Method and apparatus for supplying refrigerant fluid
a technology of refrigerant fluid and refrigerant, applied in the field of refrigerant fluid supply, can solve the problems of difficult use of fluid supply apparatus and probe, high inconvenient problem of probe blocking, and vulnerable micro expansion orifice in the probe to be blocked
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
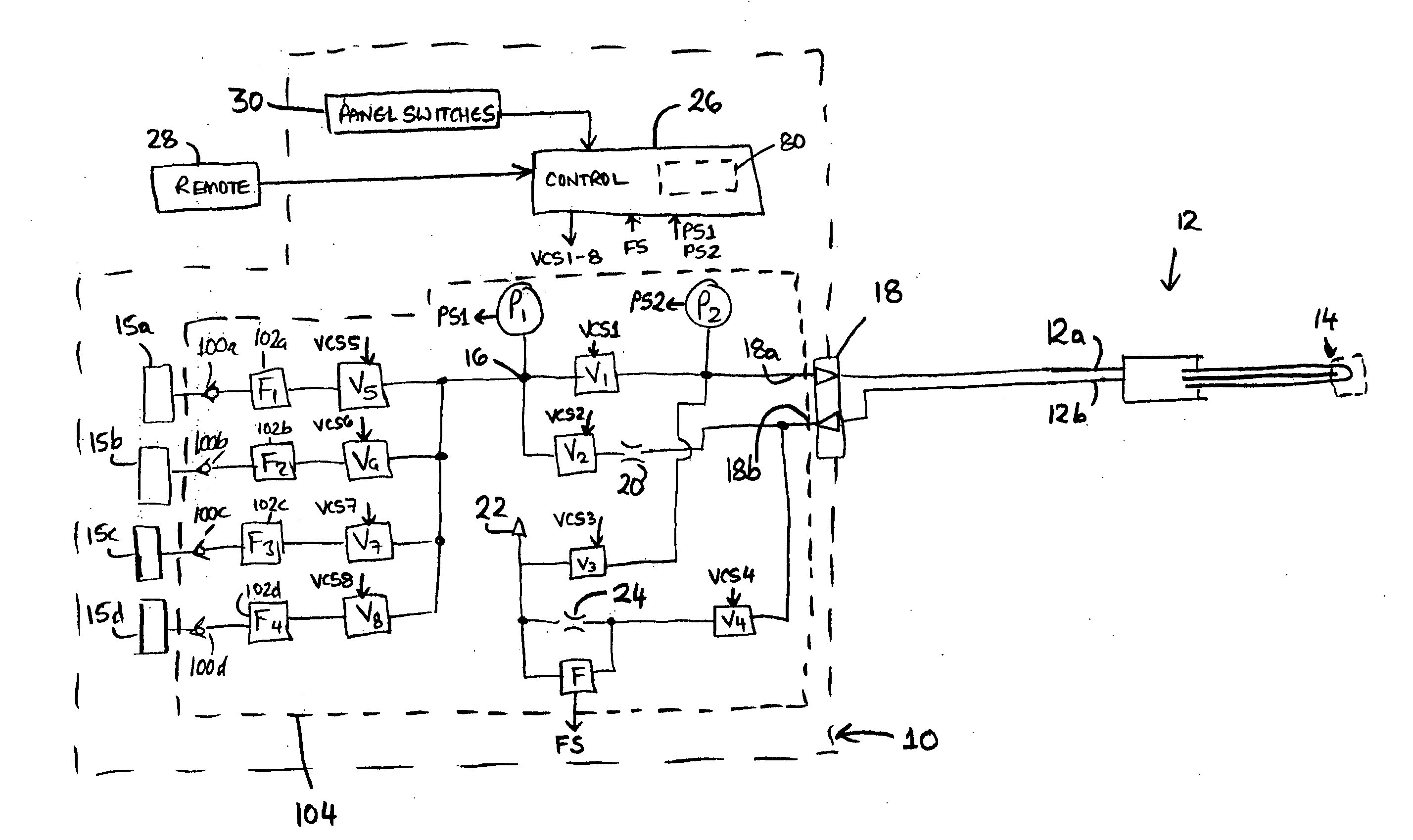
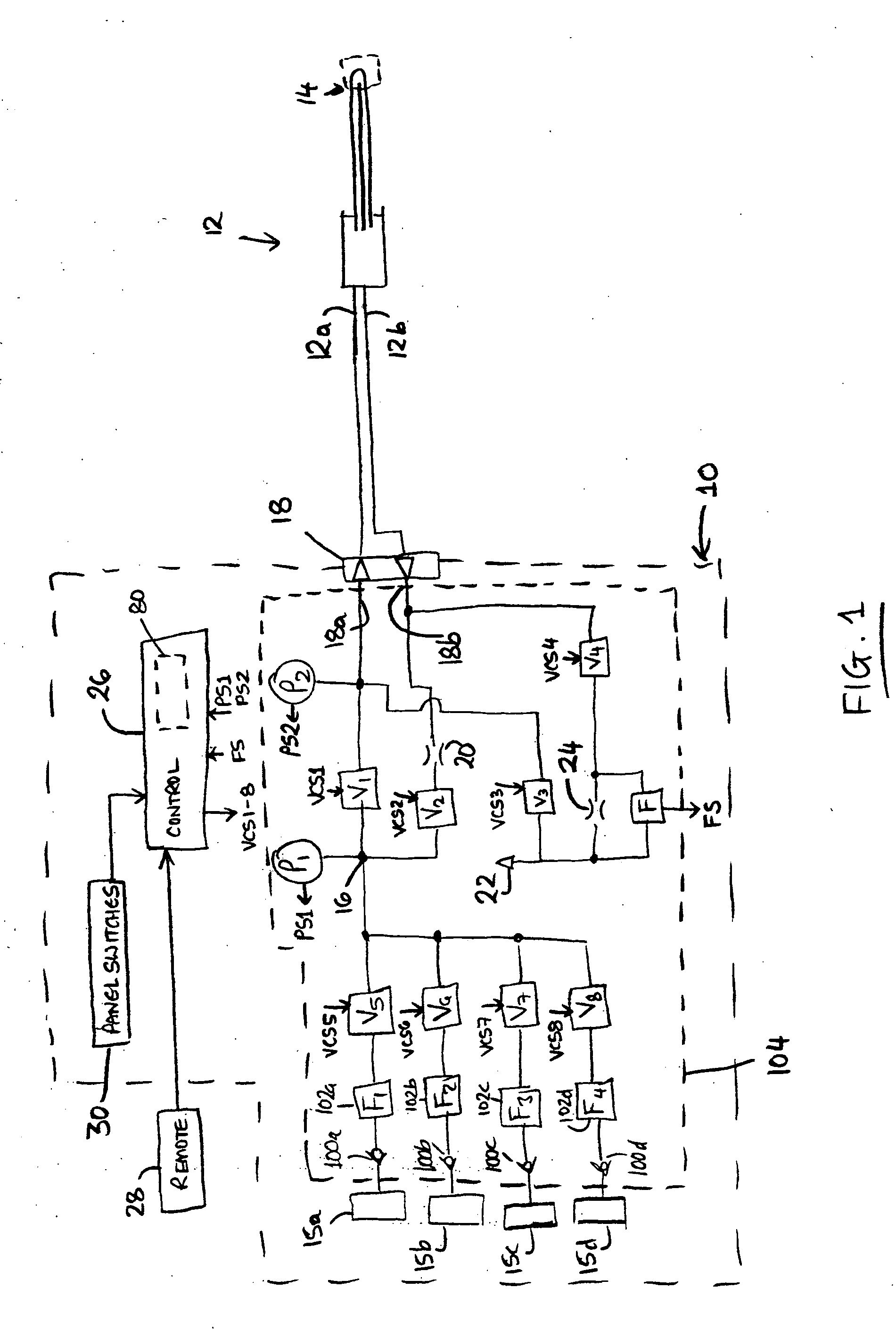
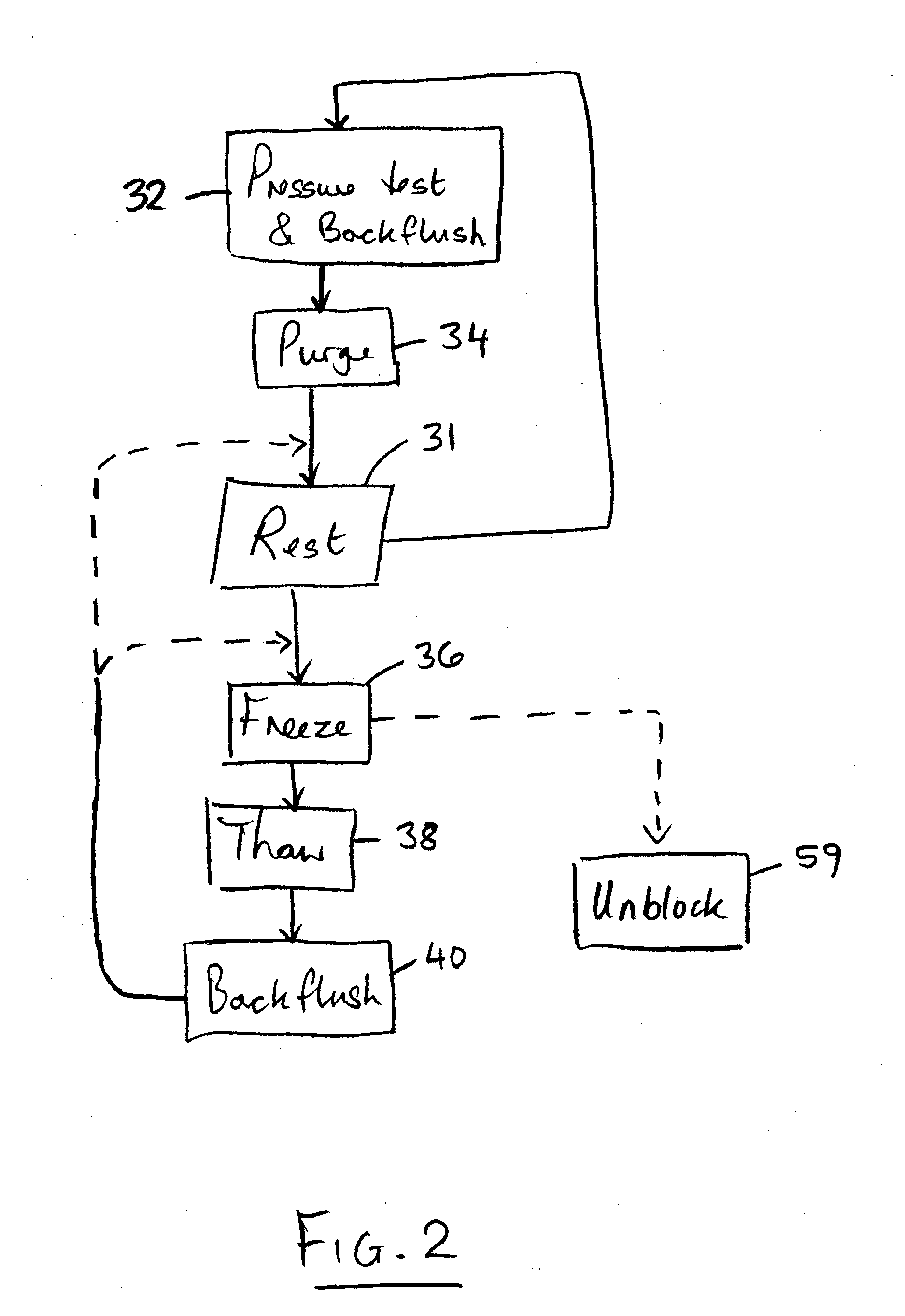
[0022]FIG. 1 may generally illustrate a fluid supply apparatus 10 for supplying and controlling the flow of a refrigerant fluid to a cooling device 12. The cooling device 12 may be detachably connectible to a coupling 18 of the apparatus 10. The cooling device 12 may be a medical or surgical probe. The cooling device 12 may include a small orifice (depicted schematically at 14) for generating a freezing effect by the Joule-Thompson principle of isenthalpic expansion when fluid is forced through the orifice 14 from an inlet side 12a to an outlet side 12b. The terms “inlet side” and “outlet side” may refer to a normal direction of fluid flow through the cooling device 12 for generating the intended freezing effect. The refrigerant fluid may be any suitable fluid for generating significant cooling upon isenthalpic expansion. Such a fluid may often be referred to as a Joule-Thompson fluid and may be a gas. For example, the gas may be nitrous oxide.
[0023] The supply apparatus 10 may gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com