Semiconductor device having heat radiation plate and bonding member
a technology of heat radiation plate and bonding member, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device details, electrical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of not substantially reducing the performance of heat radiation, and achieve the effects of preventing cracking, high reliability of bonding member, and improving strength of bonding member
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
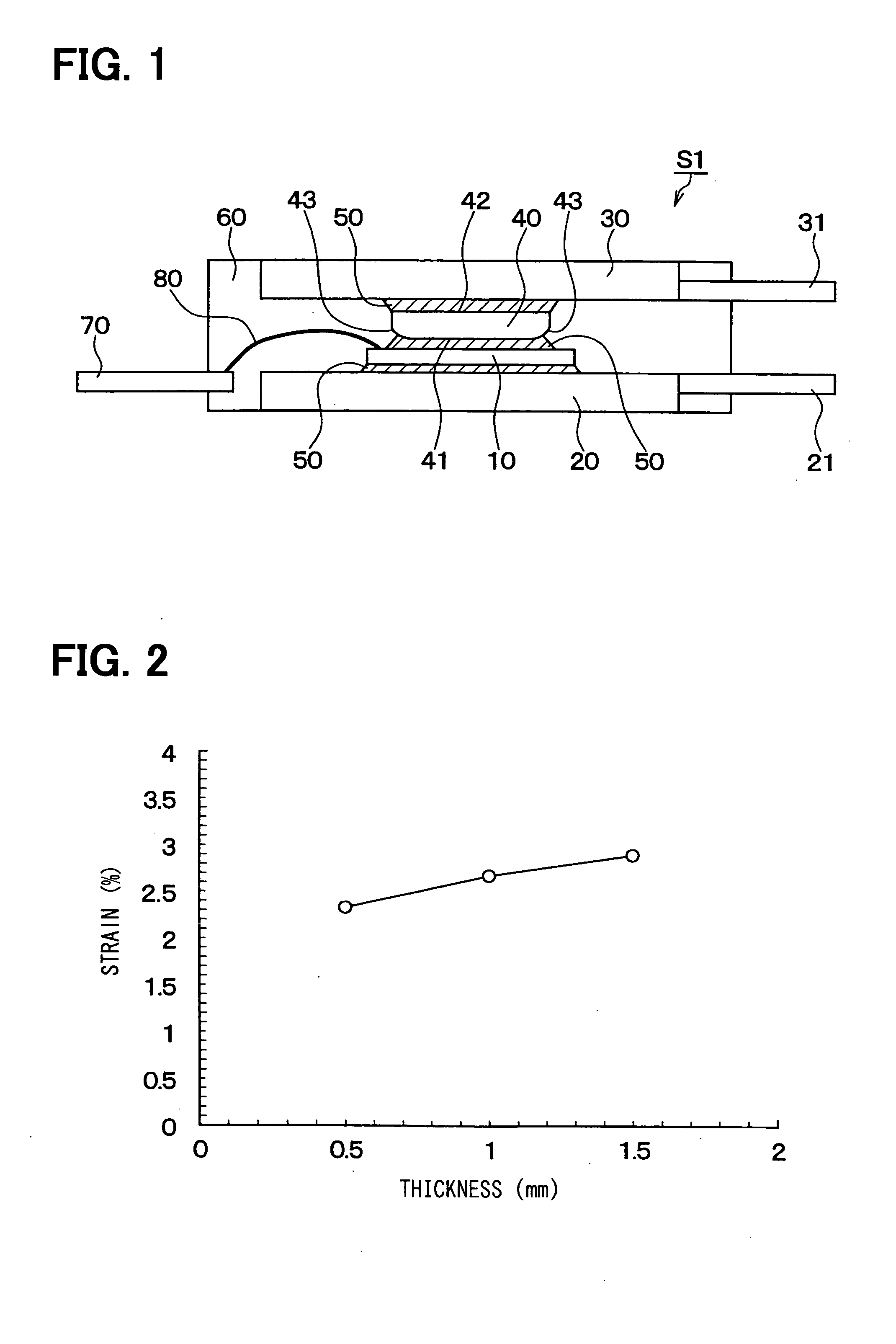
[0036] The inventors have studied about a heat radiation block (i.e., a heat sink block) in a semiconductor device. This is because dimensions and shape of the heat radiation block may affect a distortion at a bonding portion between the heat radiation block and a solder layer. Specifically, the distortion is analyzed by a finite element method (i.e., FEM). As a result, for example, when the heat radiation block is thick, a bonding member disposed between a heat generation element, i.e., a semiconductor chip and the heat radiation block becomes distorted largely. In this case, the bonding member may crack by a heat cycle stress. The detailed description is described as follows.
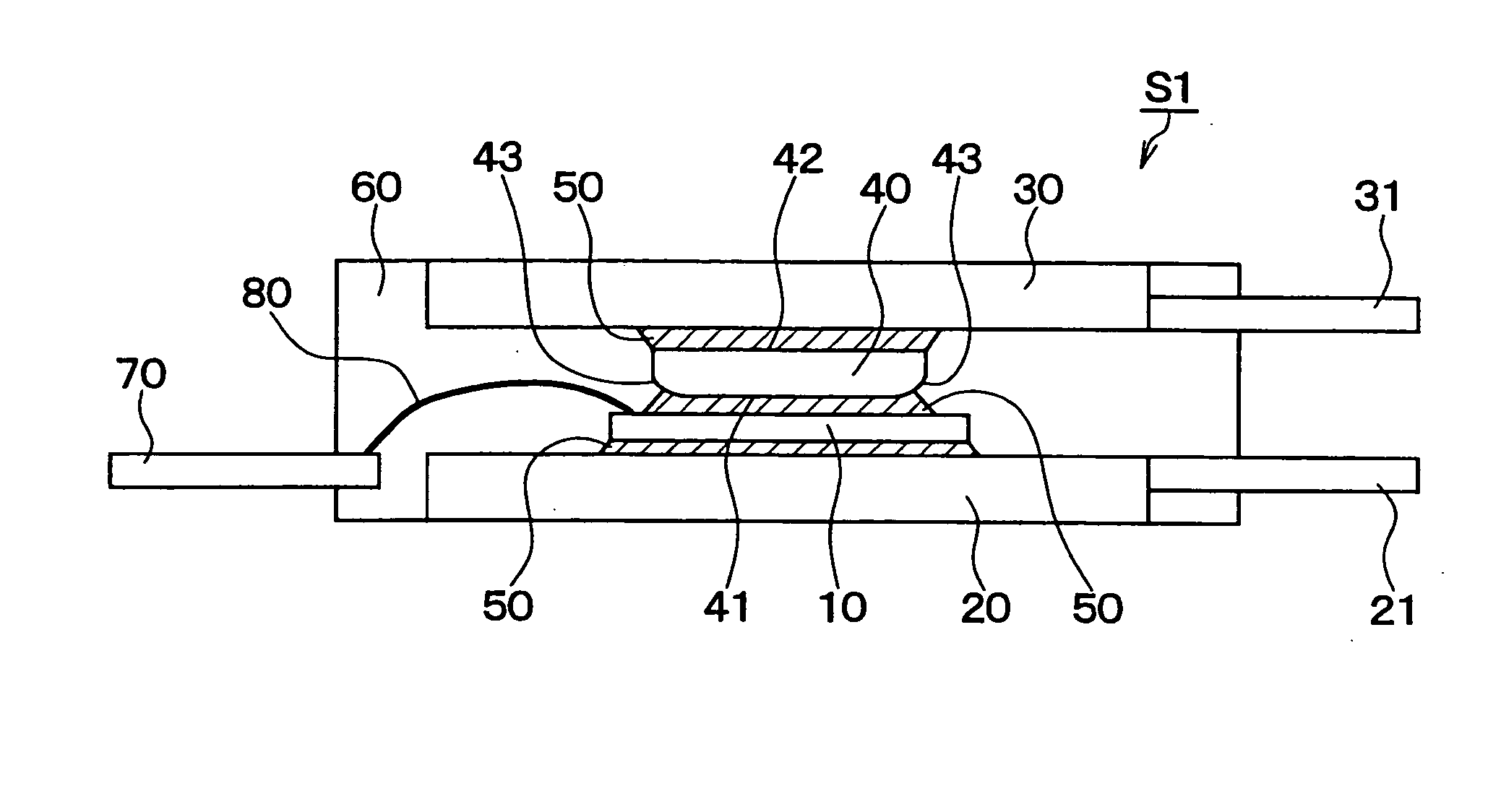
[0037]FIG. 1 shows a semiconductor device S1 according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The device S1 includes a semiconductor chip 10 as a heat generation element, upper and lower heat sinks 20, 30 as a heat radiation plate, a heat sink block 40 as a heat radiation block, a bonding member 50 d...
second embodiment
[0067] A semiconductor device S2 according to a second embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 5. The bottom 41 of the heat sink block 40 disposed on the chip side is rounded. Specifically, whole bottom surface 41 of the heat sink block 40 is formed to be a spherical surface. Here, at least one of the top 42 and the bottom 41 of the heat sink block 40 can be the spherical surface. The top 42 of the heat sink block 40 is disposed on the upper heat sink side.
[0068] In FIG. 5, the bottom 41 of the heat sink block 40 disposed on the semiconductor chip side is formed into the spherical shape. However, the top 42 of the heat sink block 40 disposed on the upper heat sink side can be formed into the spherical shape. Further, both of the bottom 41 and the top 42 of the heat sink block 40 can be formed into the spherical shape. Here, the device S2 has the heat sink block 40 with the thickness in a range between 0.5 mm and 1.5 mm.
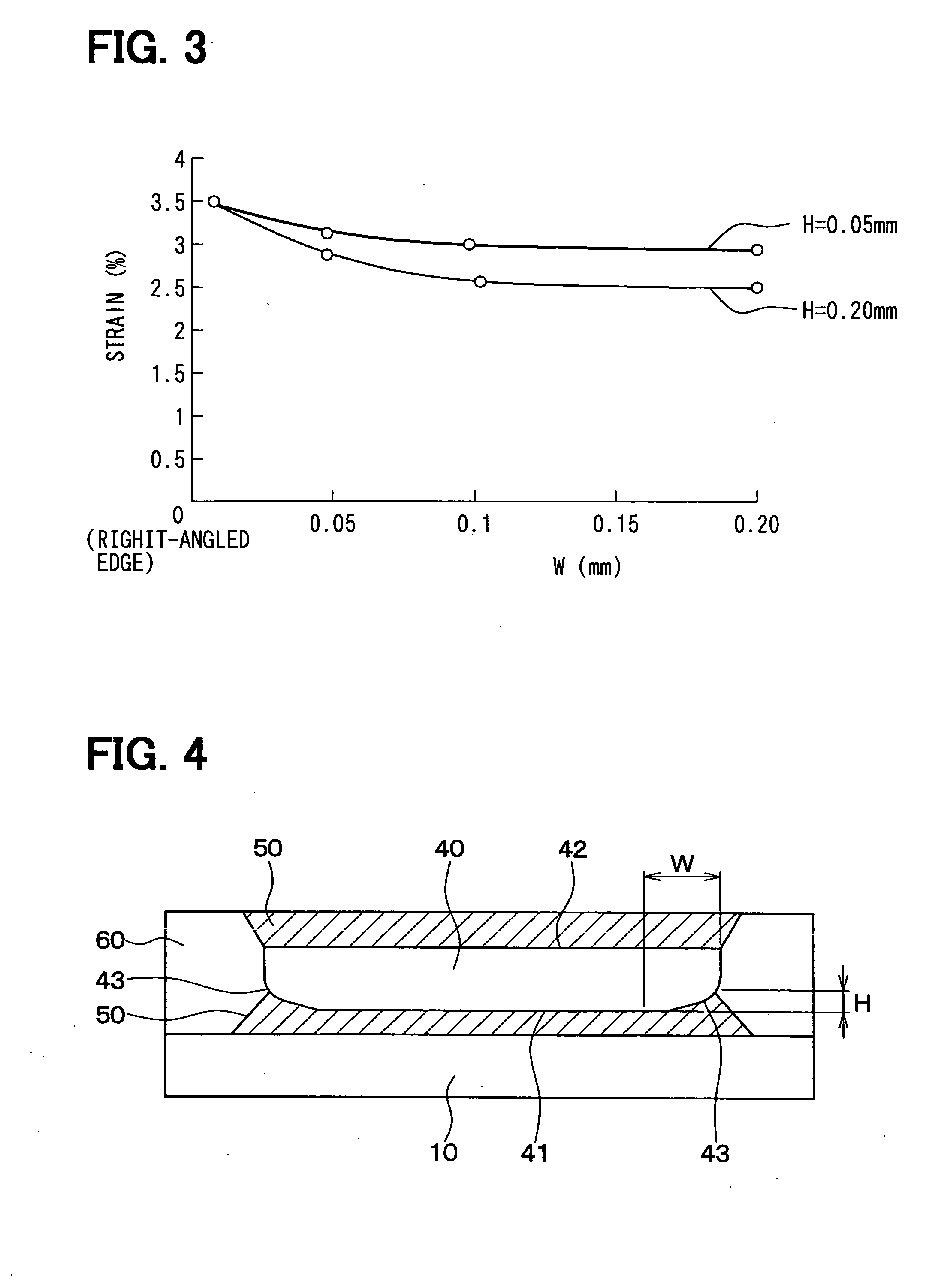
[0069] The width W of the edge portion 43 of the ...
third embodiment
[0073] A semiconductor device S3 according to a third embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 7. The semiconductor chip 10 has an edge portion 11, which is rounded so that the bonding member 50 contacting the chip 10 becomes thicker. Specifically, the edge 11 of the chip 10 is formed into a R-shape so that the bonding member 50 disposed at the edge portion 11 of the chip 10 and disposed between the chip 10 and the lower heat sink 20 becomes thicker.
[0074] In FIG. 7, the device S3 has the heat sink block 40 with the rounded edge portion 43 thereof. However, the device S3 can have the heat sink block 40 having the spherical shaped bottom 41 thereof.
[0075] In this case, the device S3 has the same advantages (i.e., functions and effects) as the device S1 having the edge portion 43 of the heat sink block 40 formed into the rounded edge.
[0076] According to the FEM analysis, the stress in the bonding member 50 disposed between the chip 10 and the lower heat sink 20 is conce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com