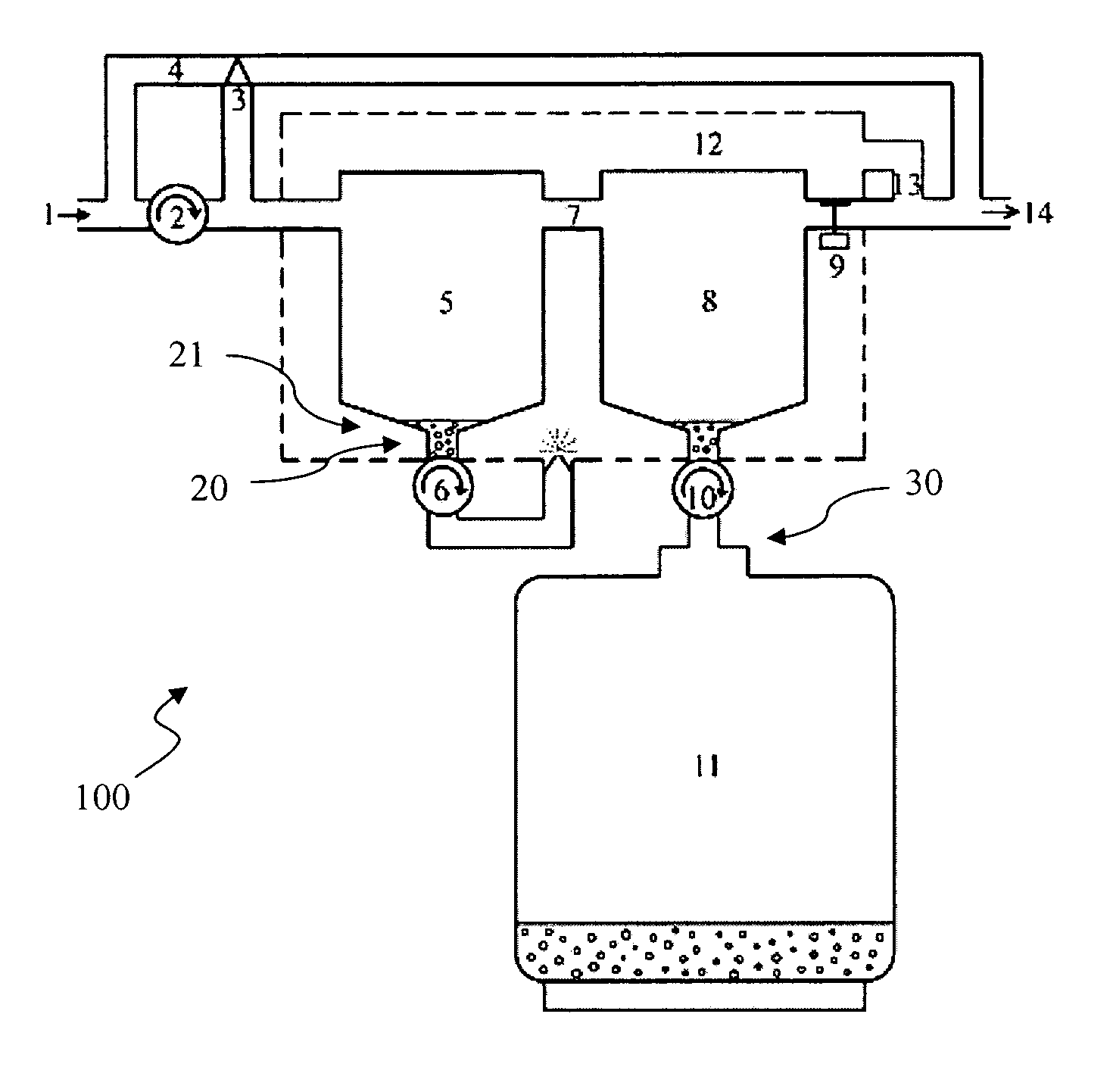
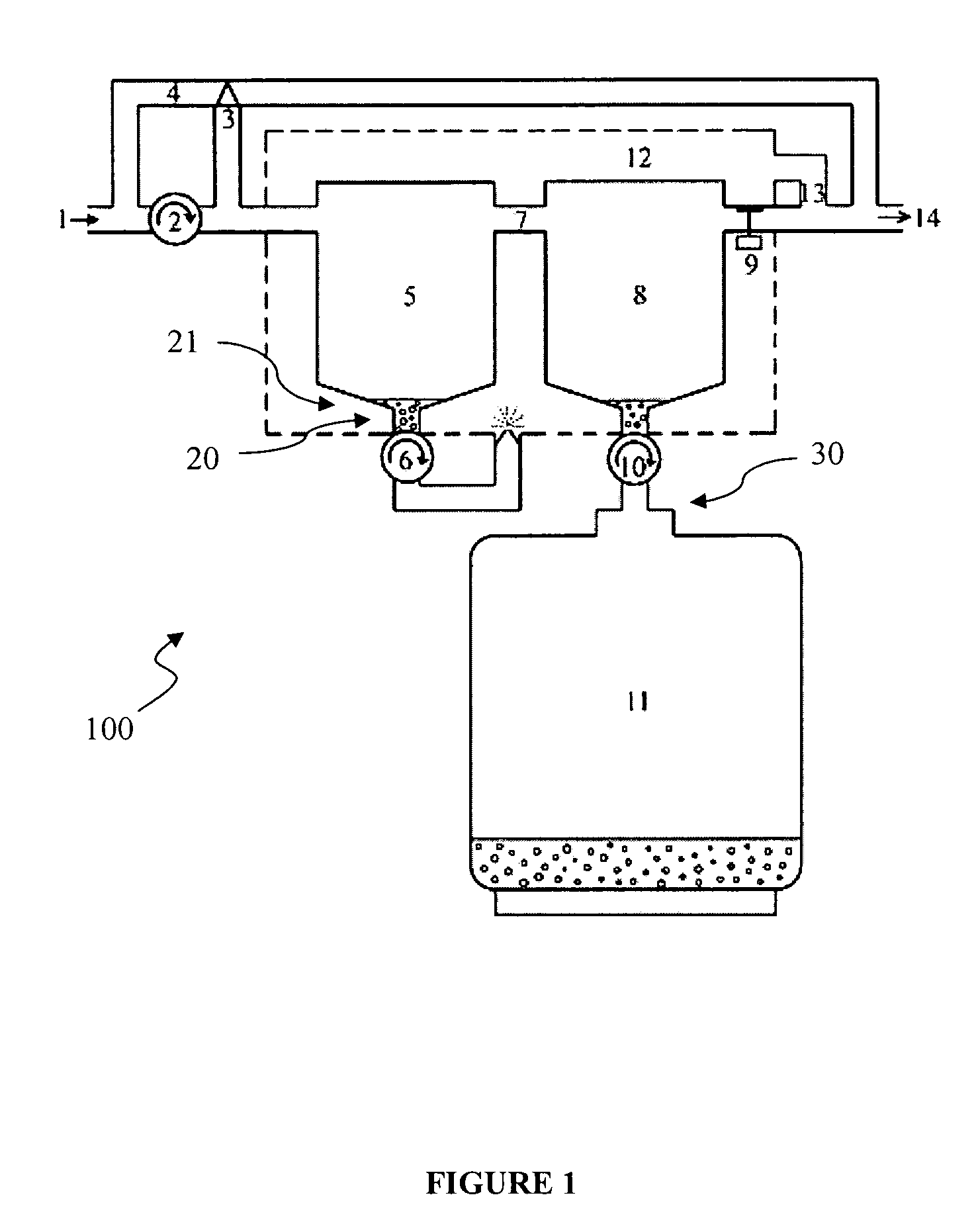
Anesthetic agent recovery
a technology of anesthetic agents and recovery methods, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of difficult and expensive production process of fluorine-based anesthetic agents, difficult and expensive sevoflurane production, and the inability to produce sevoflurane, and achieve the effect of reducing the cost of production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] (a) Anesthetic Gas Properties
[0039] Current anesthetic practice in the United States employs the three agents previously mentioned. A significant majority of cases use DESFLURANE and SEVOFLURANE. ISOFLURANE is still used in some institutions for longer cases and for some cardiac bypass cases. HALOTHANE has mostly disappeared because of its potential to cause malignant hyperthermia, and because the byproducts of reductive metabolism (implies poor liver perfusion) can cause liver damage. It is estimated that over 90% of all cases in the United States use DESFLURANE and SEVOFLURANE. The physical properties of exemplary gases contemplated herein are tabulated below.
TABLE 1Physical Properties of Exemplary Gases:PropertyDESFLURANESEVOFLURANEISOFLURANEFormulaCHF2—O—CHF—CF3CH2F—O—CH(CF3)2CHF2—O—CHCl—CF3Mol. Weight168 g200 g184.5 gml. Vapor / ml. Liquid641763704MAC#5-8%1.5-2.5%1-1.6%Density*1.4651.5201.502Boiling Point22.8° C.58.5° C.48.5° C.SVP@18° C.653219SVP@20° C.700157240SVP@22°...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com