In-situ blade sharpener
a blade and in-situ technology, applied in grinding machines, other manufacturing equipment/tools, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient removal of blades from driving parts, limited devices, and more difficult use and accurately positioning, so as to achieve maximum sharpening capability, safe in use, and easy, stably and accurately aligned and positioned.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
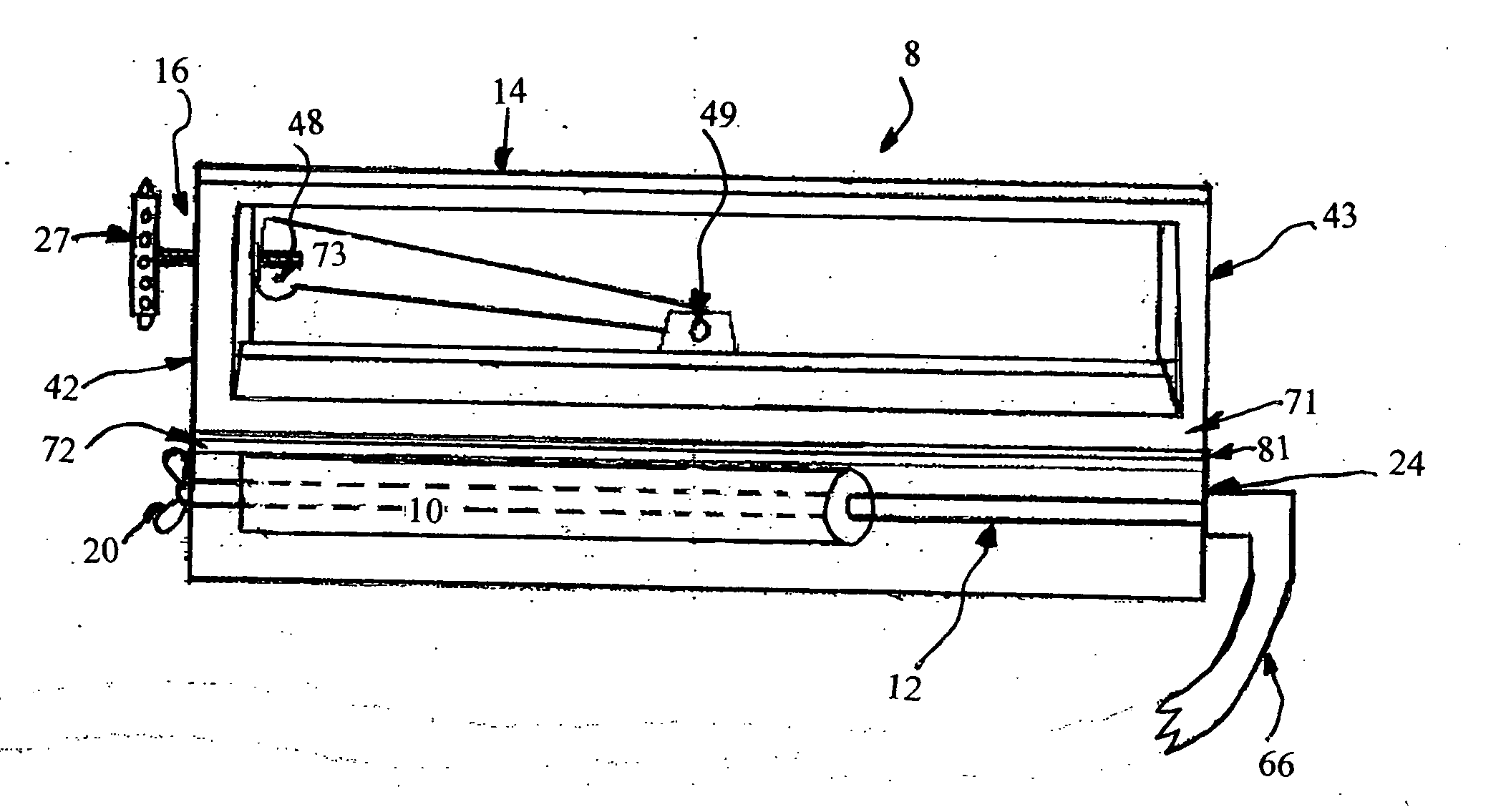
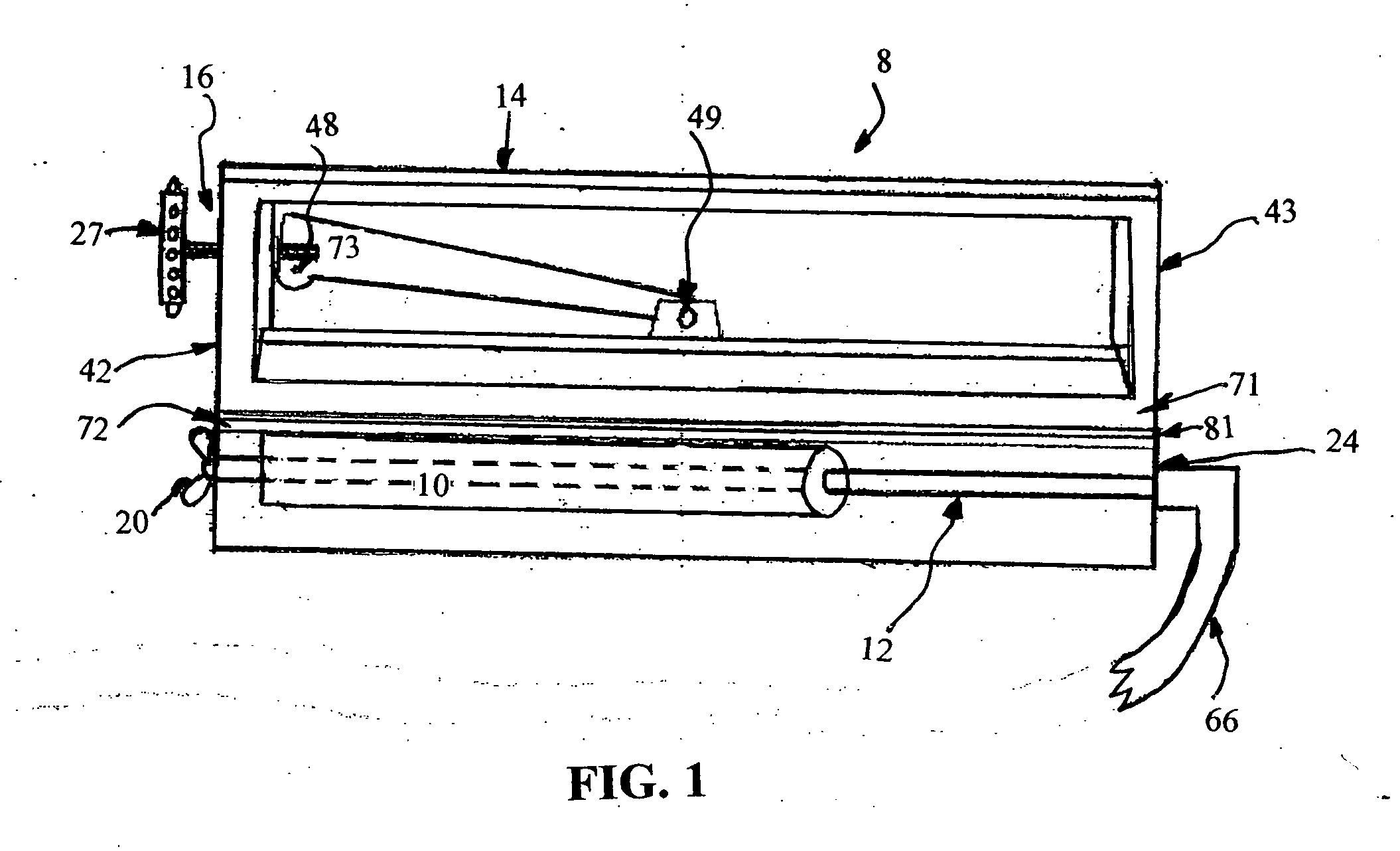
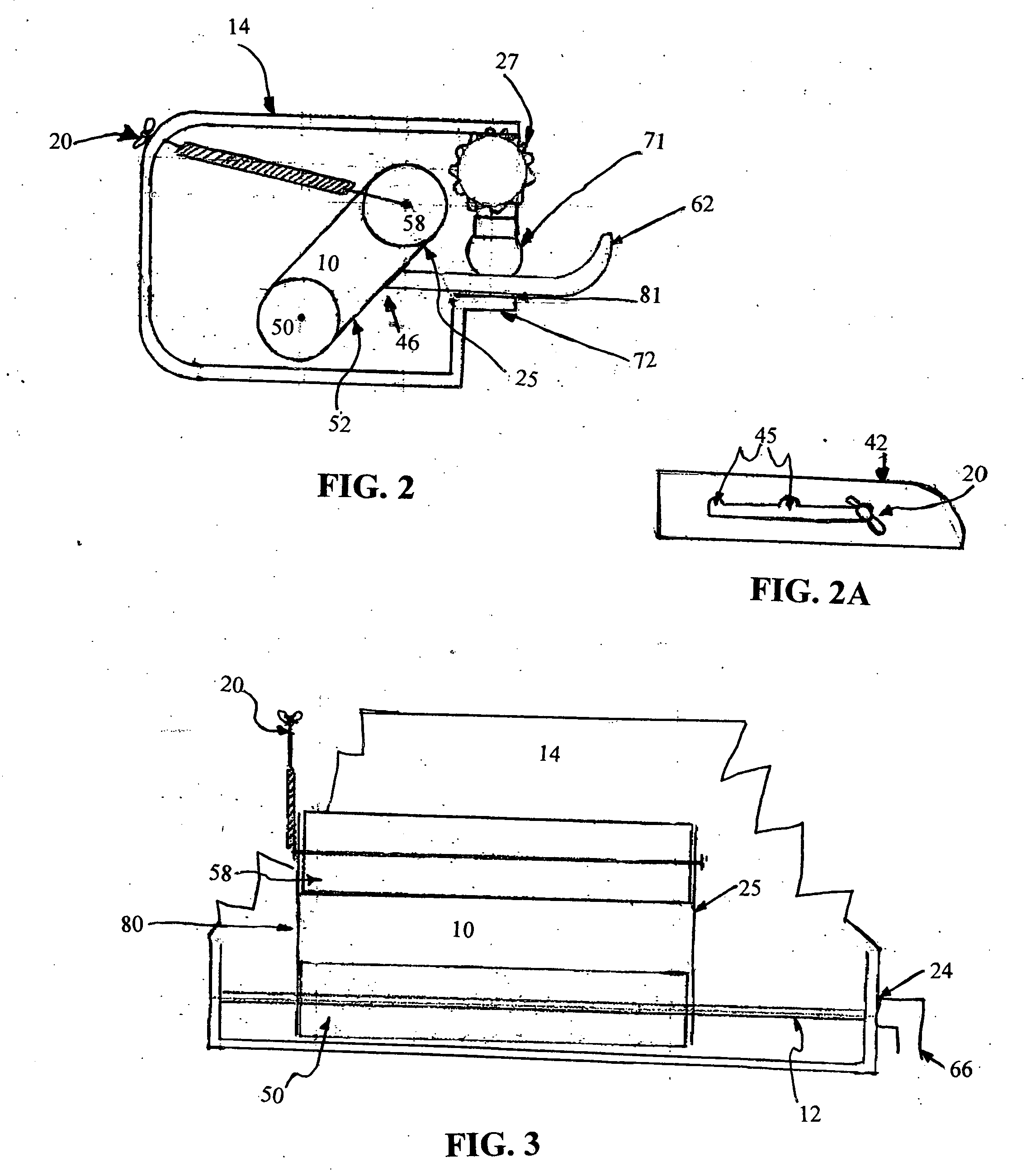
[0028]FIG. 1 shows the preferred, exemplary embodiment of the blade sharpening device 8 of the invention with the main elements of the device including a grinding member 10; a shaft member 12; a housing member 14, which can be transparent if so desired, having an upper plate 71 and a lower plate 72; and a clamping mechanism 16 having a clamping end 27 mounted to an upper plate 71 which is movable in a vertical direction by the clamping mechanism 16. The entire invention can be constructed of any suitable material that has the strength and durability. The preferred material is a composite of man-made organic para-aramid fibers.
[0029] The shaft 12 may be constructed of any material which has sufficient torsional strength to rotate and carry the grinding member 10. Suitable shaft constructing materials include metals, such as steel, fiberglass, and plastics having the required torsional strength. In the preferred embodiment shaft member 12 is constructed of a man-made organic para-ara...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com