Non-woven fabrics of wind-shrink fiber and laminate thereof
a technology of wind-shrink fiber and non-woven fabrics, which is applied in the directions of weaving, filament/thread forming, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve problems such as unstable spinnability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0096] Using a propylene homopolymer having the melting point of 162.degree. C. and MFR of 60 g / 10 min (as measured at a temperature of 230.degree. C. under a load of 2.16 kg in accordance with ASTM D1238; hereinafter the same unless otherwise indicated) as the first propylene-based polymer and as the second propylene-based polymer a propylene-ethylene random copolymer having the melting point of 142.degree. C., MFR of 60 g / 10 min and the ethylene unit content of 4.0 mol %, conjugate melt-spinning was carried out by a spun-bonding process to deposit an eccentric core-sheath type conjugate fiber having the core made from the propylene homopolymer and the sheath made from the propylene-ethylene random copolymer (the ratio of the core to the sheath was 20 / 80 by weight) on the collection surface. The conjugate fiber was then subjected to emboss processing at an emboss temperature of 110.degree. C. with an emboss pattern (emboss area percentage: 18.2%, non-emboss unit area: 0.74mm.sup.2)...
example 2
[0097] A nonwoven fabric composed of crimped conjugate fibers having the basis weight of 25 g / m.sup.2 and the fineness of the constituent fiber of 2.4 deniers was produced in a manner similar to EXAMPLE 1, except that a propylene-ethylene random copolymer having the melting point of 138.degree. C., MFR of 60 g / 10 min and the ethylene unit content of 5.0 mol % was used as the second propylene-based polymer and the emboss temperature was changed to 100.degree. C. The details of the propylene-based polymer components are shown in TABLE 1 and the measurement / evaluation results on the nonwoven fabric obtained are shown in TABLE 2.
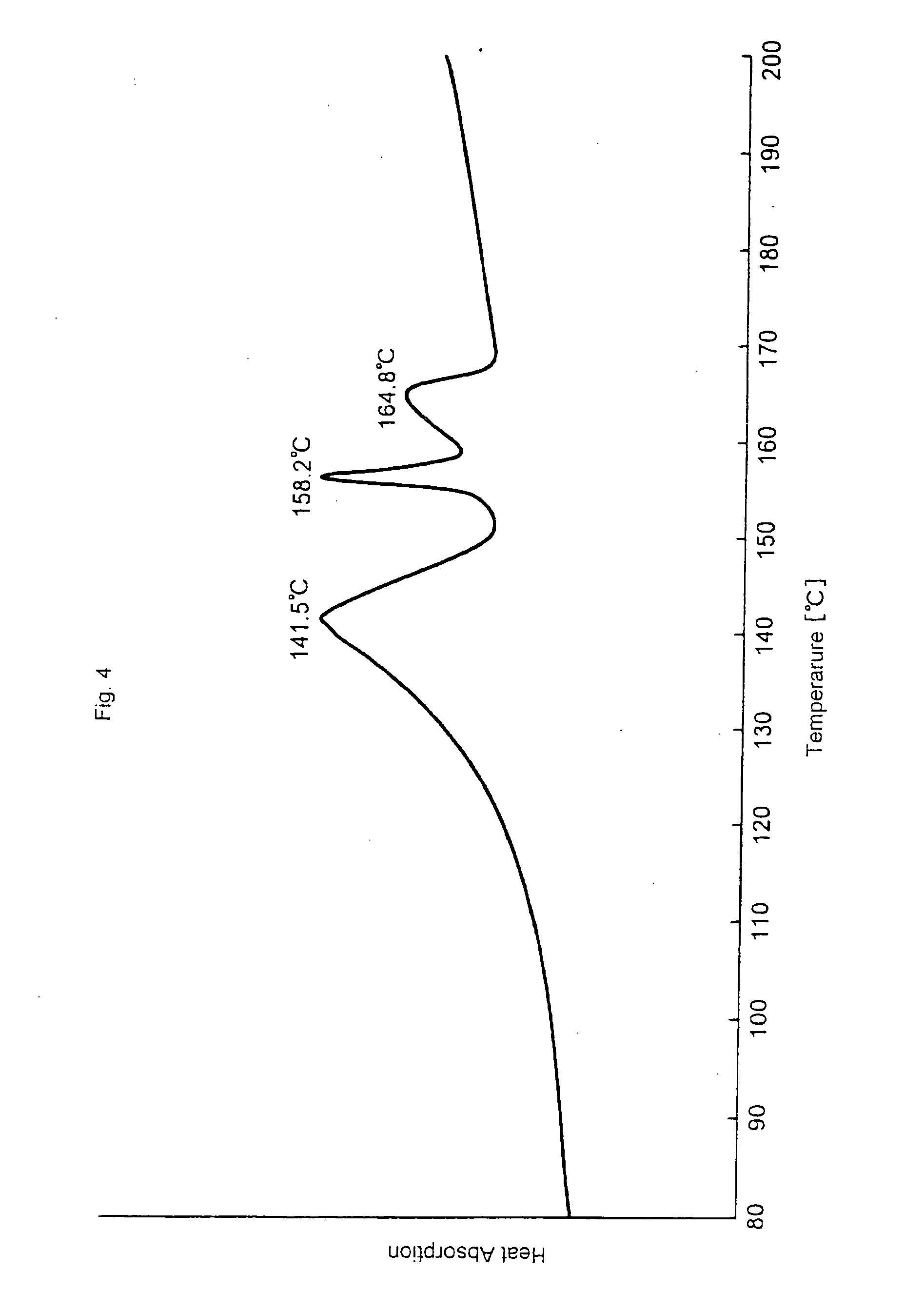
[0098] The melting point peaks of the thus obtained conjugate fibers by DSC in the first run were observed at 141.5.degree. C., 156.2.degree. C. and 164.8.degree. C., and the peak area percentages were 80%, 10% and 10%, respectively. The measurement curve by DSC is shown in FIG. 4.
example 3
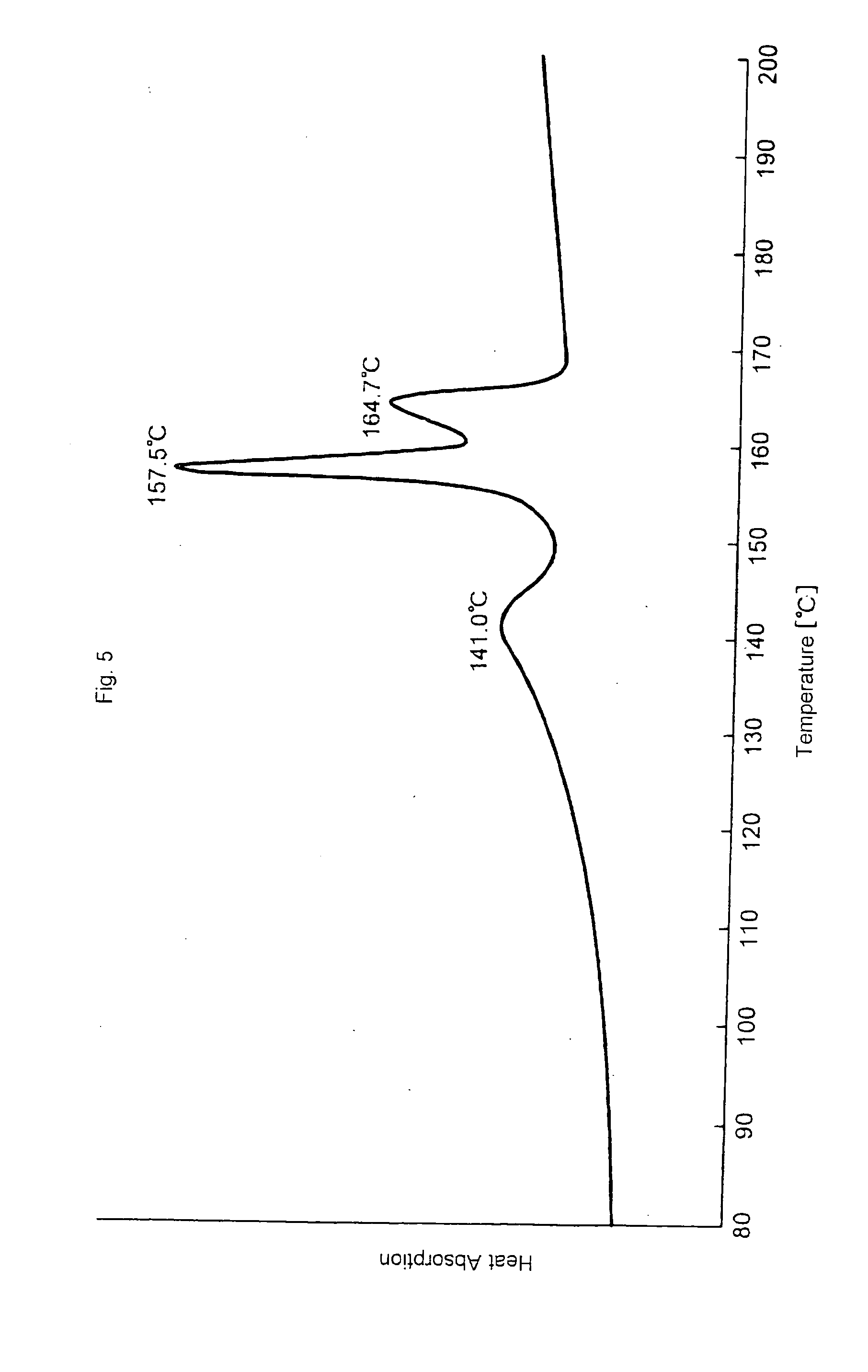
[0099] A nonwoven fabric composed of crimped conjugate fibers having the basis weight of 25 g / m.sup.2 and the fineness of the constituent fiber of 2.4 deniers was produced in a manner similar to EXAMPLE 2, except that the eccentric core-sheath type conjugate fiber had the core / sheath=30 / 70 (by weight ratio). The details of the propylene-based polymer components are shown in TABLE 1 and the measurement / evaluation results on the nonwoven fabric obtained are shown in TABLE 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com