Fiber optic sensing instrument and system with fiber of adjustable optical path length and method of using it
a fiber optic and optical path technology, applied in the field of fiber optic sensing instruments, can solve the problems of ambiguity rendering the detection ambiguous or even meaningless, the simplest form cannot detect the location of pressure or temperature in the extended area, and the use of fairly complicated mathematics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
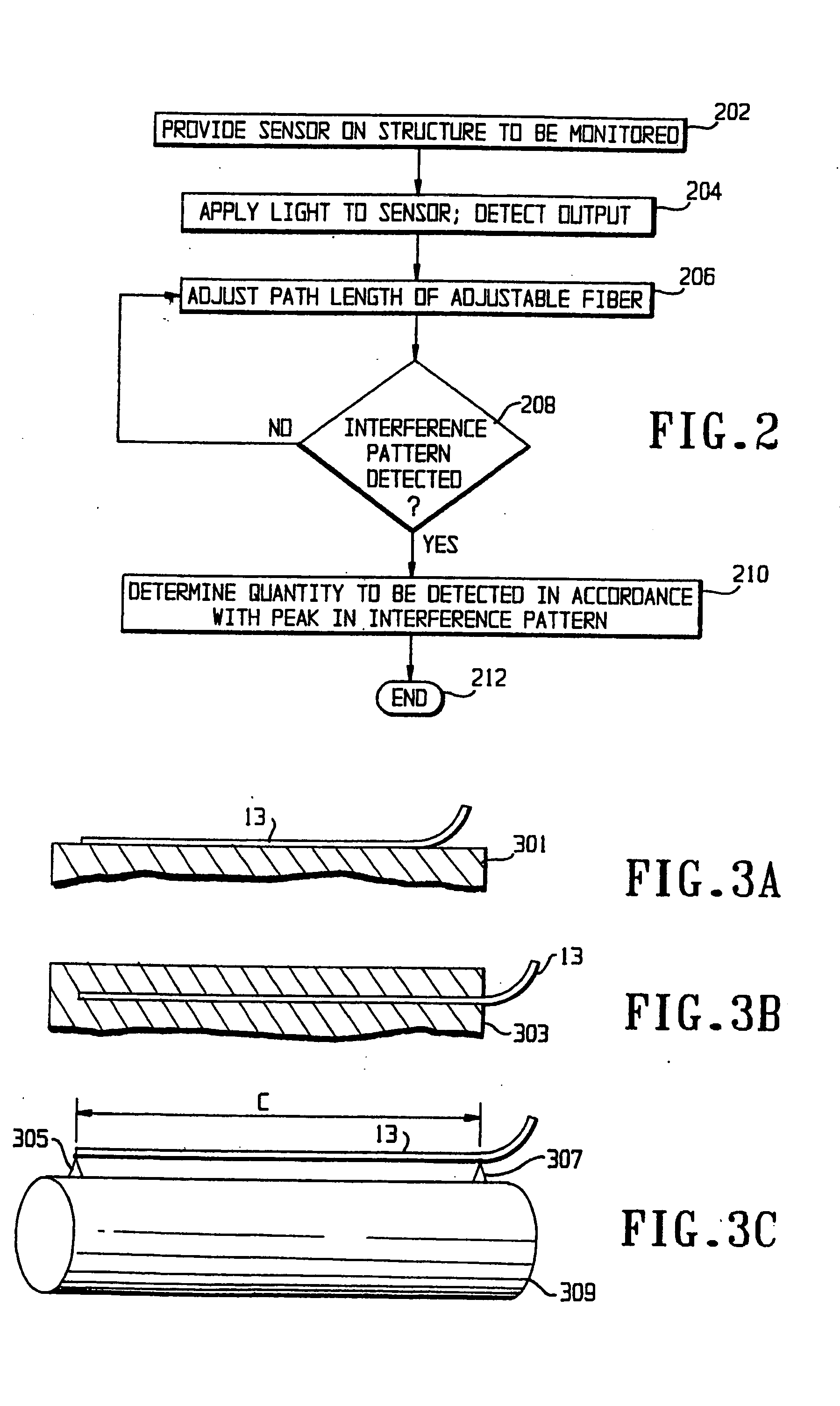
A preferred embodiment of the present invention and variations thereon will be described in detail with reference to the drawings, in which like reference numerals refer to like elements throughout.
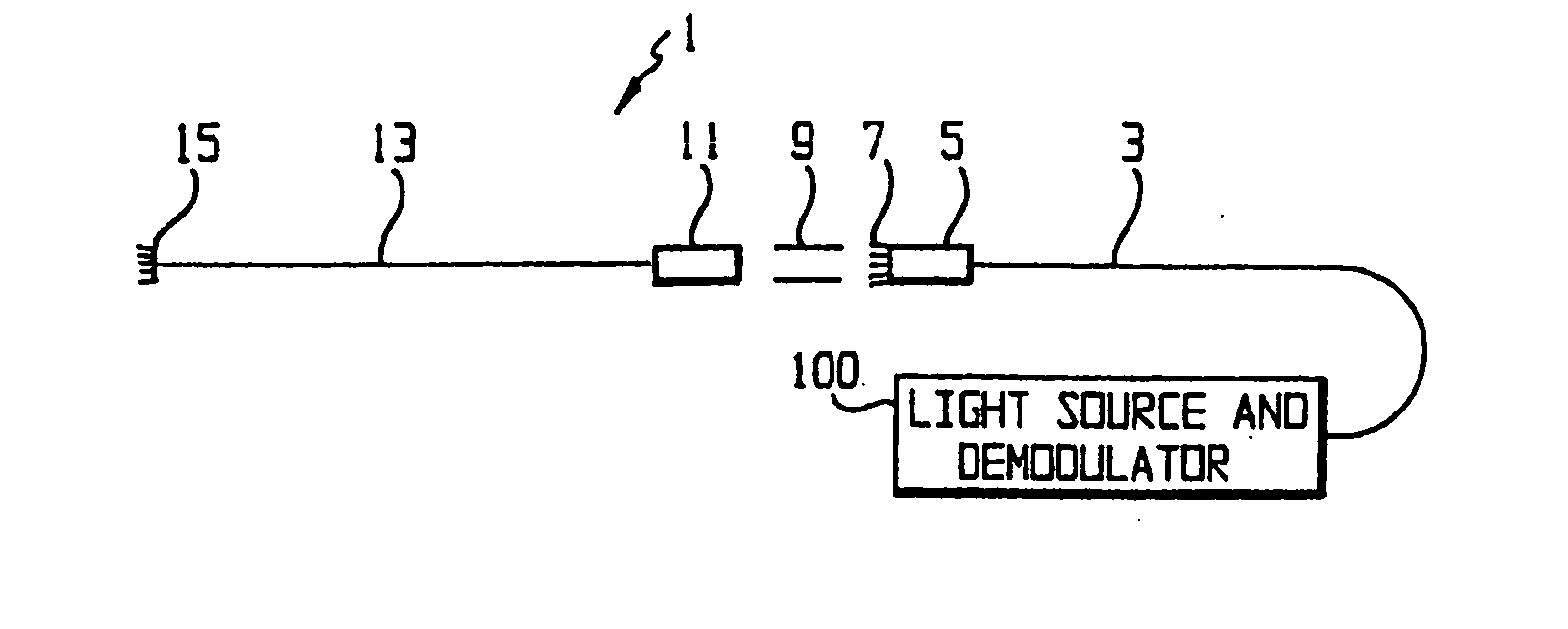
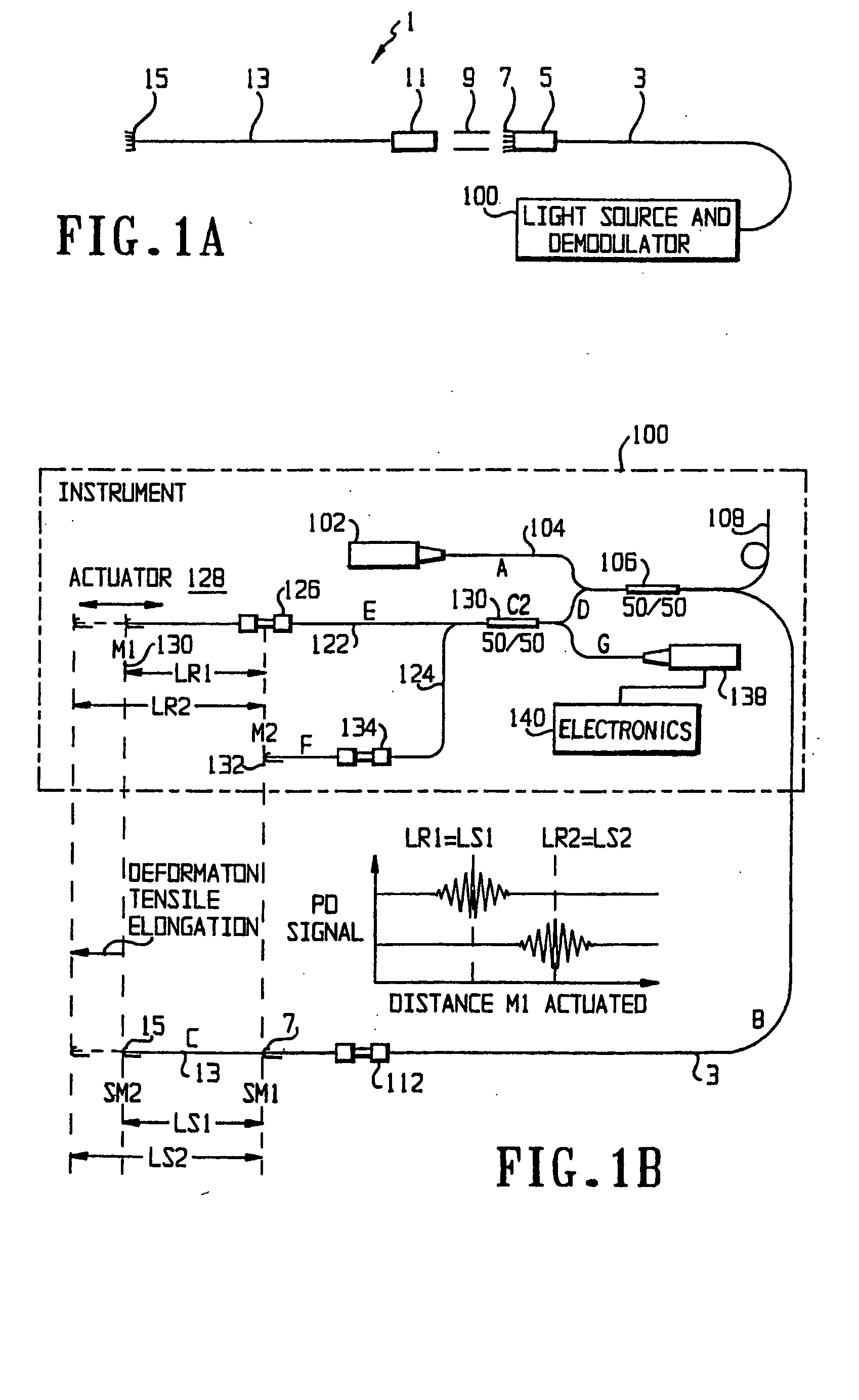
FIG. 1A shows a schematic diagram of a sensor for use with the instrument according to the preferred embodiment. The sensor 1 includes a lead fiber 3, preferably a single-mode optical fiber, terminated by a lead ceramic ferrule 5 and a lead mirror 7 formed as a partially mirrored surface on the end of the lead fiber 3. A ceramic sleeve 9 is used to attach the ferrule 5 to another ceramic ferrule 11, which is in turn attached to a sensor fiber 13, which is also preferably a single-mode optical fiber. The sensor fiber 13 ends in a sensor mirror 15, which, like the lead mirror 7, is formed as a partially mirrored surface on the end of the sensor fiber 13. The sensor 1 is connected to an instrument 100 which functions as both a light source and a demodulator.
The sensor 1 is installed such t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com