Patents
Literature
384 results about "Vapor recovery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
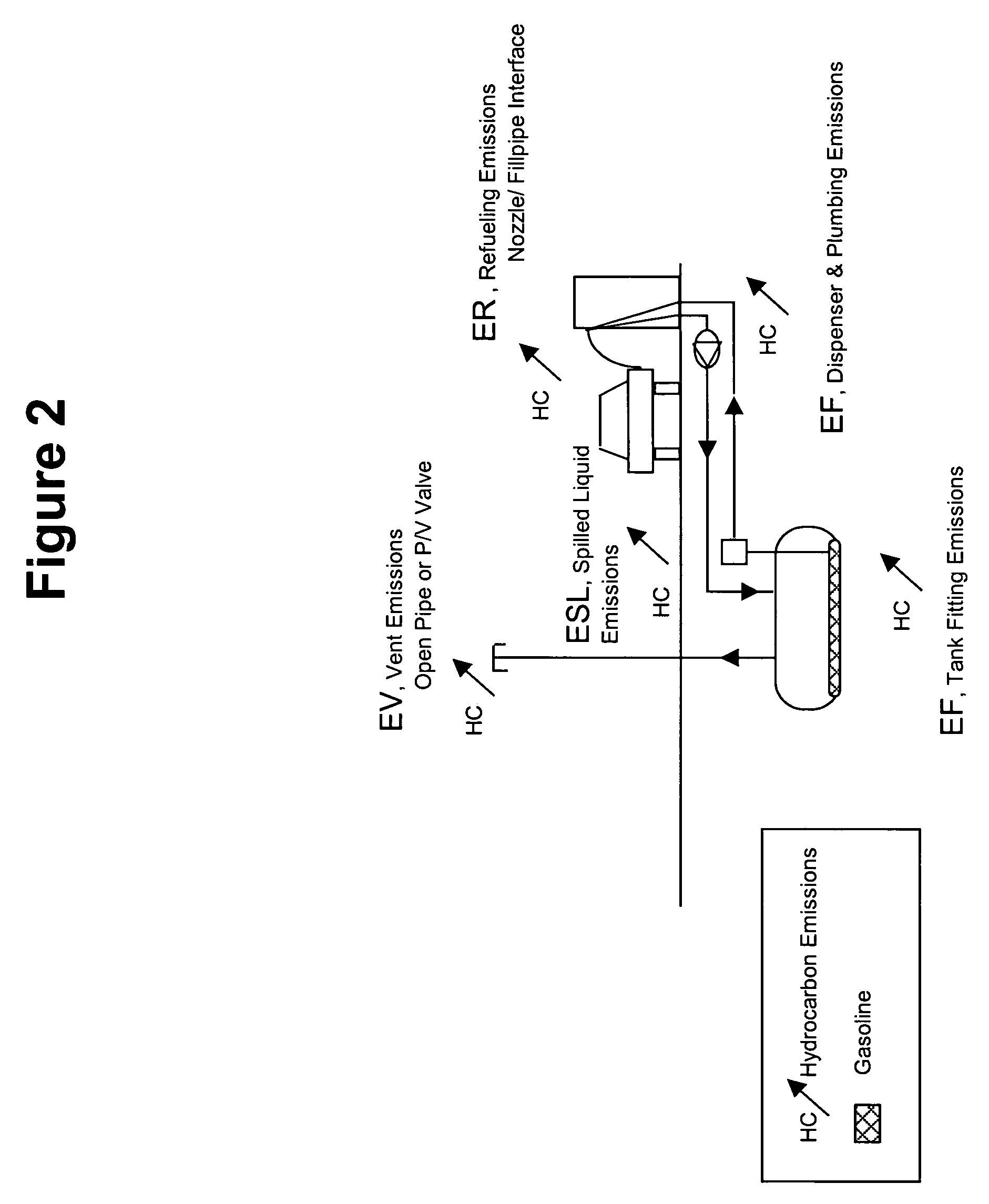
Vapor (or vapour) recovery is the process of recovering the vapors of gasoline or other fuels, so that they do not escape into the atmosphere. This is often done (or required by law) at filling stations, in order to reduce noxious and potentially explosive fumes and pollution.
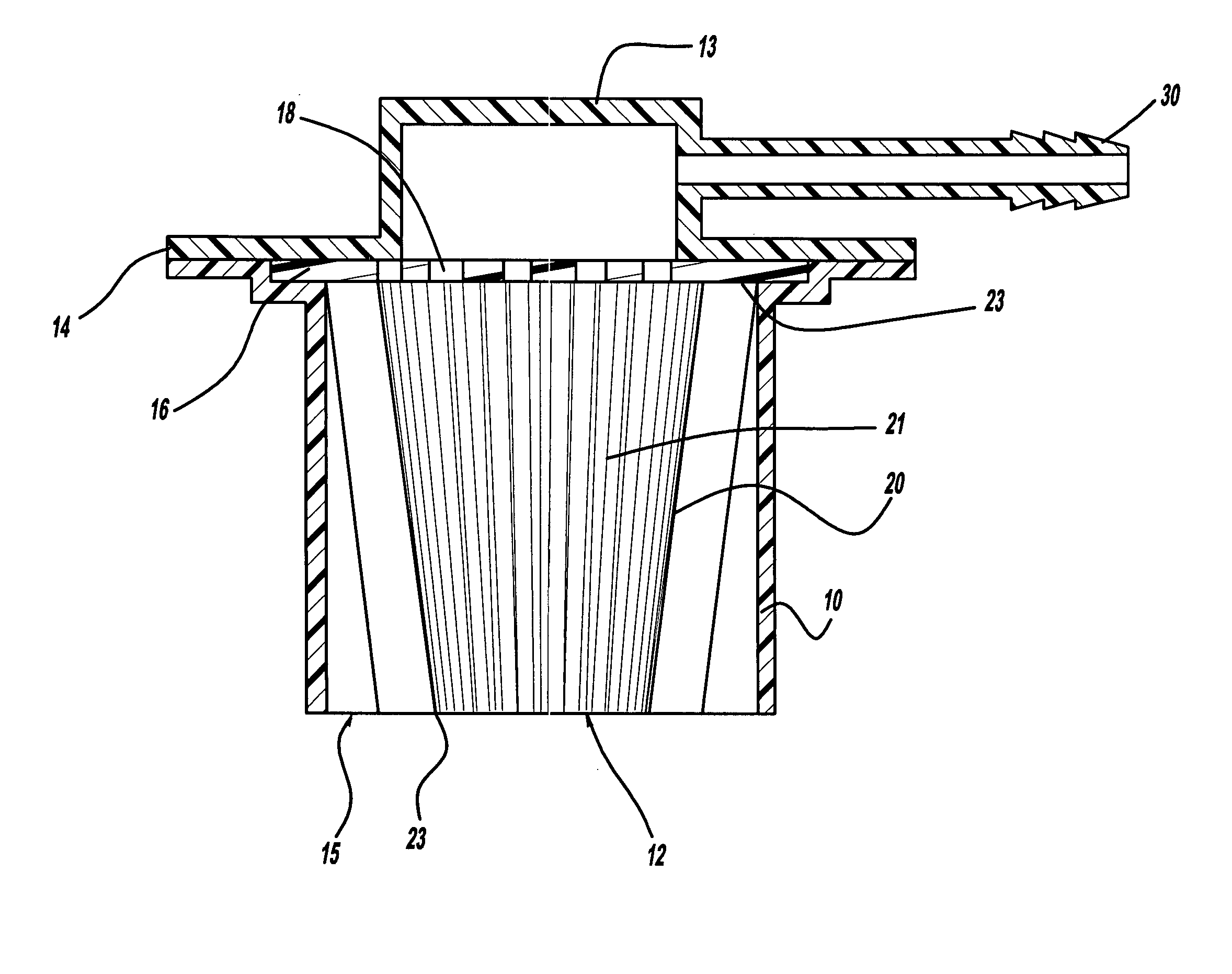
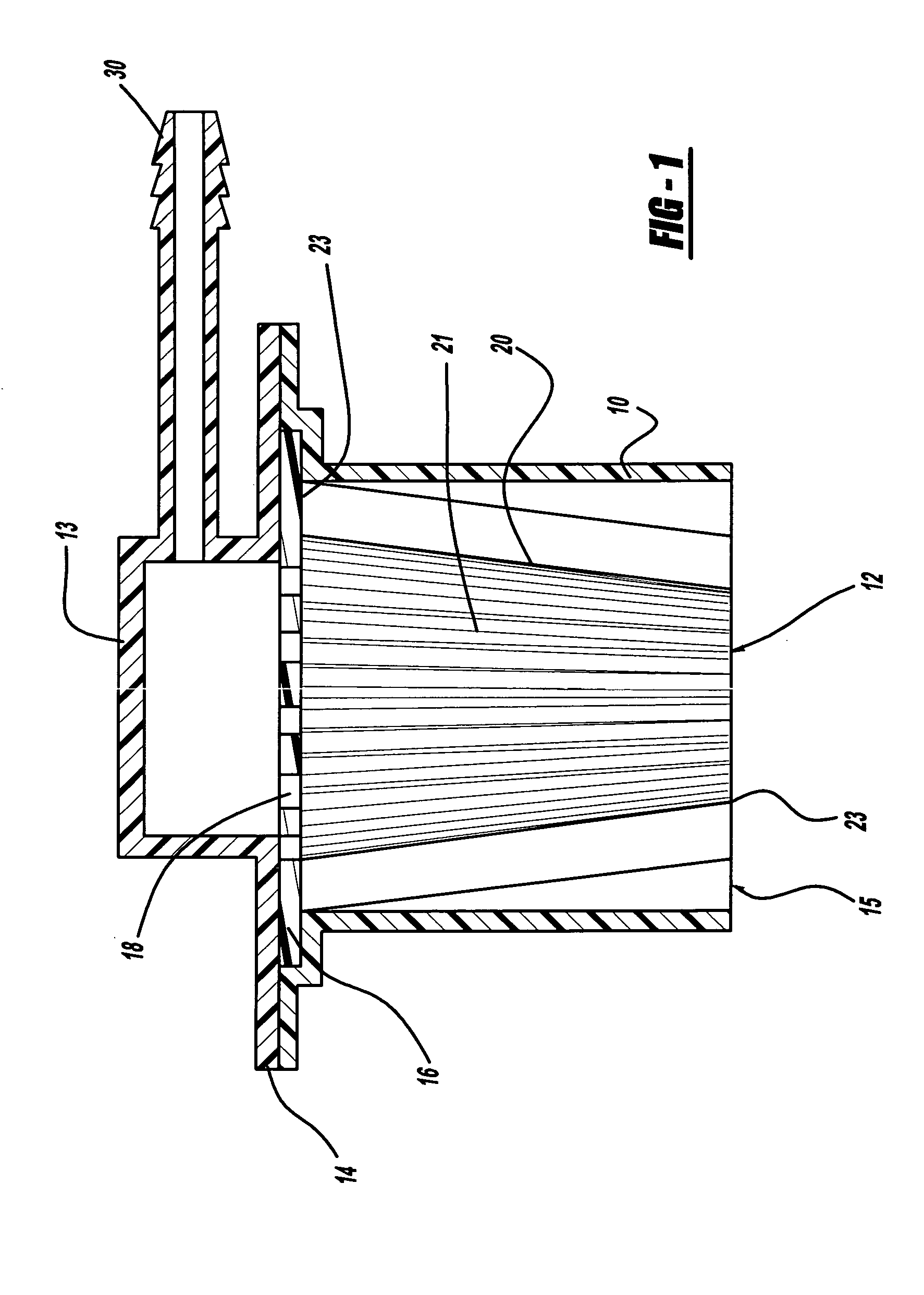
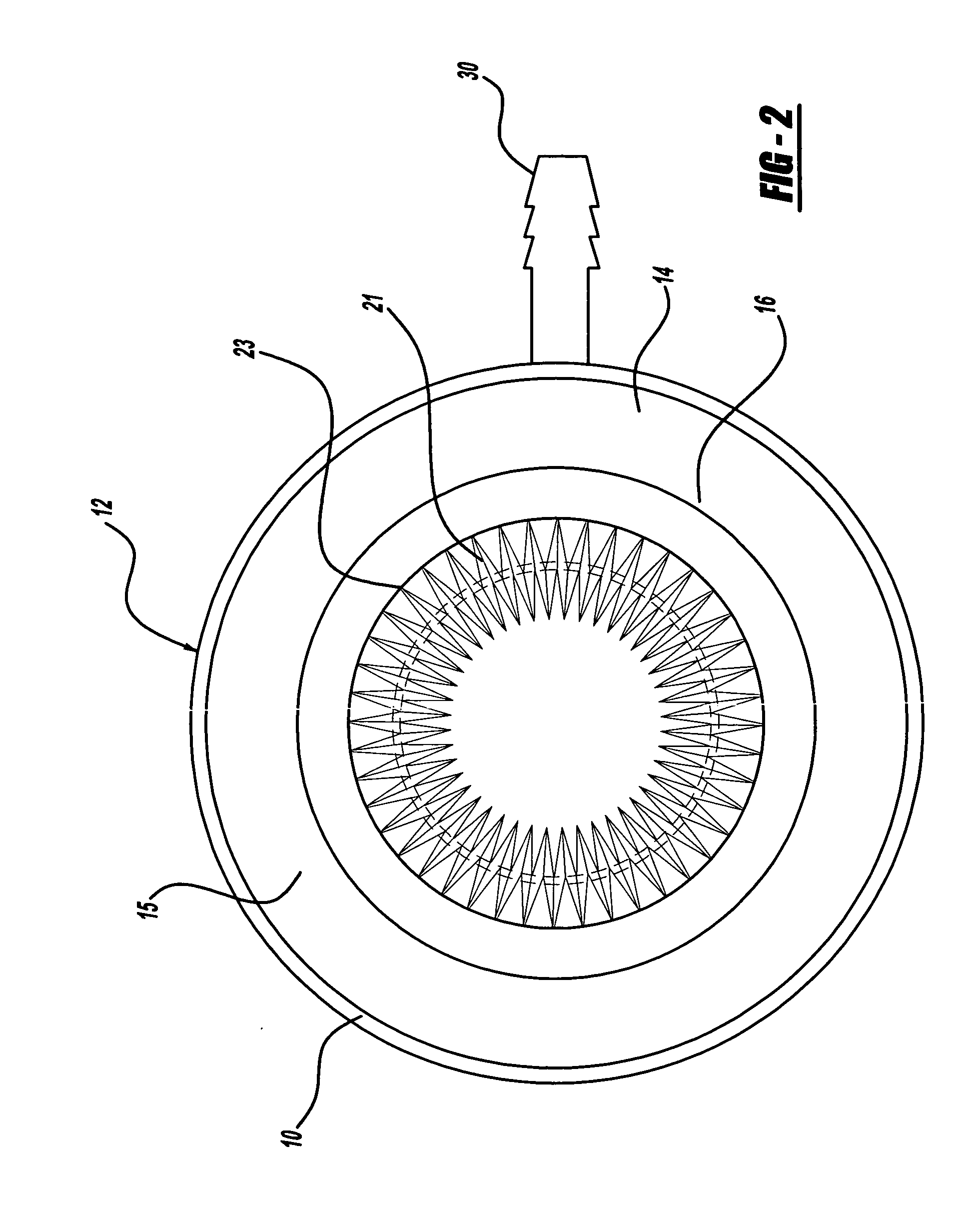
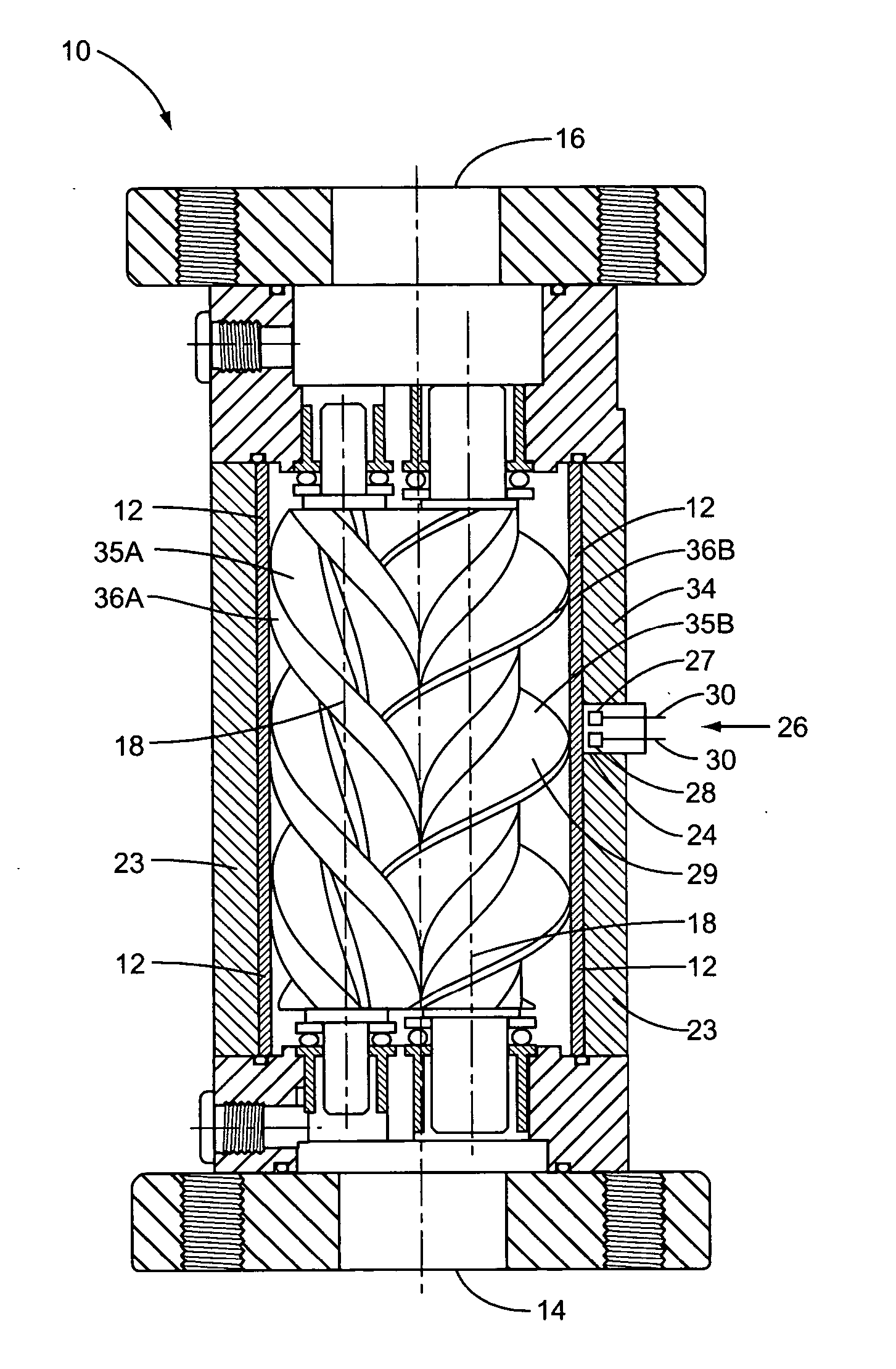
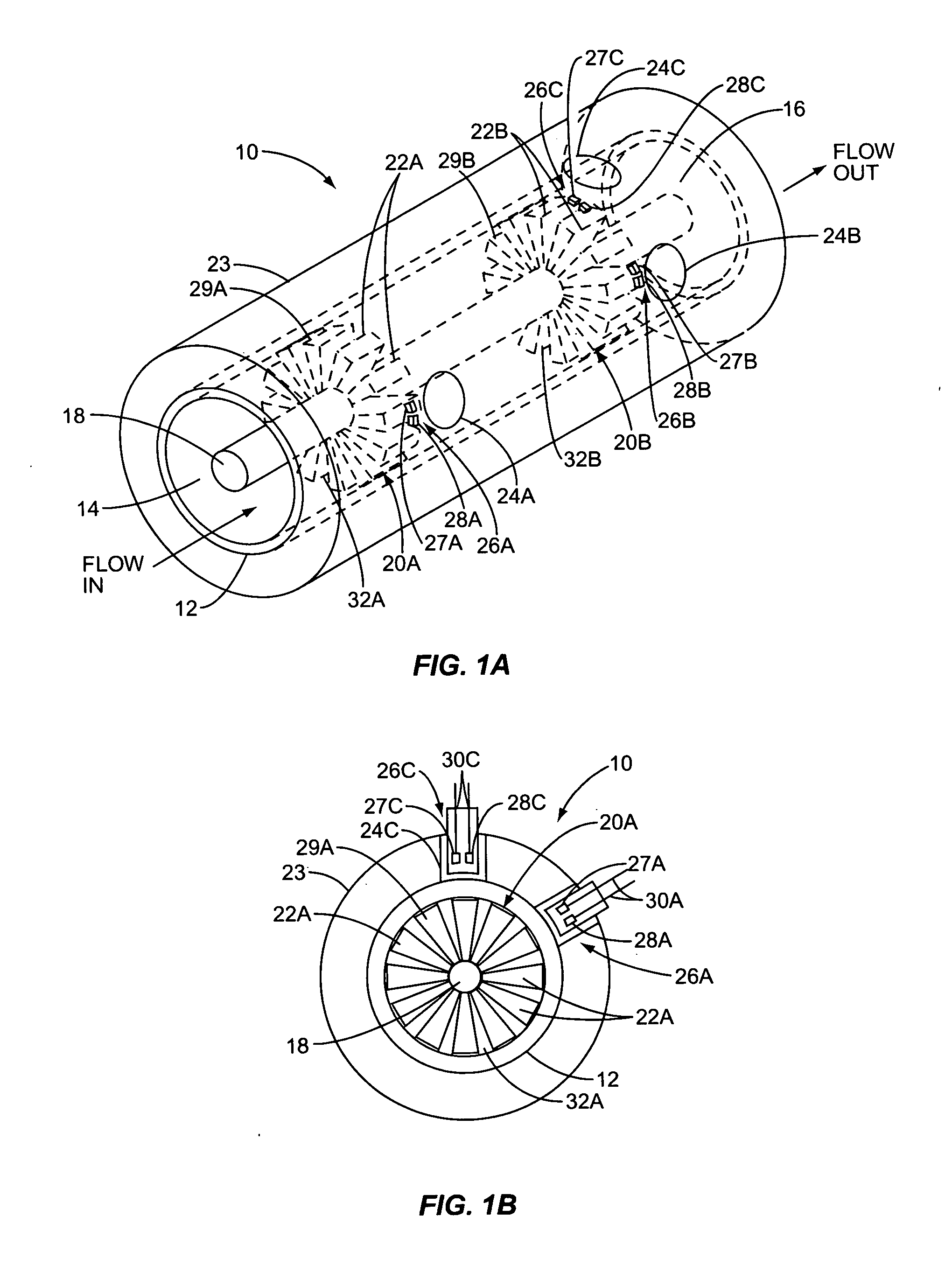
Apparatus for drying solutions containing macromolecules
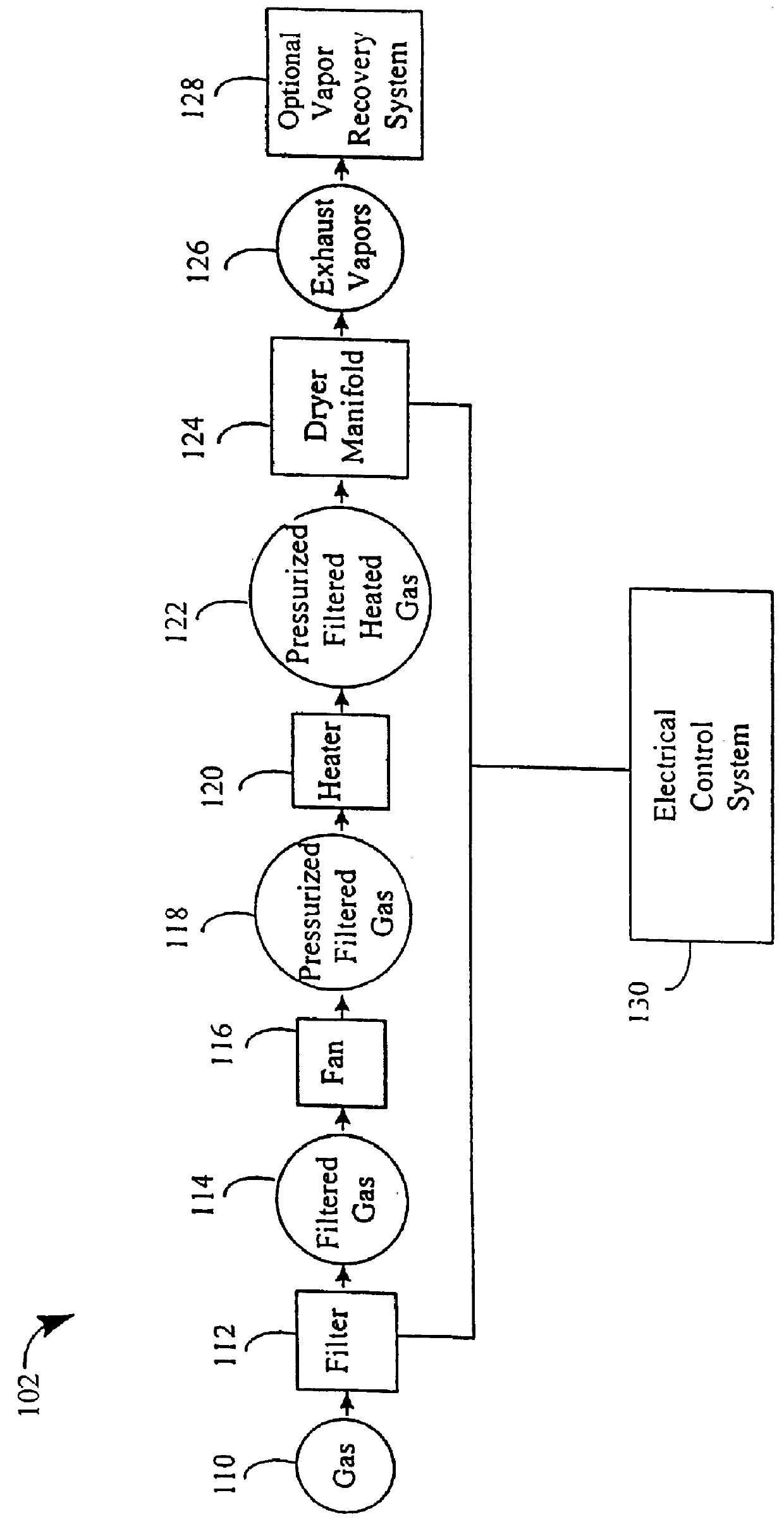
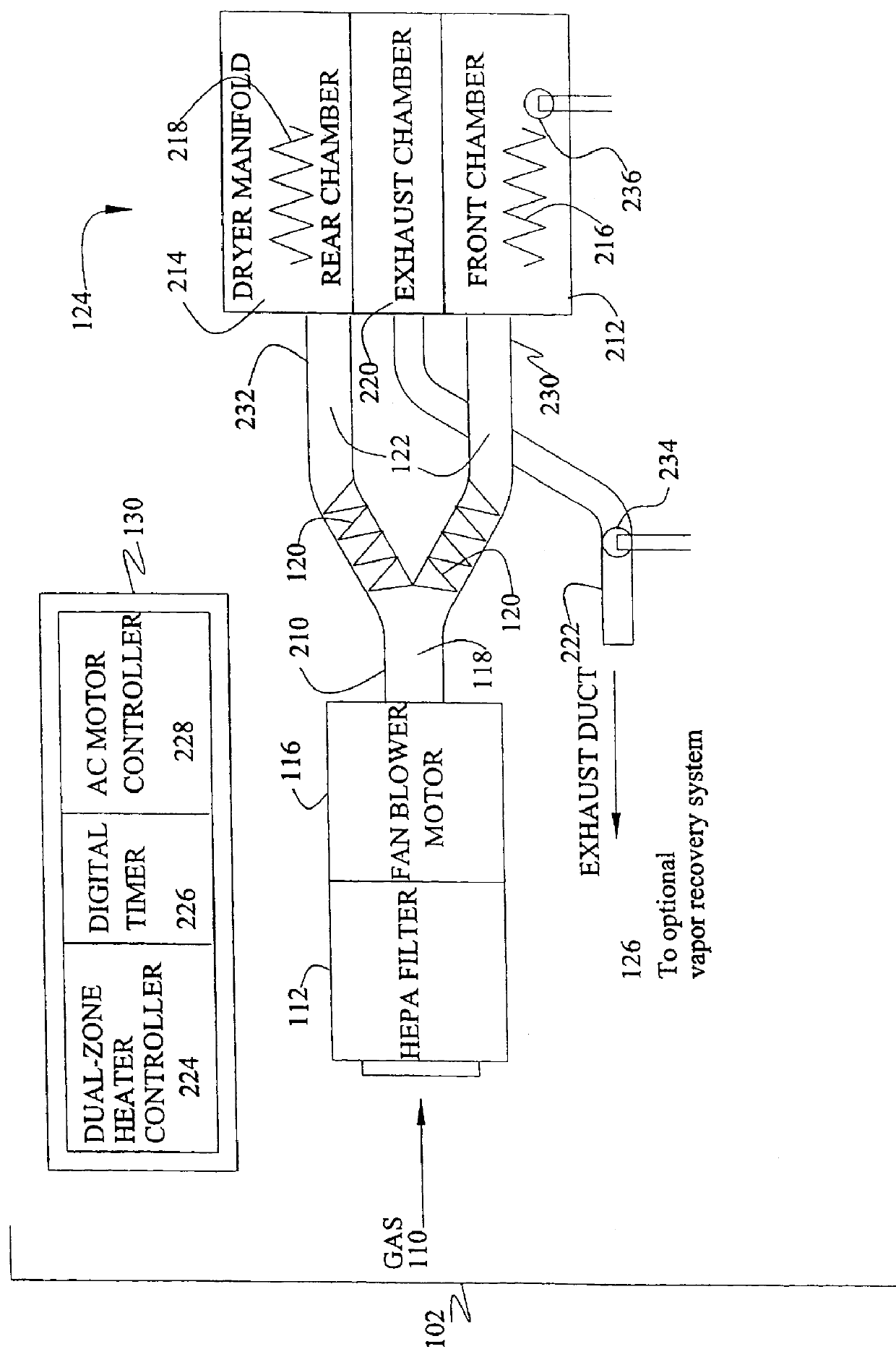
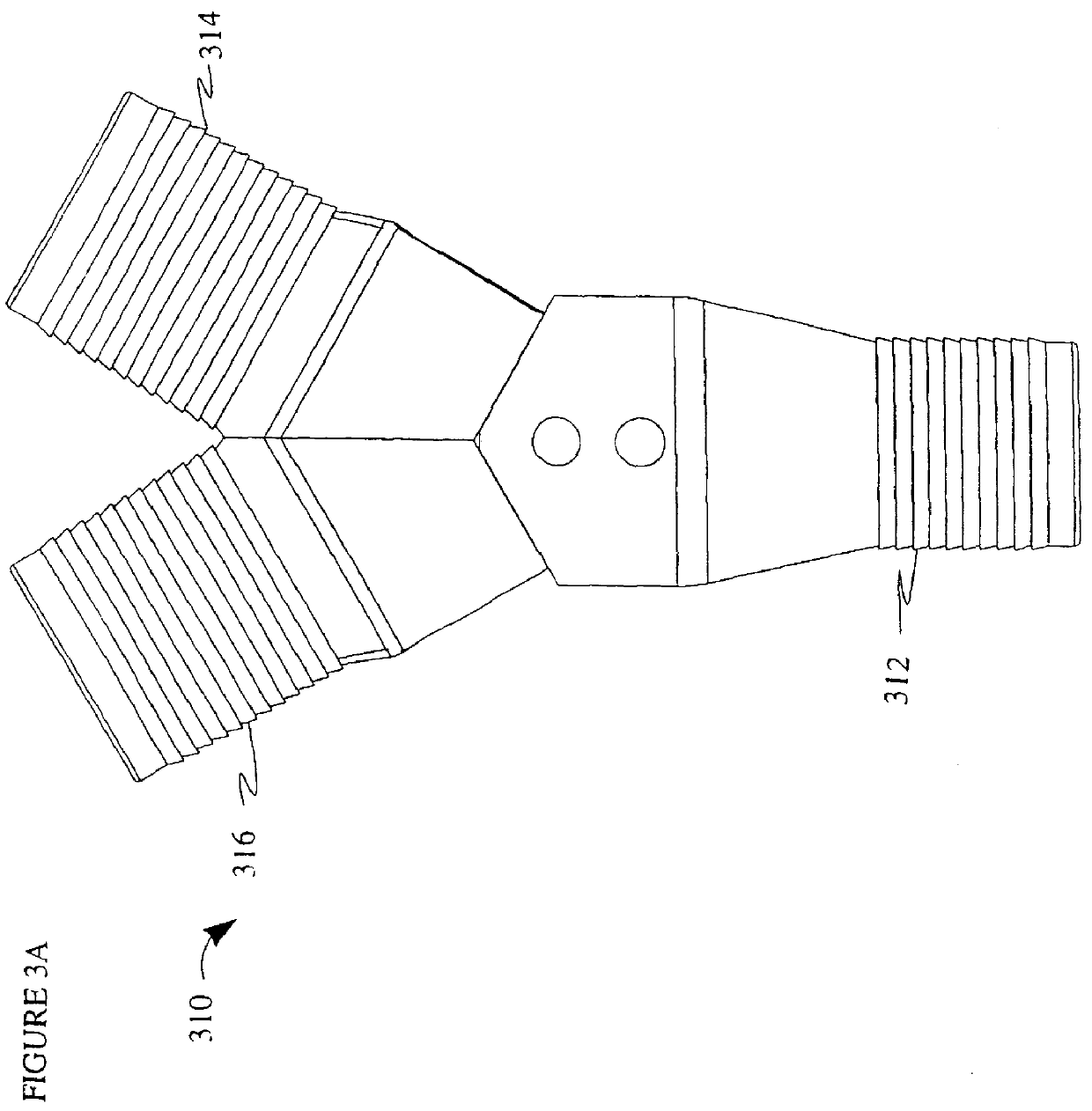
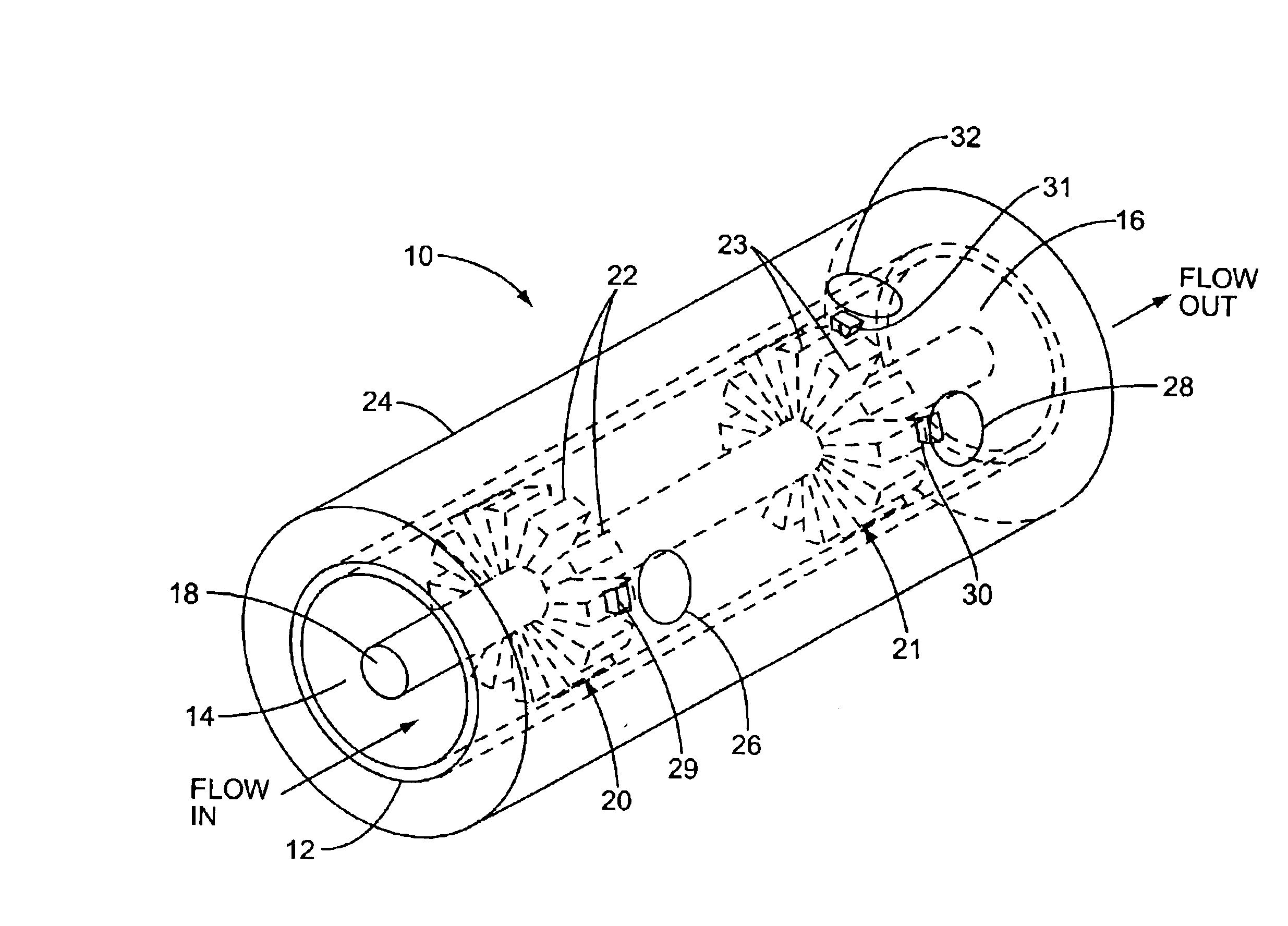
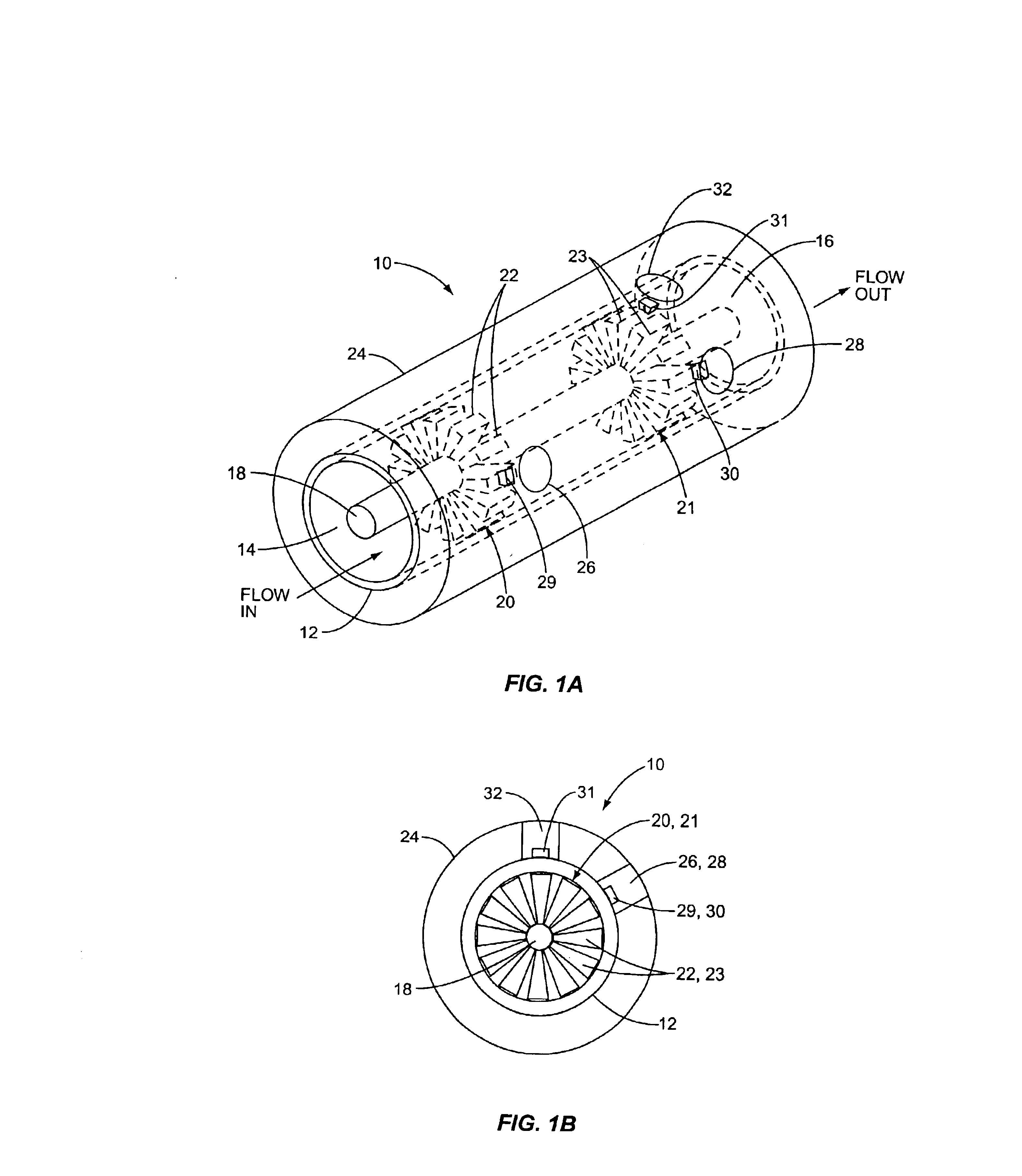
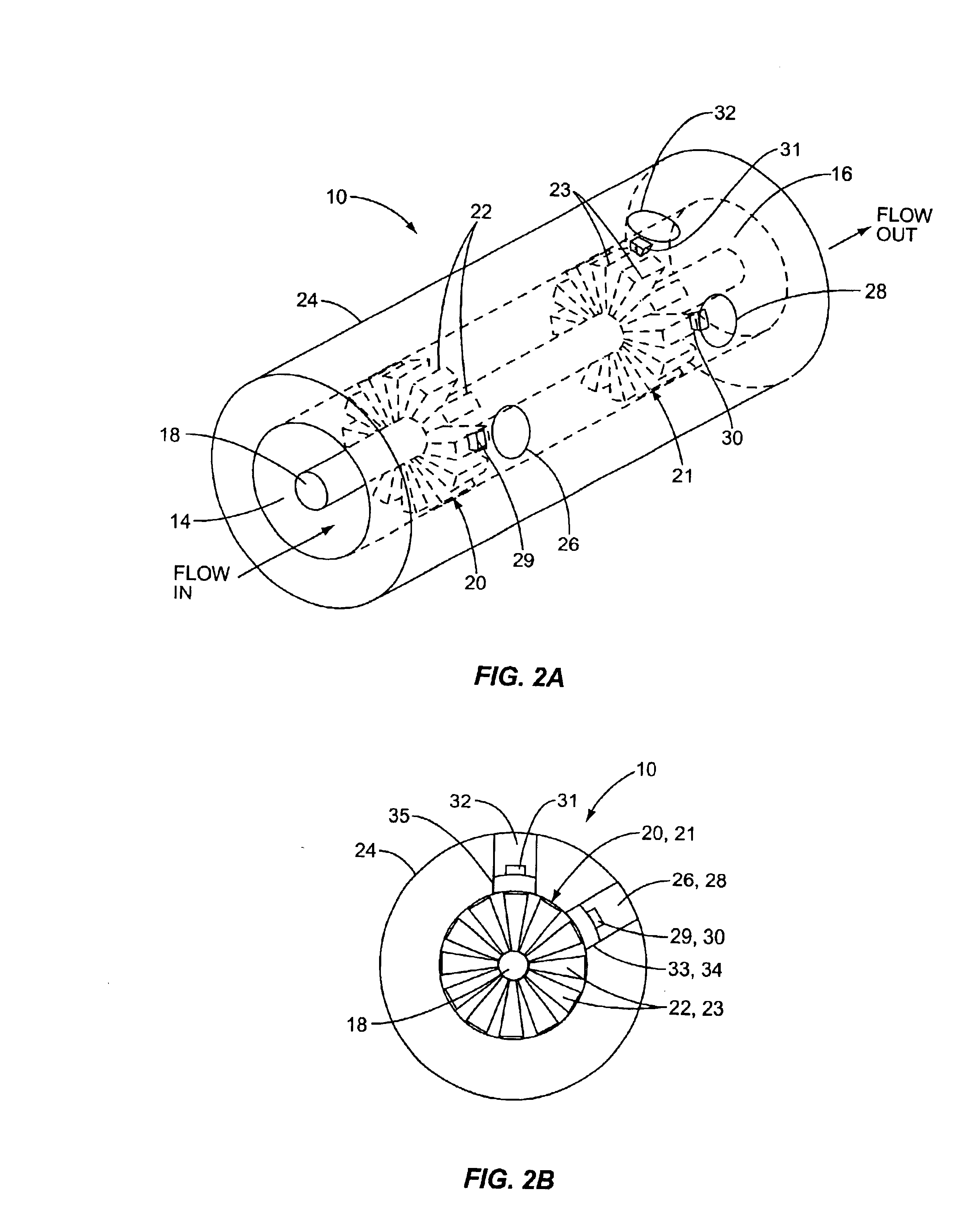
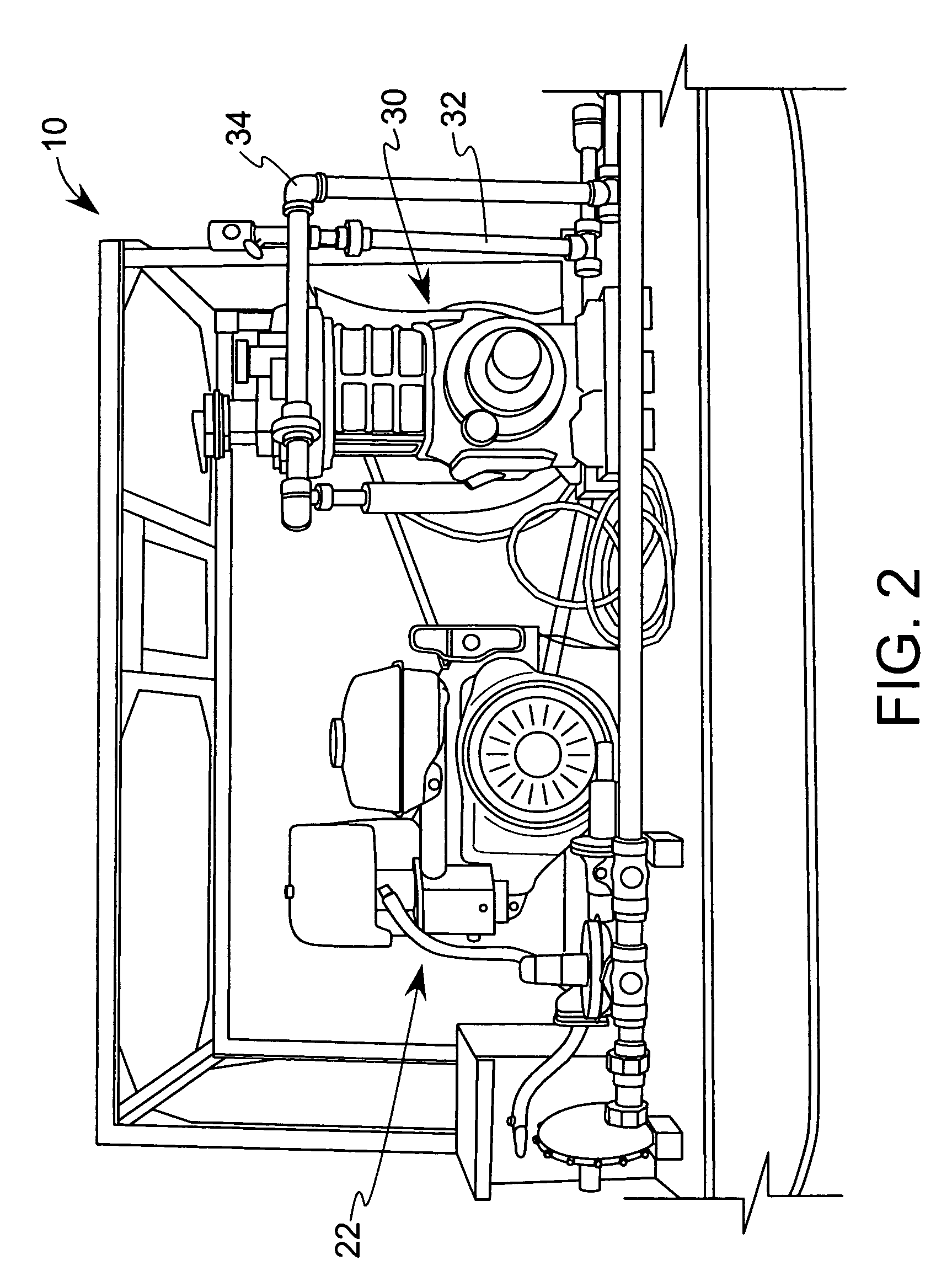
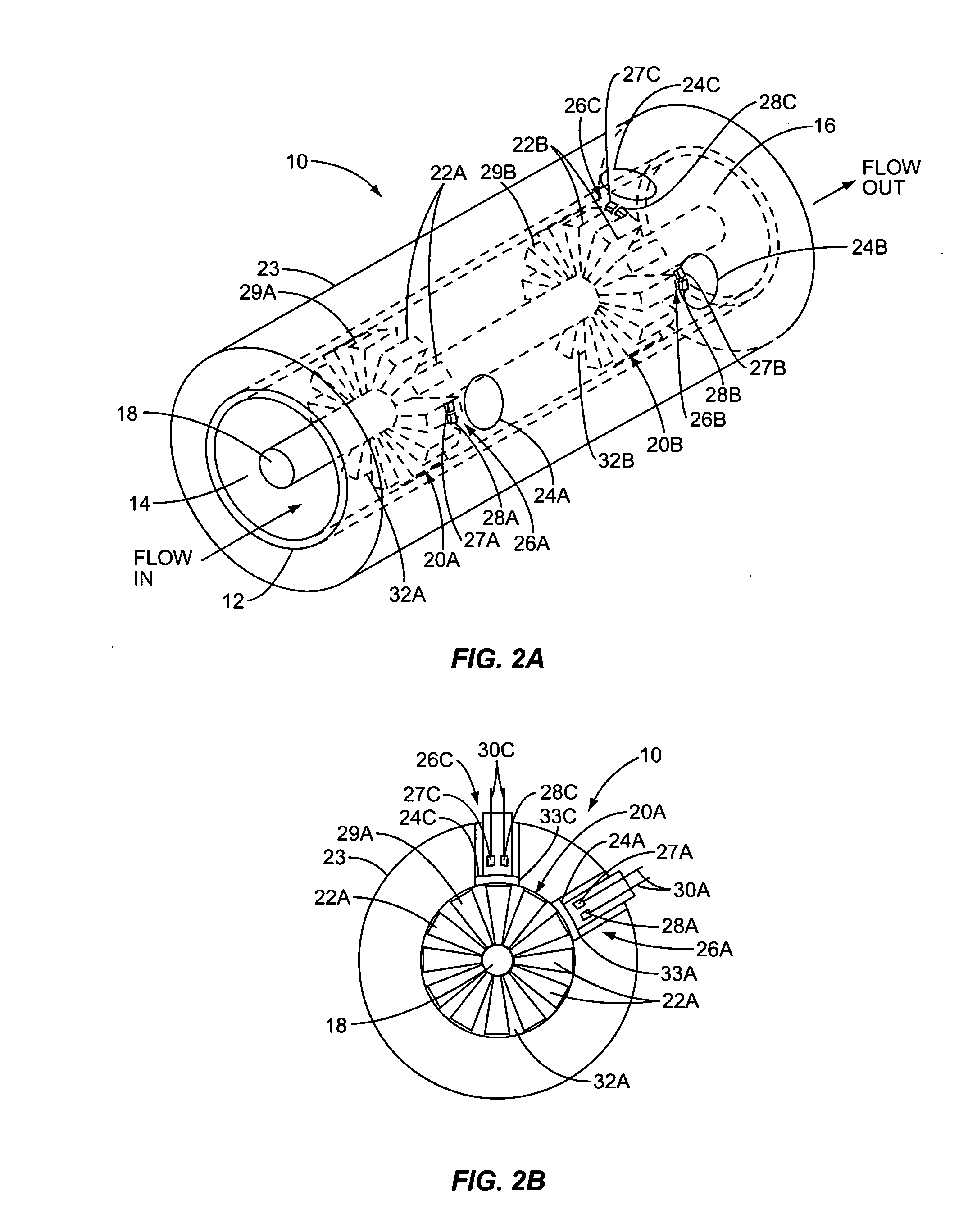
An apparatus and method for quickly drying solutions in one or more arrays of vessels includes a manifold that receives gas and a base plate that receives the one or more arrays of vessels. The manifold includes one or more hollow tubes that direct the gas into the vessels, where the gas evaporates the solutions. A variety of types of hollow tubes are disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment, the gas is filtered, pressurized and / or heated. In an exemplary embodiment, the solutions are heated. The base plate is hingeably coupled to the manifold so that the base plate has an open position and a closed position. The open position permits users to place and remove the vessels that contain solutions to be dried. In the closed position, the base plate and the manifold are in sealing engagement with one another, wherein the one or more of the hollow tubes extend into the vessels. A unique hinging system is disclosed that couples one or more base plates to a base so that, when the base plate is in the open position, the base plate is substantially horizontal. When the base plate is in the closed position, it is tilted at an angle so that the vessels are tilted at the angle, providing the solutions to be dried with a greater surface area. A variety of optional vapor recovery systems are disclosed. A variety of open loop and closed loop electrical control systems are disclosed.
Owner:INVITROGEN
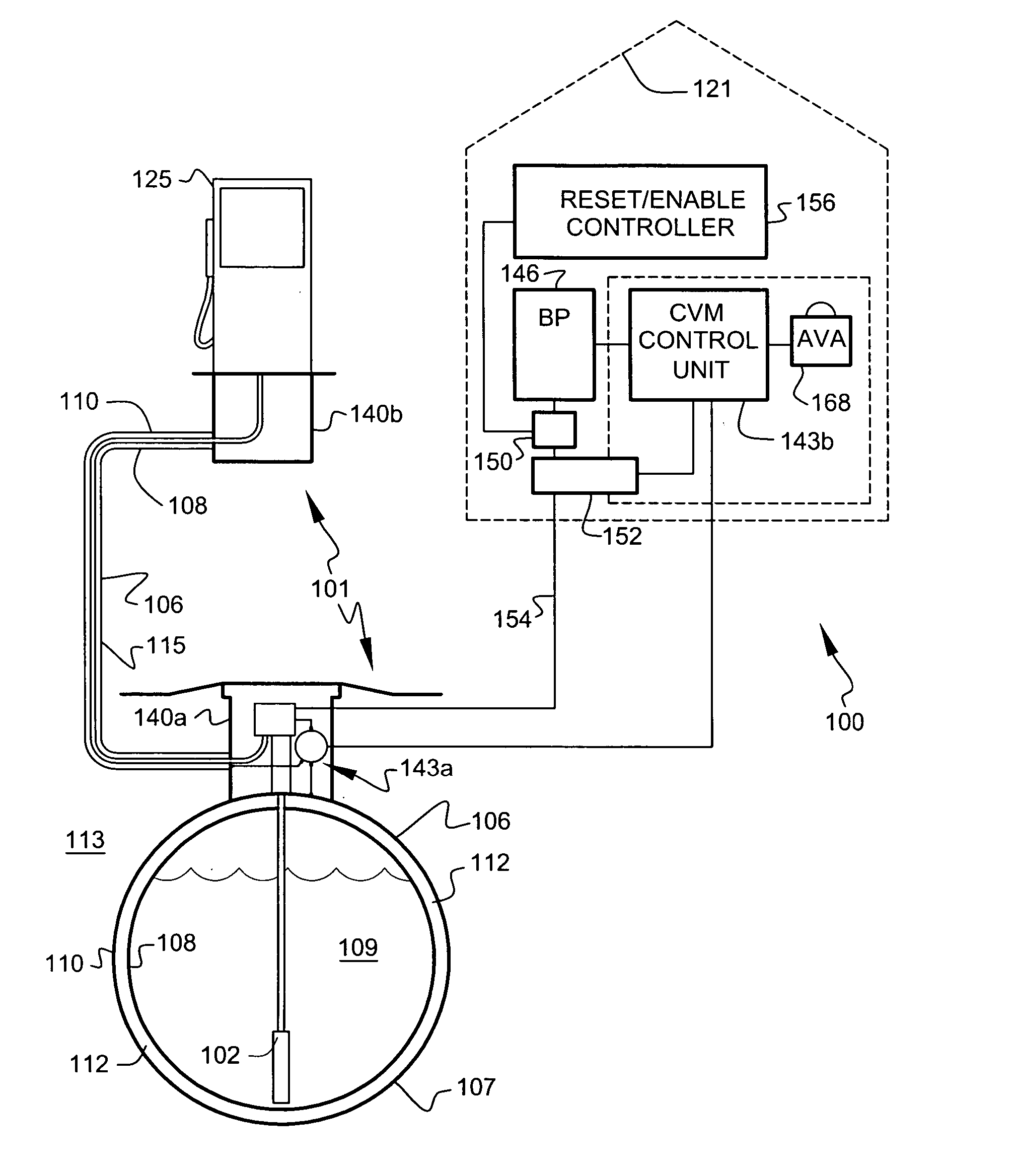
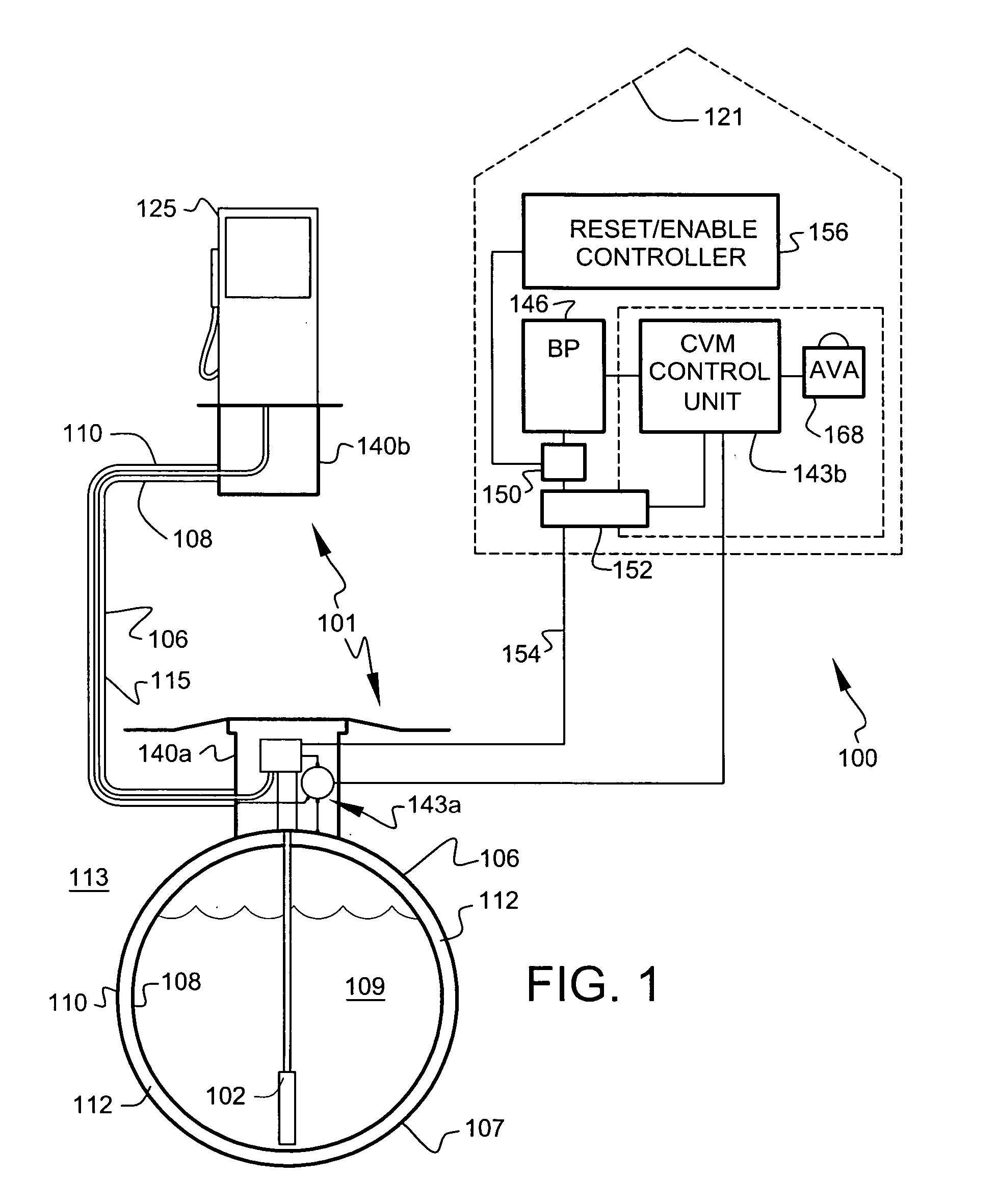
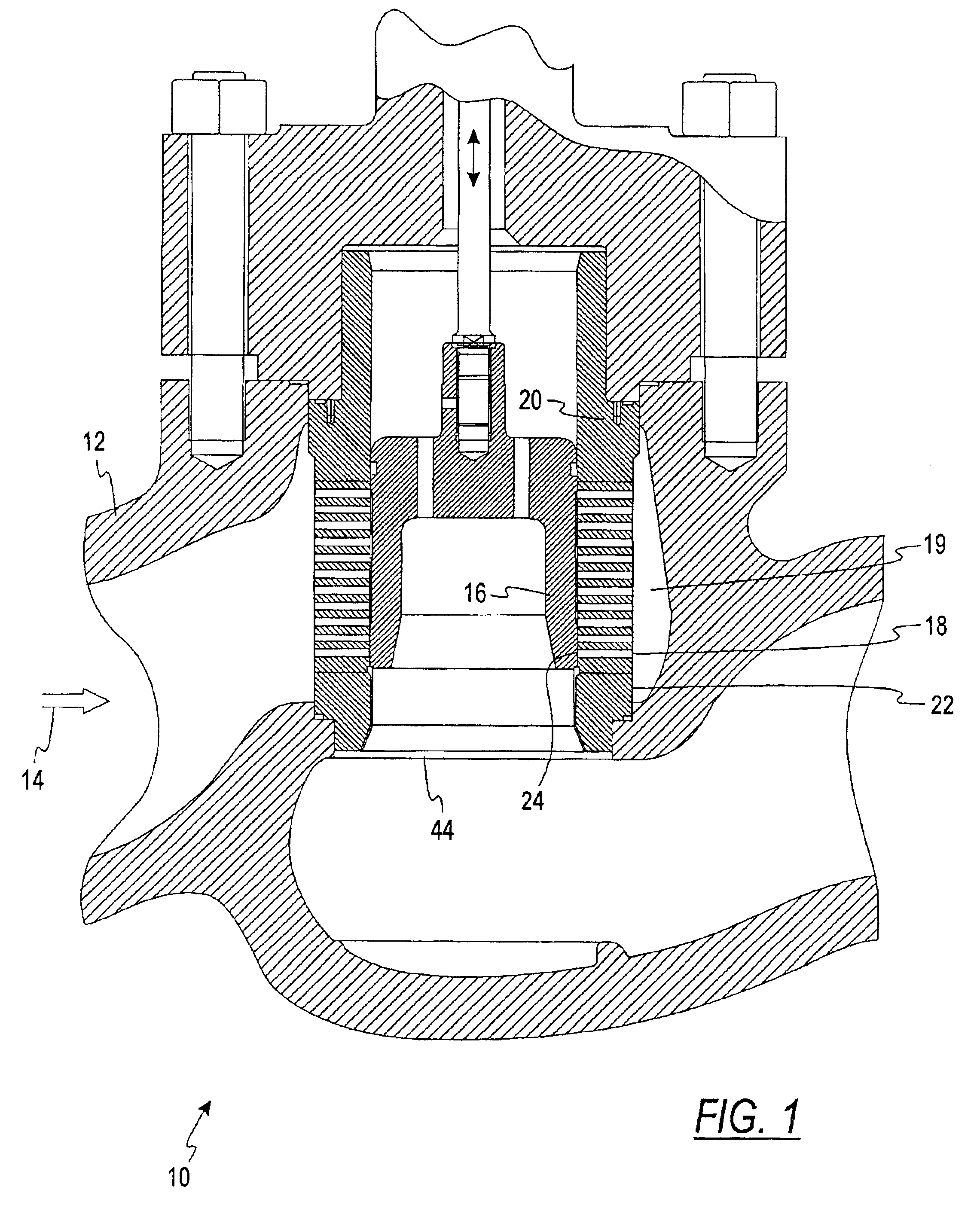
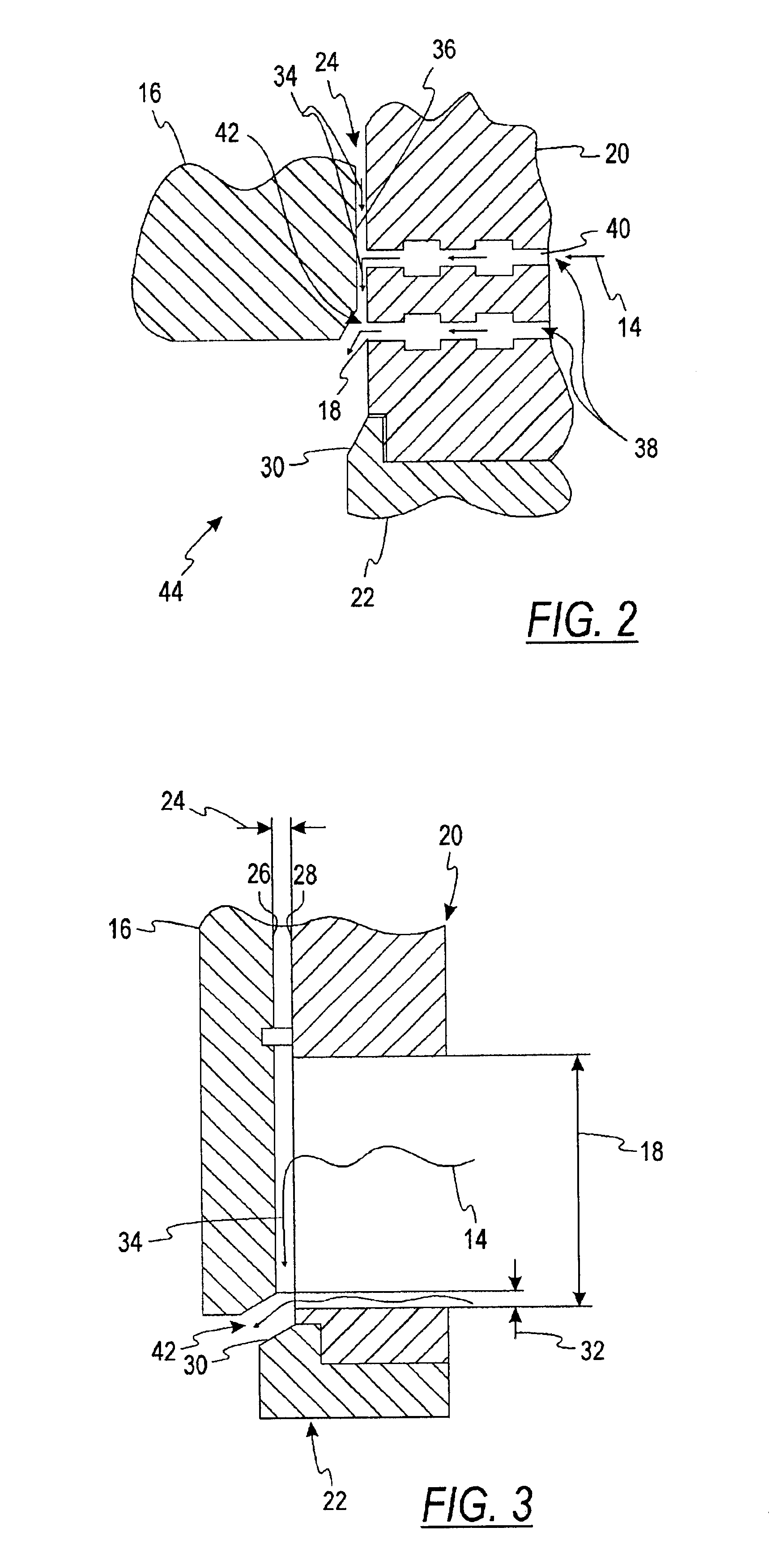
Secondary containment monitoring system
A leak detection and prevention system adapted to continuously monitor the spaces of a double wall hydrocarbon fuel handling system comprising storage tanks, product lines, vapor recovery lines, tank vent lines, etc. The system establishes and monitors a resident gas-pressure within the interstitial space to monitor the integrity of the primary and secondary containment. Change in resident gas-pressure in excess of a calibrated vacuum flow rate or the presence of liquid in any monitored space initiates an alarm. Once an alarm is signaled, the product delivery system is shut down and an audio-visual alarm is activated in close proximity to operating personnel. An onsite service call by qualified personnel is required to return the product handling system back into service. A qualified service technician connects to a communication port on the system control module to evaluate the cause of the failure. The system utilizes vacuum pressure to monitor for containment breaches. Furthermore, the system utilizes a Bernoulli-based device to produce the monitoring vacuum.
Owner:OPW FUEL MANAGEMENT SYST A DIV OF DOVER RESOURCES
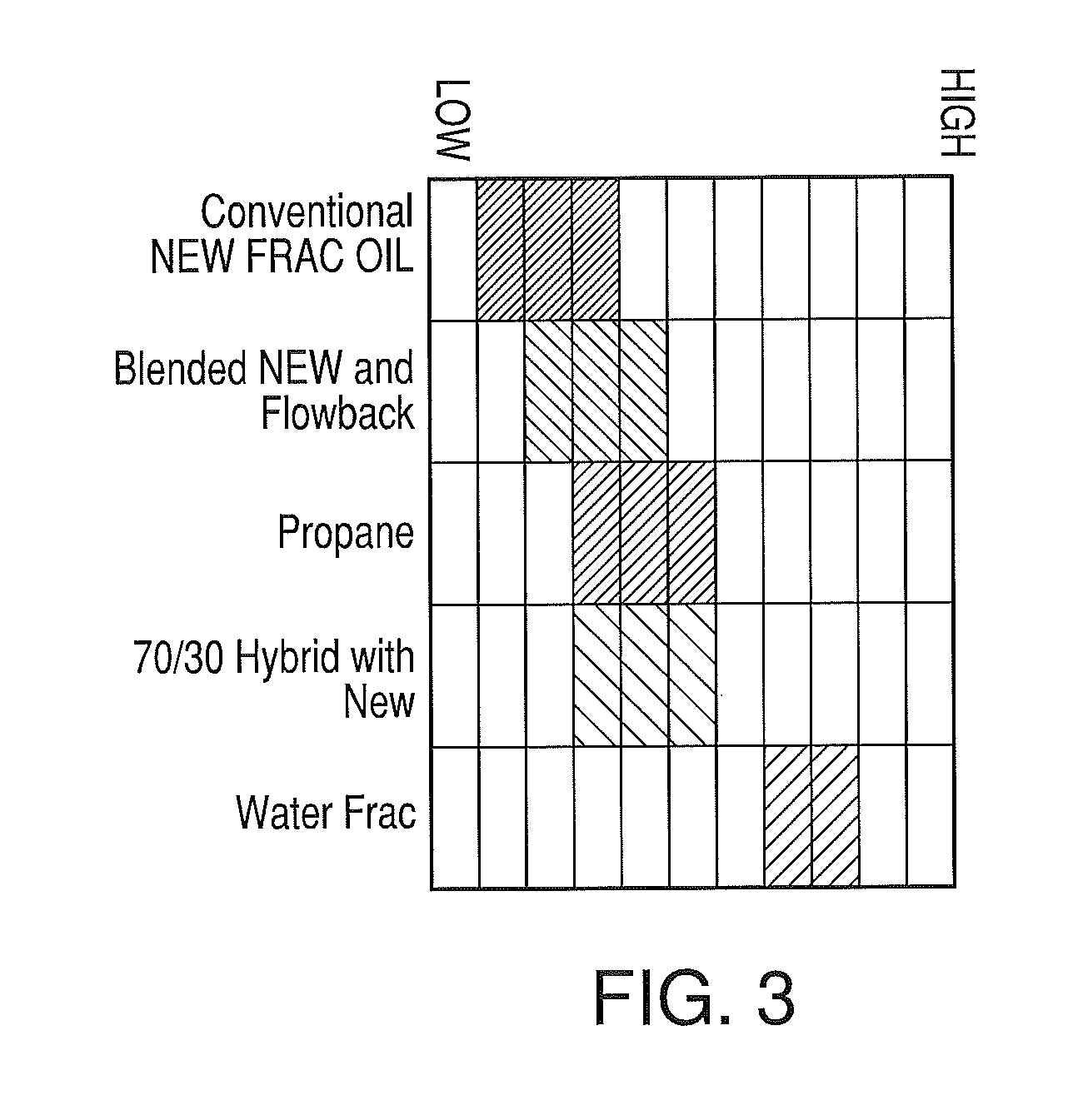
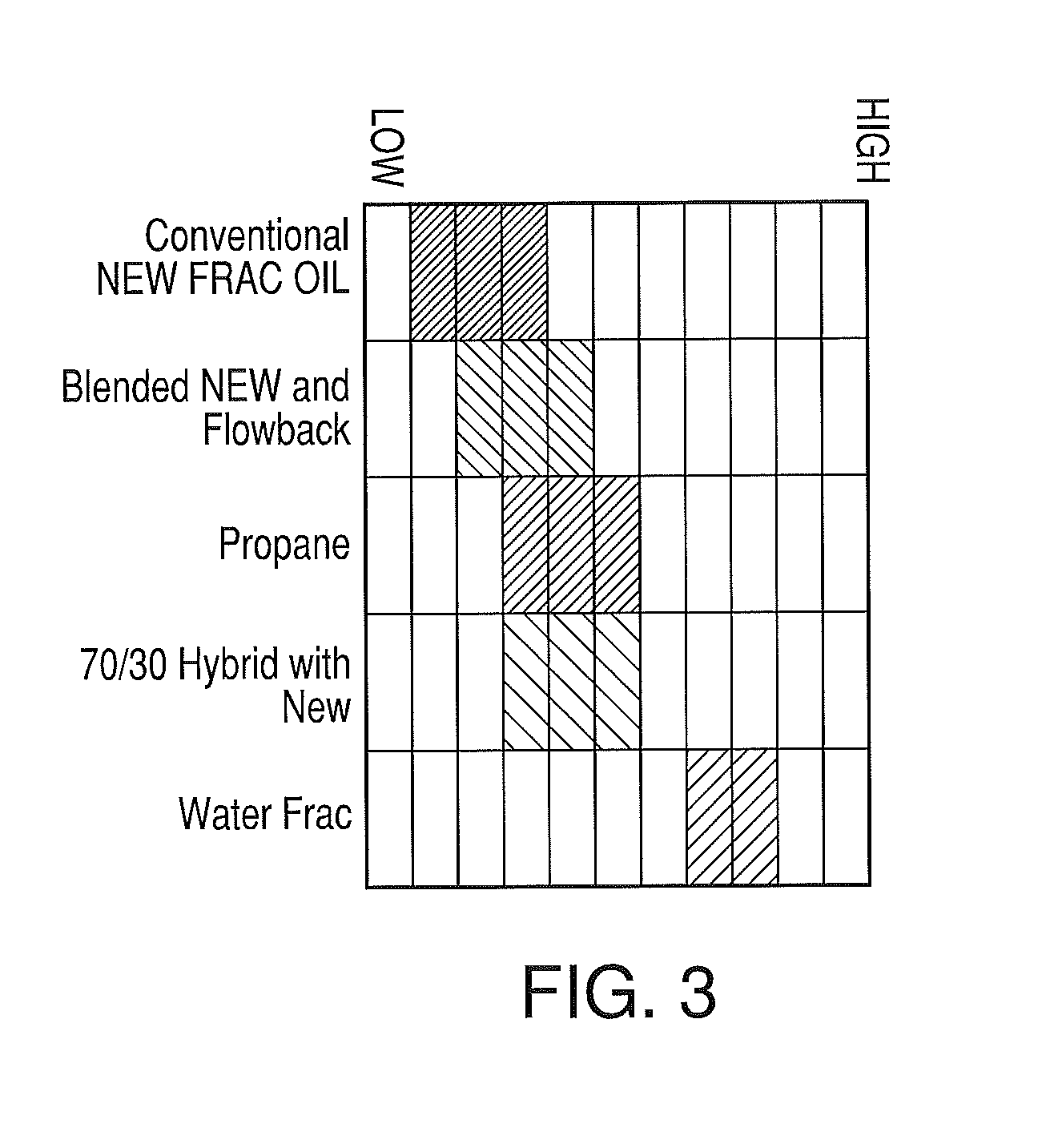
Environmentally sealed system for fracturing subterranean formations
An environmentally sealed system for fracturing subterranean systems including a fracturing fluid source, a proppant source, a proppant hopper comprising a variable proppant regulator, a blender comprising a blender inlet and a blender outlet, a high pressure pump comprising a high pressure pump inlet and a high pressure pump outlet, and a well head; wherein the fracturing fluid source is connected to the blender inlet through a fracturing fluid supply connection and a fracturing vapor recovery connection, the proppant source is connected with the proppant hopper through a proppant supply connection and a proppant vapor recovery connection, the proppant hopper is connected to the blender inlet through a proppant transfer connection, the blender outlet is connected to the high pressure pump inlet, and the high pressure pump is outlet connected to the well head.
Owner:TUDOR ROBIN
Increased sensitivity for turbine flow meter
InactiveUS6854342B2Low costThe material is lowVolume/mass flow by mechanical effectsSignal onEngineering
A lower cost turbine flow meter comprised of an inner housing constructed out of a high permeable material surrounded by an outer housing constructed out of a lower cost, lower permeable material. A port is placed in the outer housing that runs down to the surface of the inner housing to detect the rotation of turbine rotors that rotate inside the meter as fluid or gas flows through the meter. A pickoff coil is placed in the port to generate a magnetic signal to penetrate through the inner housing wherein the turbine rotor vanes superimpose a pulse signal on the magnetic signal. The lower cost turbine flow meter can be used for any application for measuring fluid or gas, and may be used in a service station environment for measuring fuel or vapor in vapor recovery applications.
Owner:GILBARCO
Increased sensitivity for liquid meter
A lower cost meter comprised of an inner housing constructed out of a high permeable material surrounded by an outer housing constructed out of a lower cost, lower permeable material. A port is placed in the outer housing that runs down to the surface of the inner housing to detect the rotation of a rotational component that rotates inside the meter as fluid or gas flows through the meter. A sensor is placed in the port to detect rotation of the rotational component through the lower permeable material inner housing. The lower cost meter can be used for any application for measuring fluid or gas, and may be used in a service station environment for measuring fuel or vapor in vapor recovery applications.
Owner:GILBARCO
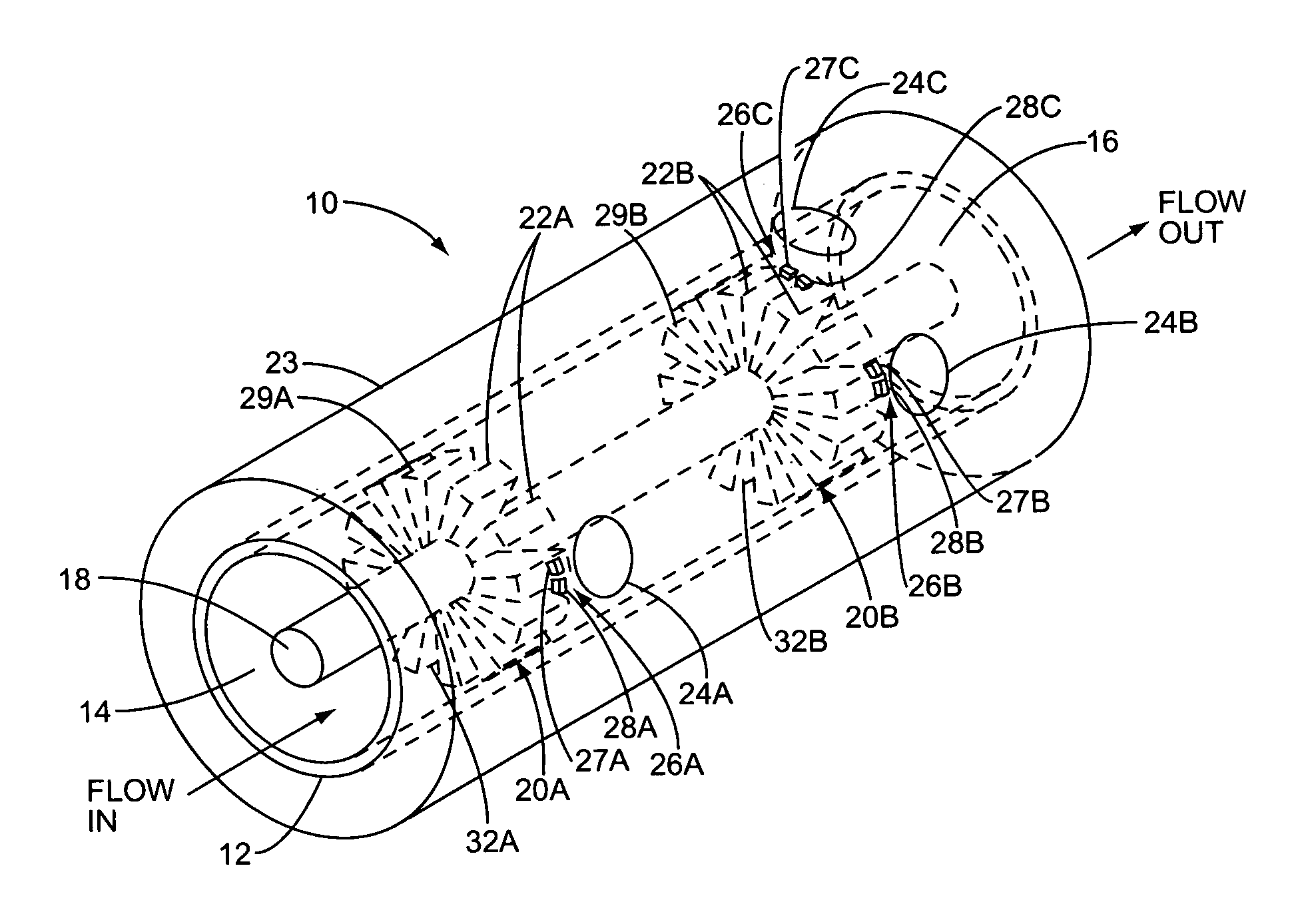
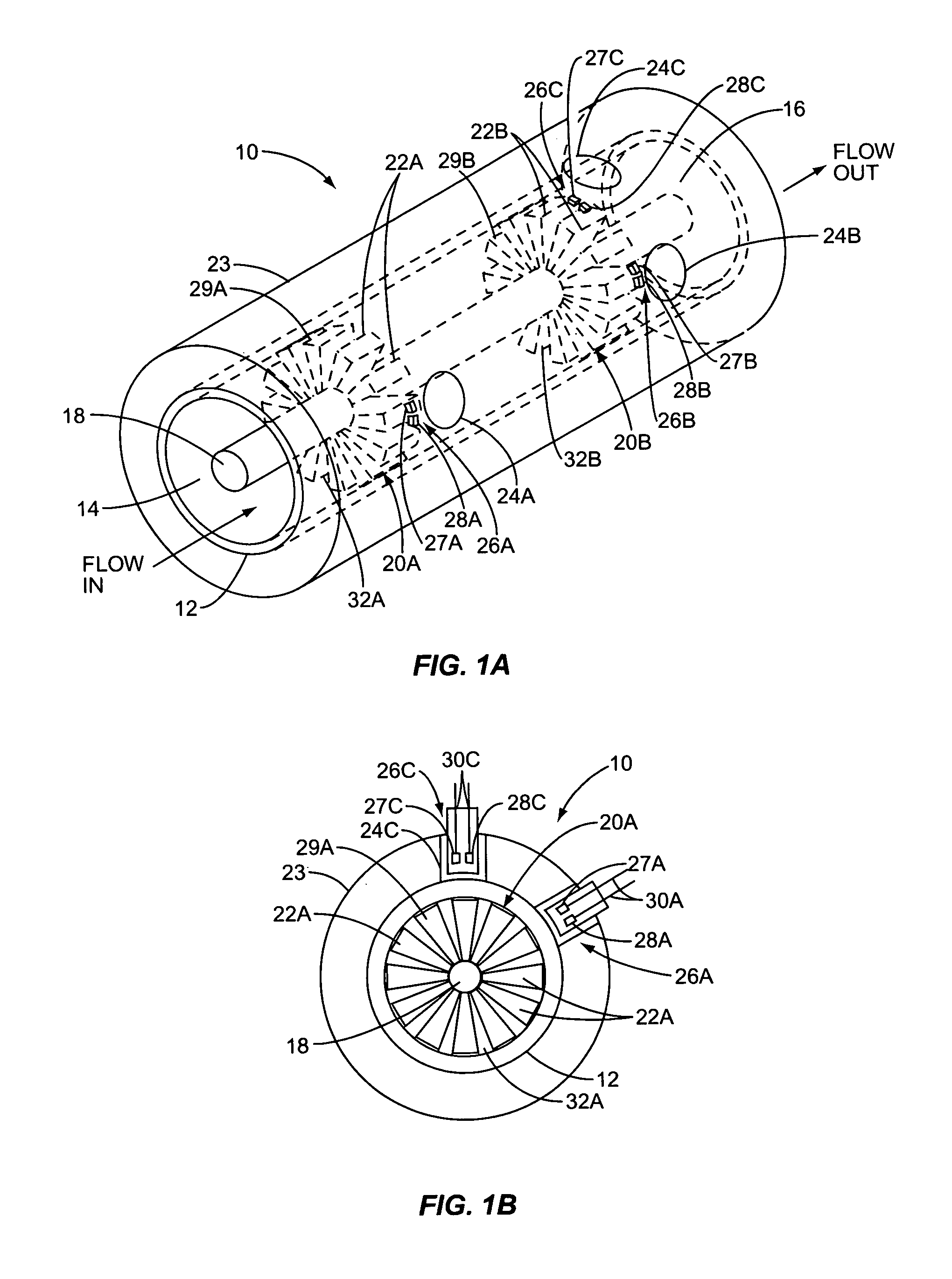
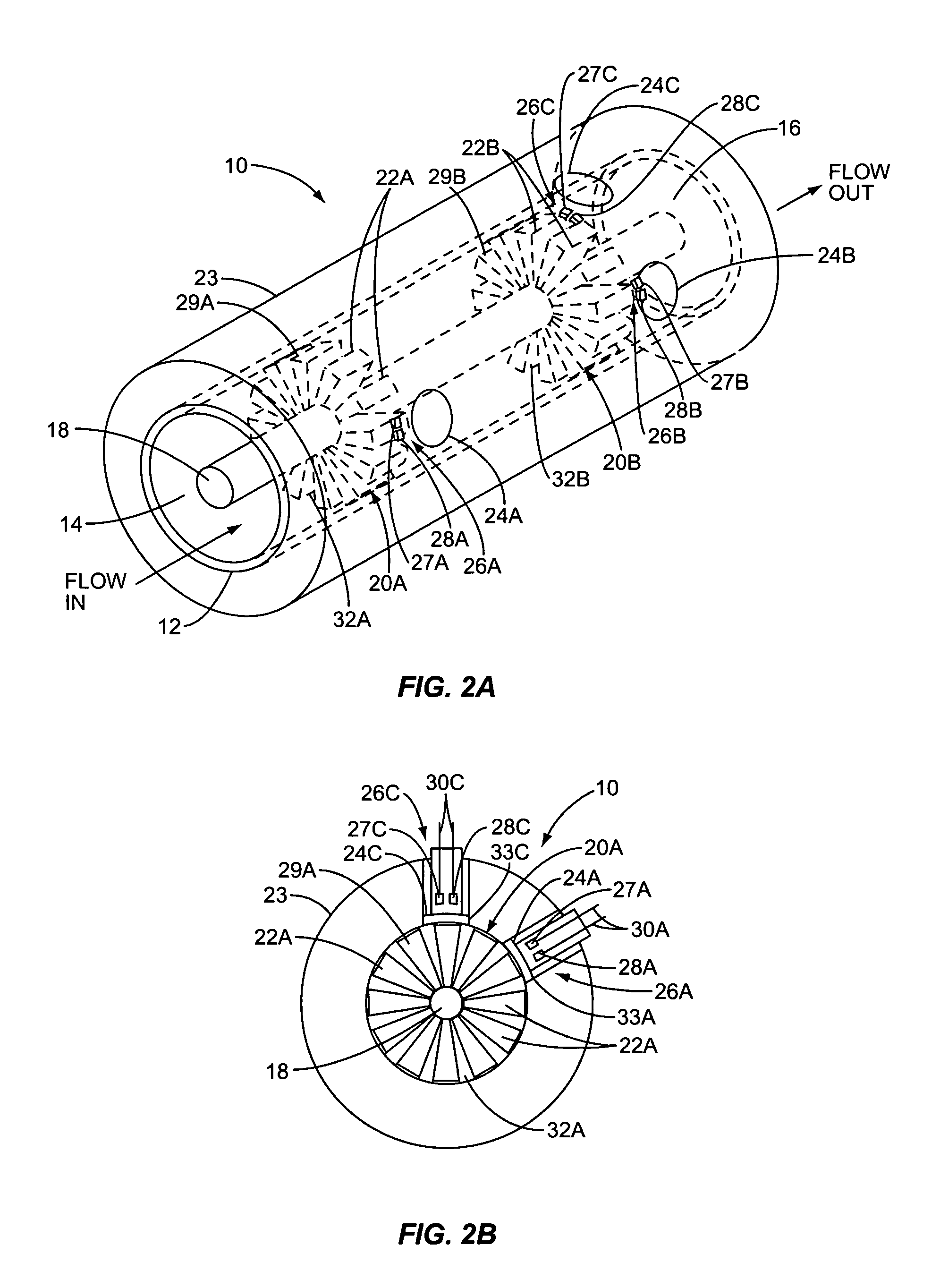
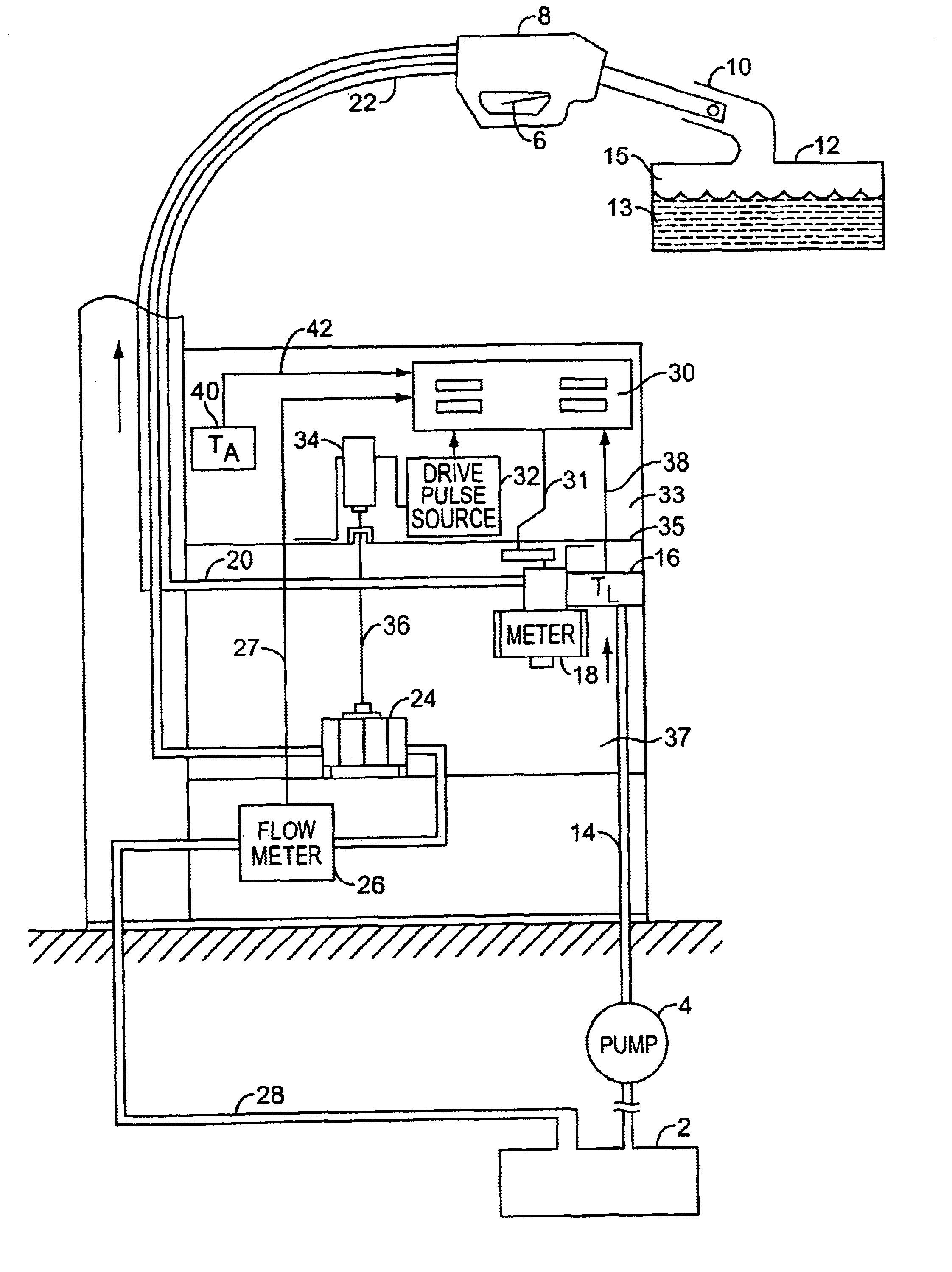
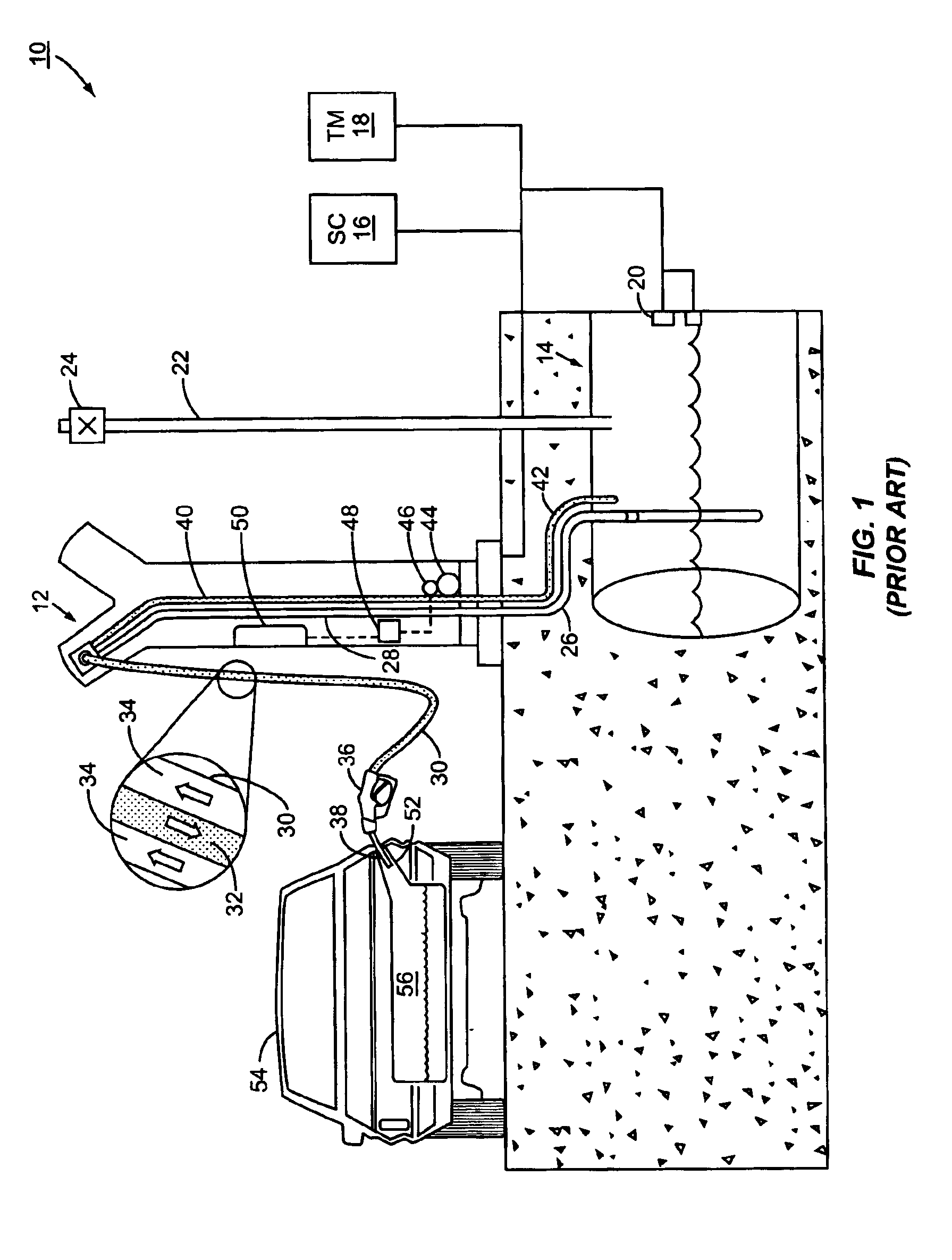
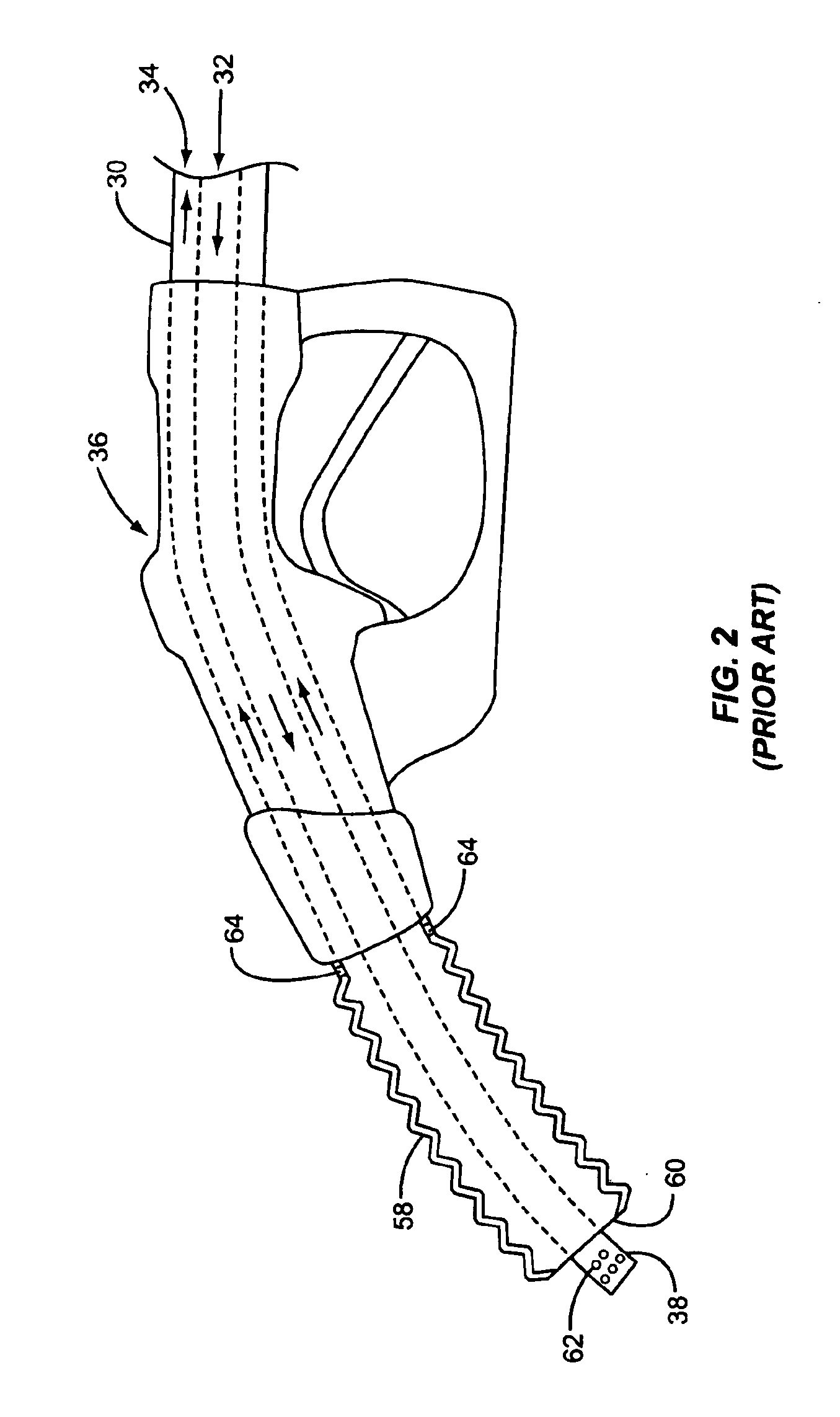
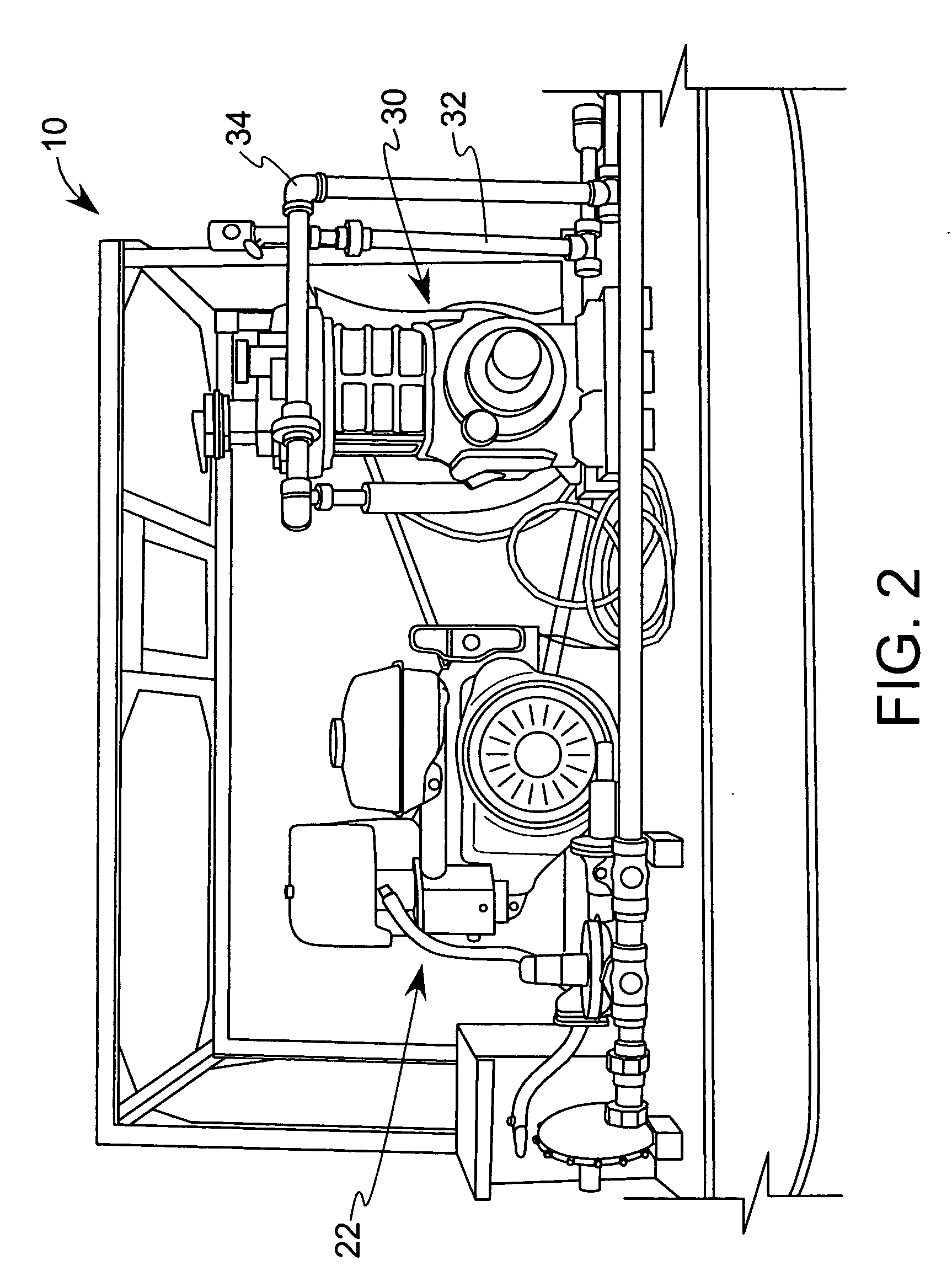
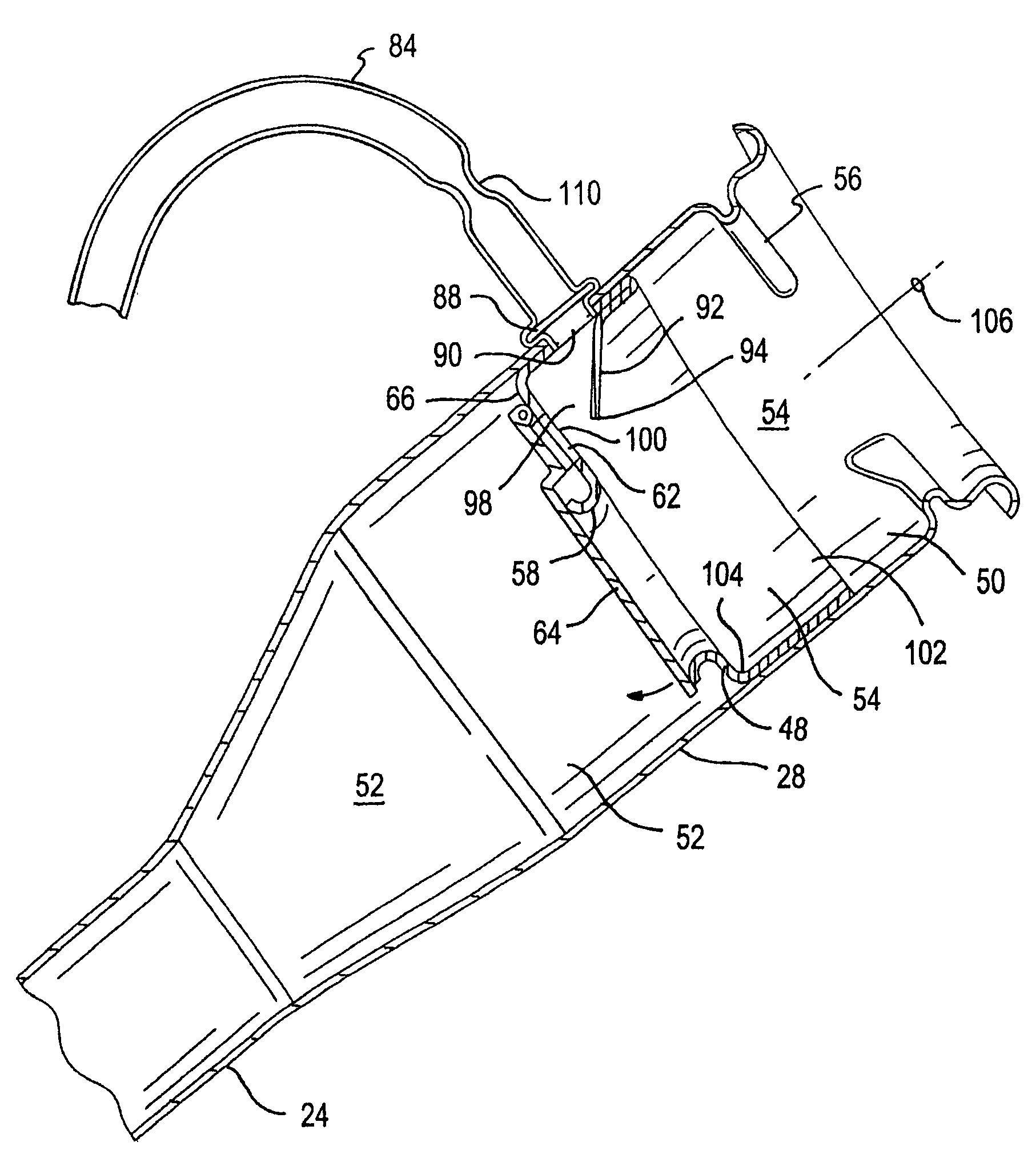
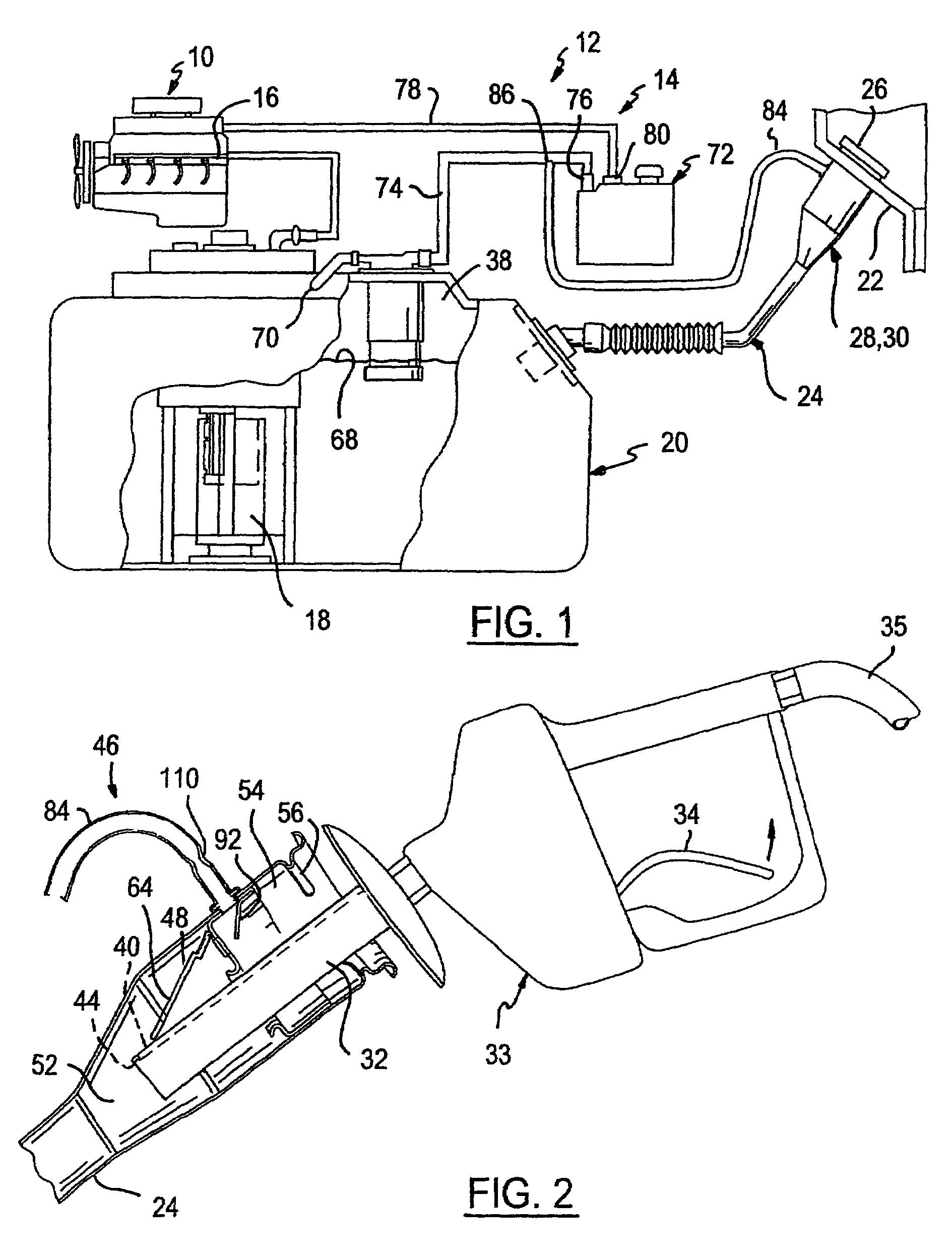
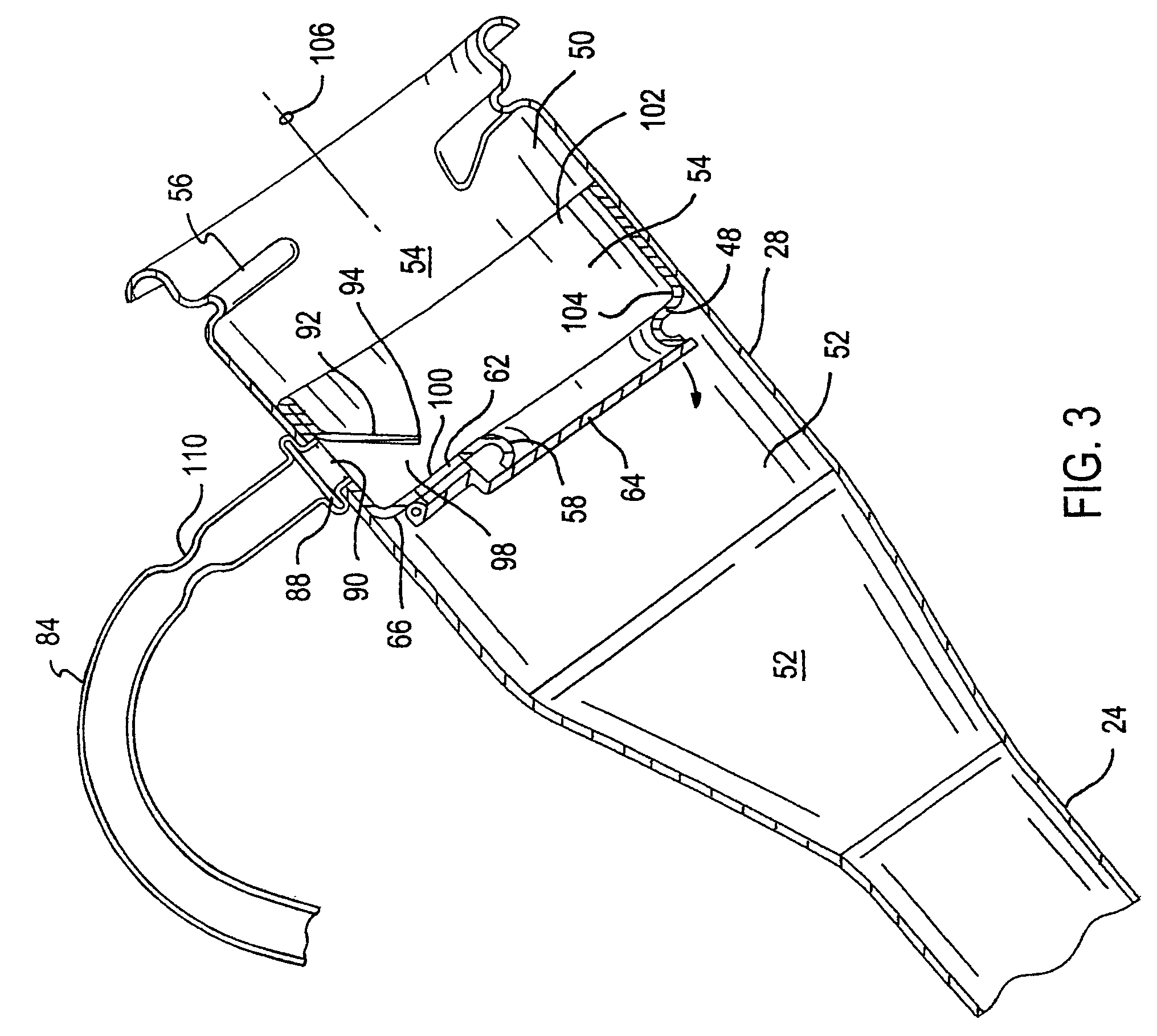
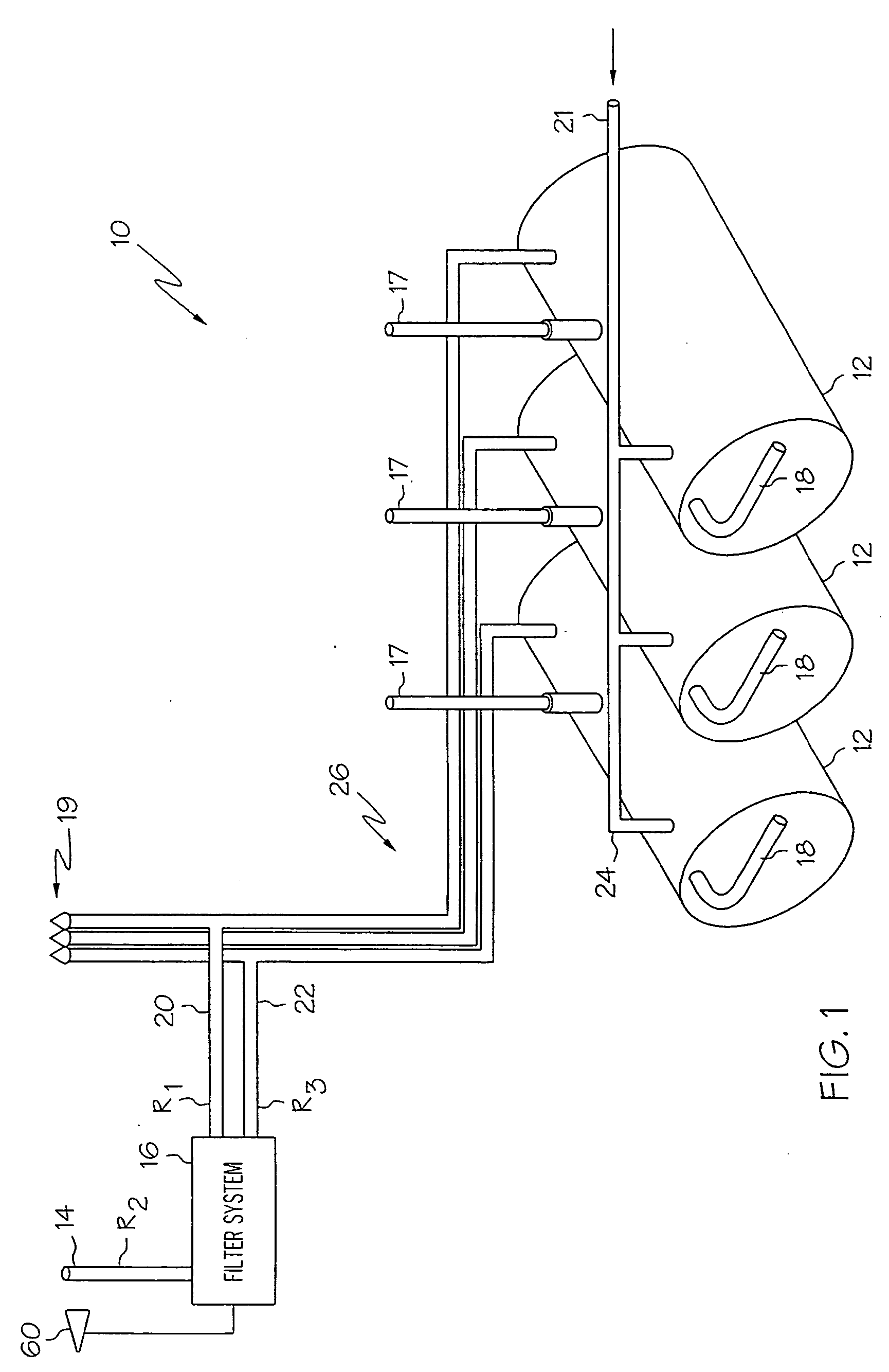
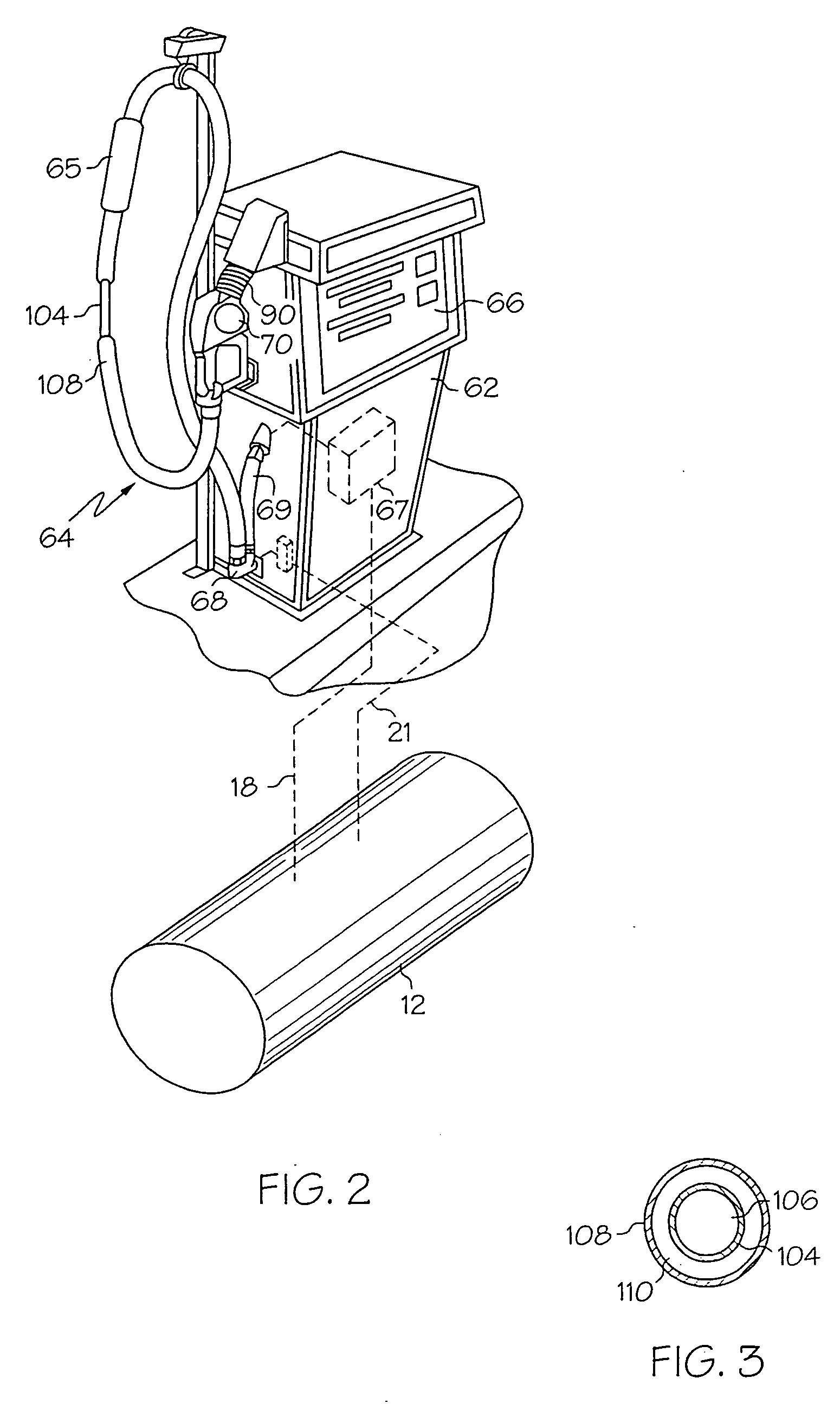
Vapor recovery fuel dispenser for multiple hoses
InactiveUS6899149B1Difficult to useCumbersome and difficult to useLiquid transferring devicesSolid materialMotor driveHand held
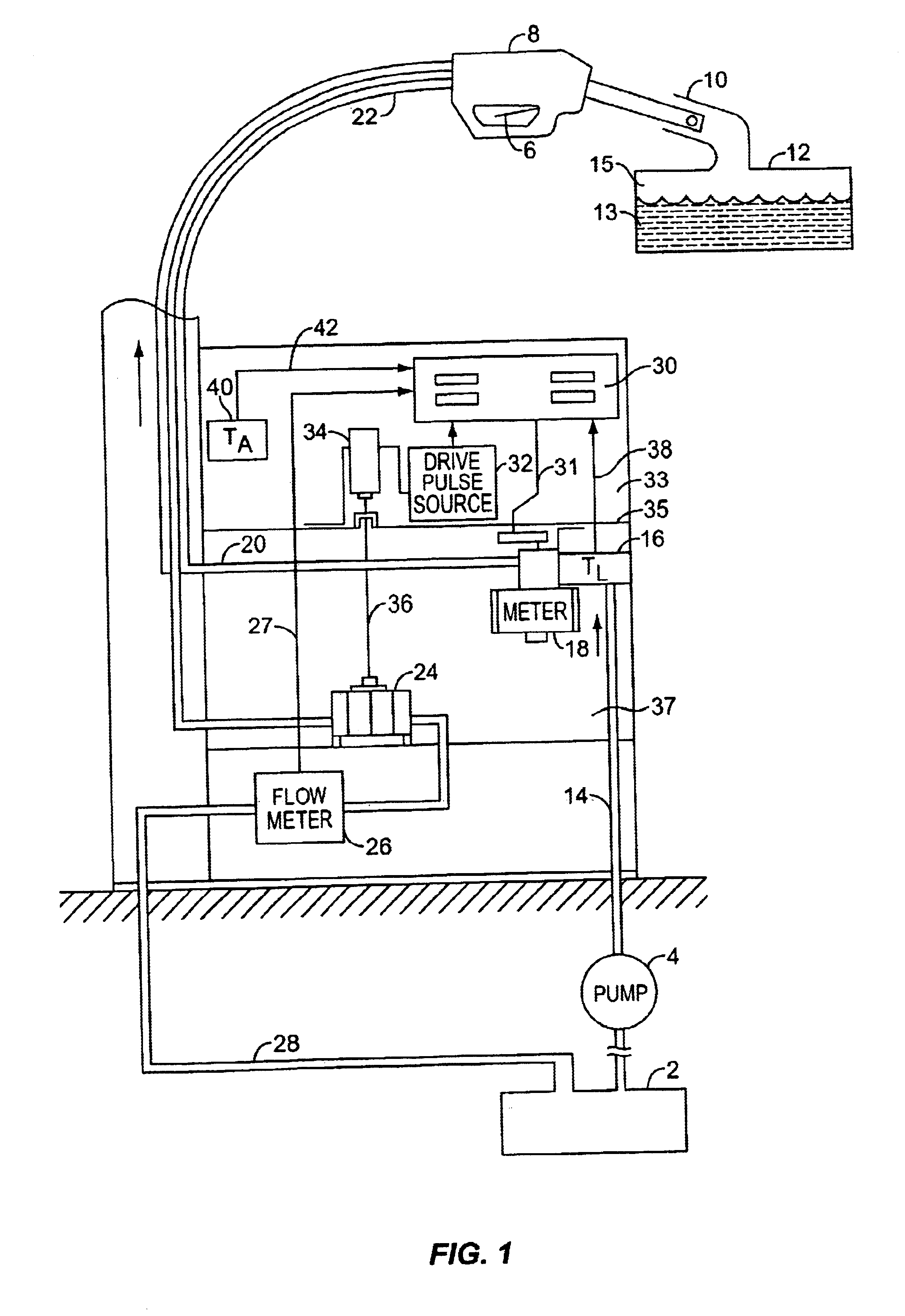
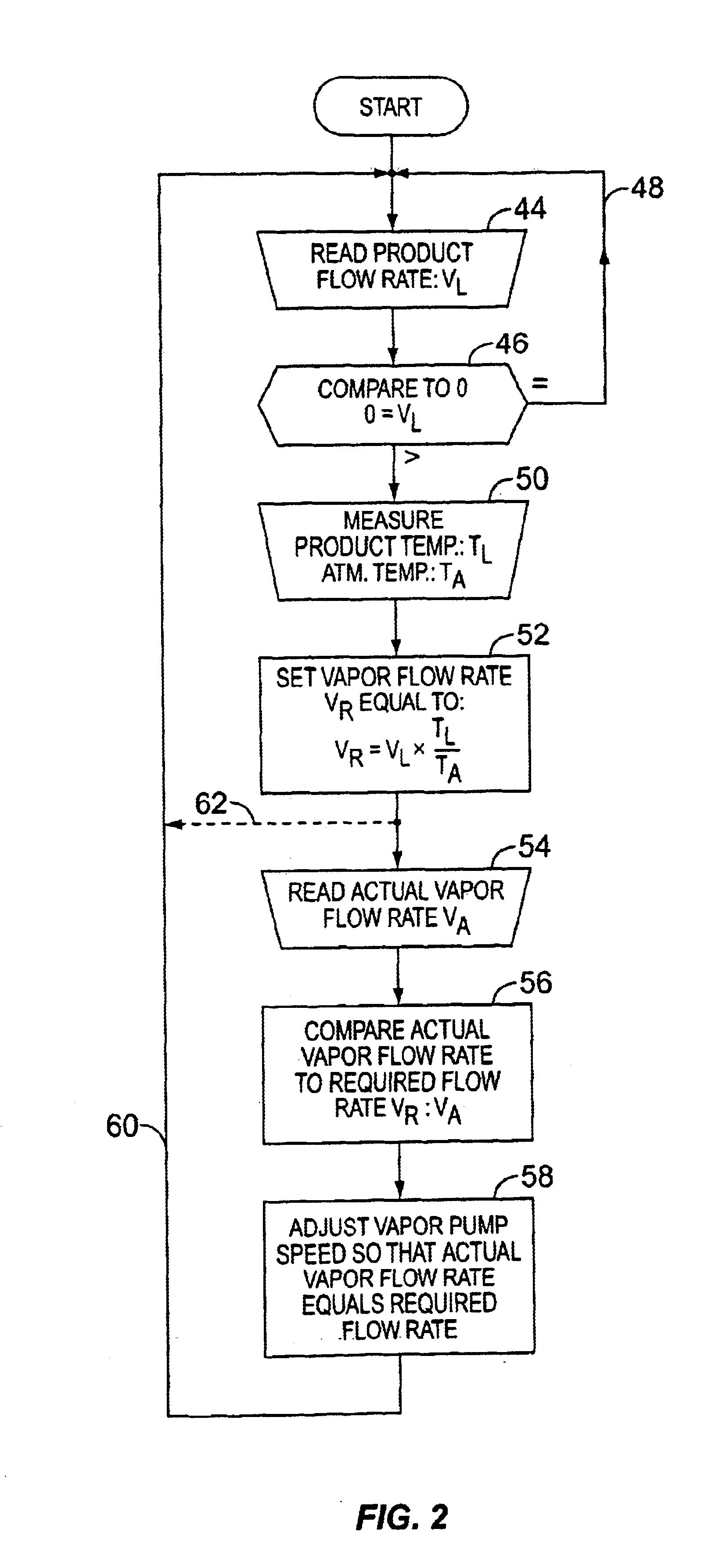
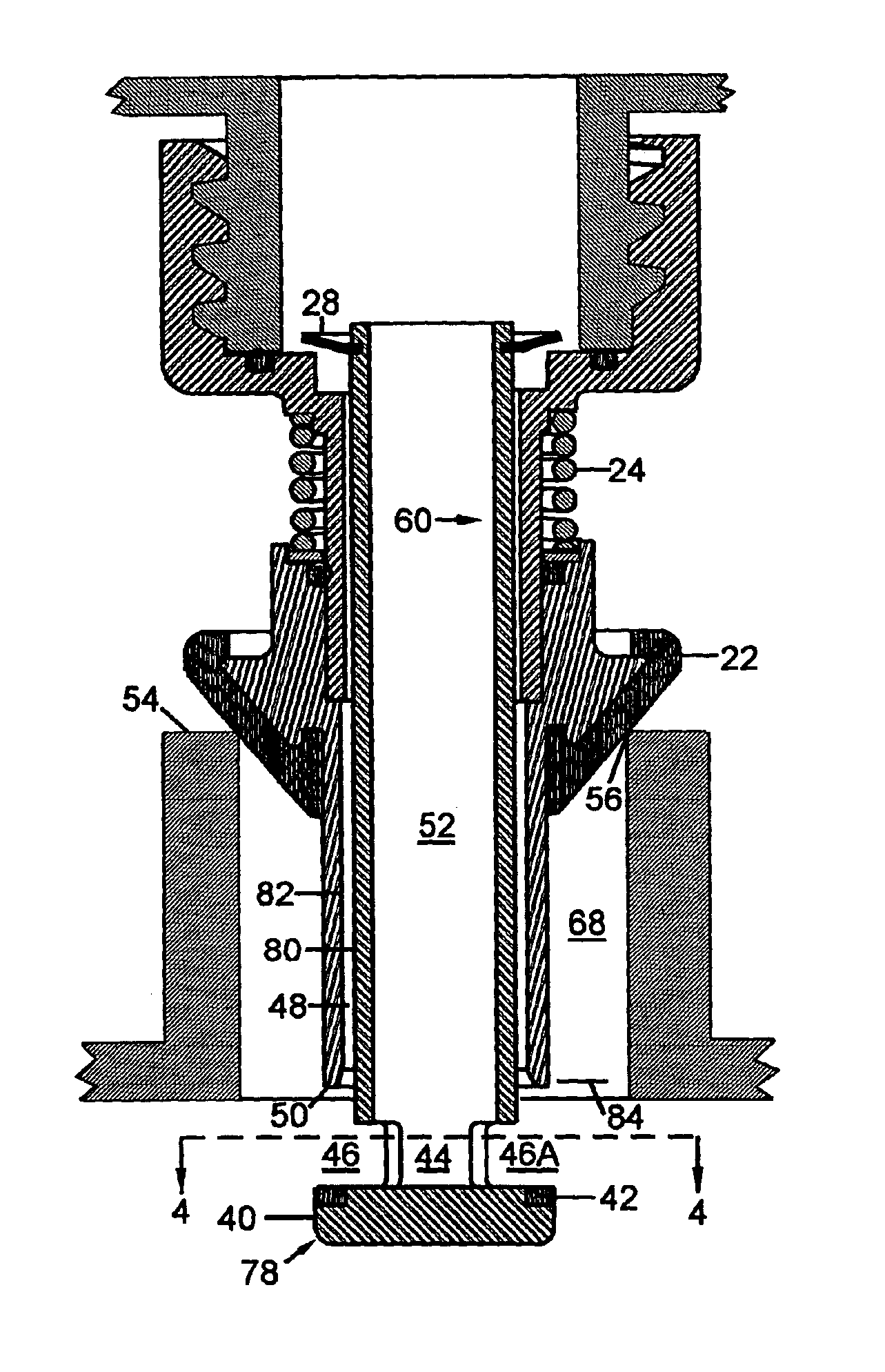
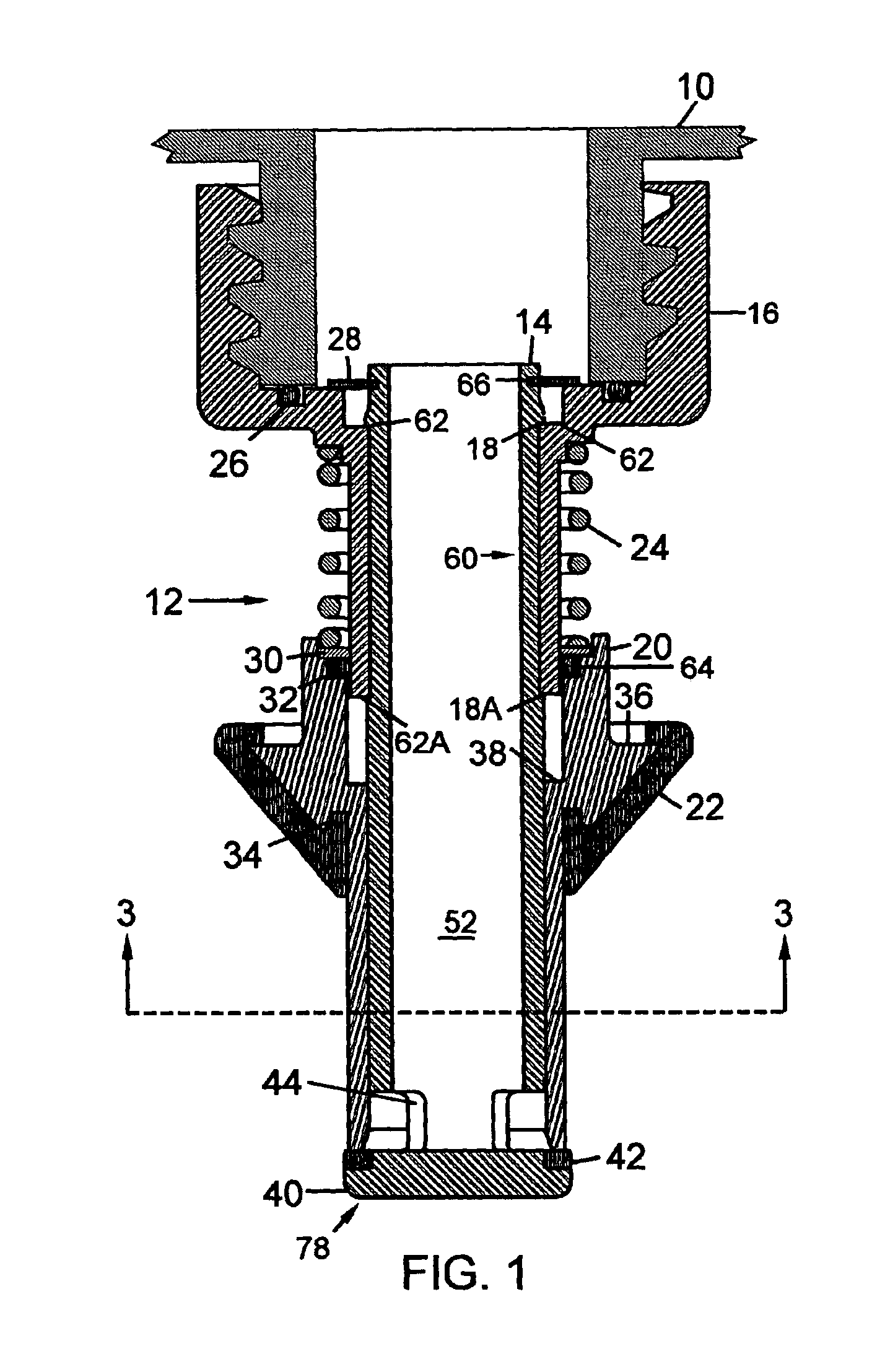
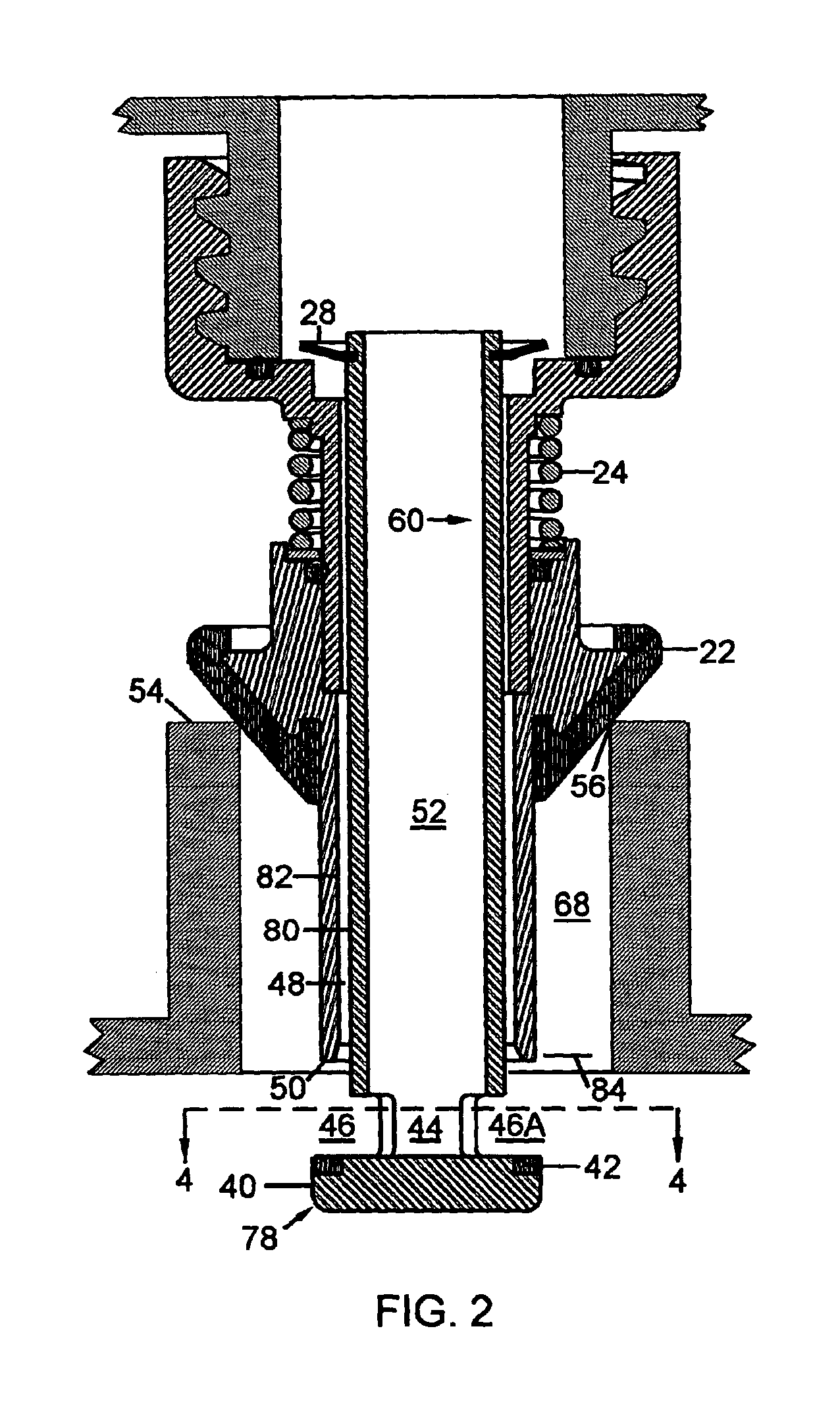
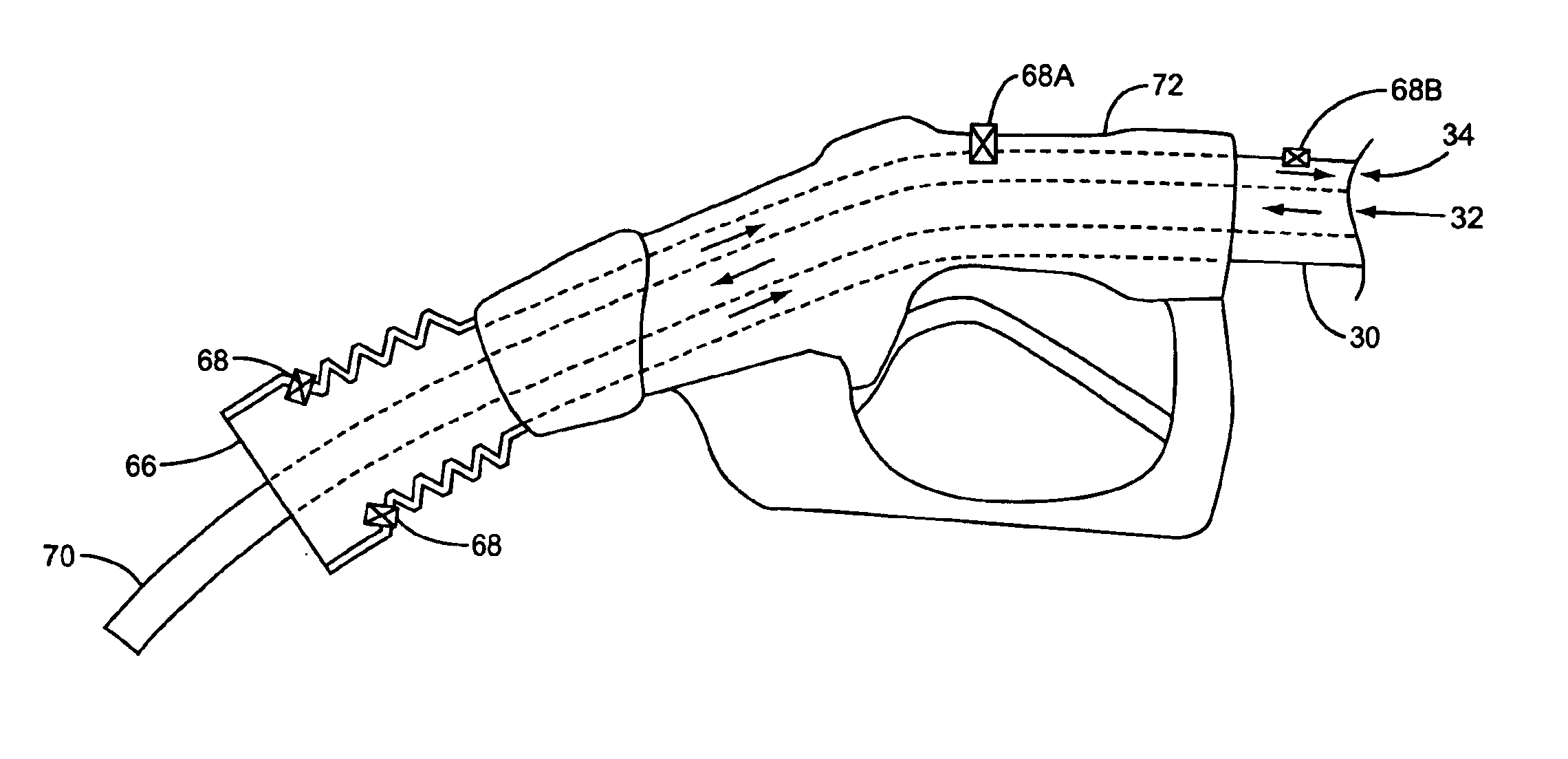
A dispensing system for dispensing volatile liquids such as hydrocarbon fuel for vehicles into a tank having a filler neck also collects the vapors to reduce atmospheric pollution. A fuel delivery hose includes a hand-held fuel valve and nozzle for insertion in the opening of the tank. A means delivers fuel under pressure to the fuel delivery hose, and another means provides electrical pulses corresponding to the volumetric flow of liquid through the fuel delivery hose when the fuel valve is open. A vapor recovery hose includes a vapor intake connected to the hand-held nozzle for insertion in the opening of the tank without sealing with the tank, and a motor driven vapor pump produces a volumetric flow through the vapor recovery hose corresponding to a signal applied to the motor. A processing means produces the signal applied to the motor in response to the electrical pulses to produce a volumetric flow of vapor slightly greater than the volumetric flow of fuel to the tank.
Owner:GILBARCO
Environmentally sealed system for fracturing subterranean formations
An environmentally sealed system for fracturing subterranean systems including a fracturing fluid source, a proppant source, a proppant hopper comprising a variable proppant regulator, a blender comprising a blender inlet and a blender outlet, a high pressure pump comprising a high pressure pump inlet and a high pressure pump outlet, and a well head; wherein the fracturing fluid source is connected to the blender inlet through a fracturing fluid supply connection and a fracturing vapor recovery connection, the proppant source is connected with the proppant hopper through a proppant supply connection and a proppant vapor recovery connection, the proppant hopper is connected to the blender inlet through a proppant transfer connection, the blender outlet is connected to the high pressure pump inlet, and the high pressure pump is outlet connected to the well head.
Owner:TUDOR ROBIN
Fuel vent assembly with floatless rollover protection
ActiveUS20050098160A1Reduce manufacturing costNon-fuel substance addition to fuelLarge containersRolloverFuel tank
A valve for use between a vehicle fuel tank vent and a vapor recovery canister in a vehicle fuel tank containing liquid fuel, such a valve comprises: a housing having a fuel tank side and a vapor recovery canister side; and a vapor permeable membrane fixed to the housing to block the passage of liquid fuel.
Owner:FCA US
High rangeability control valve
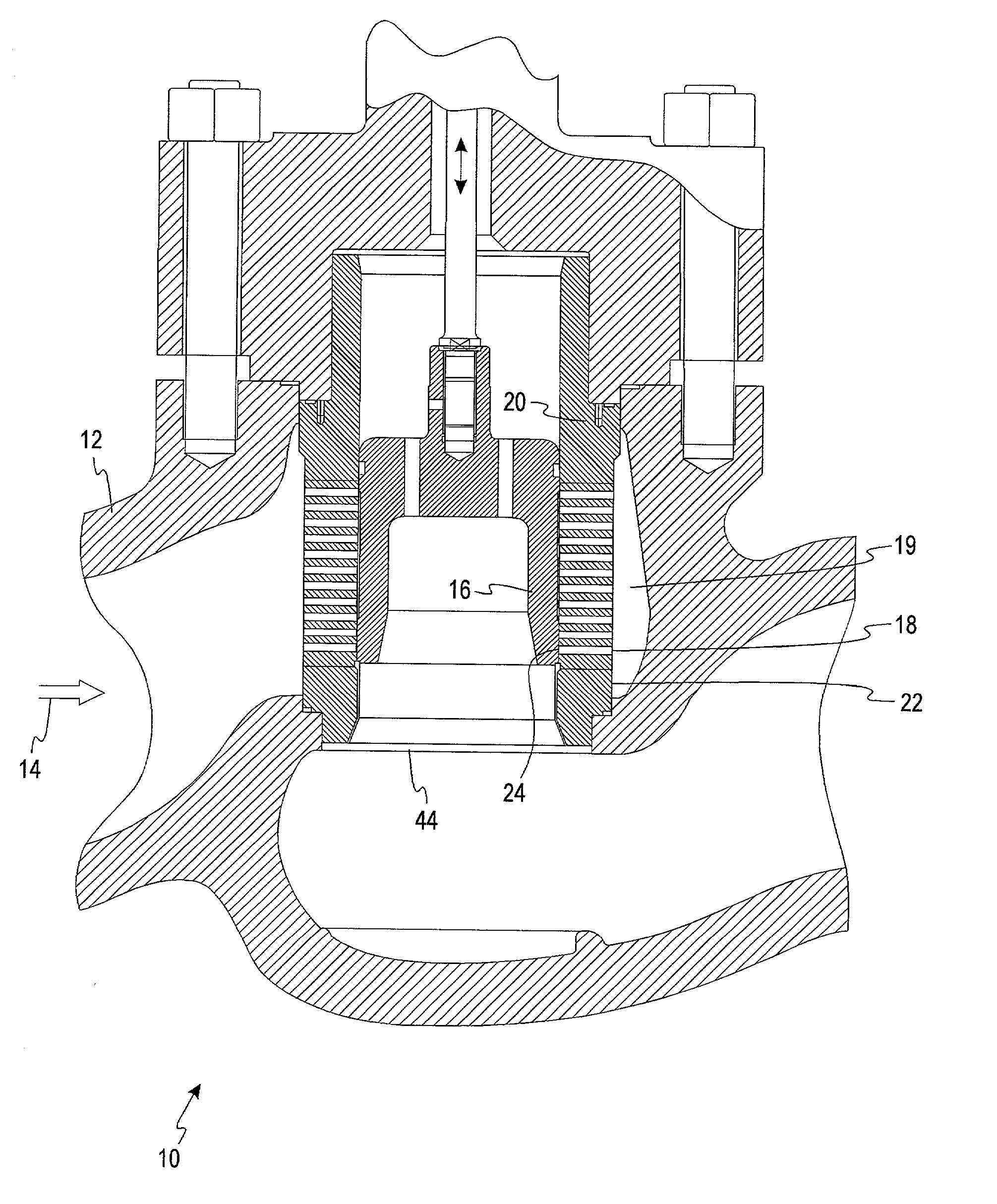
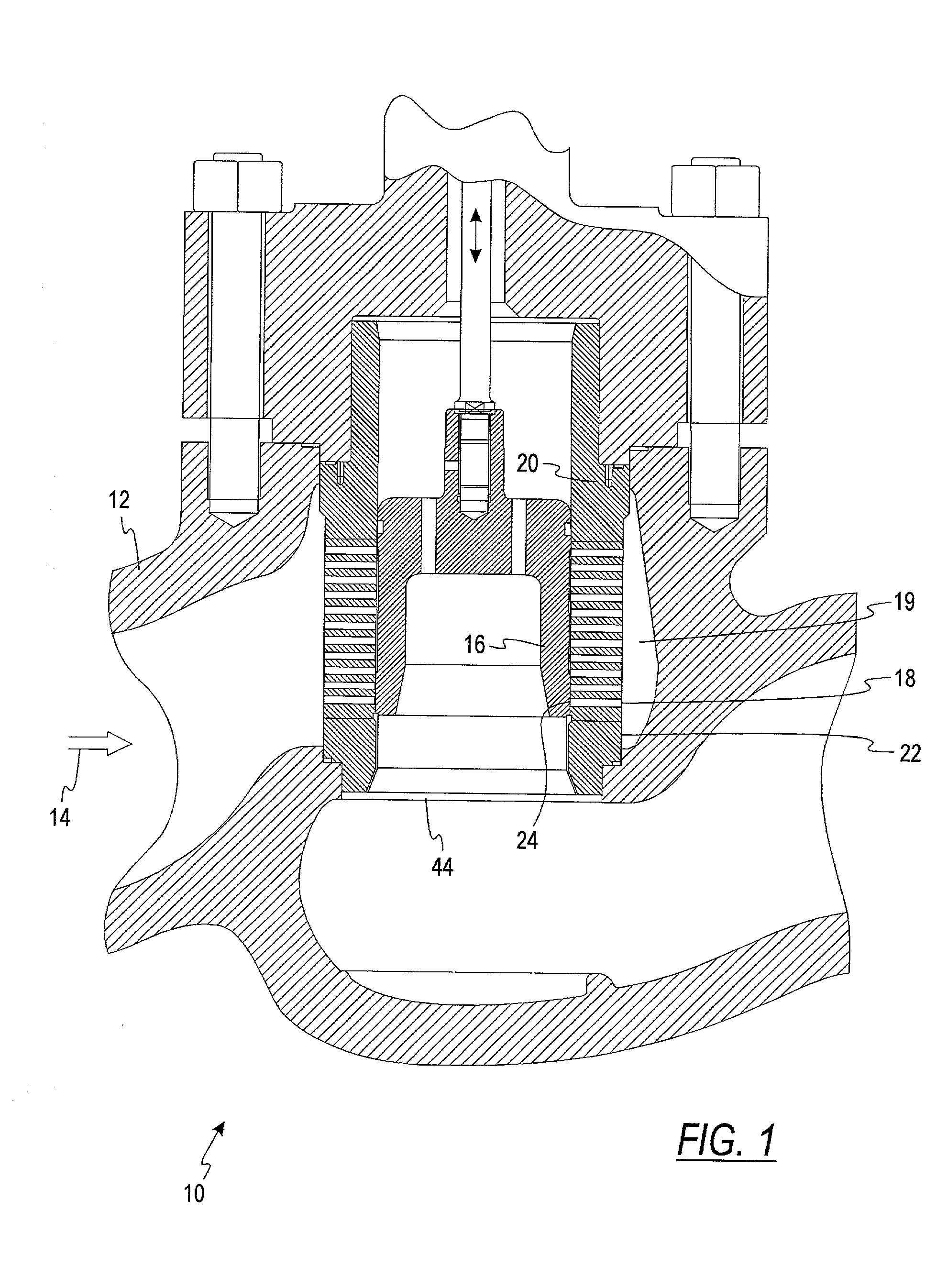
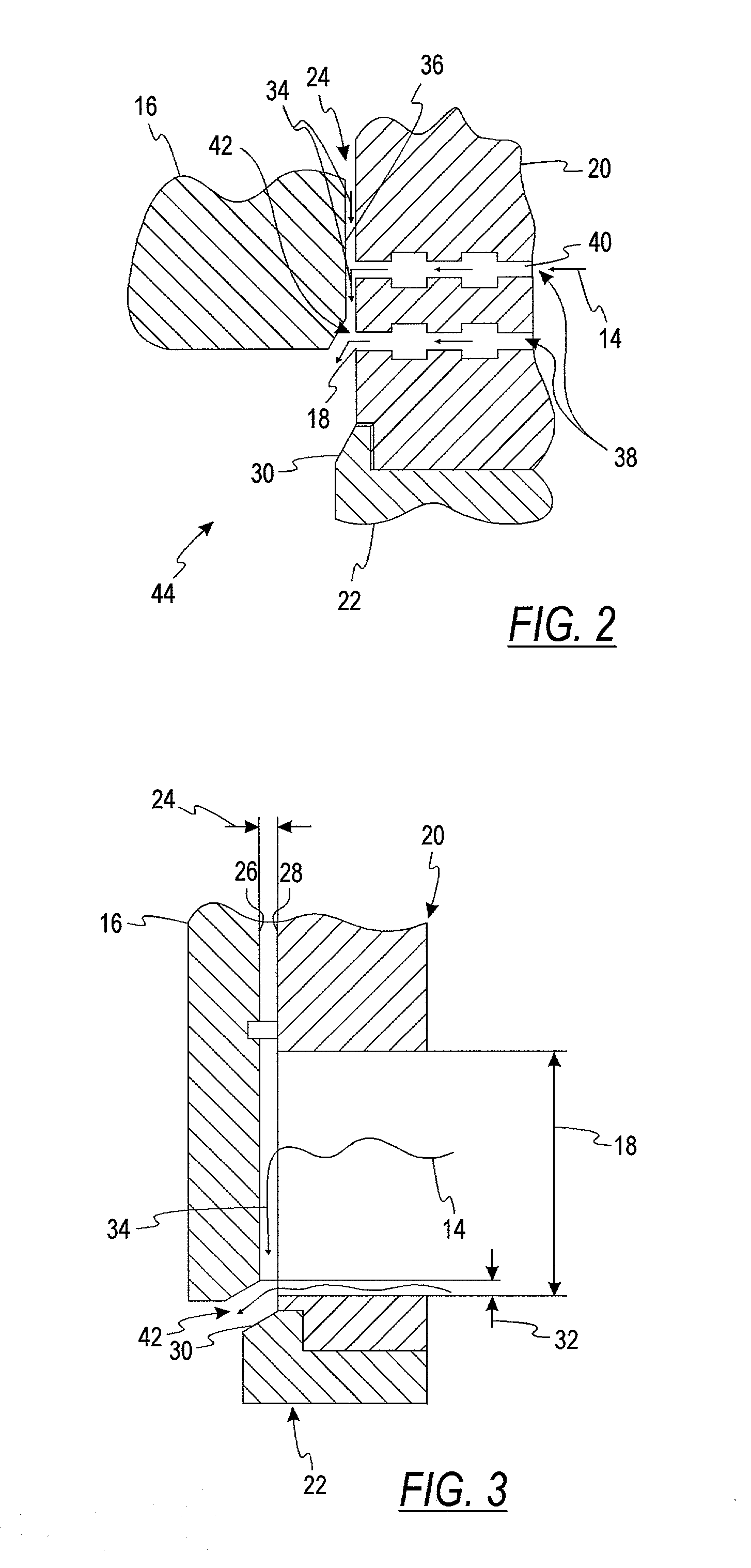
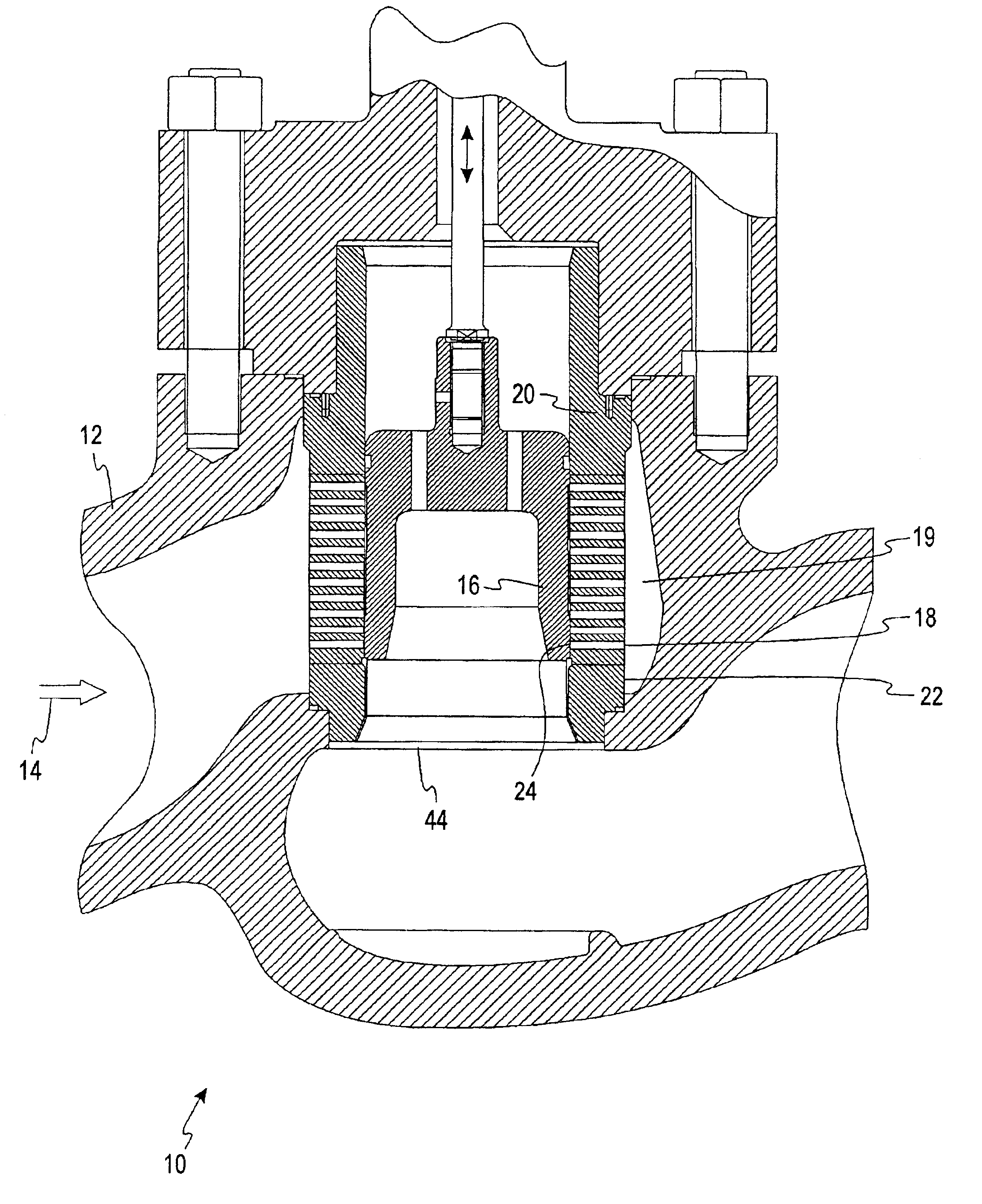
InactiveUS20030226600A1Reduce gapReduces and eliminates cavitation erosion damageValve members for absorbing fluid energySlide valveVapor bubbleEngineering
A guided control valve comprising a vapor recovery area that encourages collapse of vapor bubbles. In a cage-guided valve, a seal comprising inner and outer members reduces flow through a radial clearance between a plug and a cage. The vapor recovery area is positioned below the seal and above a seat interacting with the plug. The vapor recovery area encourages collapse of vapor bubbles to reduce damage to the valve trim.
Owner:DRESSER LLC
High rangeability control valve
InactiveUS6807985B2Reduces and eliminates cavitation erosion damageExpand the adjustment rangeValve members for absorbing fluid energyMultiple way valvesVapor bubbleControl valves
A guided control valve comprising a vapor recovery area that encourages collapse of vapor bubbles. In a cage-guided valve, a seal comprising inner and outer members reduces flow through a radial clearance between a plug and a cage. The vapor recovery area is positioned below the seal and above a seat interacting with the plug. The vapor recovery area encourages collapse of vapor bubbles to reduce damage to the valve trim.
Owner:DRESSER LLC
Fuel vent assembly with floatless rollover protection
InactiveUS6895943B1Reduce manufacturing costNon-fuel substance addition to fuelLarge containersRolloverFuel tank
A valve for use between a vehicle fuel tank vent and a vapor recovery canister in a vehicle fuel tank containing liquid fuel, such a valve comprises: a housing having a fuel tank side and a vapor recovery canister side; and a vapor permeable membrane fixed to the housing to block the passage of liquid fuel.
Owner:FCA US
On board refueling vapor recovery system and fuel vapor passage using for the same
InactiveUS6851458B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce in quantityLarge containersUnderstructuresMan-hourOn board
An on board refueling vapor recovery system includes a first fuel vapor passage for connecting a fuel tank with a canister, a second fuel vapor passage for connecting an inlet portion of a fuel filler pipe with the fuel vapor passage (a tank main body) and a check valve in the second fuel vapor passage. The check valve is integrated with a first quick connector of a resin hose (a resin tube) which constitutes the second fuel vapor passage. Therefore, the number of man hours required for assembling the on board refueling vapor recovery system can be reduced. In addition, the space required for installing any of the on board refueling vapor recovery system can also be reduced. Furthermore, the amount of released fuel evaporative emissions or fuel evaporative emissions can be reduced.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
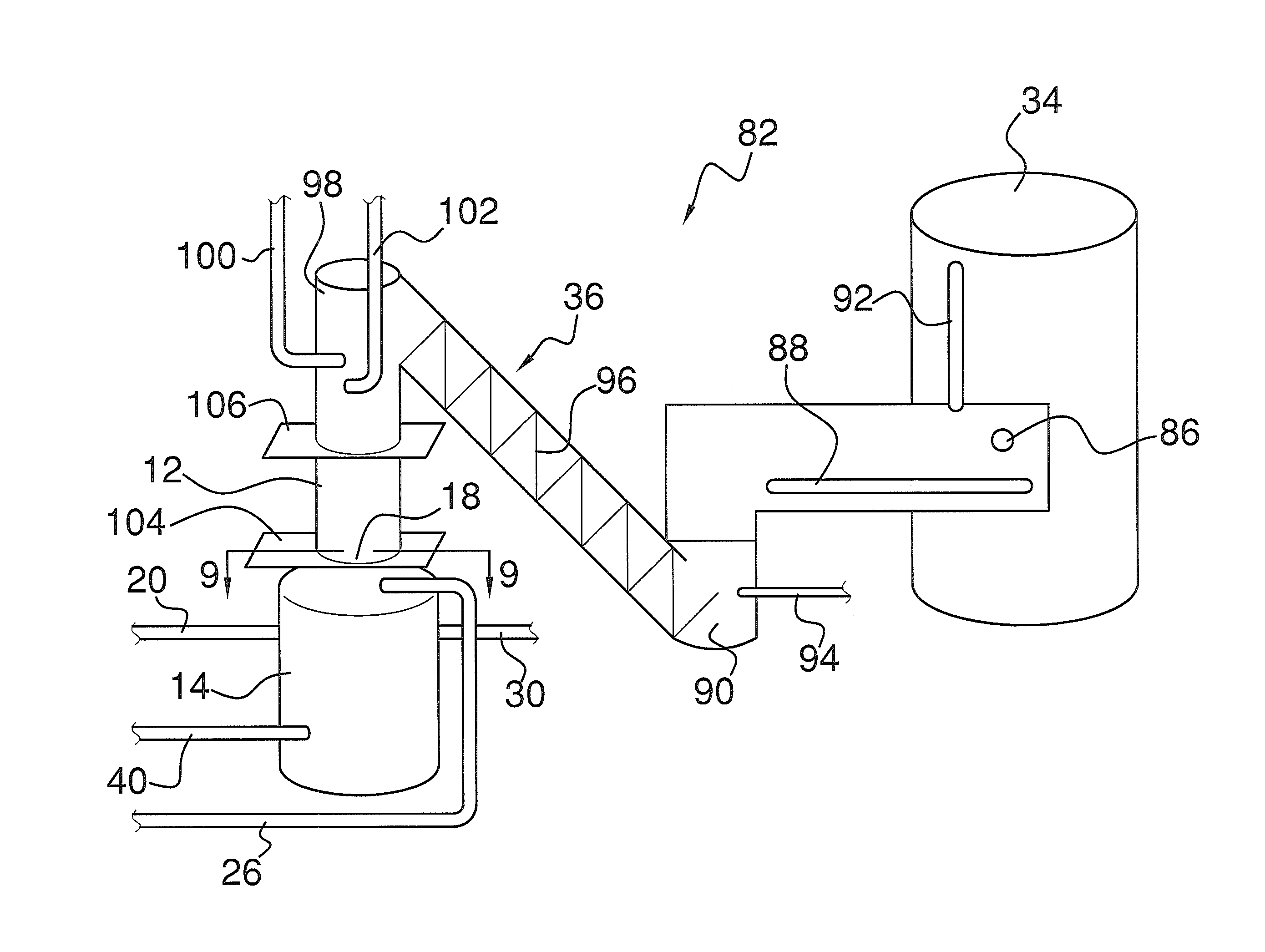
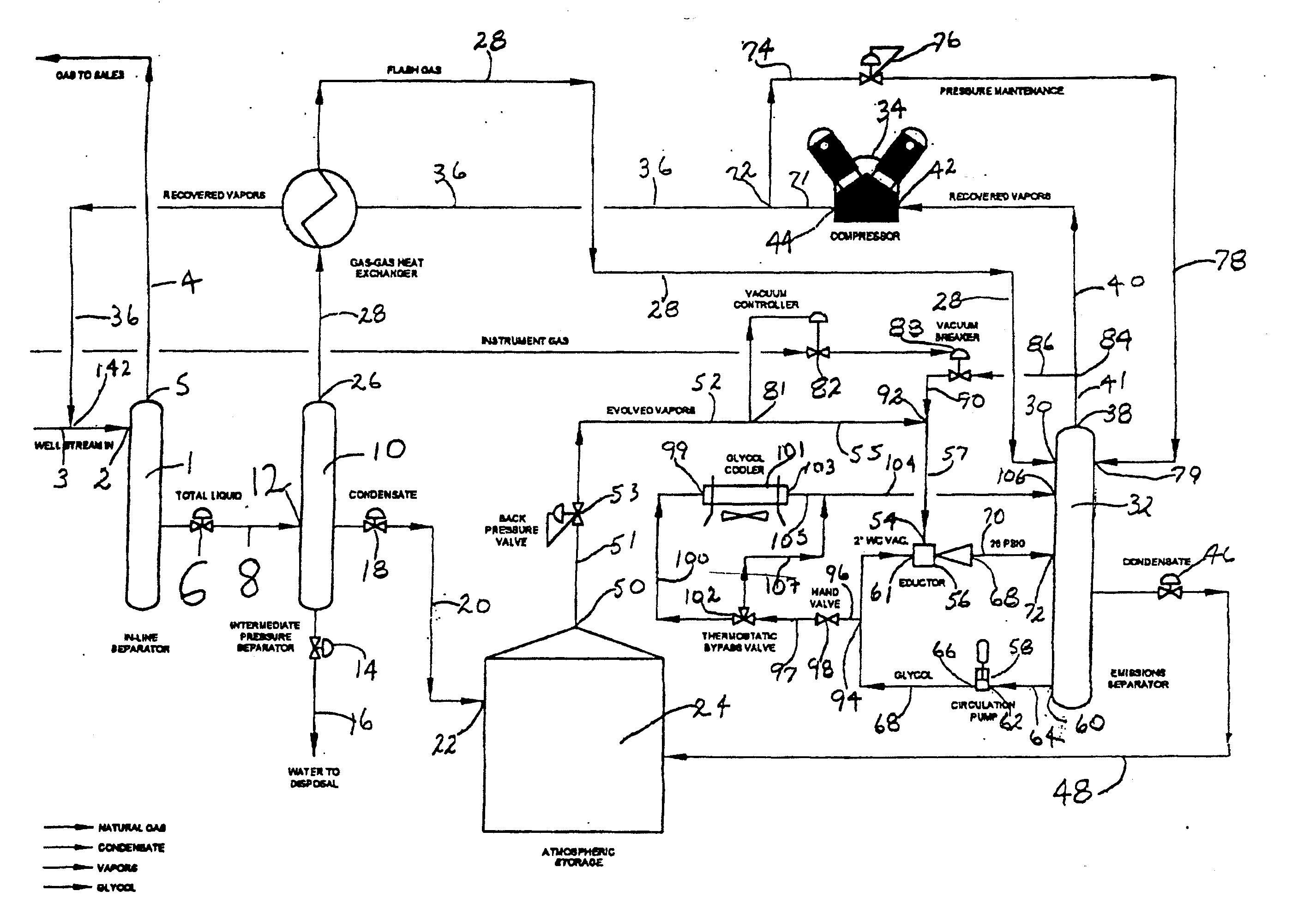
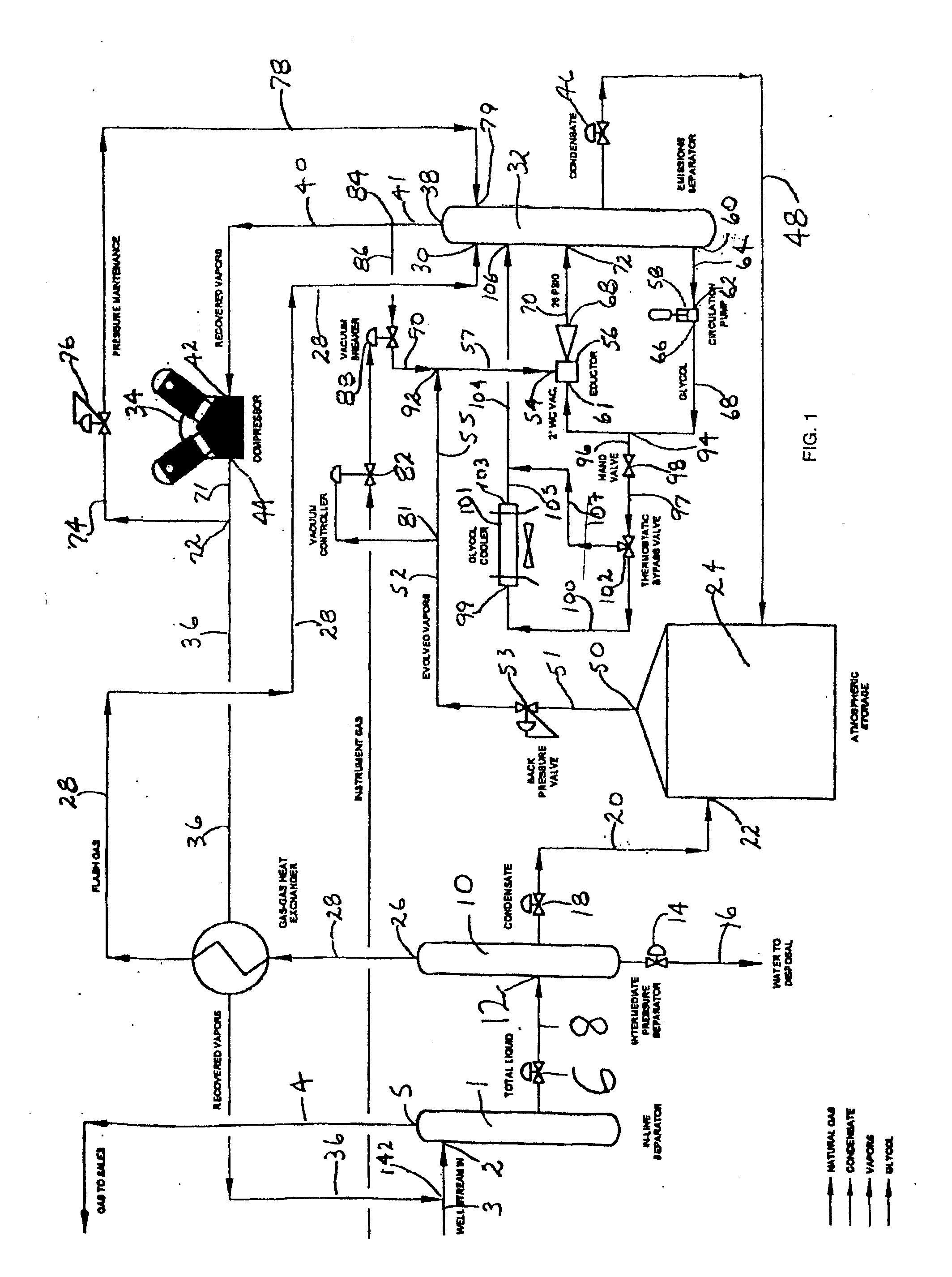
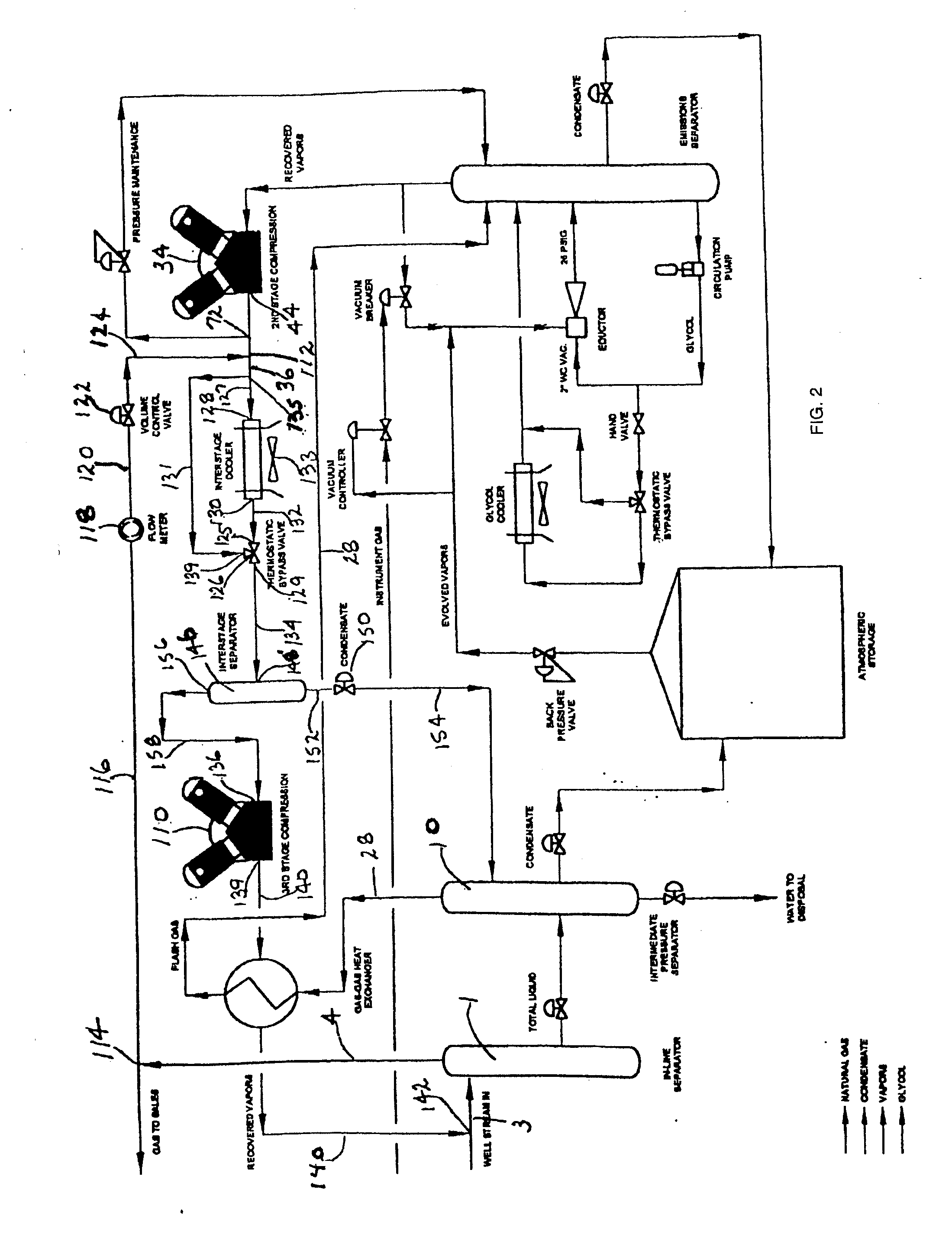
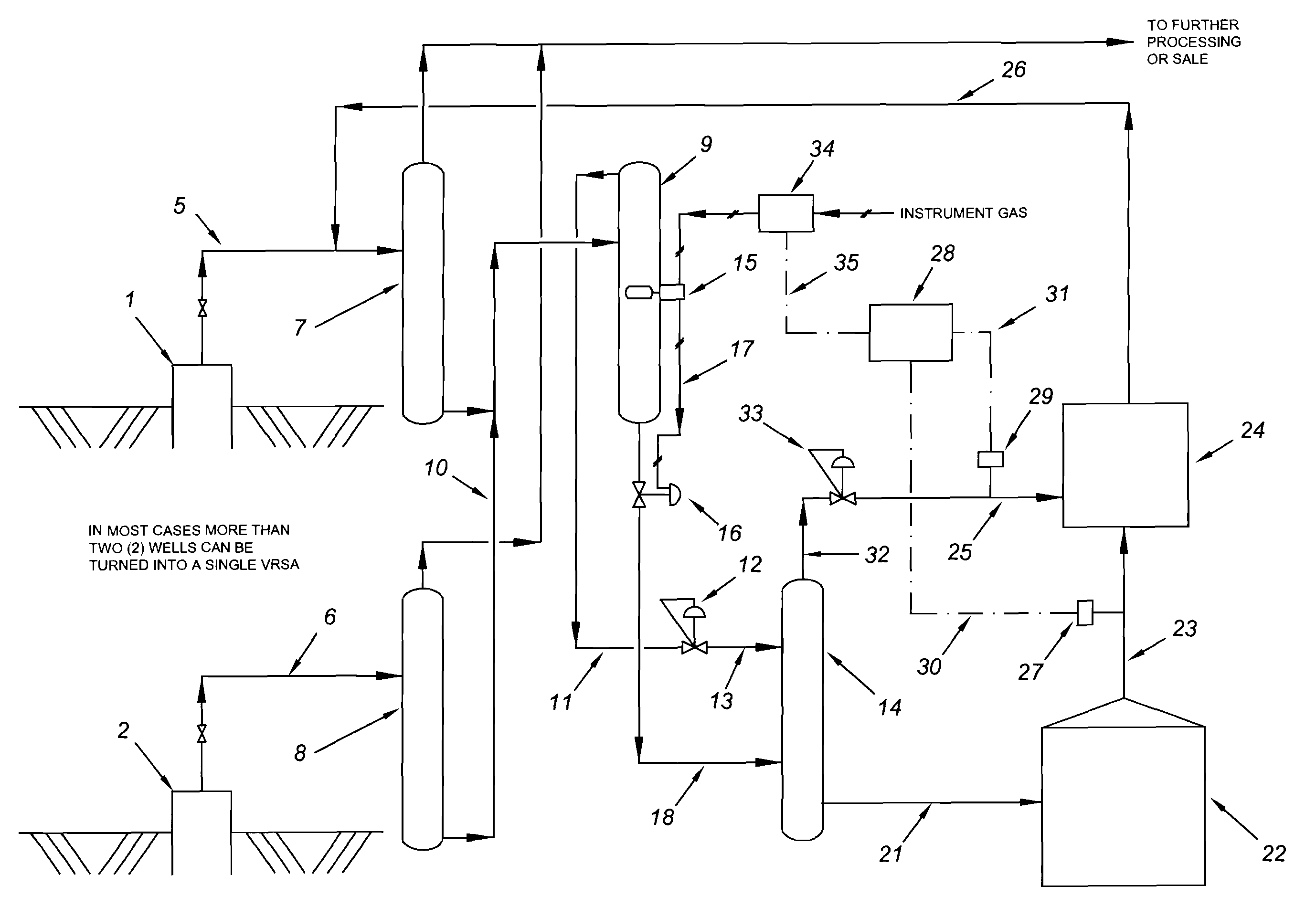
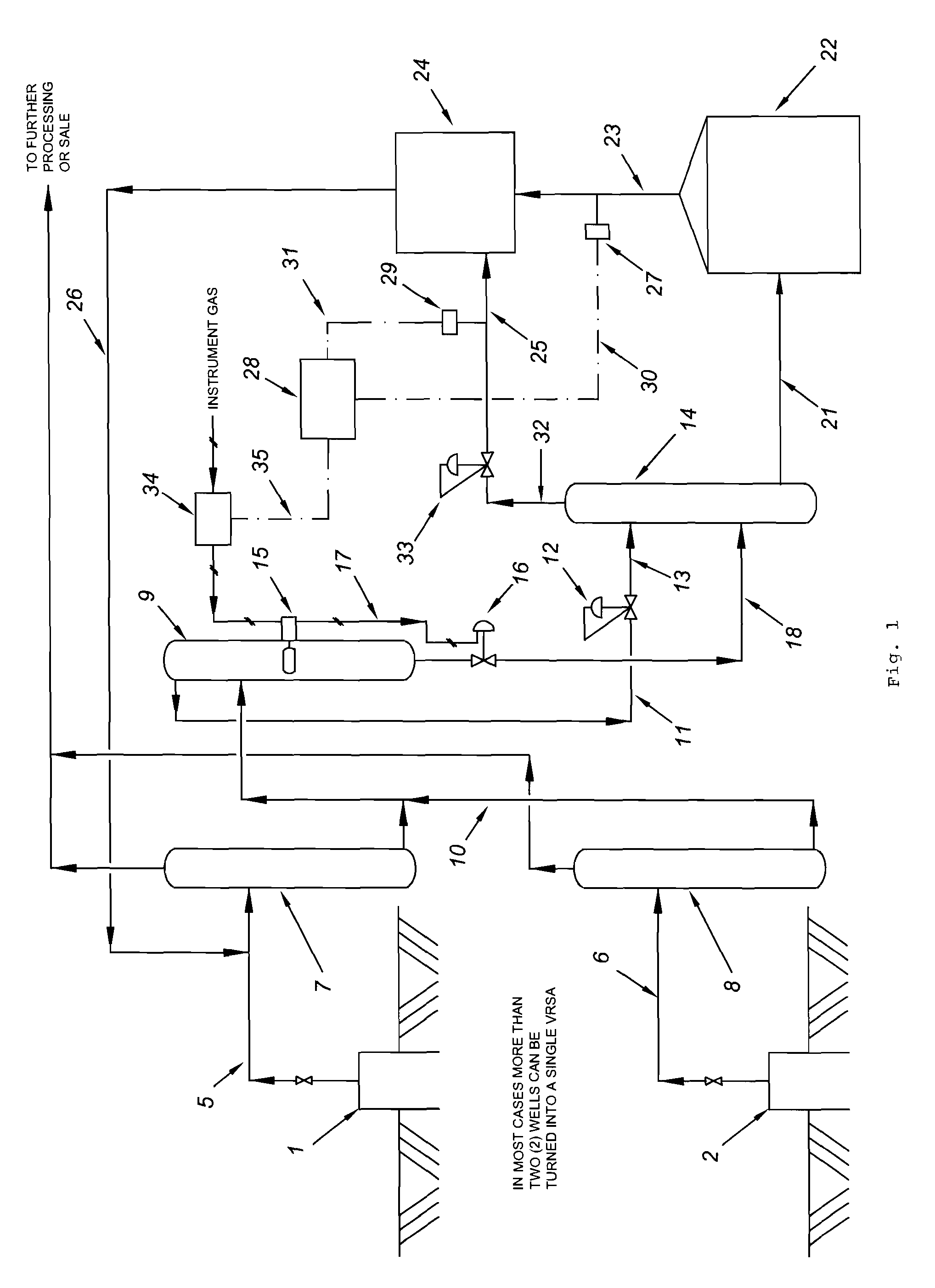
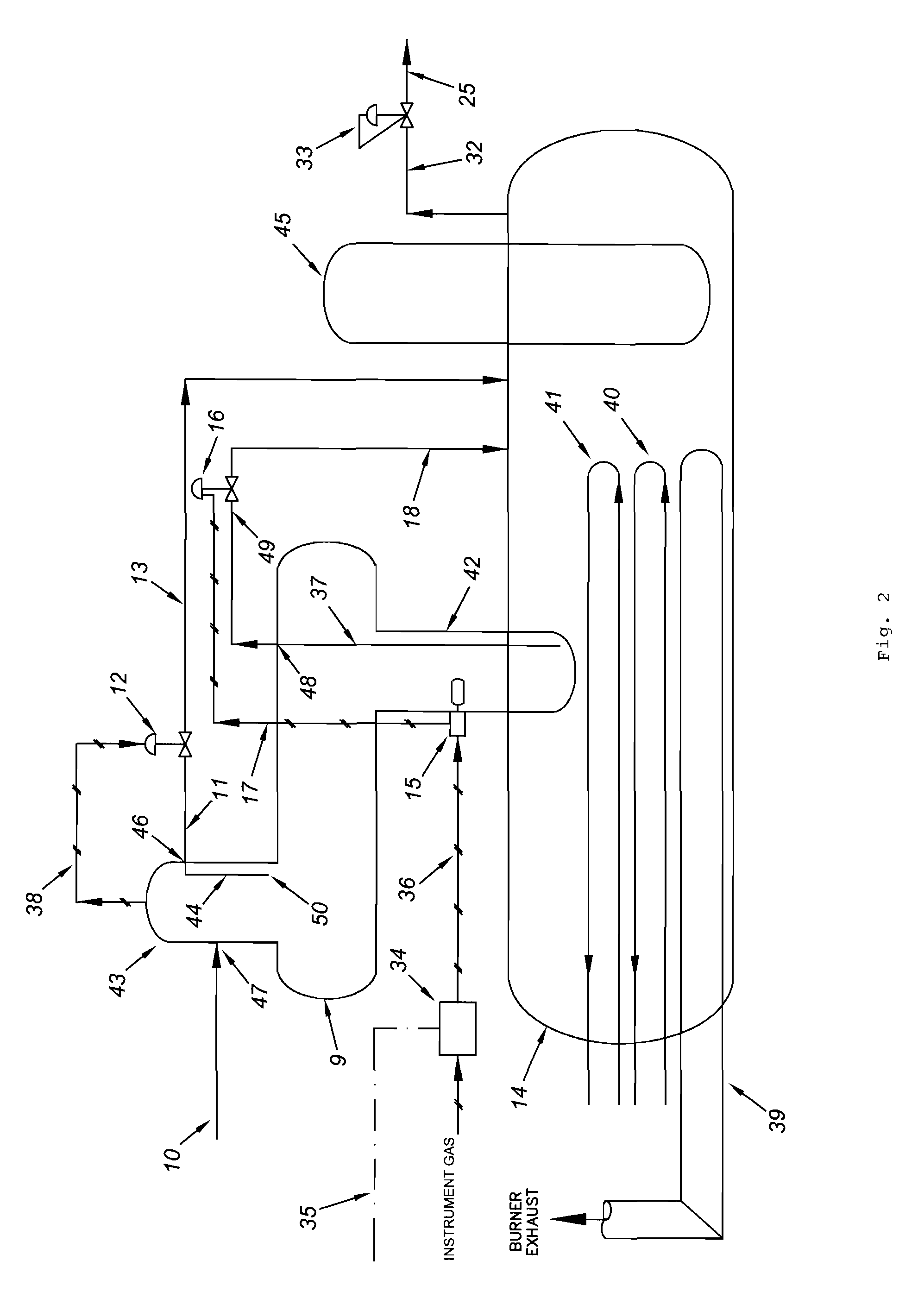
Natural Gas Vapor Recovery Process System
InactiveUS20070186770A1Reduce BTU and partial pressureIncrease partial pressureLiquid degasificationDispersed particle separationProcess systemsLiquid state
The present invention provides for a natural gas well vapor recovery processing system and method comprising recovering gaseous hydrocarbons to prevent their release into the atmosphere including providing a method for preventing the gaseous hydrocarbons from returning to a liquid state.
Owner:HEATH RODNEY T +2
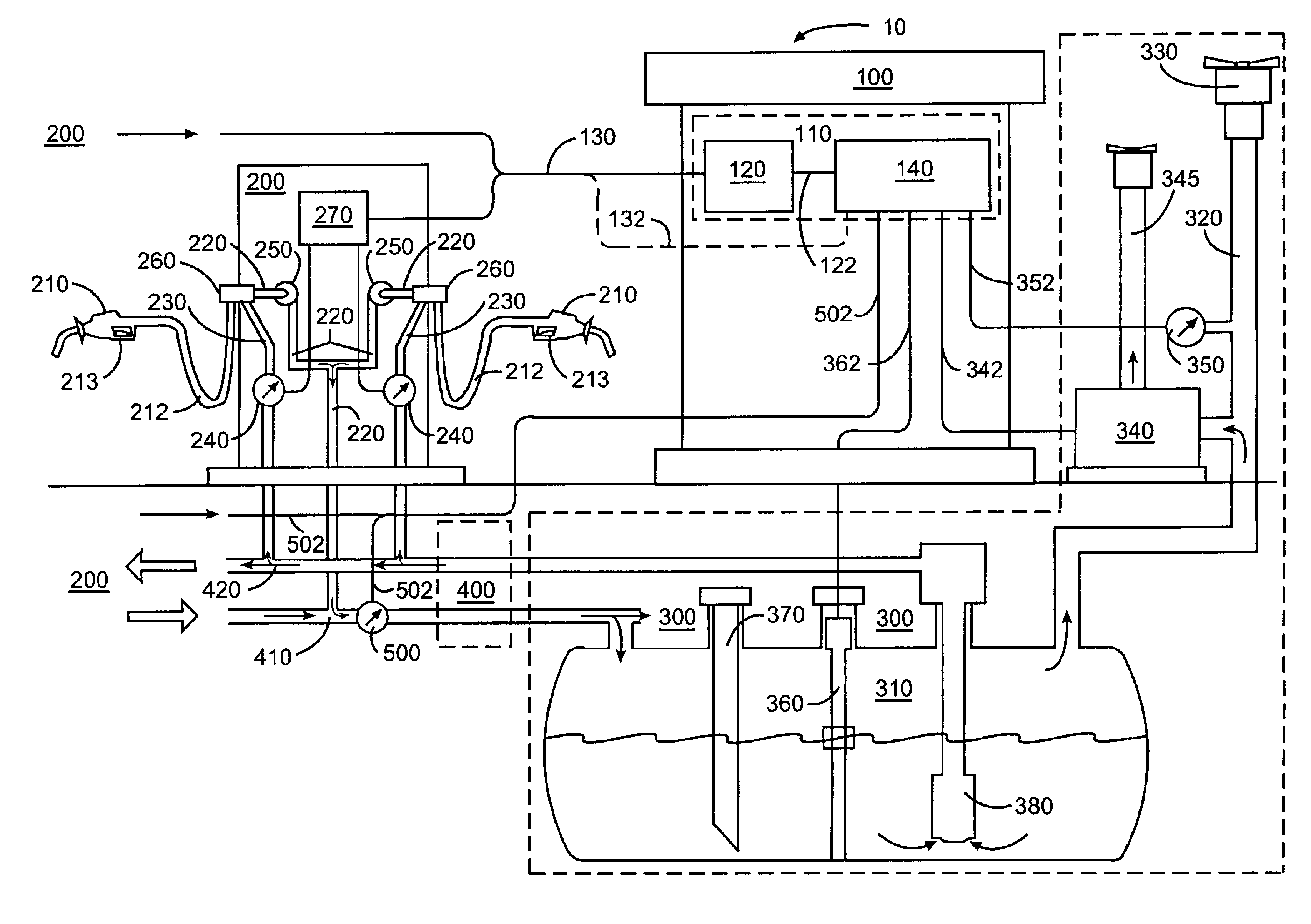
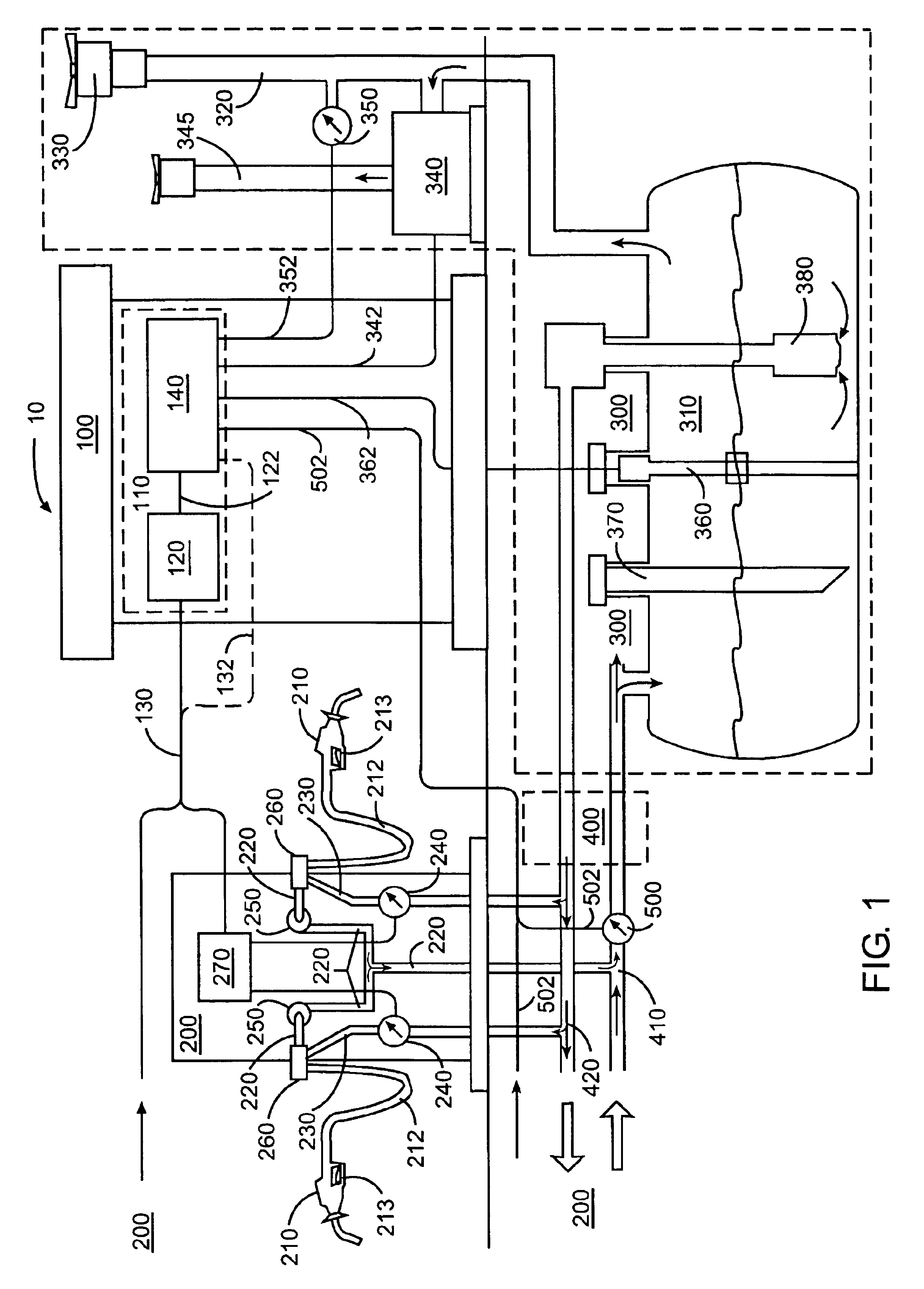
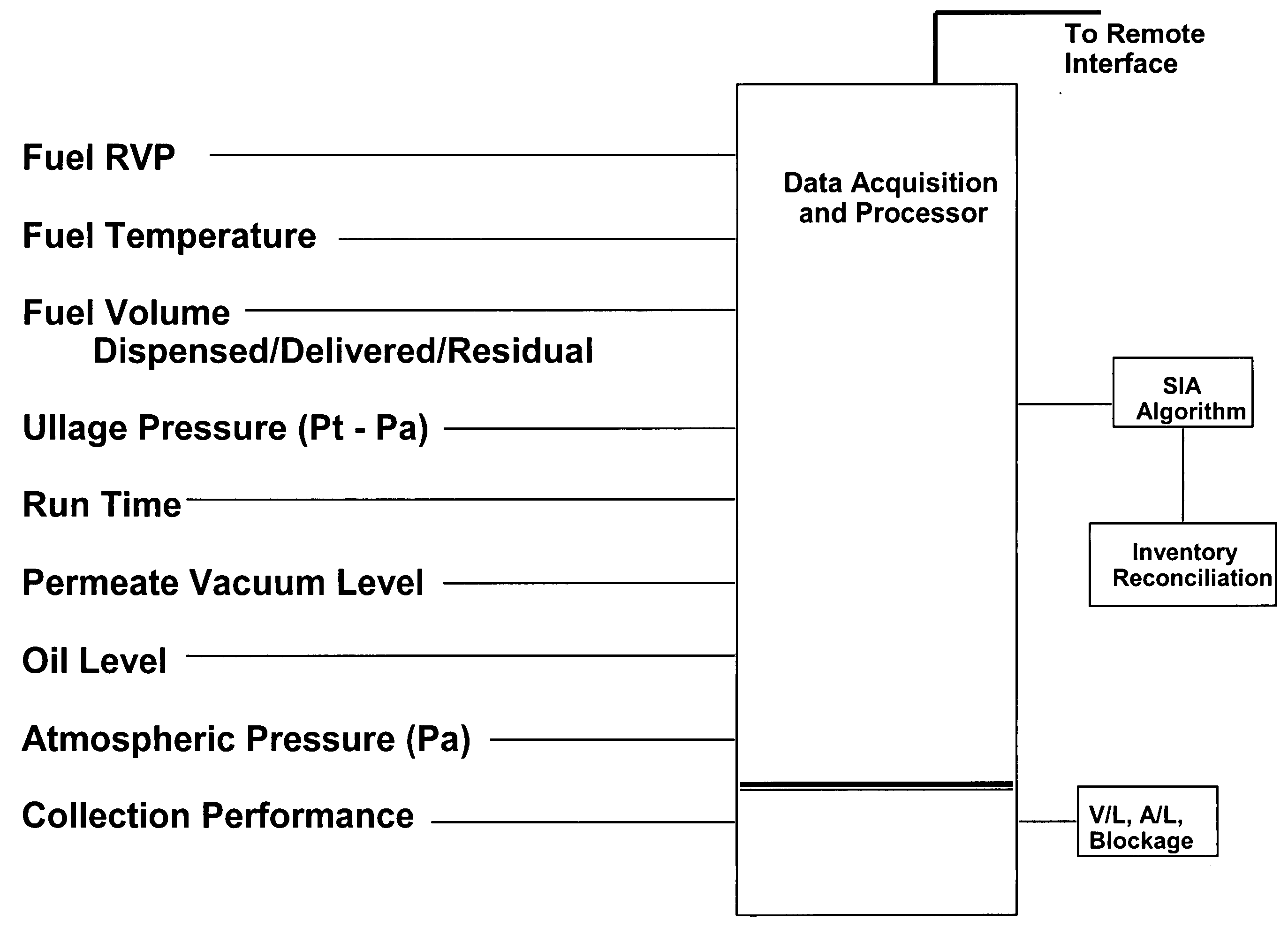
Fueling system vapor recovery and containment performance monitor and method of operation thereof
InactiveUS6880585B2Reduce in quantityMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateLiquid fillingRecovery performanceLiquid fuel
Owner:VEEDER ROOT
Vapor recovery system
A vapor recovery apparatus for oil and gas well production that is used in combination with a liquid separator, a sales line and a holding tank includes a compressor, which is drivingly linked to an engine. A first conduit extends from fluid communication with the holding tank to a compressor inlet, while a second conduit extends from a compressor outlet to fluid communication with the sales line. The vapor recovery apparatus also has an electronic controller that is connected to the engine and to a pressure sensor, which is in fluid communication with the gas in the tank.
Owner:ELECTRONICS DESIGN FOR IND
Vapor recovery gas pressure boosters and methods and systems for using same
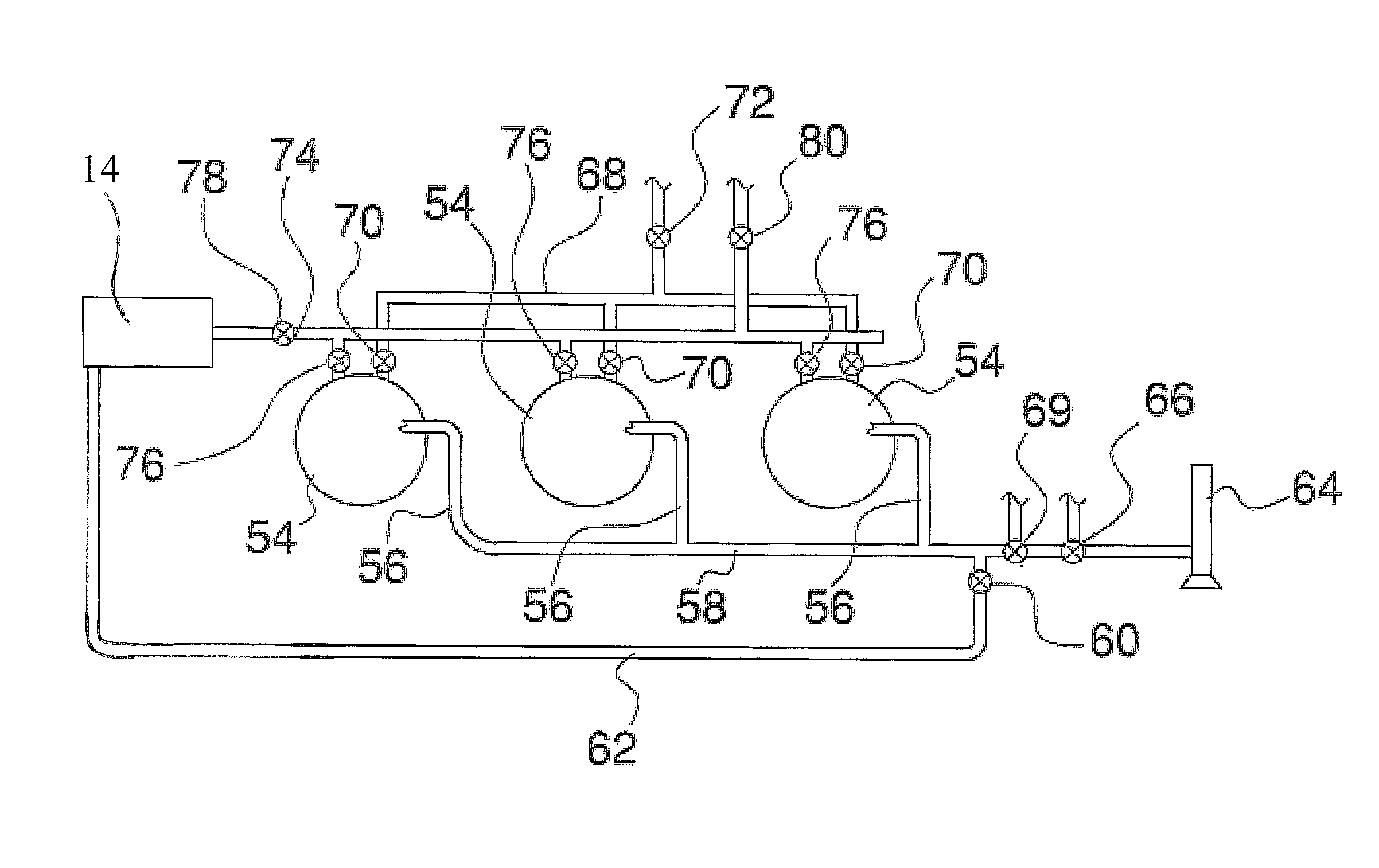
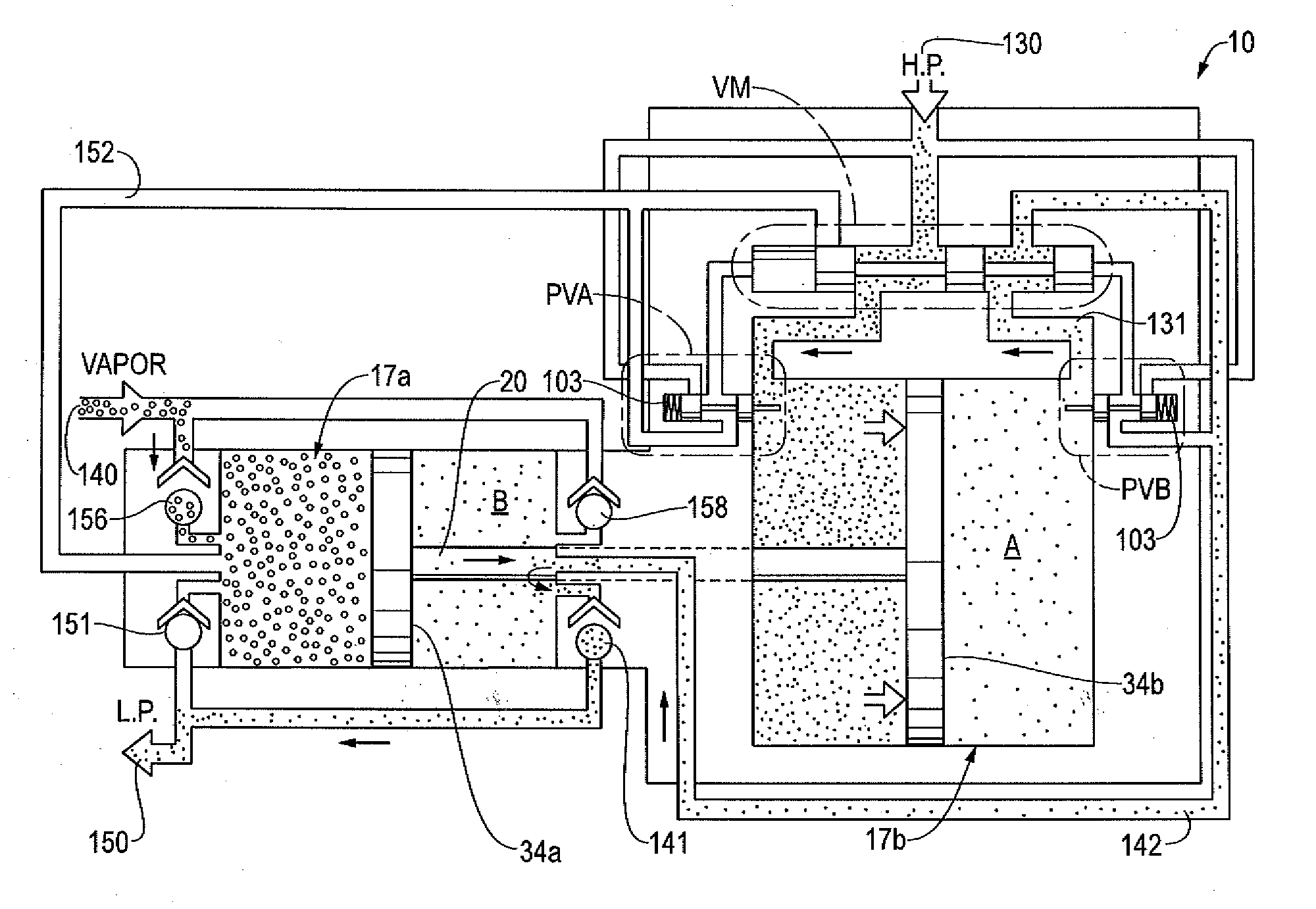
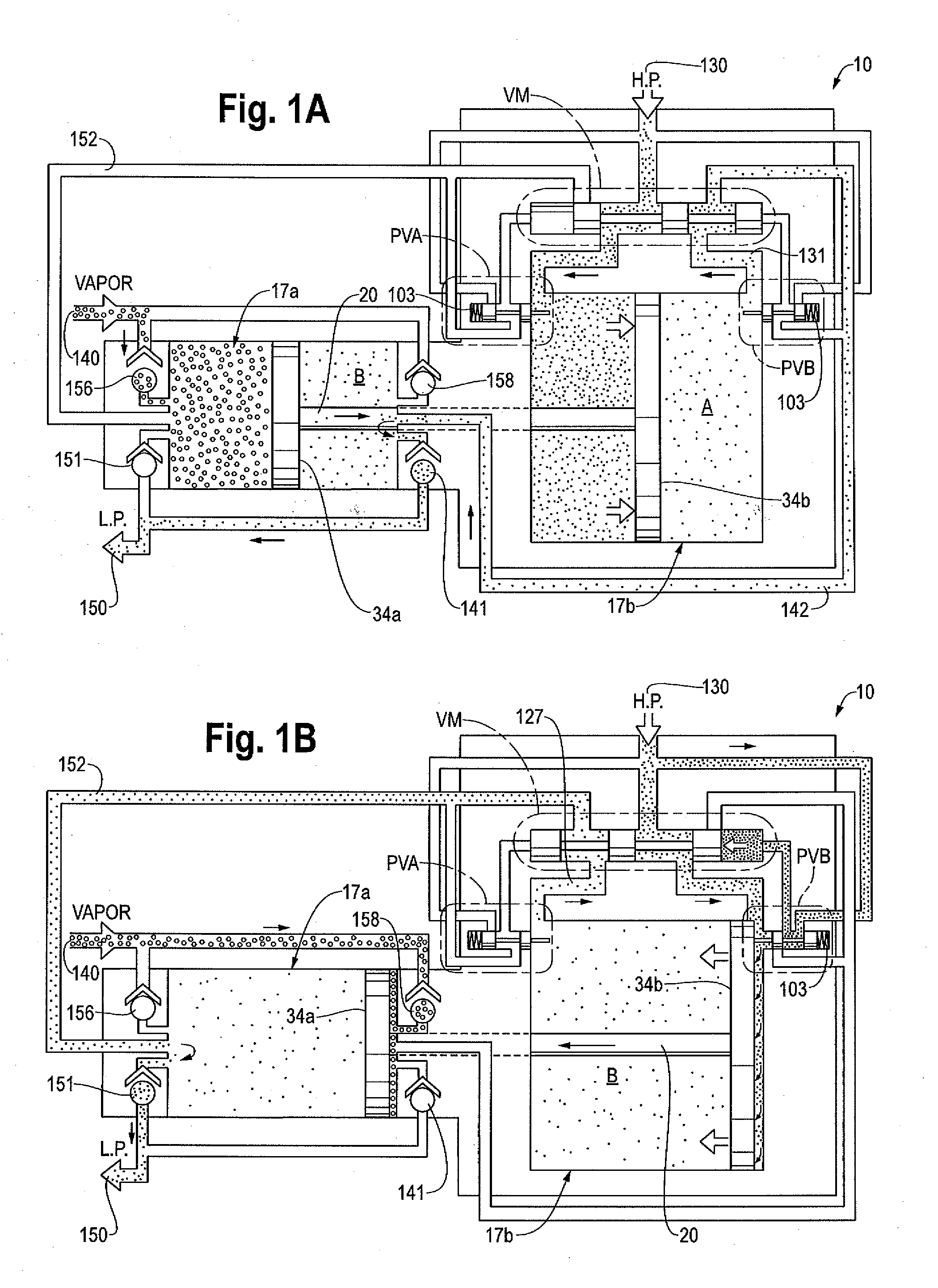
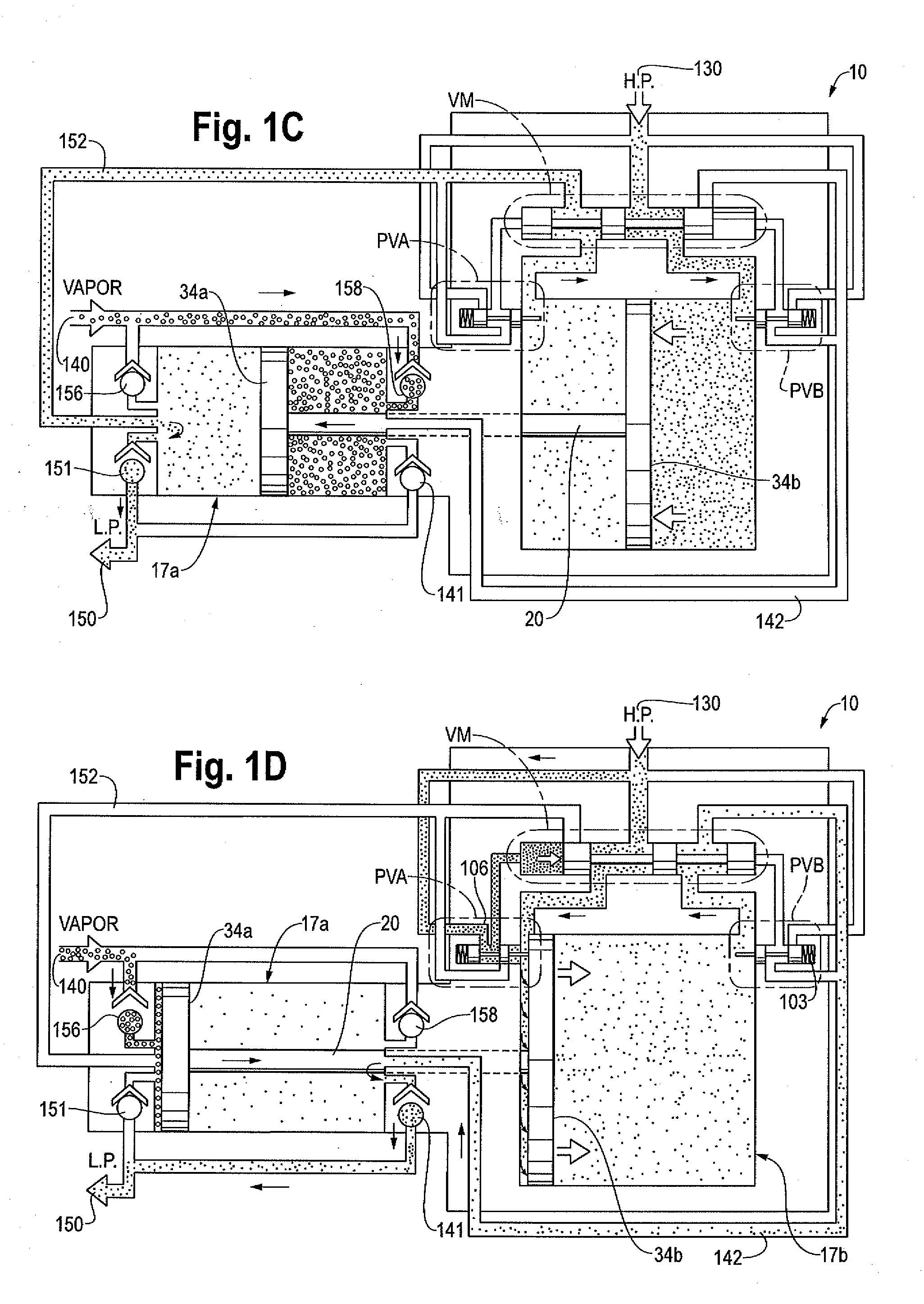
A gas pressure booster and a method for using it, which recovers fugitive gas emissions such as at atmospheric pressure, boosts them such as to the pressure level of the low pressure gas sink, and returns them to, e.g., the low pressure gas sink, in a single stage of compression. No electricity or cooling water is required. All gas used to drive the vapor recovery booster may be recovered and vented to the low pressure gas sink.In one preferred embodiment, the gas pressure booster includes a drive cylinder and a boost cylinder interconnected by reciprocating drive and boost pistons. The drive piston supplies force powered by a first gas stream within the drive cylinder which exhausts to a second gas stream at a lower pressure. Fugitive gas emissions may be captured and transported to the lower pressure second gas stream to eliminate gas discharged to atmosphere. The need for boosting a gas multiple ratios is eliminated, as the pressure of the fugitive emission vapor is equalized to the low pressure gas sink at the end of the piston suction stroke. Preferably, a four-way valve operating on differential gas pressure may be used to automatically actuate the reciprocating piston.
Owner:MIDWEST PRESSURE SYST
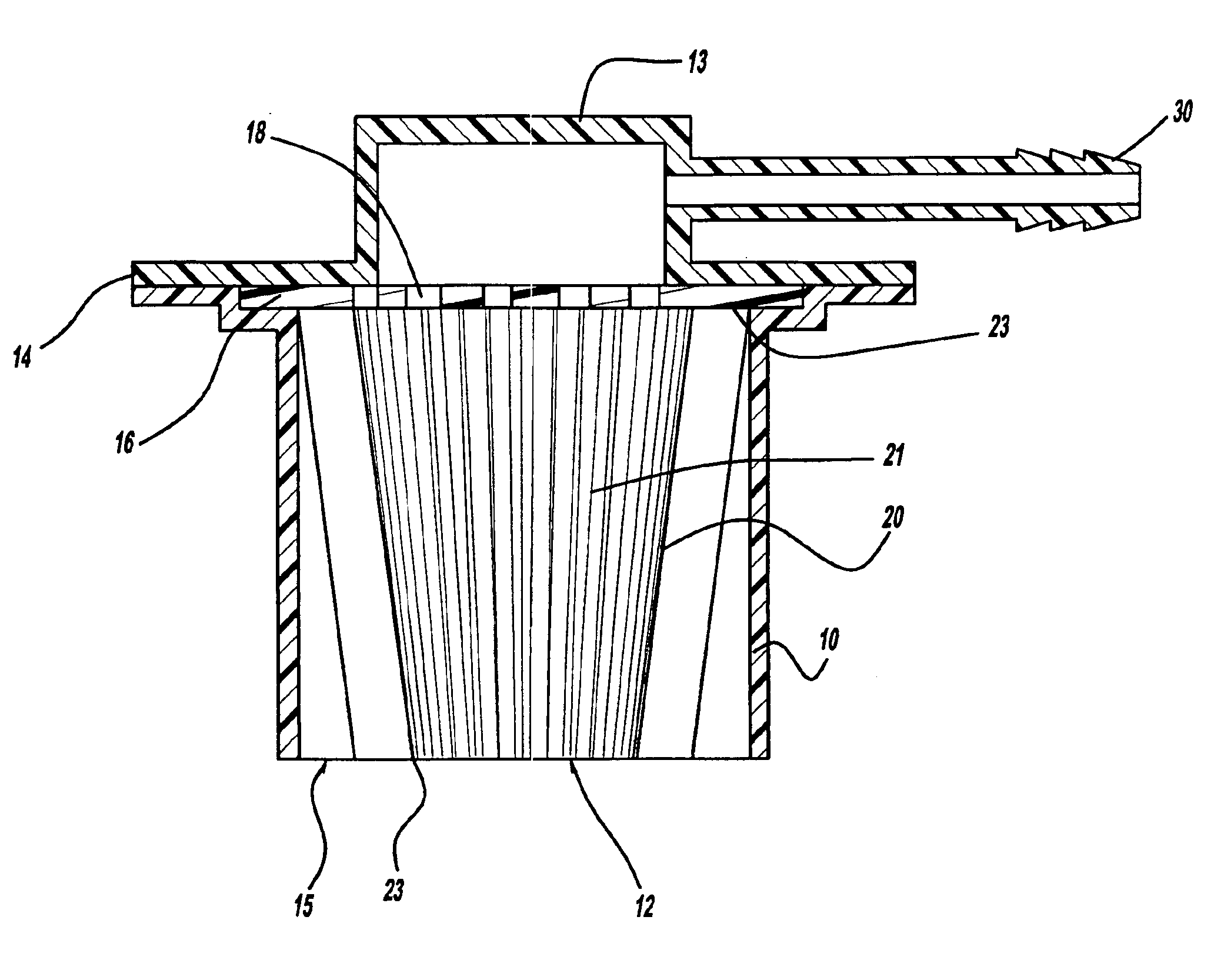
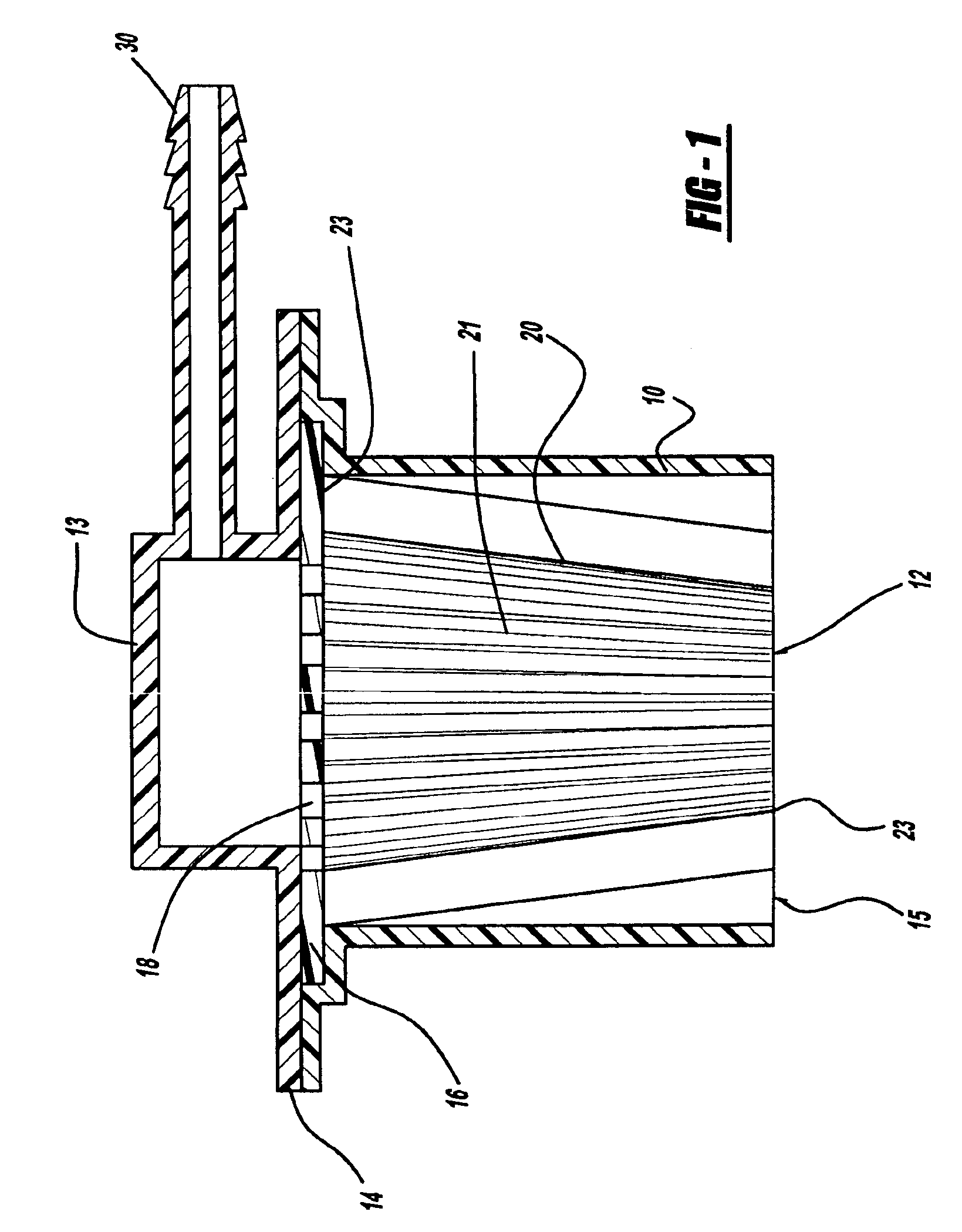
No-spill, vapor-recovery, container spout
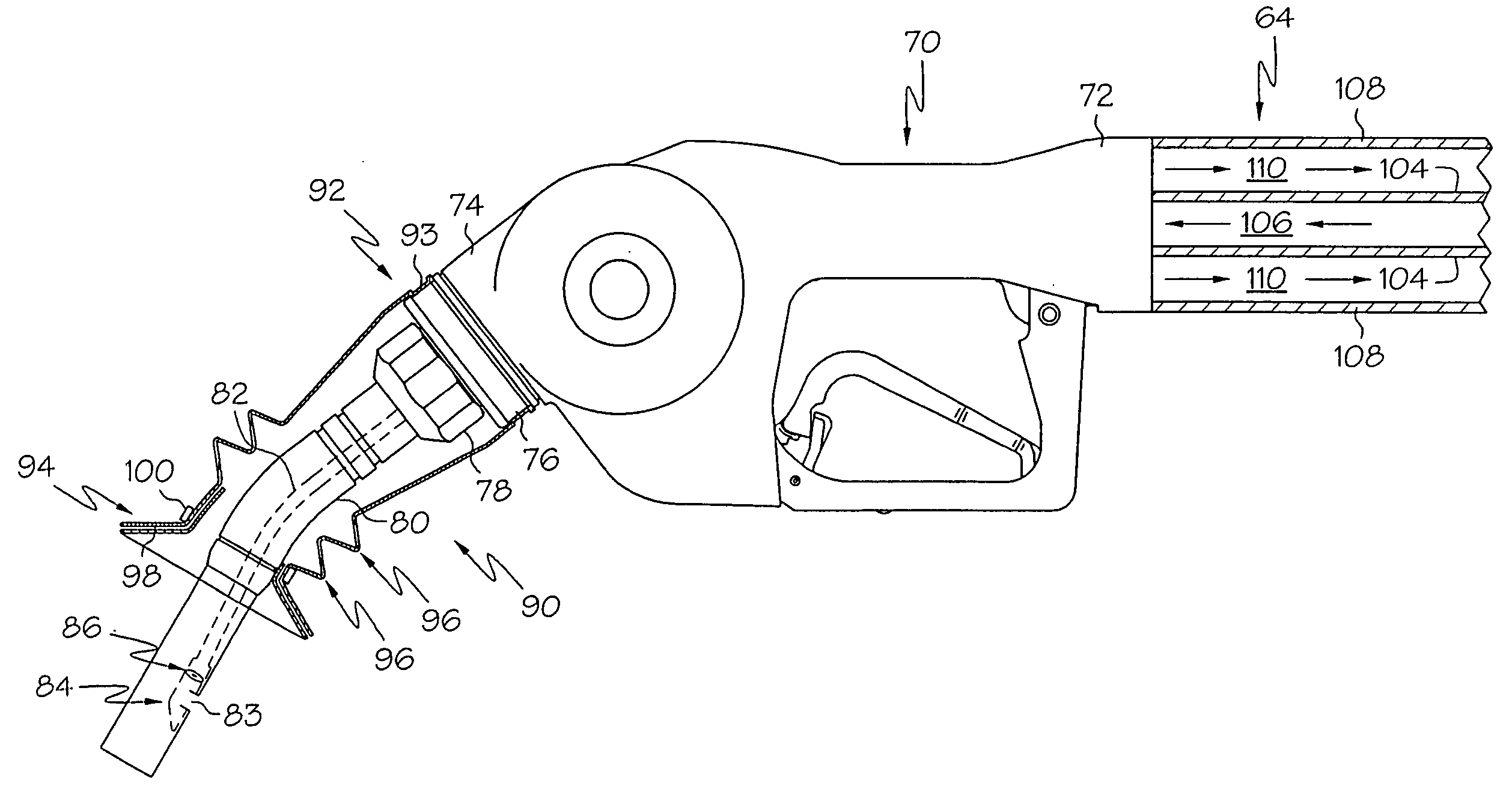
InactiveUS6889732B2Prevent escapeBarrels/casks fillingLiquid transferring devicesFuel tankEngineering
A vapor recovery spout for a portable fuel container. The spout includes an inner sleeve attached to the container to provide a fuel flow passage through the spout. The passage has an outlet port for fuel to flow through into a tank. A sliding sleeve is mounted on the inner sleeve for sliding axial movement from an outwardly extended position to a retracted position. A radially extending annular seal is mounted on the sliding sleeve for sealing the fuel tank opening when the spout is inserted. Vapor recovery passages are provided between the inner sleeve and the sliding sleeve for displaced vapor to flow from the tank to the container. The sliding sleeve closes the fuel passage and the vapor recovery passageways when in its extended position and opens the fuel passage and the vapor recovery passageways when in its retracted position. A spring urges the sliding sleeve to its extended position.
Owner:FLORENCE E ALLEN SUCCESSOR TRUSTEE OF THE CLIFFORD H ALLEN TRUST DATED JULY 22 1998
Vapor recovery system with ORVR compensation
A fuel dispenser with a booted nozzle for vapor recovery is modified to include check valves in a vapor return path. The check valves selectively allow atmospheric air into the vapor return path to alleviate nuisance shut offs at the nozzle when ORVR vehicle is being fueled. The check valves may be included anywhere in the vapor return path between the nozzle and the vapor recovery vacuum assist pump. The fuel dispenser may further include a pressure sensor in the vapor return line so that the fuel dispenser can determine if the vehicle is an ORVR vehicle or not. If the fuel dispenser determines that an ORVR vehicle is present, the fuel dispenser may modify the operation of the vapor recovery system.
Owner:VEEDER ROOT
Fueling system vapor recovery and containment leak detection system and method
InactiveUS6901786B2Shut downDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateProcess engineeringLeak detection
A method and apparatus for monitoring a fuel vapor recovery system to determine if a leak condition exists in either the vapor return passage in a fuel dispenser or a common vapor return pipe. An air-flow sensor (AFS) may be located in the common vapor return pipe for all of the dispensing points at a service station, or in each fuel dispenser and coupled to the dispensing points of the fuel dispenser. The AFS registers vapor flow recovered by a dispensing point(s) that is returned back to the storage tank. If the AFS measures vapor flow when such dispensing point(s) coupled to such AFS is not actively recovering vapor, this is indicative of a leak in such dispensing point(s). The leak condition is reported by a tank monitor or other reporting system so that appropriate measures can be taken.
Owner:VEEDER ROOT
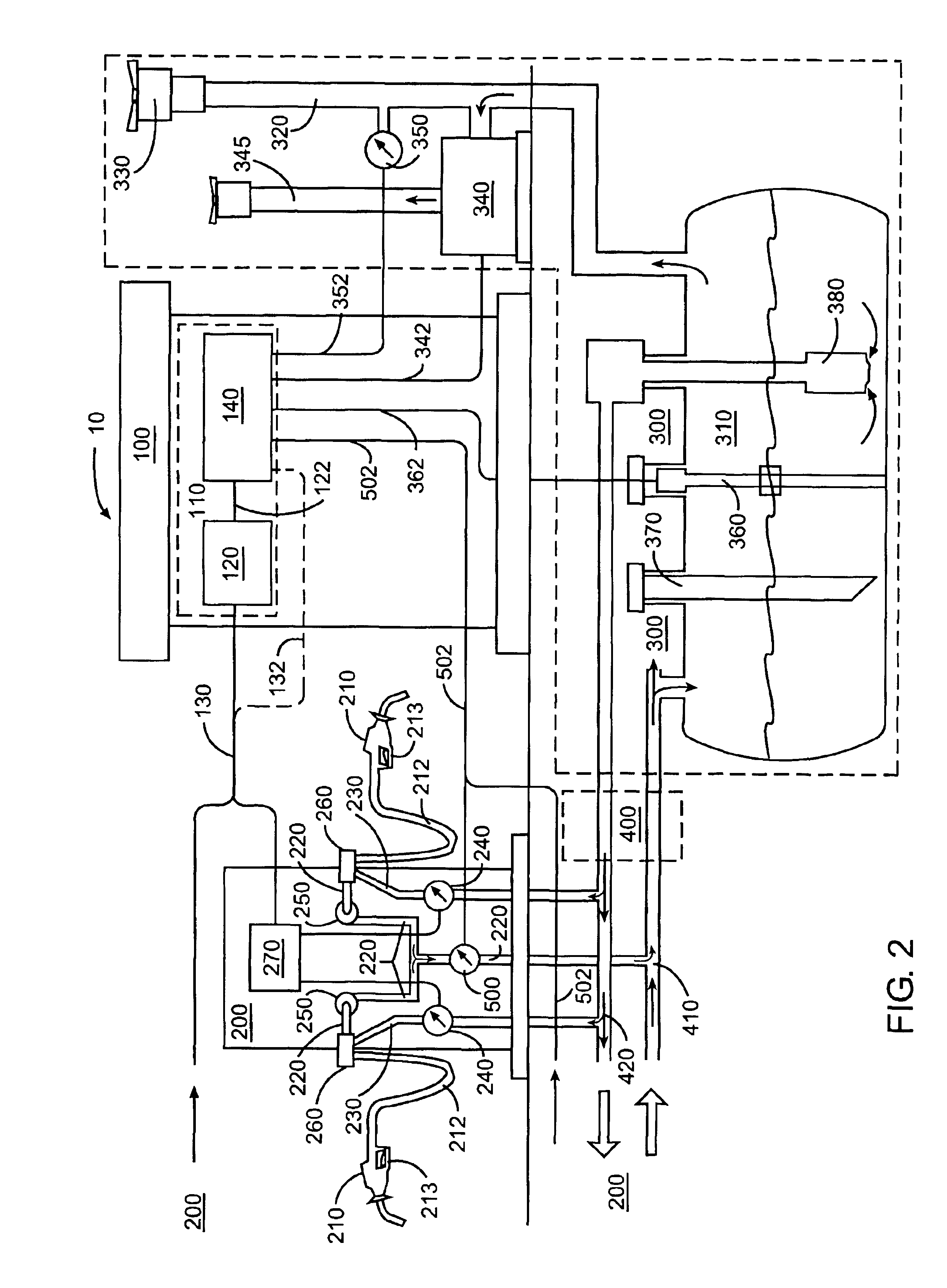
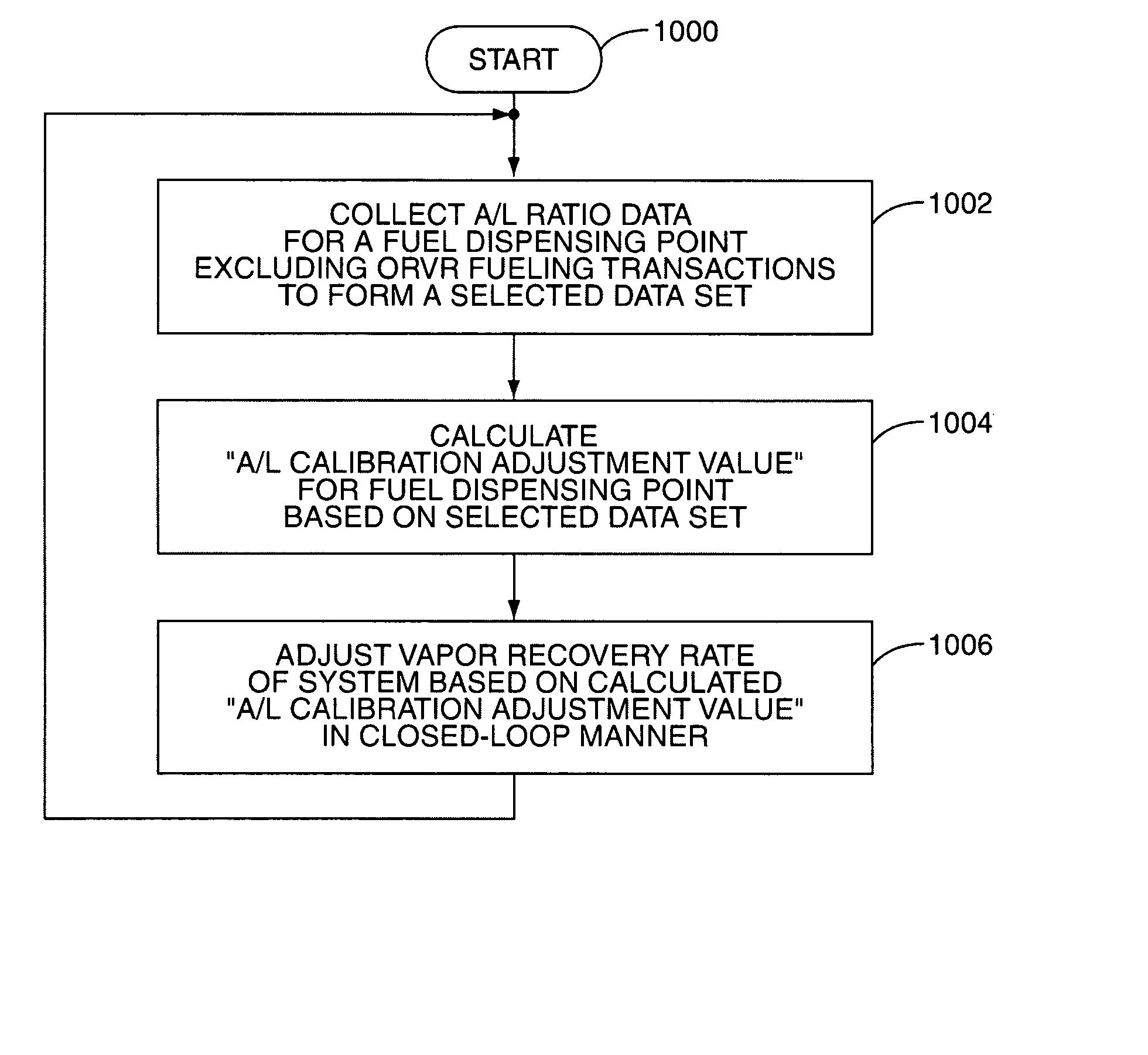
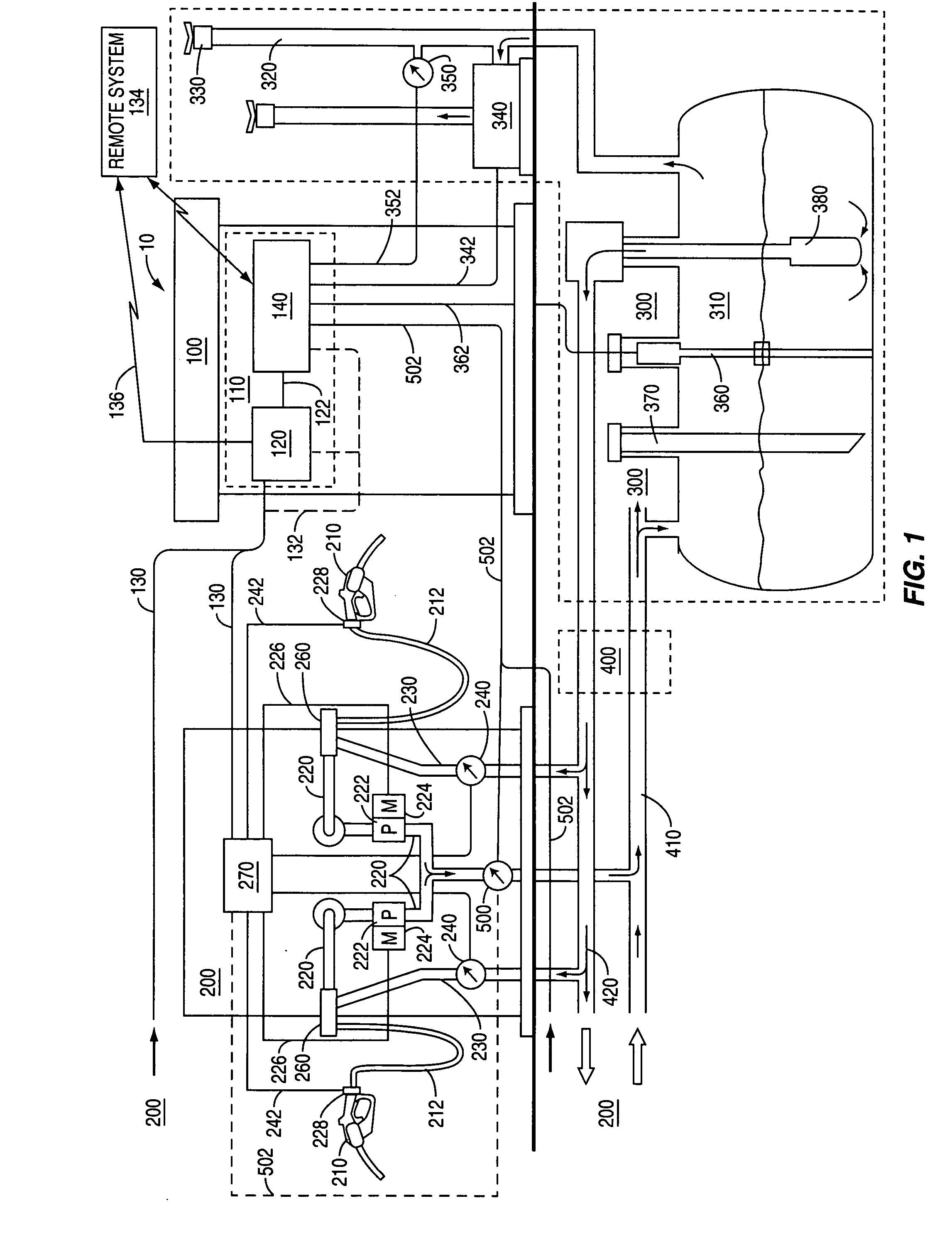
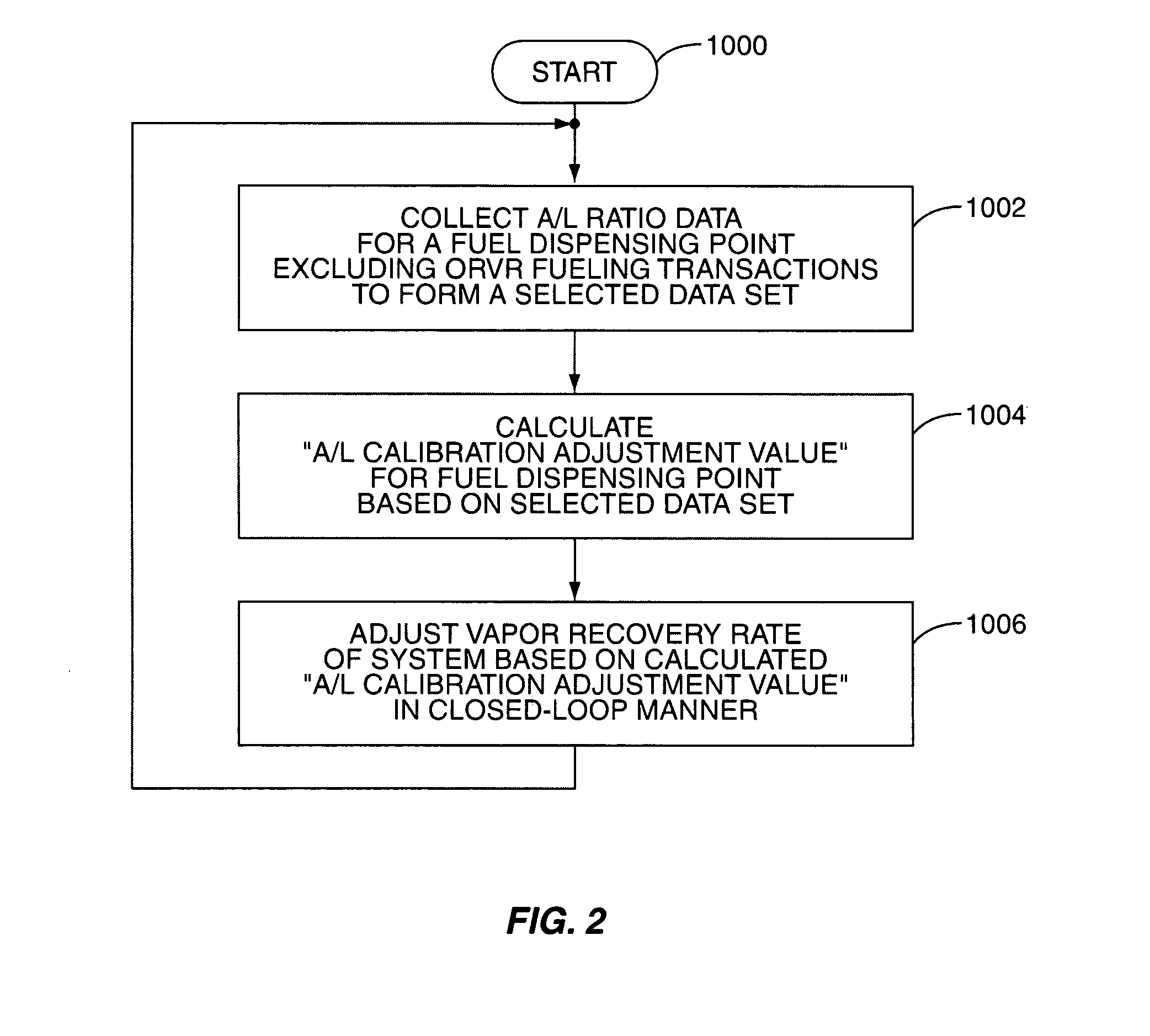
System and method for automatically adjusting an ORVR compatible stage II vapor recovery system to maintain a desired air-to-liquid (A/L) ratio
ActiveUS20070267088A1Effective recoveryLiquid transferring devicesPackaging under special atmospheric conditionsProcess engineeringFinancial transaction
A system and method for automatically adjusting an ORVR-compatible Stage II vapor recovery system to maintain the air-to-liquid (A / L) ratio within desired tolerances or limits to meet regulatory and / or other requirements. An air flow sensor (AFS) or vapor flow meter measures the amount of recovered vapor for a dispensing point to calculate the recovery efficiency of the system in the form of the A / L ratio. Volume or flow rate measurements can be used. ORVR fueling transactions are either minimized or excluded from the A / L ratio, so that the A / L ratio is not artificially lowered due to a blocked or altered recovery. The A / L ratio is then compared to a desired or nominal A / L ratio. Adjustments to the recovery system are made within prescribed safety tolerances if the A / L ratio differs from the desired ratio.
Owner:VEEDER ROOT
Flue gas waste heat recovery and negative energy consumption dust-removal system for electric stove
InactiveCN101539369AEasy to recycleSave on wear and maintenance costsDispersed particle filtrationIncreasing energy efficiencyCombustion chamberEvaporation
The invention relates to a flue gas waste heat recovery and negative energy consumption dust-removal system for an electric stove, comprising a first flue gas dust-removal and waste heat recovery system for the electric stove which is connected with the smoke hole of the electric stove to absorb high temperature flue gas generated by the electric stove during smelting phase and a secondary flue gas dust-removal system for the electric stove which is in charge of absorbing the flue gas generated by the electric stove during charging and tapping phase. The first flue gas dust-removal and waste heat recovery system for the electric stove comprises a water cooling travelling tube, an evaporation cooling device, a high temperature resistant dust remover, a waste heat boiler, a dust removal fan and a chimney; wherein the evaporation cooling device replaces the original water cooling flue gas path and combustor. The secondary flue gas dust-removal system for the electric stove comprises a collecting cover, a dust remover worked at normal temperature, a dust removal fan and a chimney. The invention is high in dust removal efficiency and high in vapor recovery rate, saves a first cooling device and a secondary cooling device, reduces device investment and maintenance charge and prolongs the service life of the filter pocket of the dust remover.
Owner:BAOSTEEL ENG & TECH GRP
Vapor recovery system
A vapor recovery apparatus for oil and gas well production that is used in combination with a liquid separator, a sales line and a holding tank includes a compressor, which is drivingly linked to an engine. A first conduit extends from fluid communication with the holding tank to a compressor inlet, while a second conduit extends from a compressor outlet to fluid communication with the sales line. The vapor recovery apparatus also has an electronic controller that is connected to the engine and to a pressure sensor, which is in fluid communication with the gas in the tank.
Owner:ELECTRONICS DESIGN FOR IND
Refueling vapor recovery system
Owner:TI GRP AUTOMOTIVE SYST LLC
Liquid Hydrocarbon Slug Containing Vapor Recovery System
ActiveUS20090223246A1Flow on effectPrevent condensation and liquificationSolidificationLiquefactionProcess systemsLiquid state
A liquid hydrocarbon slug-containing vessel for incorporation into a system integrating a low-pressure separator with a vapor recovery process system, and a method for regulating the temperature of a gas to be compressed by a two stage compressor so as to prevent liquification of the gas and to prevent over-heating of the compressor.
Owner:HEATH RODNEY T +2
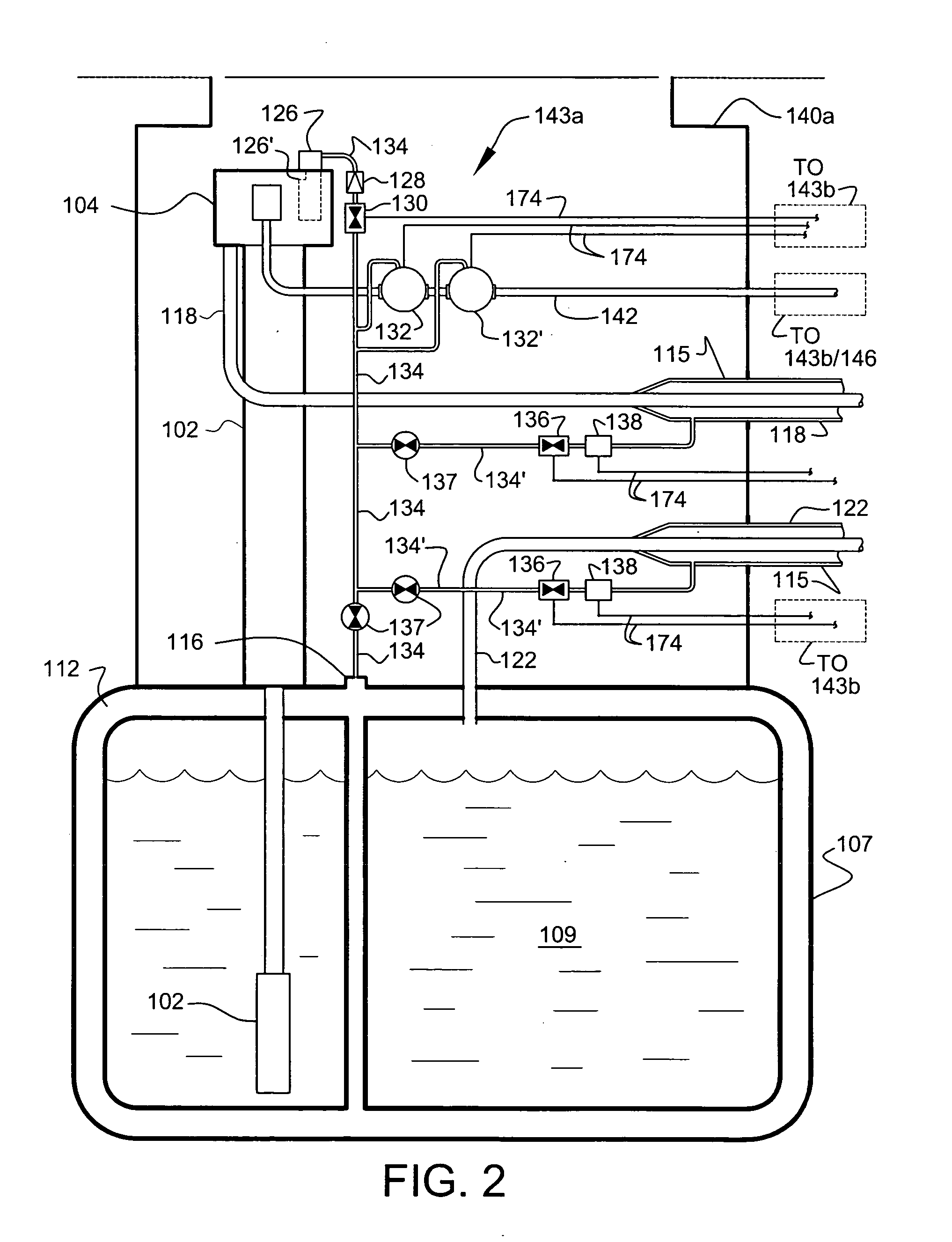
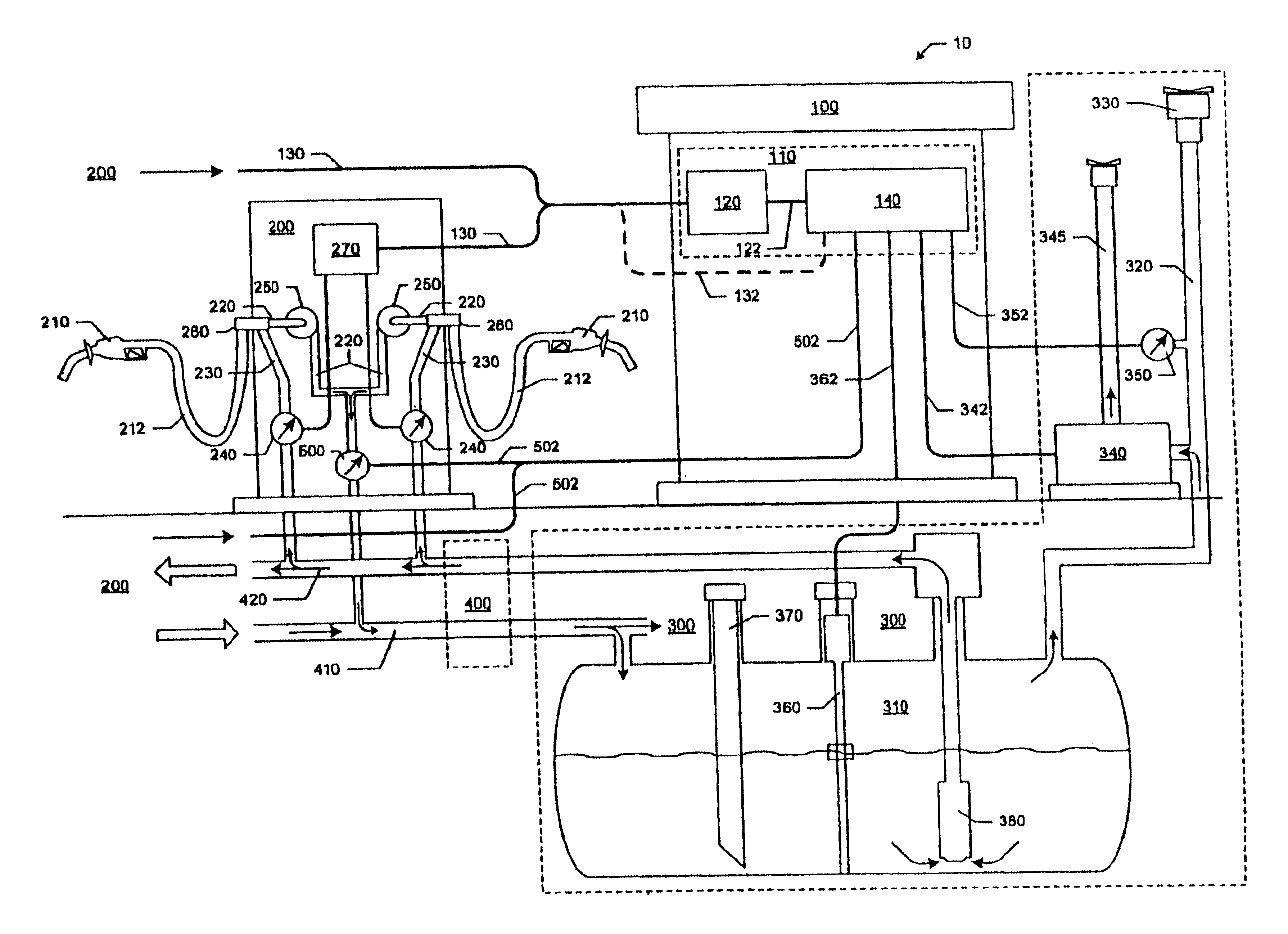
Fuel storage and dispensing system
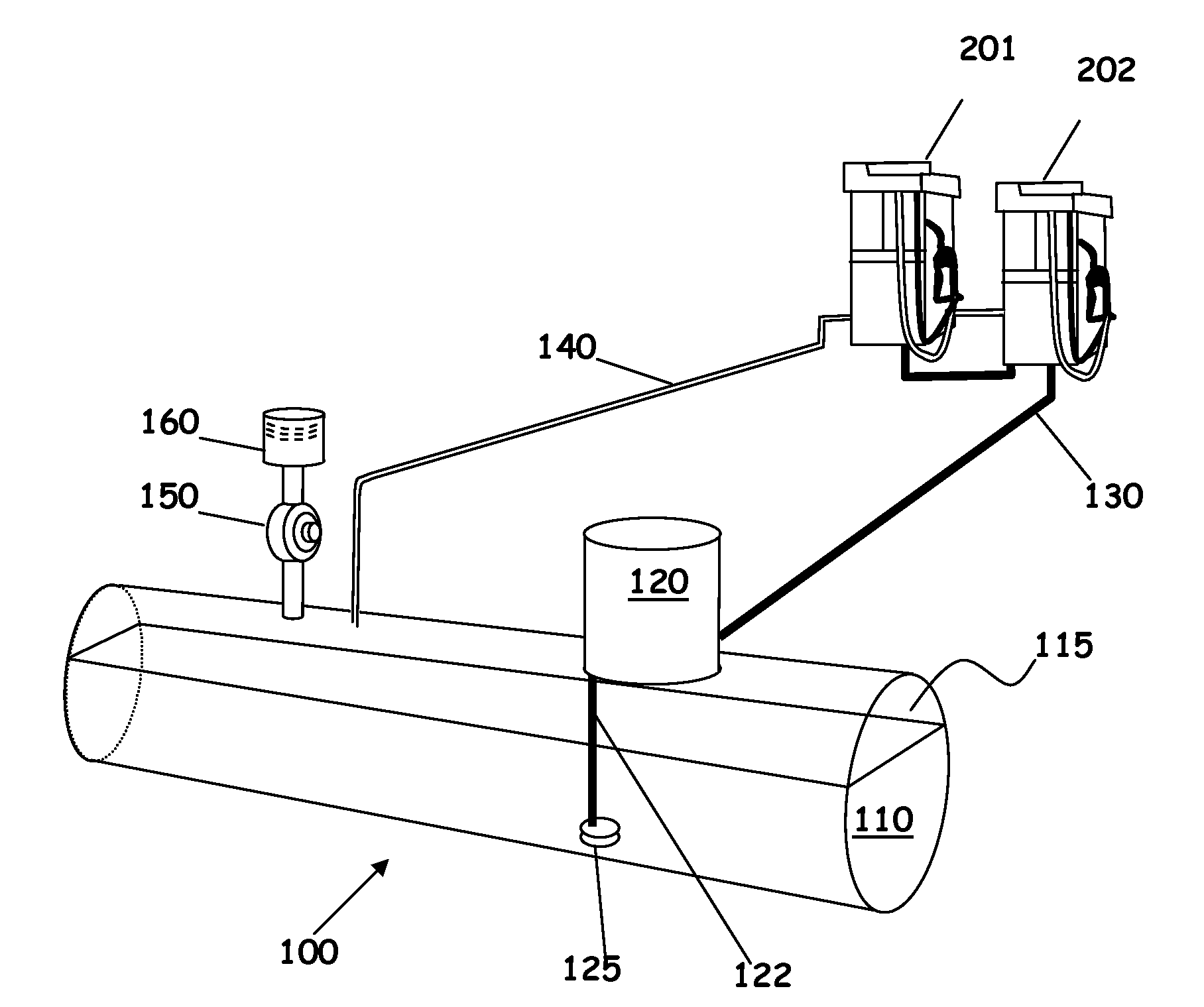
InactiveUS20050056340A1Emission reductionFull recoveryMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFilter systemStorage tank
A fuel storage and dispensing system is provided that is effective in reducing the emission of harmful volatile organic compounds. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a fuel storage and dispensing system is provided comprising at least one storage tank, an air exhaust port, at least one fuel dispenser, a fuel dispensing nozzle, a rigid, fuel dispensing spout, a boot, a pressure relief chamber, a filter system, and at least one pump. The rigid, fuel dispensing spout further defines a non-coaxial fuel tube. The boot is configured to maintain a sufficient level of vacuum within the fuel storage and dispensing system. The boot is further configured to prevent fresh air from entering the fuel dispensing nozzle. The present invention also includes additional embodiments including a pressure relief chamber that is effective in compensating for high temperature pressure build-up in a vapor assist hose, a fuel dispensing nozzle and spout assembly, a vapor recovery boot assembly, and a Venturi shut-off assembly for a fuel dispensing nozzle and spout.
Owner:VAPOR SYST TECH
Increased sensitivity for liquid meter
A lower cost meter comprised of an inner housing constructed out of a high permeable material surrounded by an outer housing constructed out of a lower cost, lower permeable material. A port is placed in the outer housing that runs down to the surface of the inner housing to detect the rotation of a rotational component that rotates inside the meter as fluid or gas flows through the meter. A sensor is placed in the port to detect rotation of the rotational component through the lower permeable material inner housing . The lower cost meter can be used for any application for measuring fluid or gas, and may be used in a service station environment for measuring fuel or vapor in vapor recovery applications.
Owner:GILBARCO
Method for preparing granular active carbon for gasoline vapor recovery by using oil tea shells
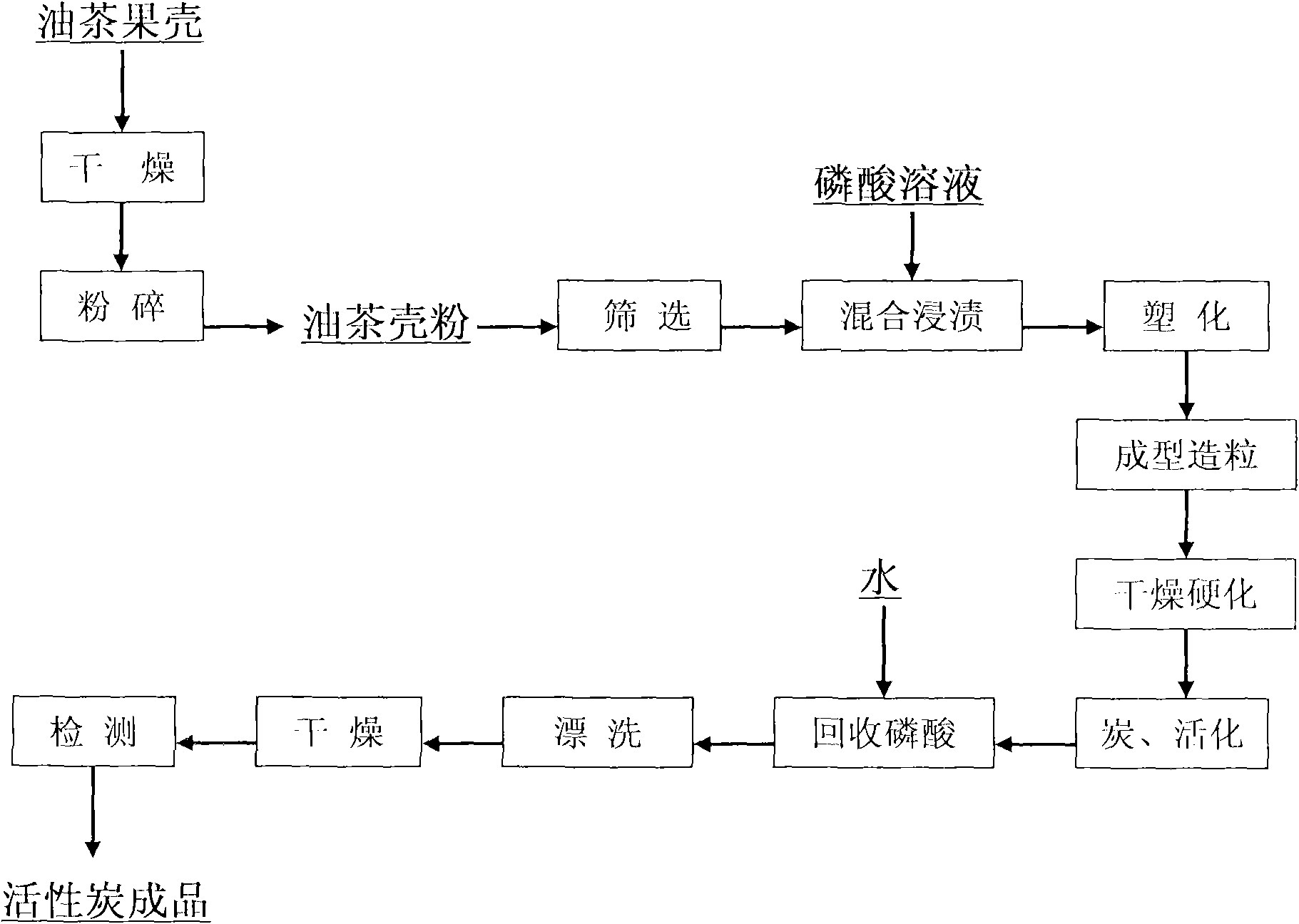
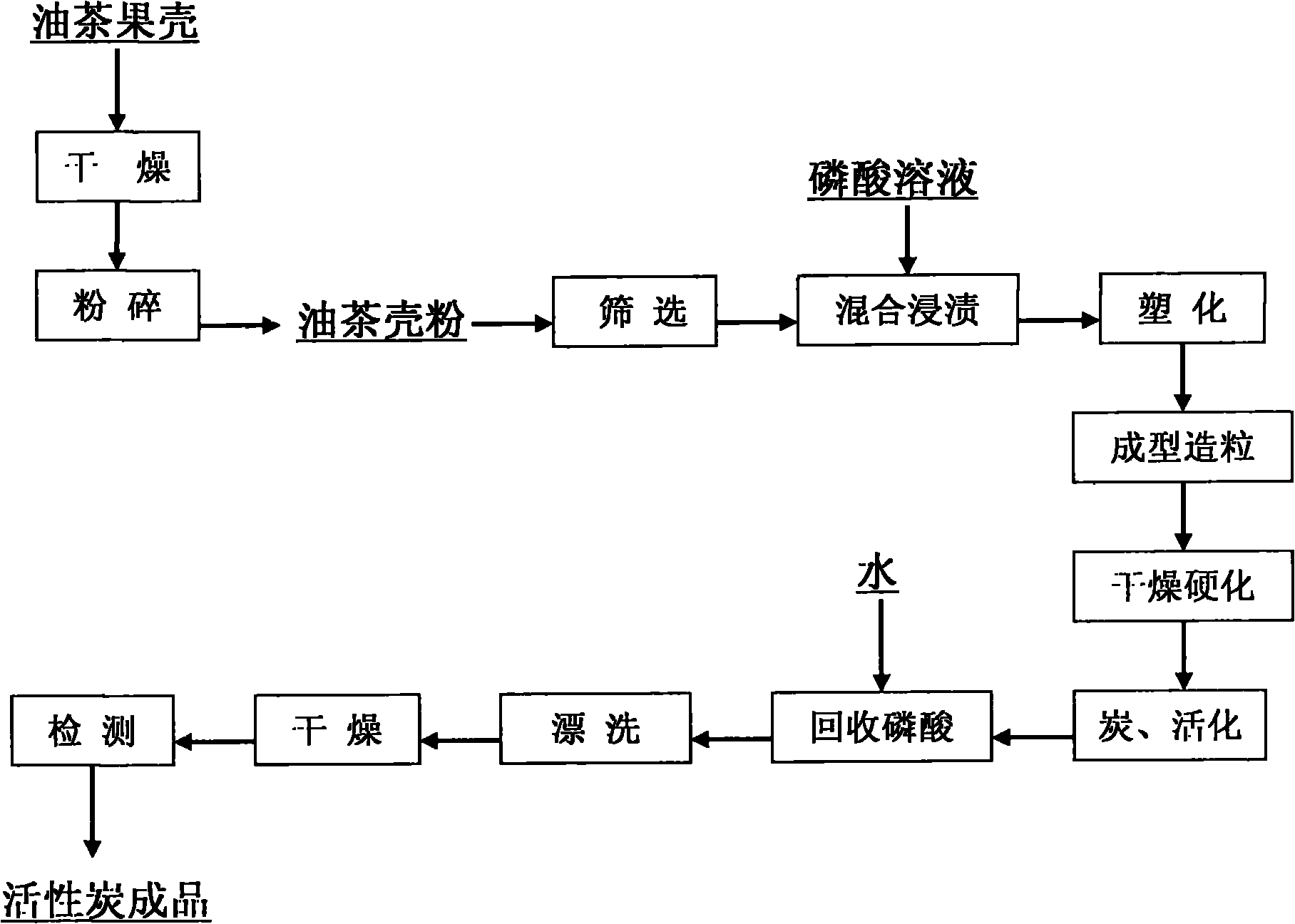
The invention discloses a method for preparing granular active carbon for gasoline vapor recovery by using oil tea shells as raw materials and phosphoric acid as an active agent. The method comprises the following steps of: drying, crushing and screening the oil tea shells to prepare oil tea shell powder with a certain fineness; mixing the oil tea shell powder with60 to 85 percent phosphoric acid solution in a ratio of 1:2-3, soaking for a certain period of time, and standing the mixed solution in a constant temperature oven for plasticized treatment at the temperature of between 90 and 100 DEG C so as to produce cohesive tar; putting the plasticized materials in a screw extrusion molding machine to prepare cylindrical granules with the diameter of 2 to 3 mm and the length of 5 to 10 mm, and drying and hardening the cylindrical granules at the temperature of between 110 and 120 DEG C; activating the cylindrical granules in activating equipment at the temperature of between 450 and 550 DEG C so as to prepare activated materials, washing the activated materials by using a proper amount of water so as to recover the phosphoric acid, and bleaching repeatedly by using water until the PH value of the bleaching solution is between 5 and 7; and finally drying and detecting to prepare the granular active carbon for gasoline vapor recovery.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD
Control of vapor emissions from gasoline stations
ActiveUS20090056827A1Enhance vapor-liquid equilibriumMinimize emission levelGas treatmentIsotope separationActivated carbonSorbent
The present invention relates to a vapor recovery system for gas station that is capable of controlling vapor emission to less than 0.38 lbs / 1000 gallons fuel dispensed. The system may include at least one canister containing adsorbents such as activated carbon, zeolite, activated alumina, silica, and other adsorbents for passive removal of hydrocarbon vapors in venting air. Additionally, the system may include a means to enhance vapor-liquid equilibrium in the ullage of the fuel tank and accordingly minimize vapor emission level.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Enhanced vapor containment and monitoring
InactiveUS20050080589A1Improve integrityFlexibility and vendor optionInflated body pressure measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesGasoline
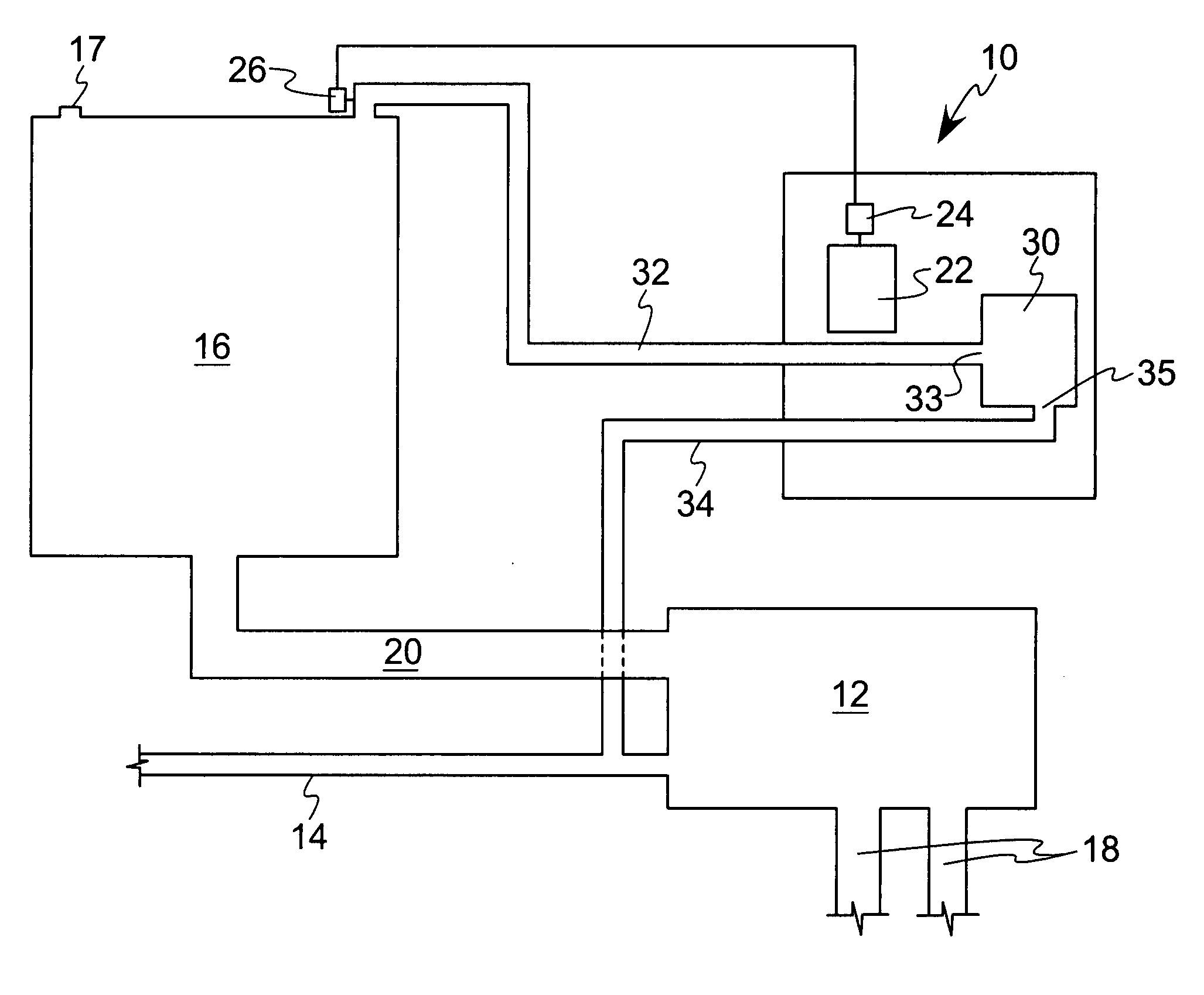
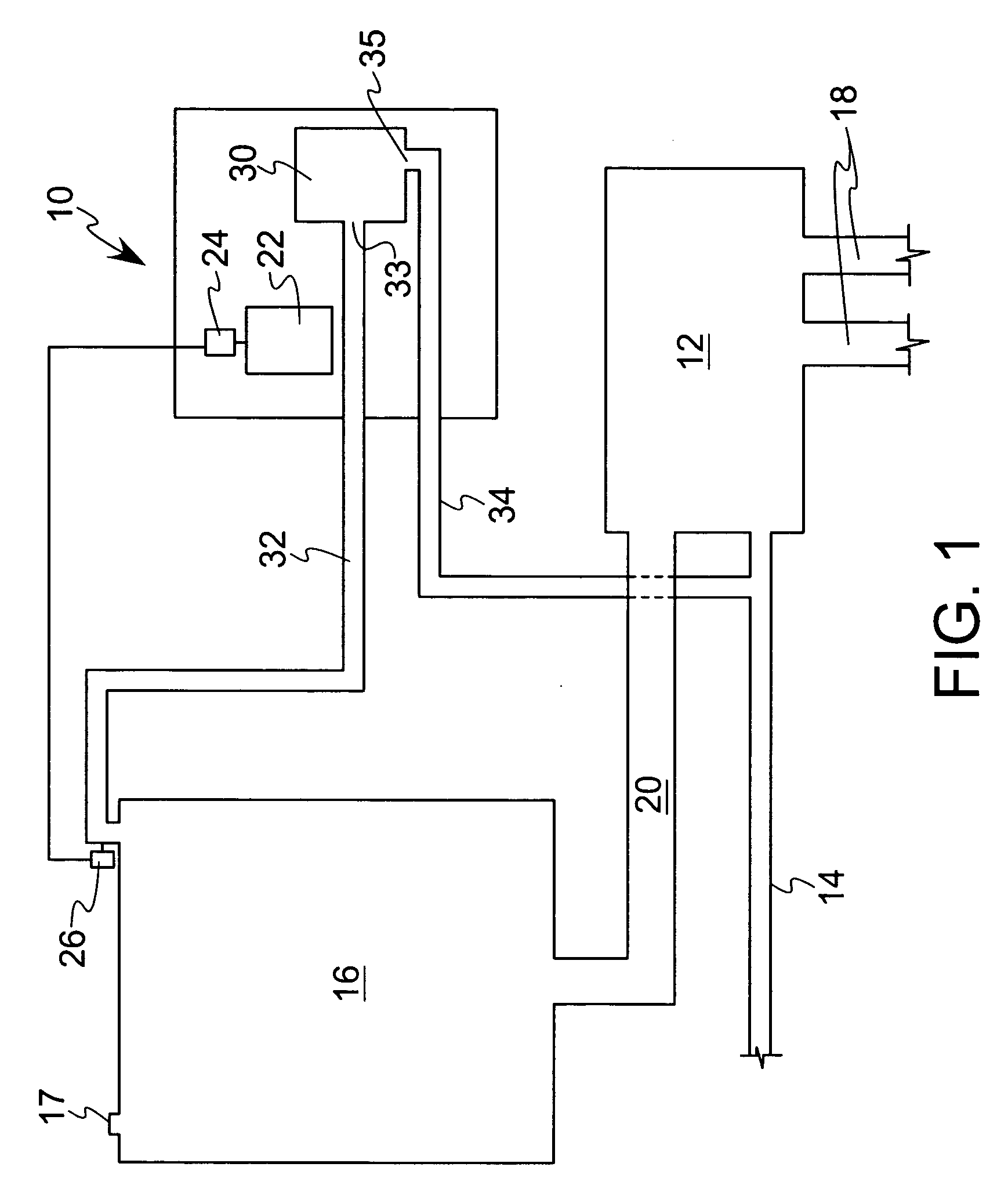
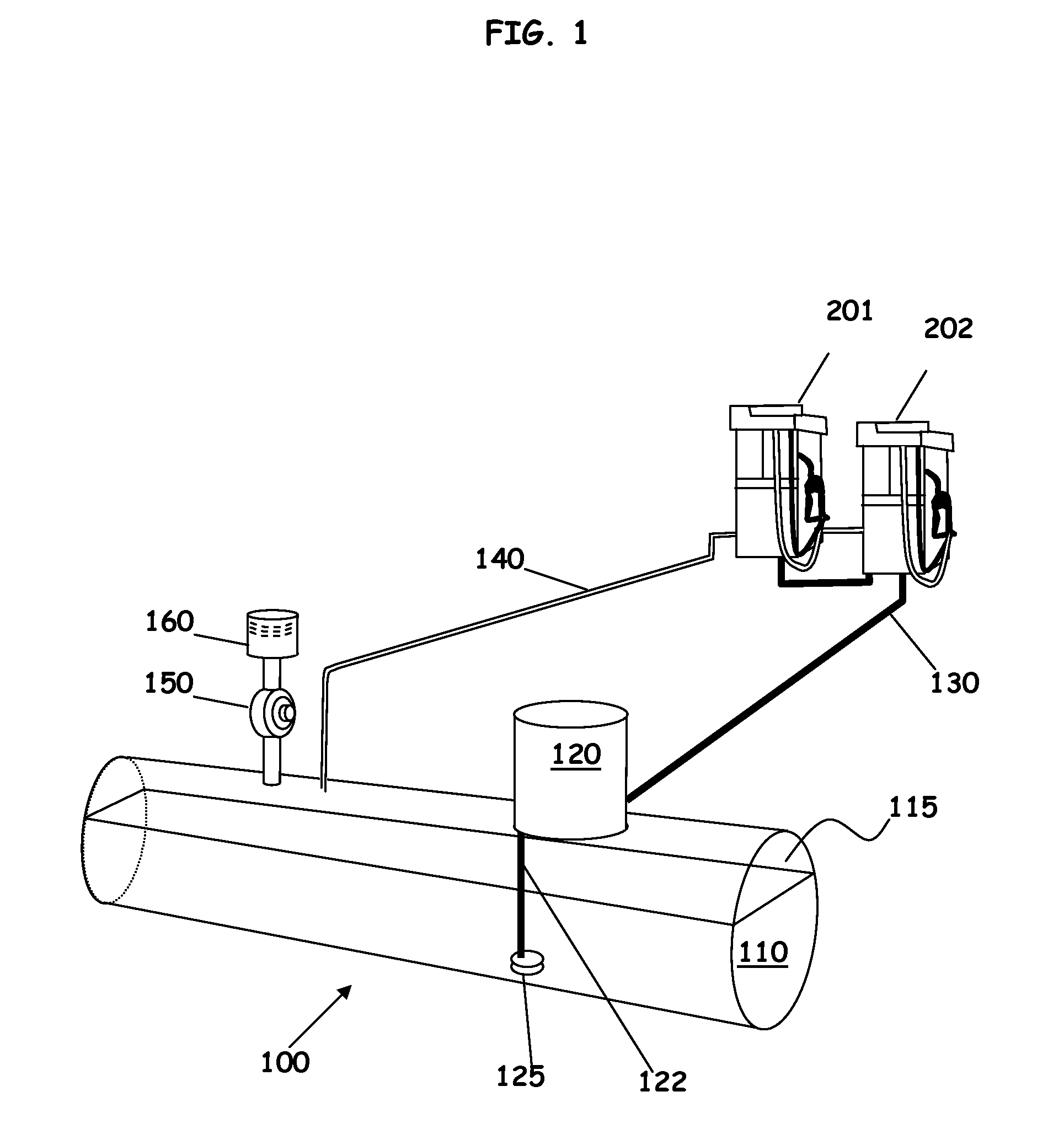
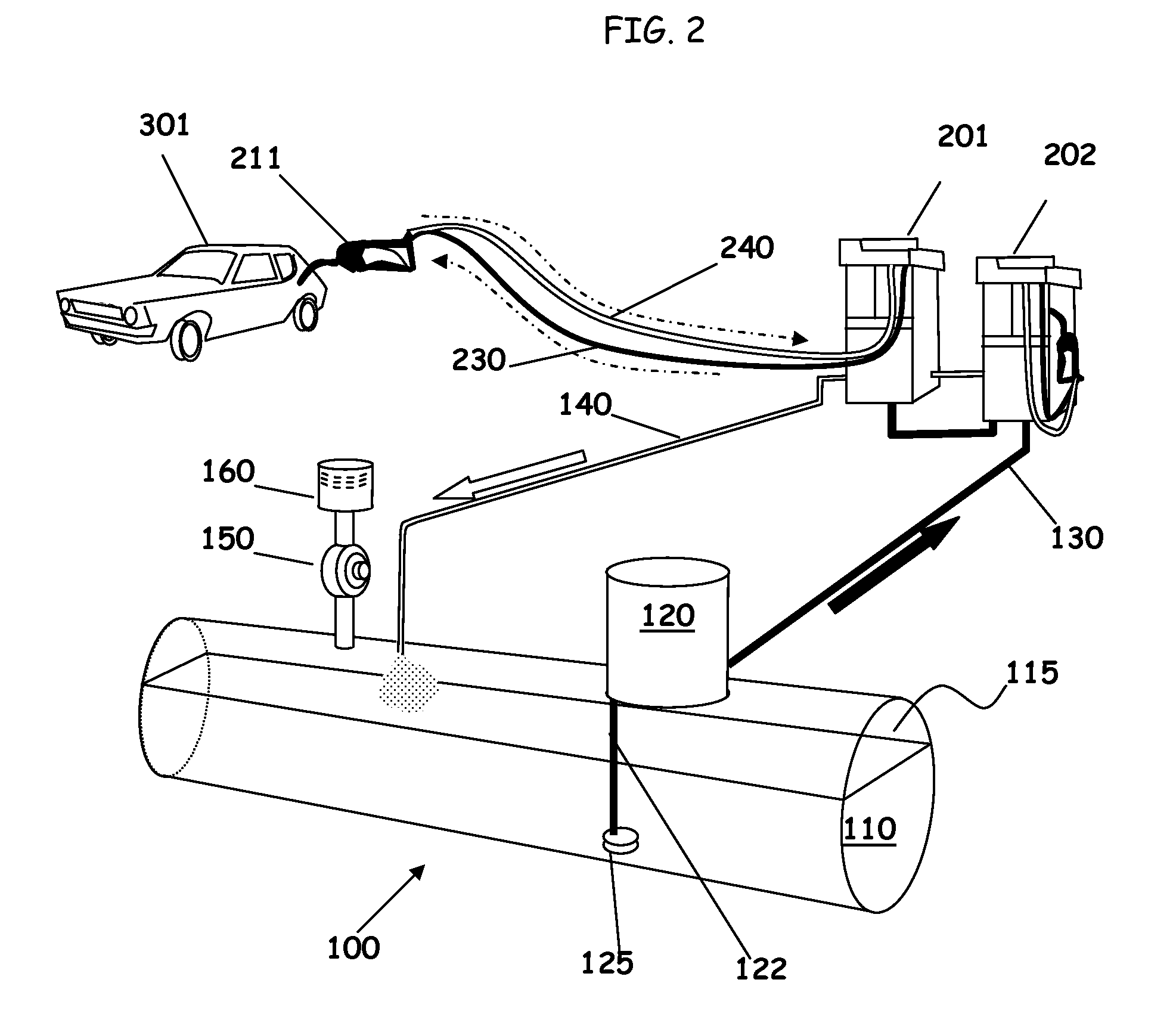
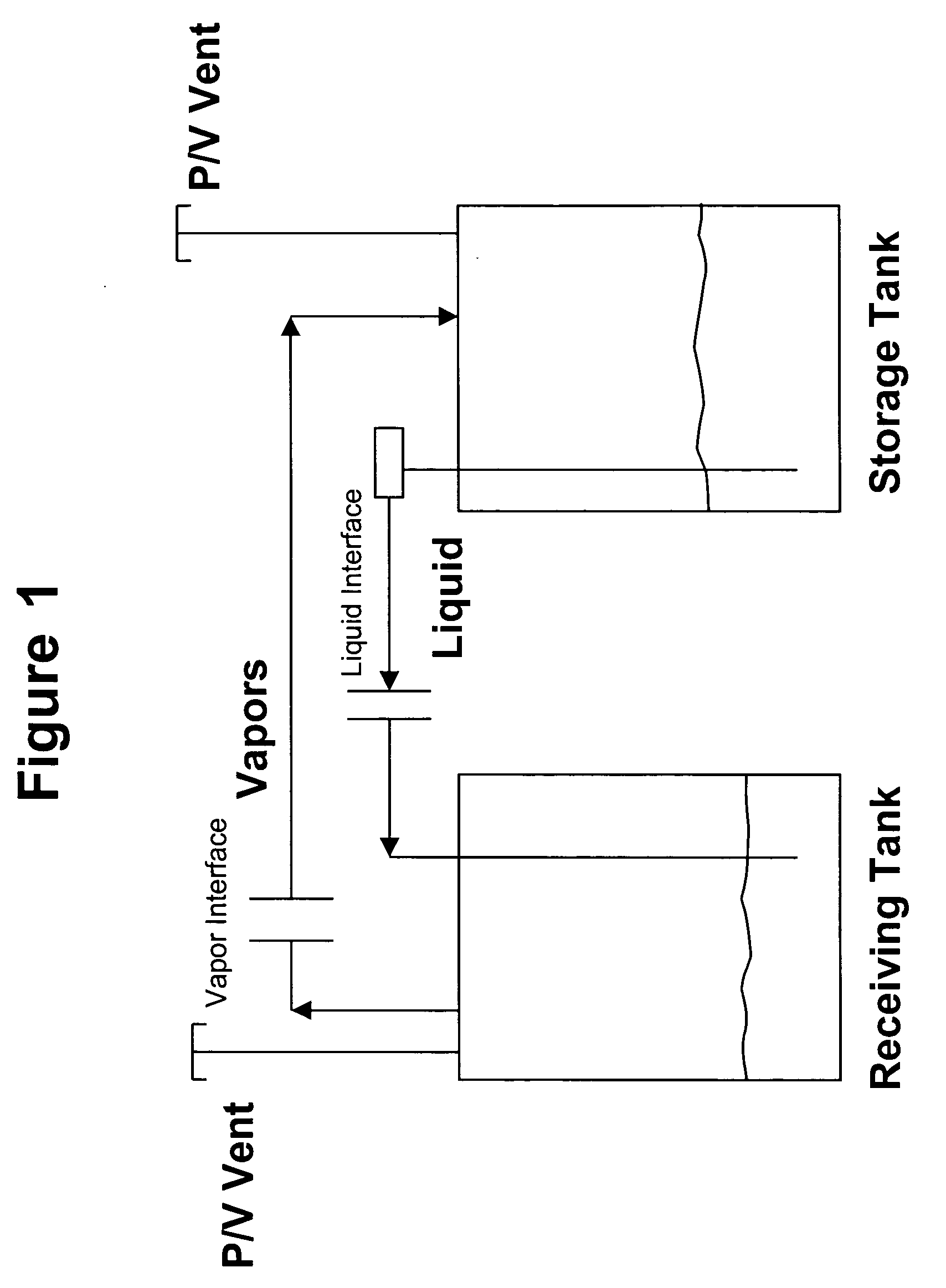
An apparatus and method for ensuring effective and efficient vehicle vapor recovery performance, storage tank system integrity relative to both vapor and liquid containment and for reducing the probability that inaccurate information causes companies to undertake unnecessary, expensive and wasteful loss investigations at gasoline dispensing facilities. A fuel storage and delivery system is transformed from an “open system” communicating directly with the environment to a “closed system” which ensures capture, containment and accurate accounting of both hydrocarbon vapors and liquid phase product.
Owner:TIBERI TEDMUND P
Non-contact Sludge Drying System With Flue Gas Heat
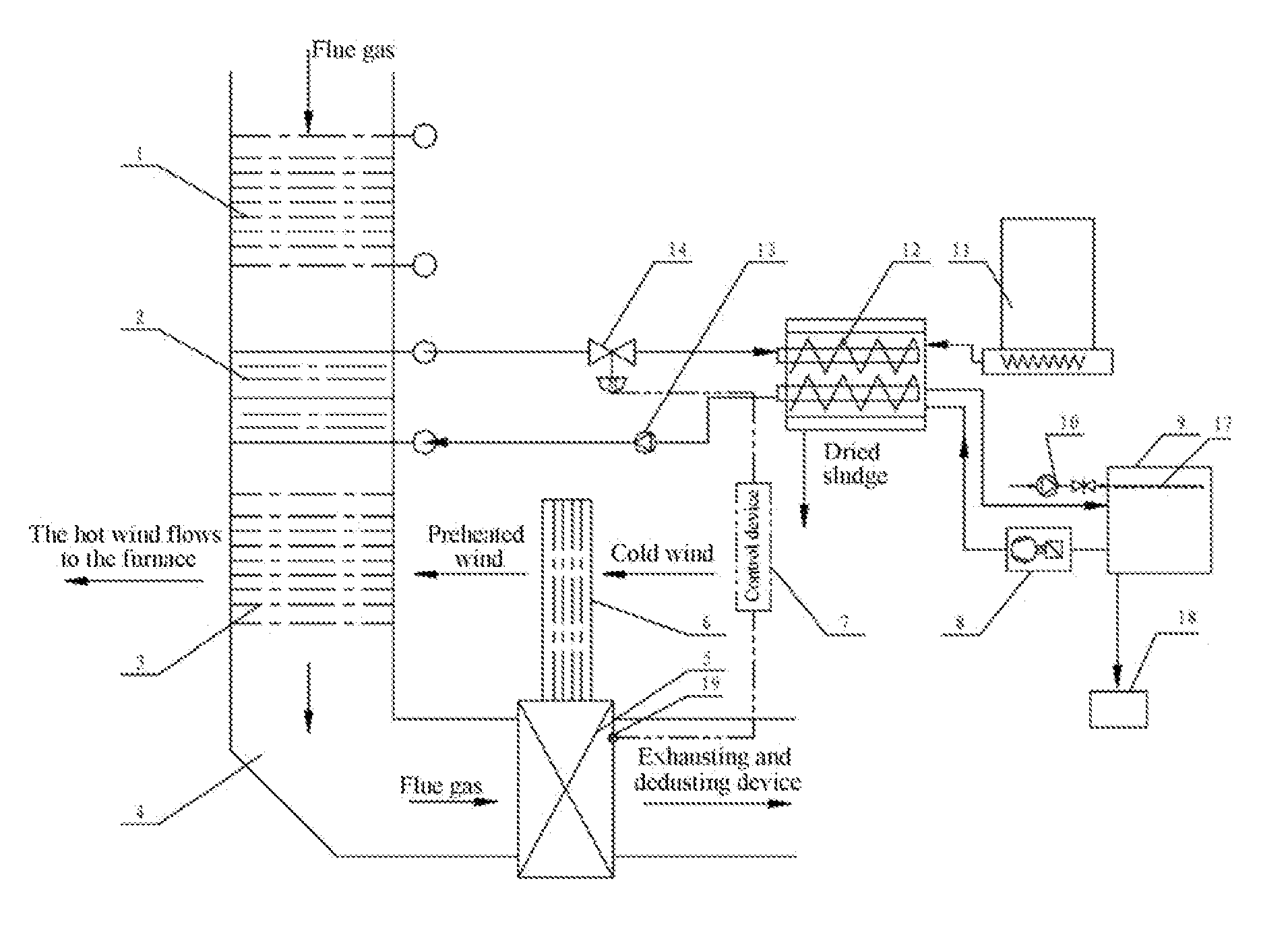
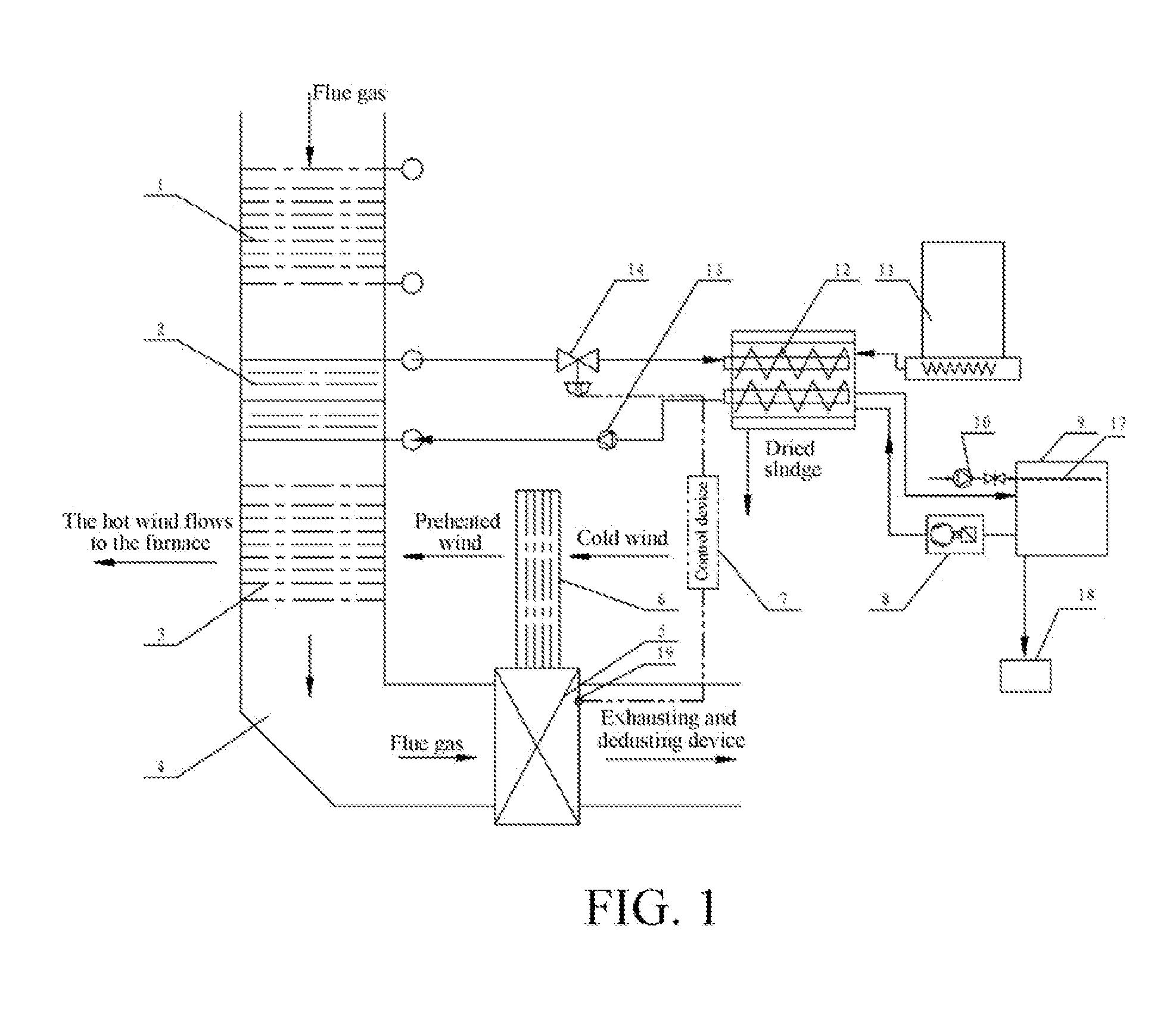
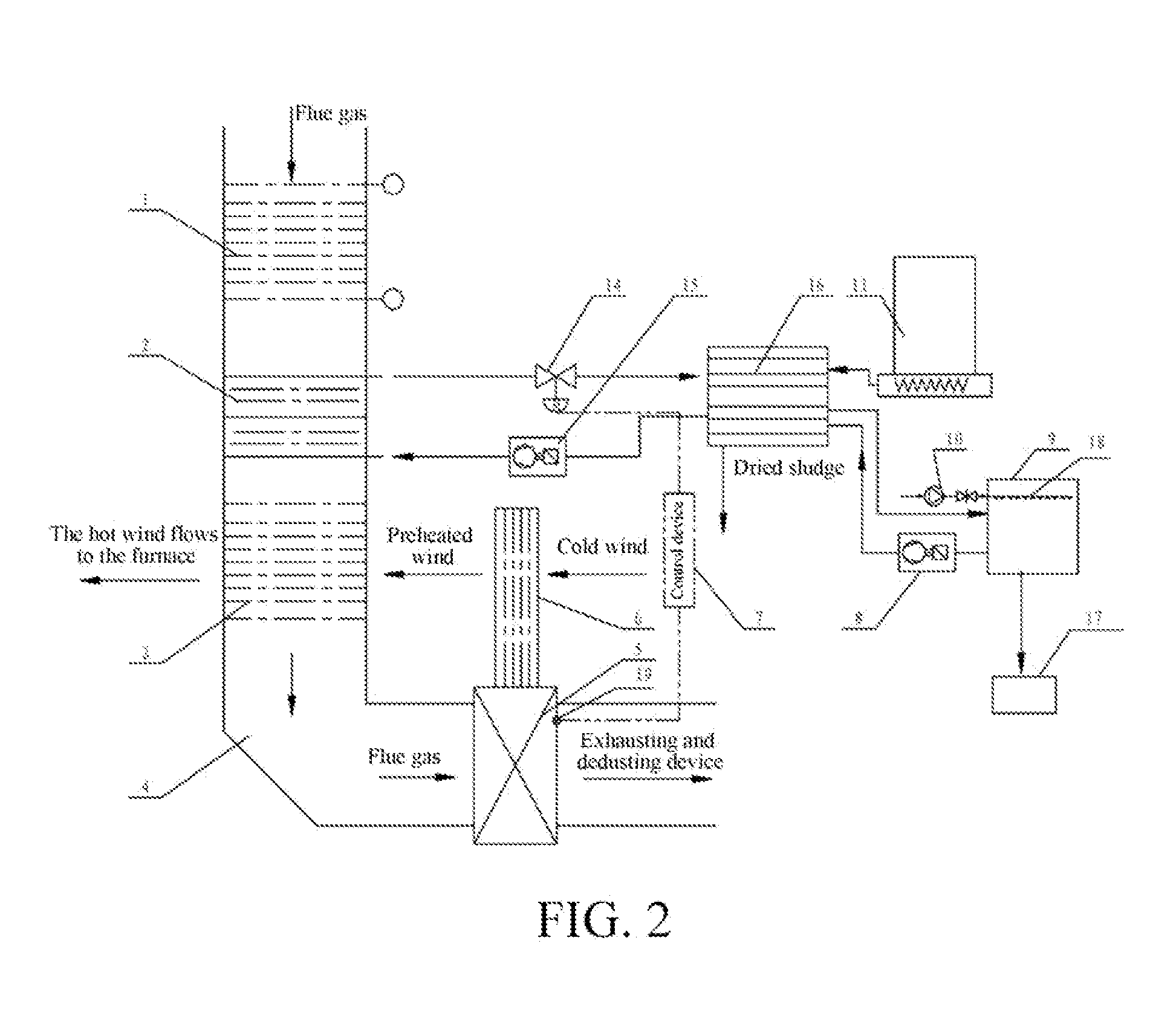
InactiveUS20130305554A1Reduce energy consumptionMaximize useSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge dryingAir preheaterSludge
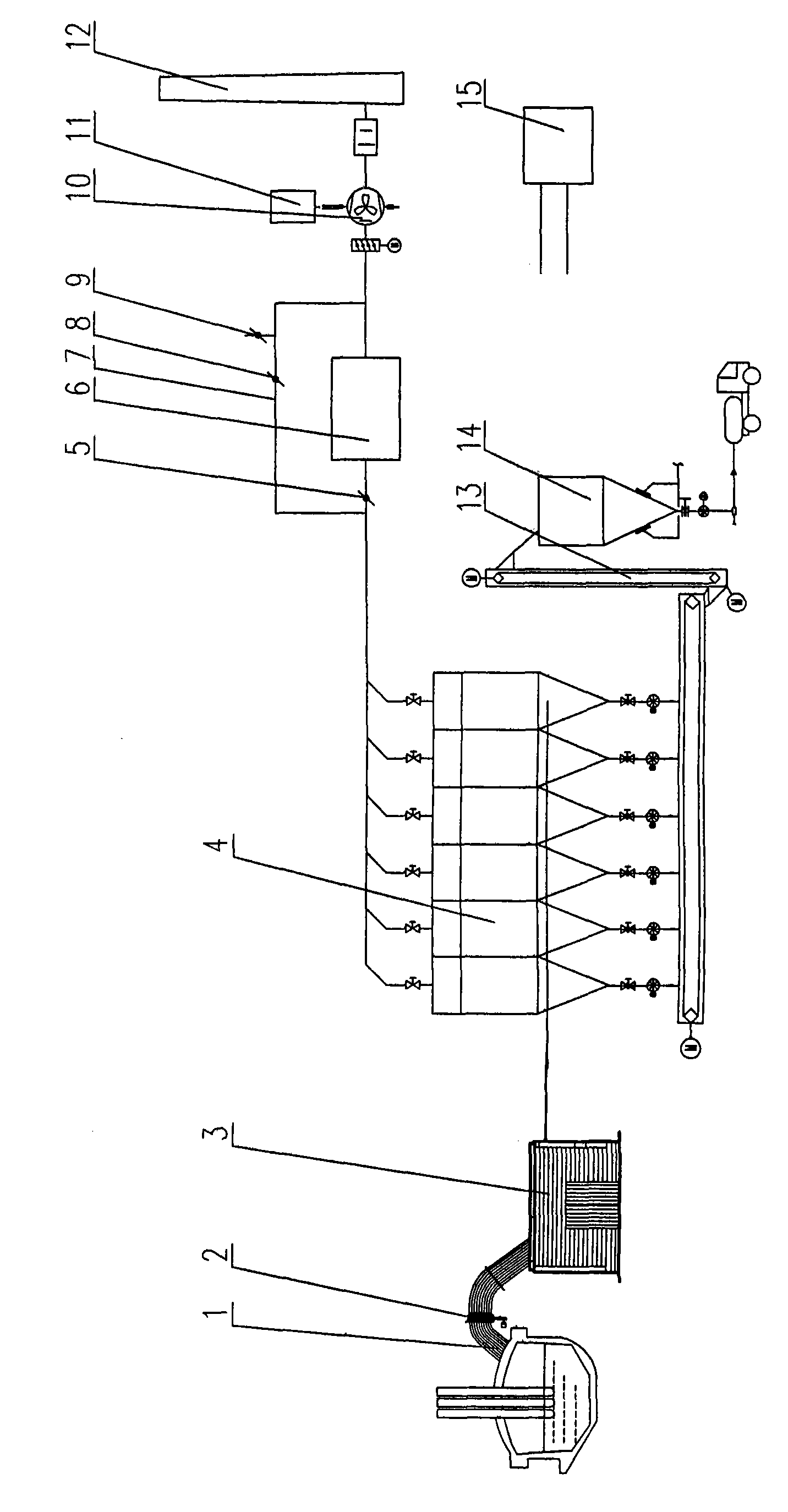
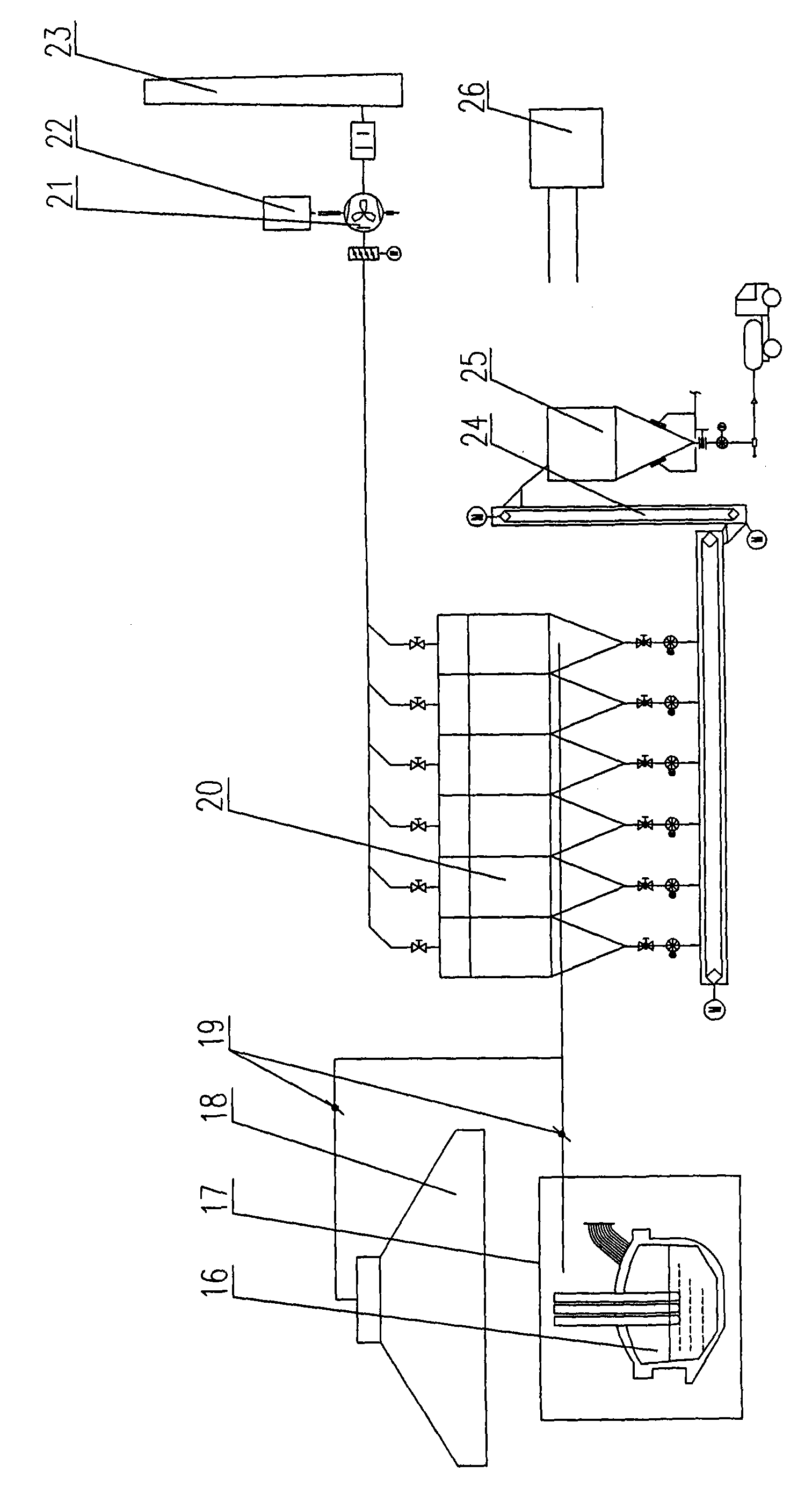
A non-contact sludge drying system with flue gas heat according to the present invention includes a dryer, and further includes an economizer, a high-temperature flue gas heat recovery device, and an air preheater that are successively disposed in the flue along a flue gas flowing direction. A heater is disposed in the dryer, the high-temperature flue gas heat recovery device is connected to the heater by a circulation pipe, a heat transfer medium is disposed in the circulation pipe, a heat transfer medium driving device is disposed on the circulation pipe, and the dryer is connected to a sludge vapor recovery system. The non-contact sludge drying system with flue gas heat according to the present invention uses the flue gas heat from a thermal power plant boiler or another industrial boiler as a heat source to further dehydrate and dry the dehydrated sludge of the sewage treatment plant, so that the dried sludge can be used as a fuel with certain heat of combustion or composted for further treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUBO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com