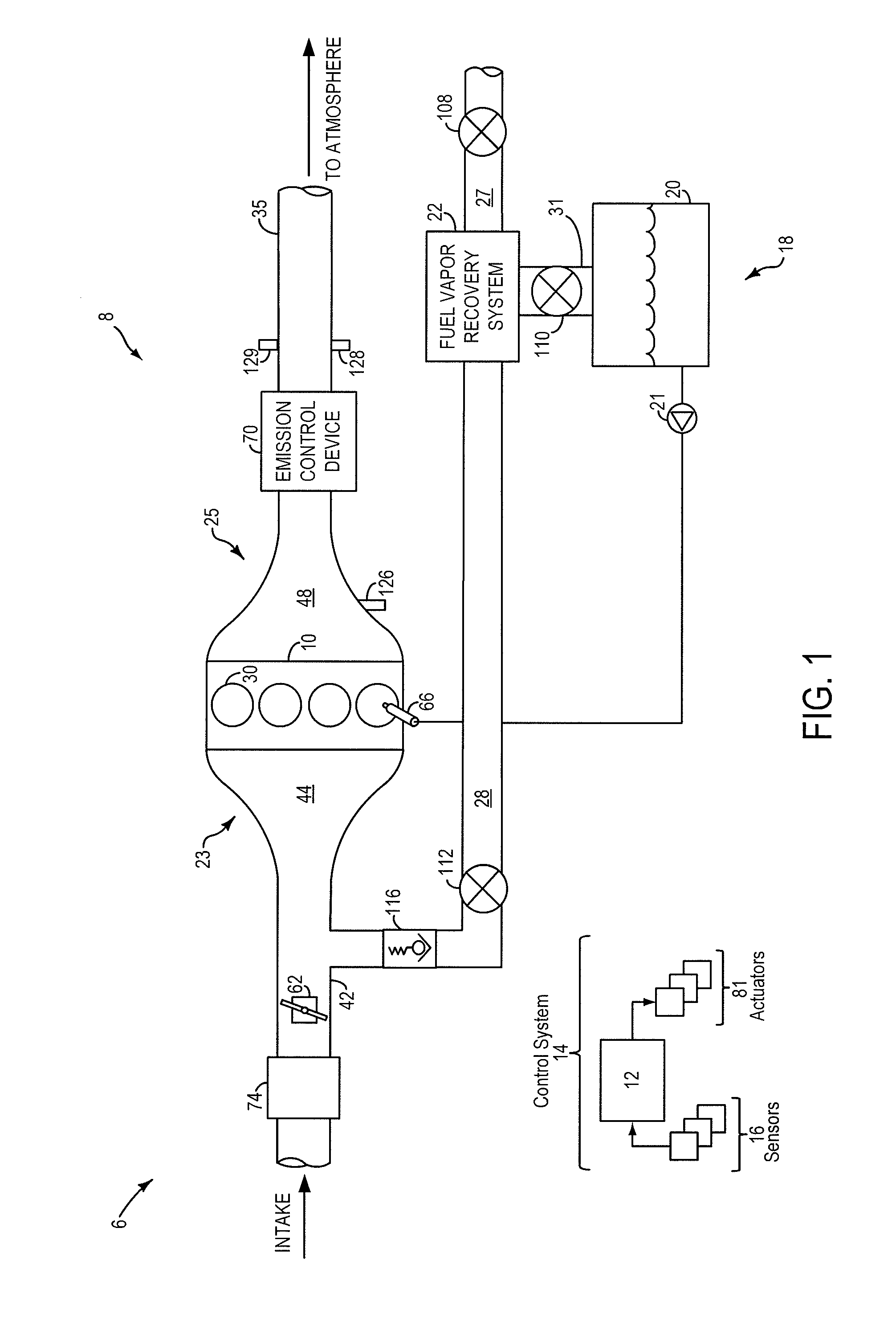
ActiveUS20110295482A1Reduce carbon emissionsShorten operation timeAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlIsolation valveHybrid vehicle
A method and system for fuel vapor control in a hybrid vehicle (HEV). The HEV fuel vapor recovery system includes a fuel tank isolation valve, which is normally closed to isolate storage of refueling from storage of diurnal vapors. The method for fuel vapor control includes selectively actuating the fuel tank isolation valve during interrelated routines for refueling, fuel vapor purging, and emission system leak detection diagnostics to improve regulation of pressure and vacuum the HEV fuel vapor recovery system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fuel vapor handling apparatus and diagnostic apparatus thereof
InactiveUS6695895B2Desorption of fuel is facilitatedFuel can be purged efficientlyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFuel injection apparatusDesorptionVaporization
A fuel vapor handling apparatus supplies a purging air to a canister by using a purge pump and purges fuel desorbed from the canister into an intake pipe. A controller intermittently operates the purge so that the canister internal temperature recovers from a reduced level caused by the latent heat of vaporization of fuel during an operating period of the purge pump. Therefore, desorption of fuel from the canister during an operating period is facilitated. Since the actual operating time of the purge pump is reduced, the life of a motor that is a power unit of the purge pump becomes longer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Engine system and dual fuel vapor purging system with cylinder deactivation
ActiveUS6820597B1Easy to operateNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngine controllersSystems designFuel vapor
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
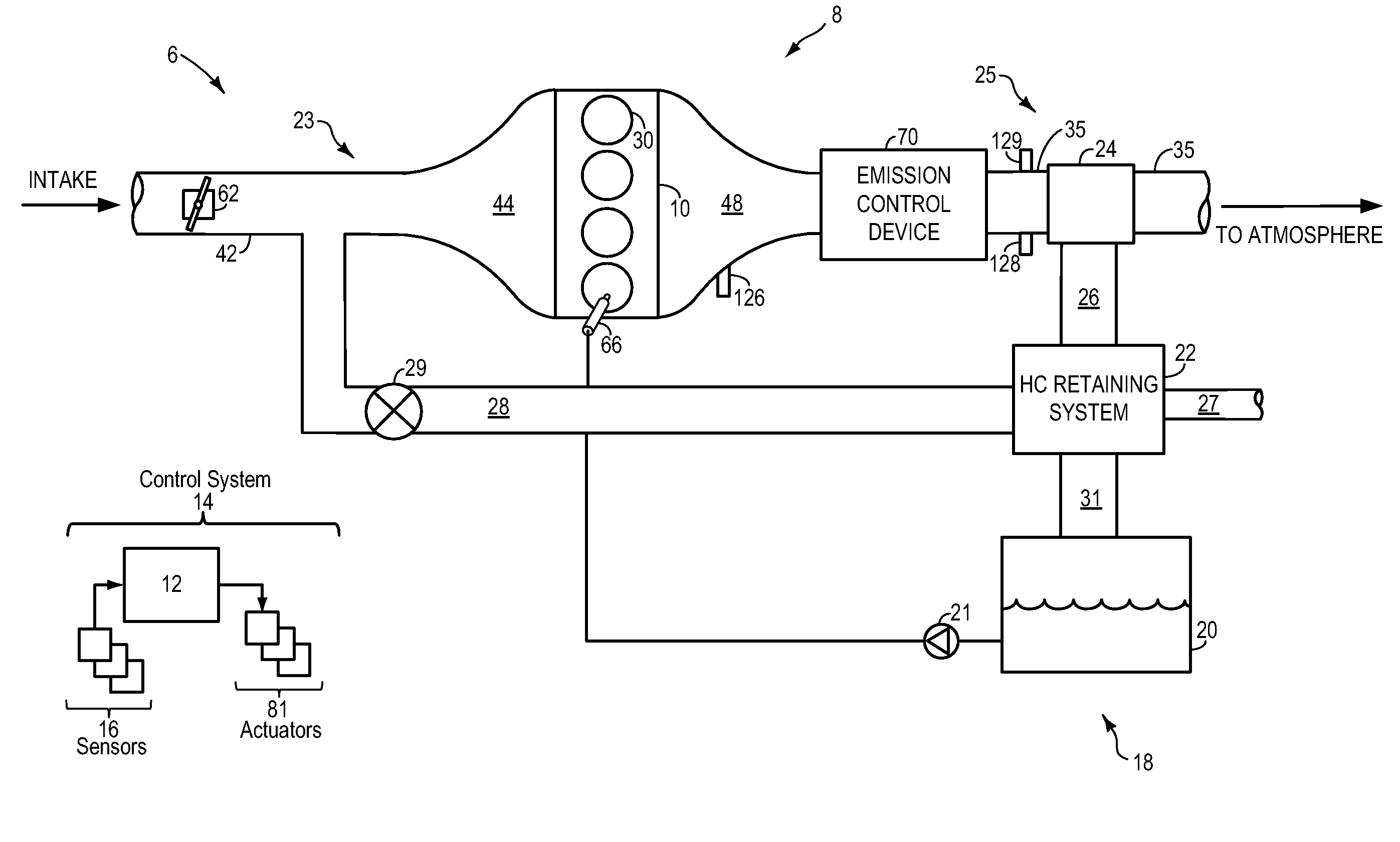
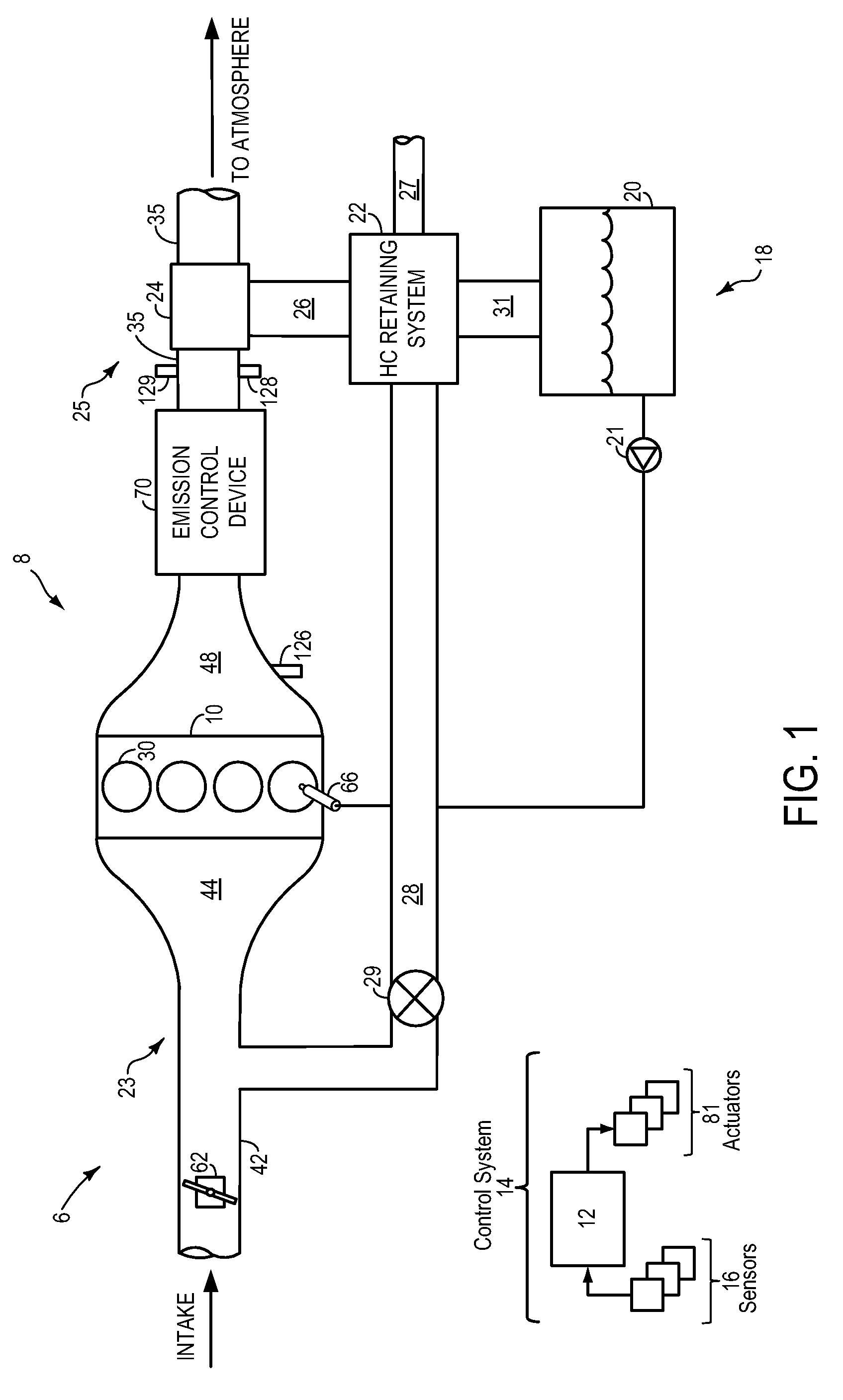
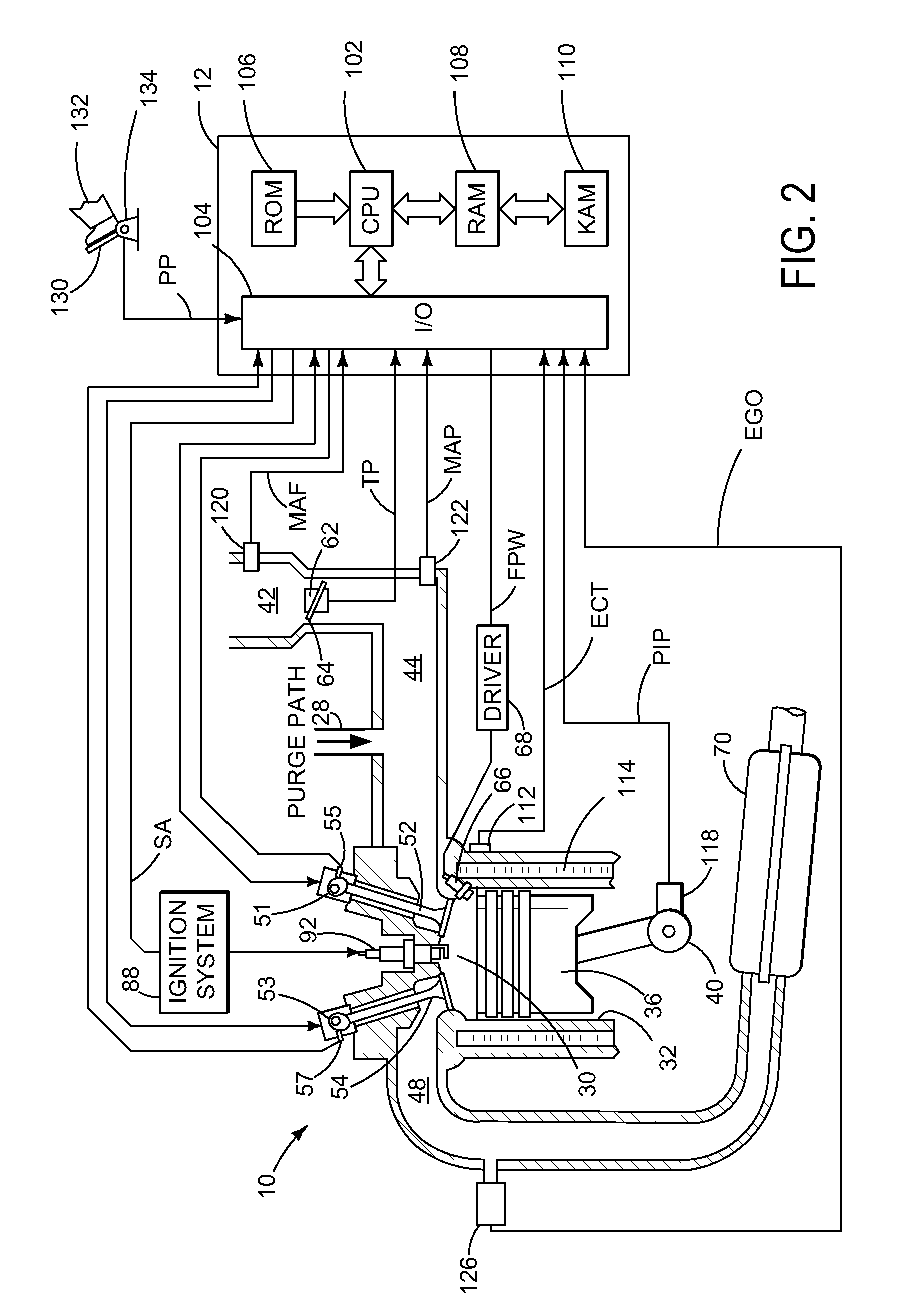
Hydrocarbon Retaining System for Flex-Fuel Combustion Engine
InactiveUS20090120071A1Reduce breakthroughLow alcohol contentElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustionProcess engineering
Systems, methods, and computer readable storage media are described in which exhaust gas is routed to a hydrocarbon retaining device during starting, and purged to the engine intake manifold. Various alternative approaches are described for controlling operation and diagnosing degradation. Further, various interrelated configurations are described.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Internal combustion engine air cleaner and adsorption filter
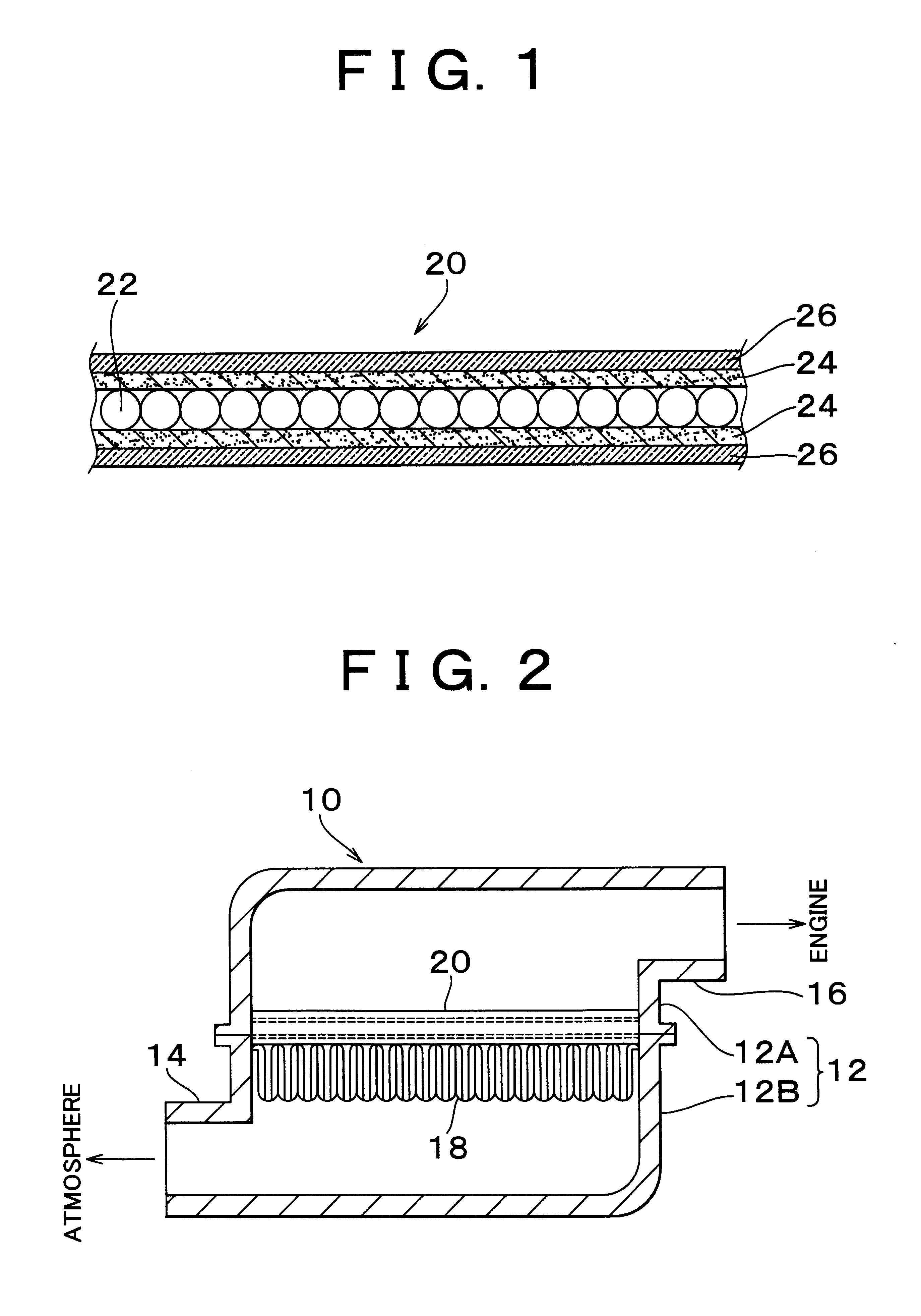
InactiveUS6692555B2Effectively prevent activated carbon powder from falling offImprove abilitiesHuman health protectionCombination devicesActivated carbonParticulates
A sheet-like adsorption filter formed by sandwiching particulate activated carbon with heat-resistant nets and non-woven fabric sheets that have a percentage of void of 90% or higher, is disposed at an internal combustion engine side of a filter element.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK +3
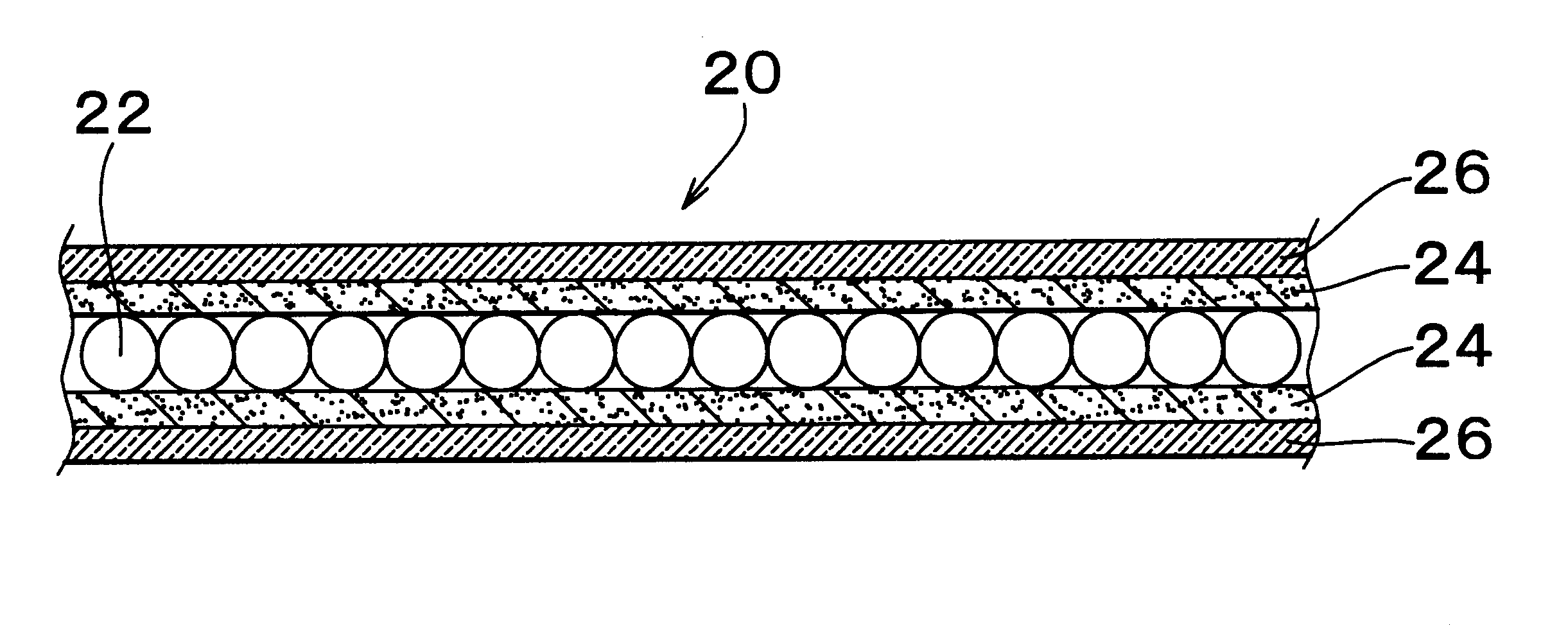
Hydrocarbon adsorpotion method and device for controlling evaporative emissions from the fuel storage system of motor vehicles
ActiveUS20070113831A1Reducing vapor releasedReduce the amount of fuelGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSlurry
The present invention is directed to an evaporative emissions control apparatus for minimizing fuel vapor emissions from a fuel storage system in a vehicle with an internal combustion engine. More specifically, the present invention is directed to an evaporative emissions control apparatus comprising a canister filled with a hydrocarbon adsorbent. The present invention is also directed an evaporative emissions control apparatus comprising a support substrate, which is coated with a hydrocarbon adsorbent slurry.
Owner:BASF CATALYSTS LLC
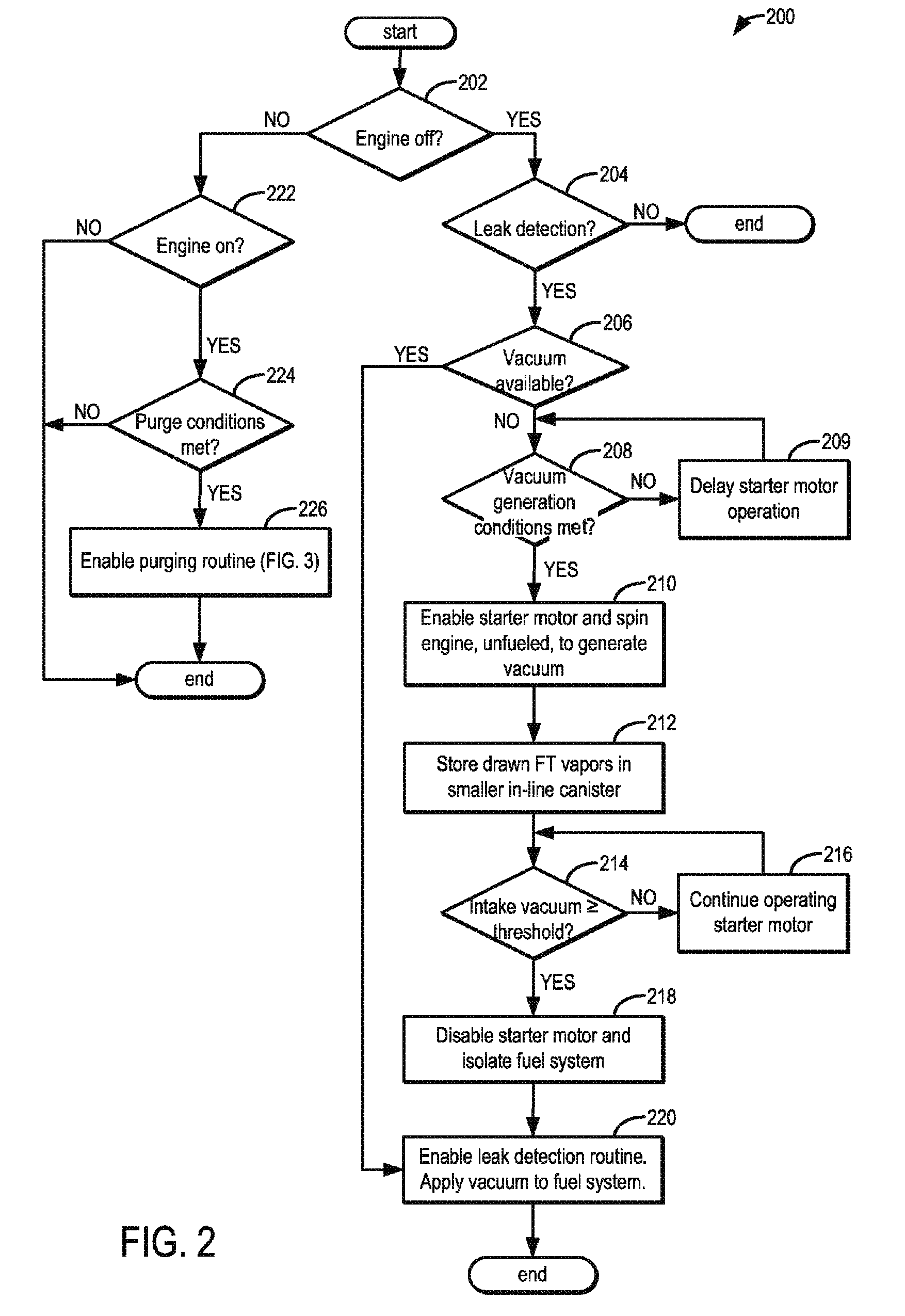
Method and system for fuel vapor control
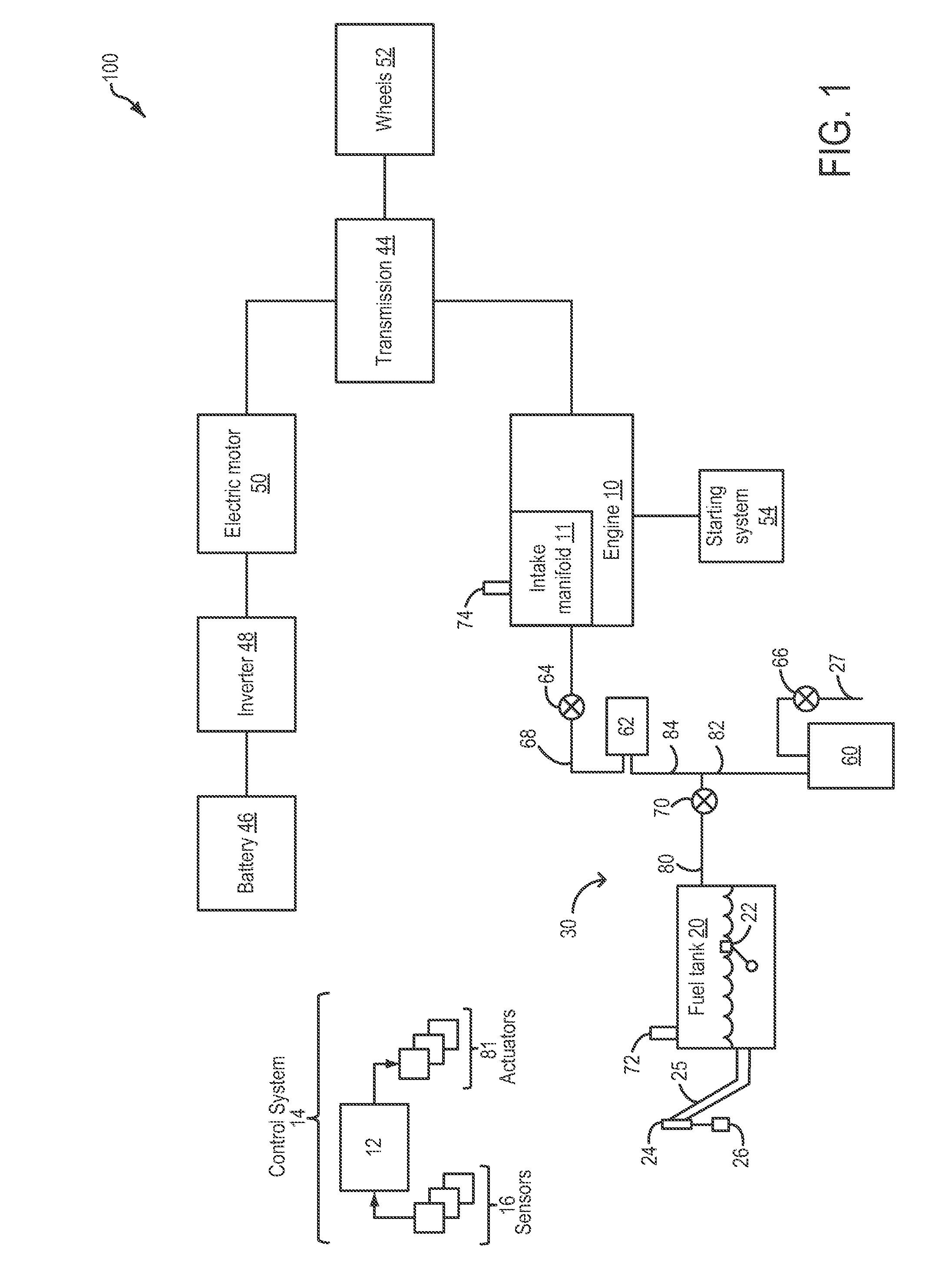
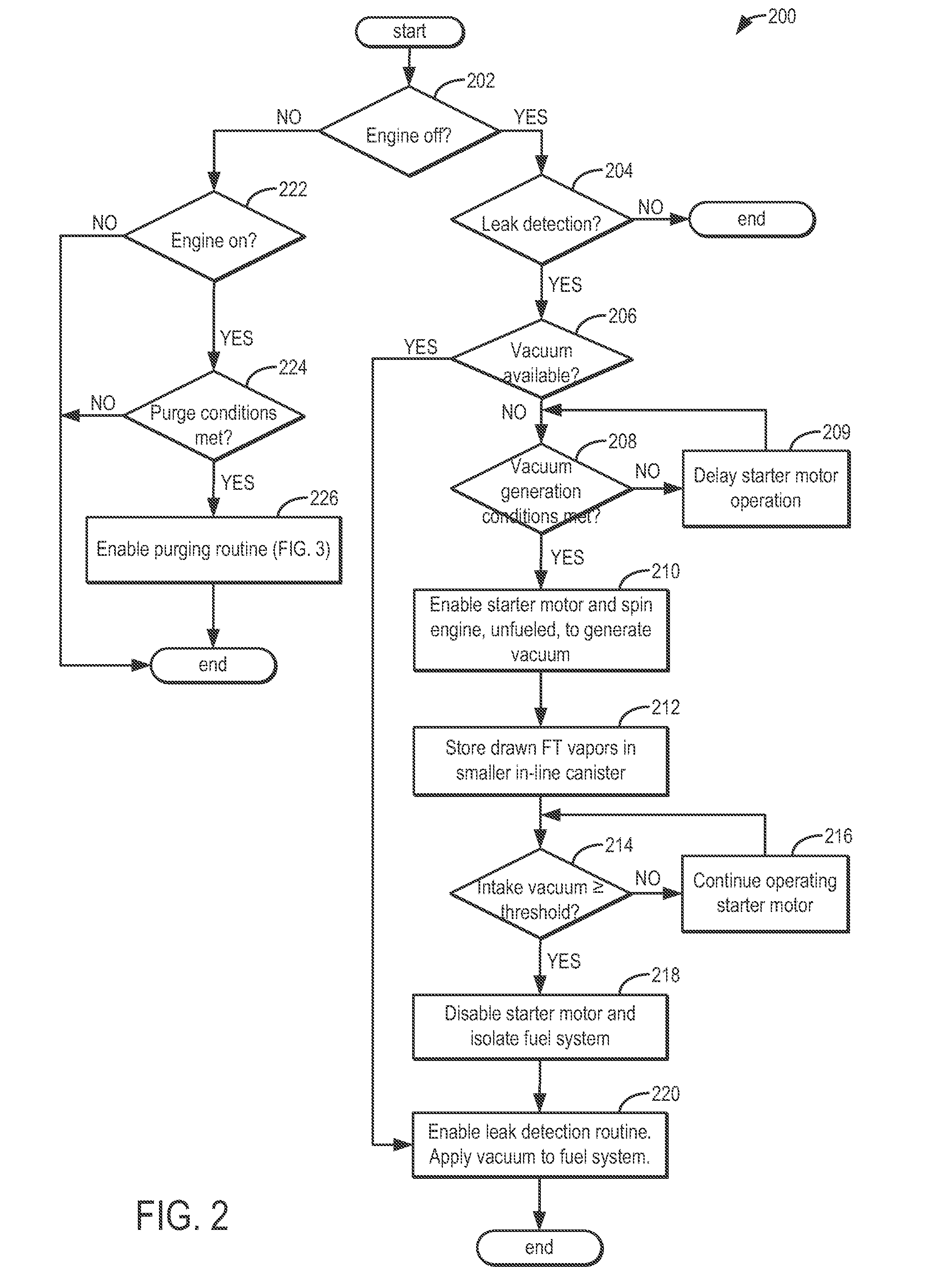
ActiveUS8739766B2Reduce stepsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelElectric motor startersLeak detectionFuel vapor
Methods and systems are provided for operating an engine to generate vacuum for a subsequent leak detection routine. During a selected key-off condition, a starter motor is operated to spin the engine unfueled and generate intake vacuum for the leak detection. Fuel vapors drawn during the spinning are stored in an auxiliary canister that is purged along with a main canister during purging conditions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for fuel vapor control
ActiveUS20110166765A1Reduce carbon emissionsShorten operation timeHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesIsolation valveHybrid vehicle
A method and system for fuel vapor control in a hybrid vehicle (HEV). The HEV fuel vapor recovery system includes a fuel tank isolation valve, which is normally closed to isolate storage of refueling from storage of diurnal vapors. The method for fuel vapor control includes selectively actuating the fuel tank isolation valve during interrelated routines for refueling, fuel vapor purging, and emission system leak detection diagnostics to improve regulation of pressure and vacuum the HEV fuel vapor recovery system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for fuel vapor control
ActiveUS20130032127A1Reduced engine operation timeInsufficient vacuumNon-fuel substance addition to fuelElectric motor startersLeak detectionFuel vapor
Methods and systems are provided for operating an engine to generate vacuum for a subsequent leak detection routine. During a selected key-off condition, a starter motor is operated to spin the engine unfueled and generate intake vacuum for the leak detection. Fuel vapors drawn during the spinning are stored in an auxiliary canister that is purged along with a main canister during purging conditions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and System for Fuel Vapor Control
ActiveUS20110265768A1Shorten operation timeEnable fuel economyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelMachines/enginesIsolation valveEngineering
Methods and systems are provided for operating a fuel vapor recovery system having a fuel tank isolation valve coupled between a fuel tank and a canister. Fuel vapors are purged from the fuel tank to a canister buffer over a plurality of purge pulses. The pulses are adjusted based on the buffer capacity, a purge flow rate, and a fuel tank pressure to improve control of canister loading and reduce air-to-fuel ratio disturbances.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com