Particle board and method of making the same
a technology of particle board and particle board, which is applied in the field of particle board, can solve the problems of creating visually identifiable voids, unfavorable water resistance, and developing moulds and the decomposition of wooden components,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1
[0053] A particle board according to embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described referring to FIGS. 1 to 8.
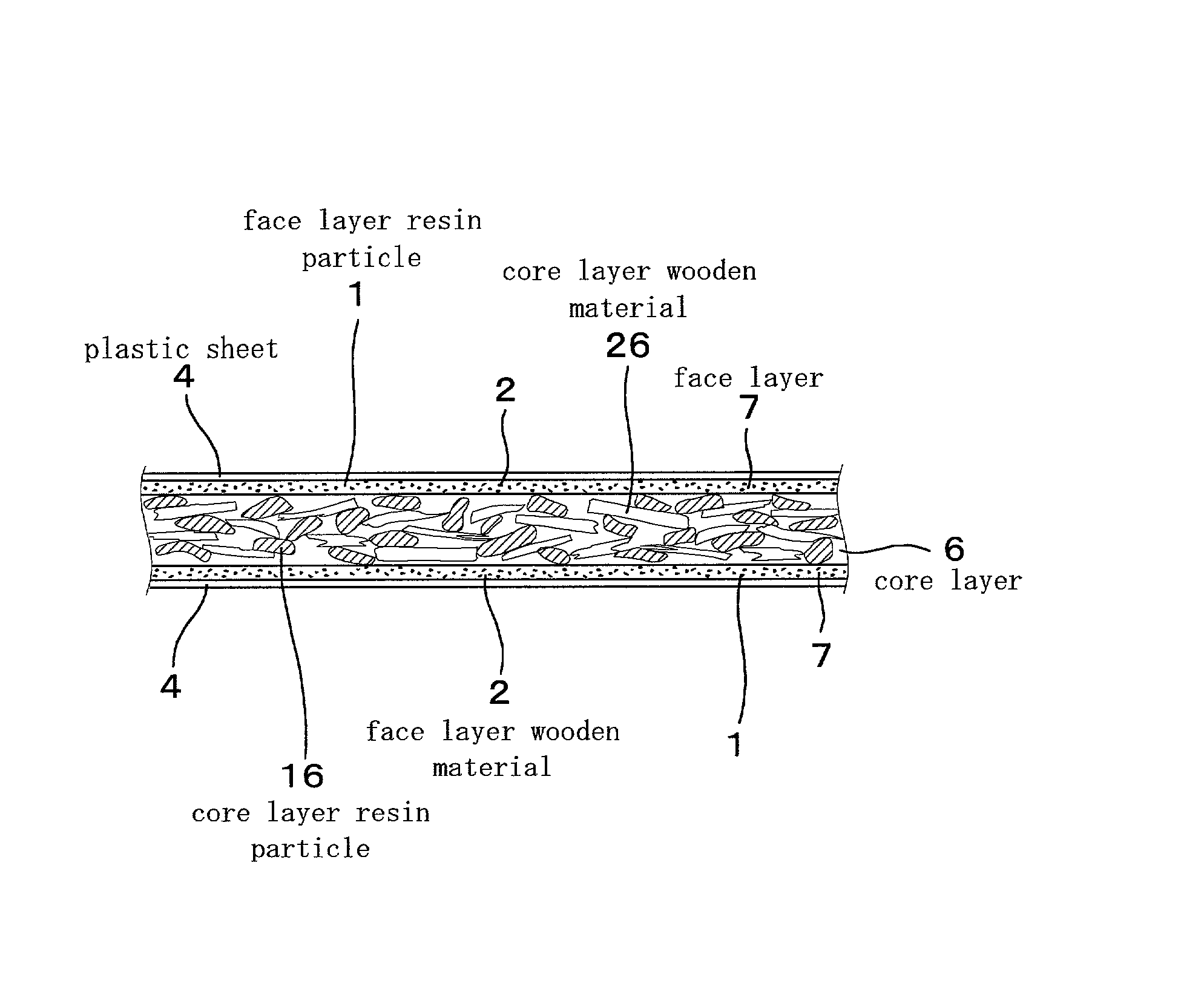
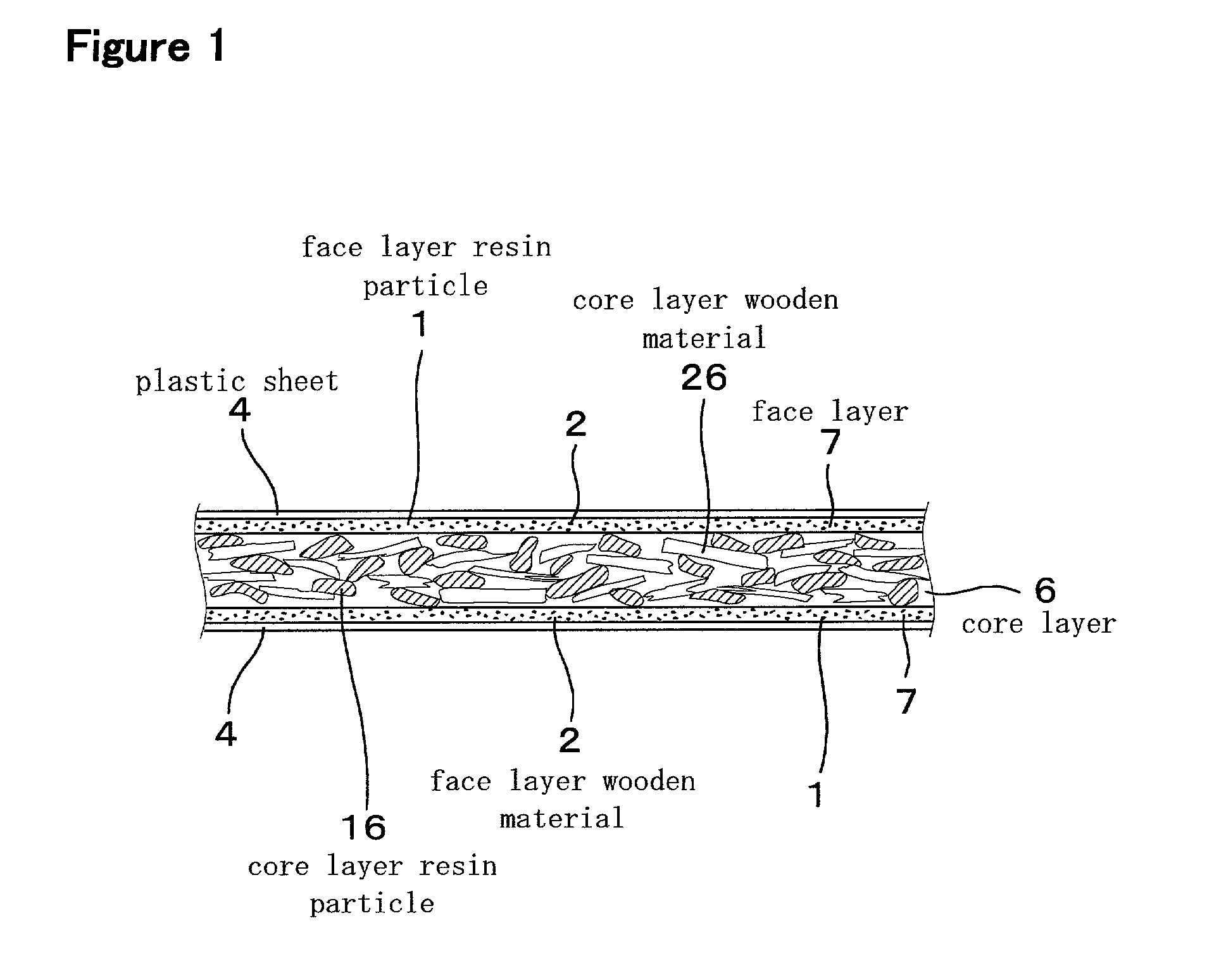
[0054] The particle board of this embodiment 1, as shown in FIG. 1, has a three-layer structure comprising a rough core layer 6 and two fine face layers 7 provided on the two, front and back, sides of the core layer 6, which is made by applying wooden materials of a needle-like (flake) shape with an adhesive, and forming.
[0055] Table 1 illustrates a distribution profile of the diameter of particles in face layer wooden materials 2 and core layer wooden materials 26. In this embodiment 1, the average particle diameter is determined from the distribution profile. As a matter of convenience, a median value of the major particle diameters in the profile shown in Table 1 is defined as the average particle diameter. More specifically, the average particle diameter of the face layer wooden materials 2 is 1.77 mm which is a median value in the profile of ...
embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2
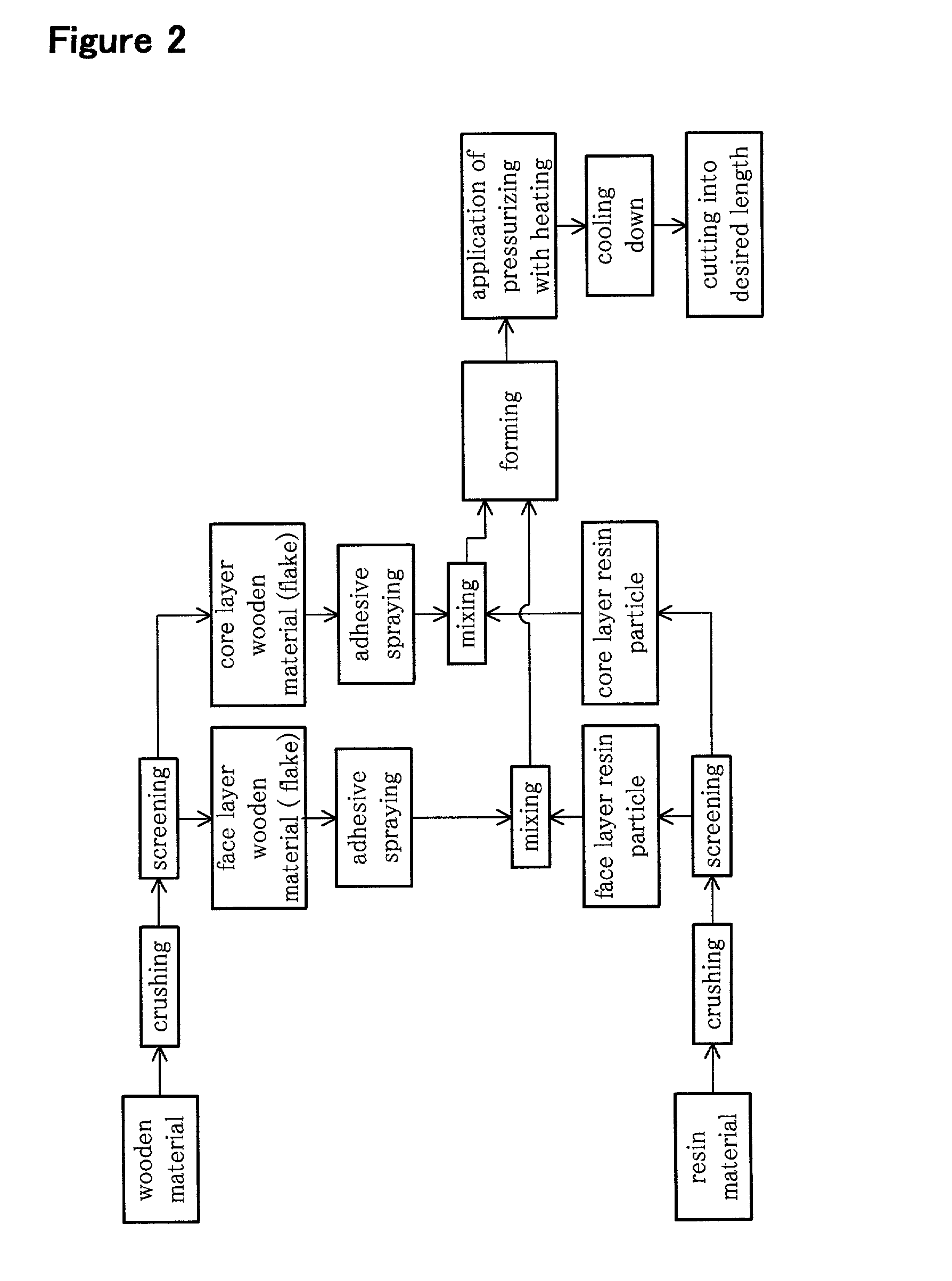
[0087] This embodiment, as shown in FIG. 9, is provided the method of making two heaped face layers constitution. To be concrete, the face layer wooden materials and the face layer resin particles are heaped two times.
[0088] The wooden materials are chopped by a crusher to have an average diameter of 2.03 mm for use as the core layer wooden materials, an average diameter of 0.89 mm for use as the first face layer wooden materials, and an average diameter of 1.77 mm for use as the second face layer wooden materials.
[0089] The profile of the average particle diameters of the core layer wooden materials and the second face layer wooden materials is substantially similar to that shown in Table 1 of Embodiment 1. The major range of the particle diameter of the first face layer wooden materials is from 0.60 mm to 1.18 mm. A median value (0.89 mm) in the major range is the average diameter.
[0090] The resin particles are crushed by a single-axis rotary shearing crusher to...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific gravity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com