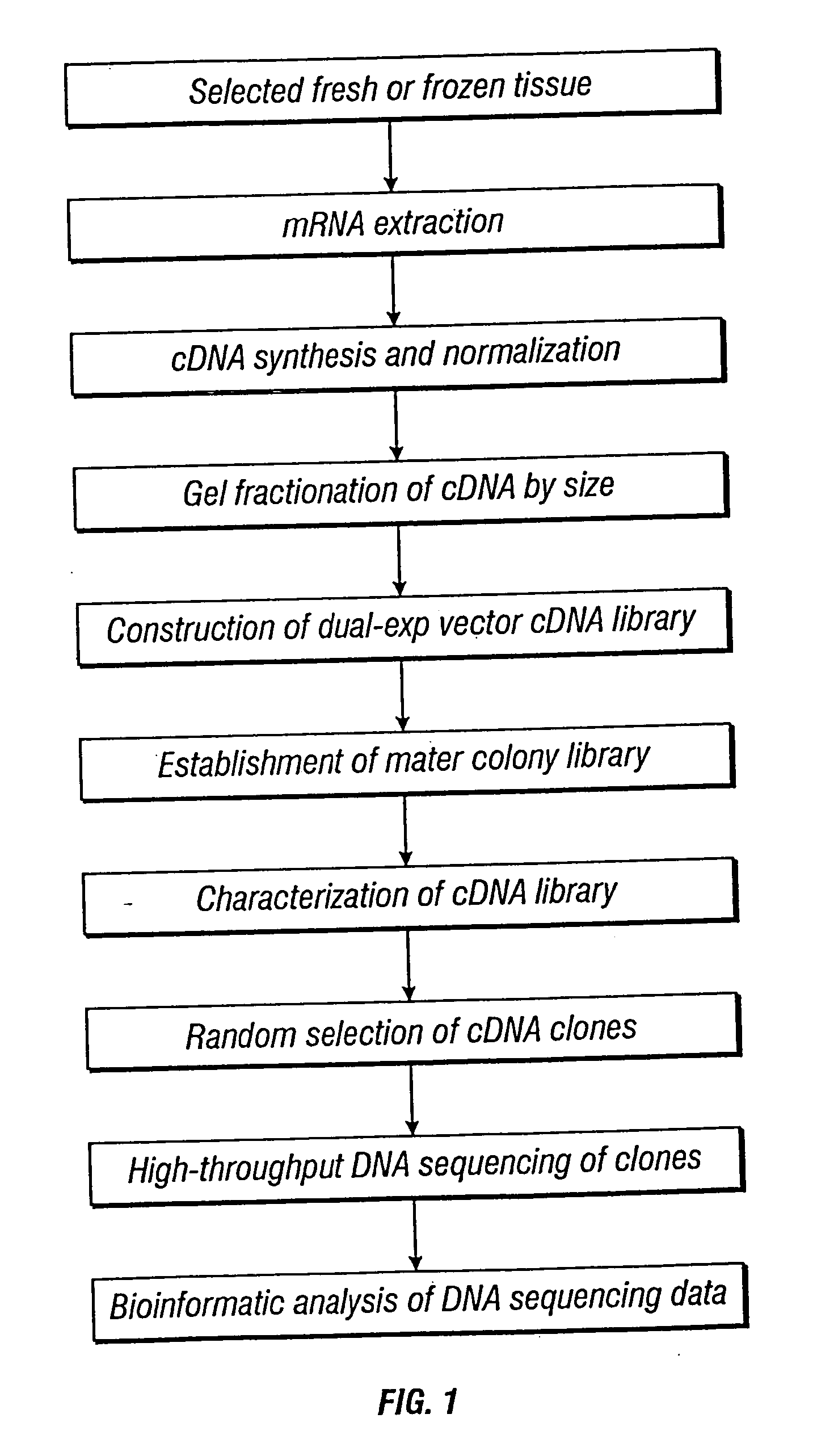
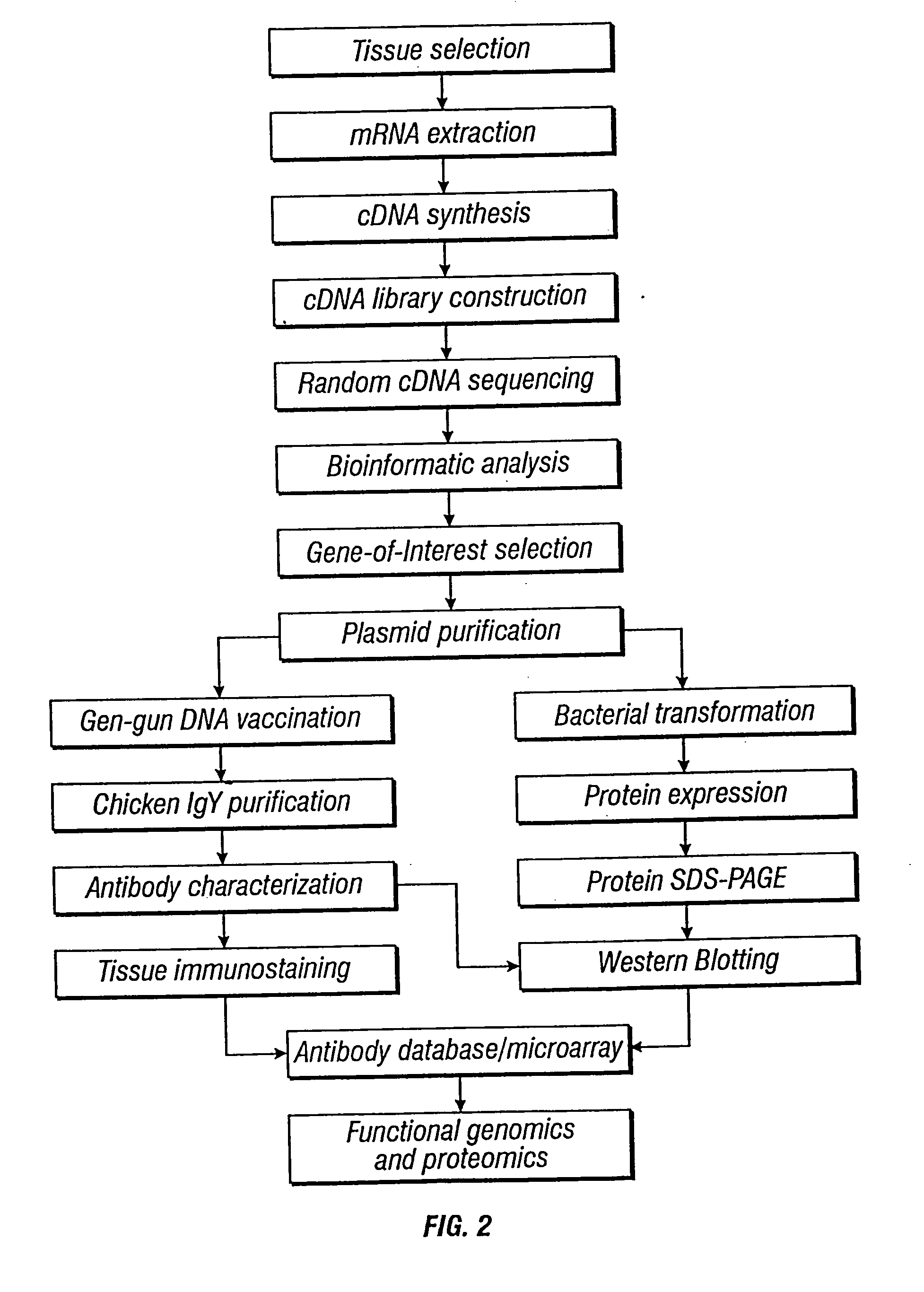
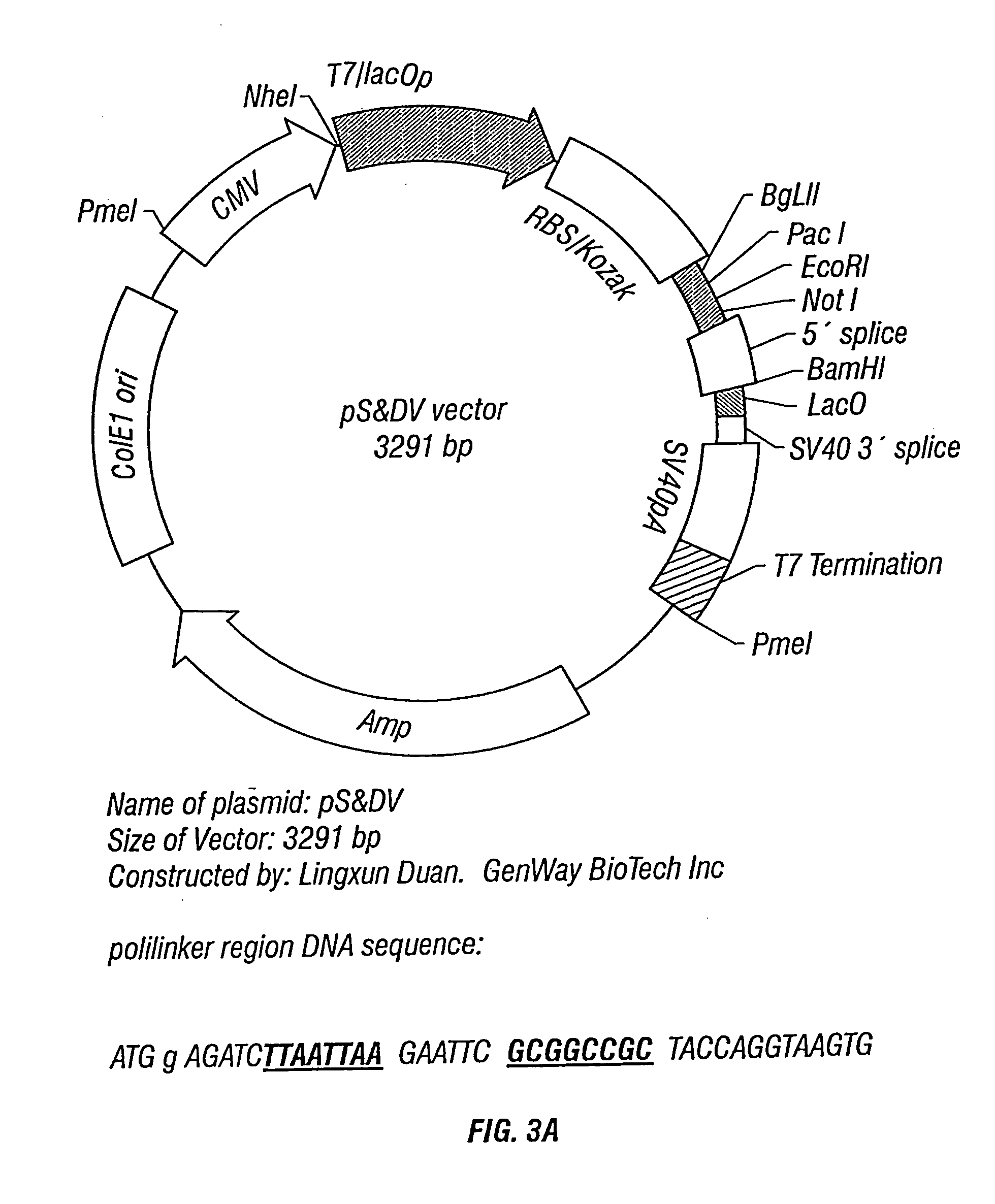
Methods and vectors for generating antibodies in avian species and uses therefor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] In addition to their therapeutic importance in medicine, monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are of great value in biological research such as gene functional analysis, where they serve as essential components in a variety of diagnostic systems used for the qualitative and quantitative determination of a wide range of specific gene coded protein expression. It is not surprising, therefore, that the growing interest in alternative methods has focused not only on the quality control of antibodies, but also on the methods used for the production of antibodies on the industrial large-scale for the high-throughput screening of gene function.
[0045] Antibody production normally requires the use of laboratory animals (mostly rabbits, but also mice, rats and guinea pigs) or larger mammals, such as horses, sheep, and goats. The procedure involves two steps, each of which not only causes distress to the animals involved but also is very expensive and labor intensive: a) the immunizati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com