Method for revamping fixed-bed catalytic reformers
a technology of catalytic reformers and fixed beds, which is applied in the field of catalytic reformers to achieve the effect of avoiding major expense, improving reformate quality and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
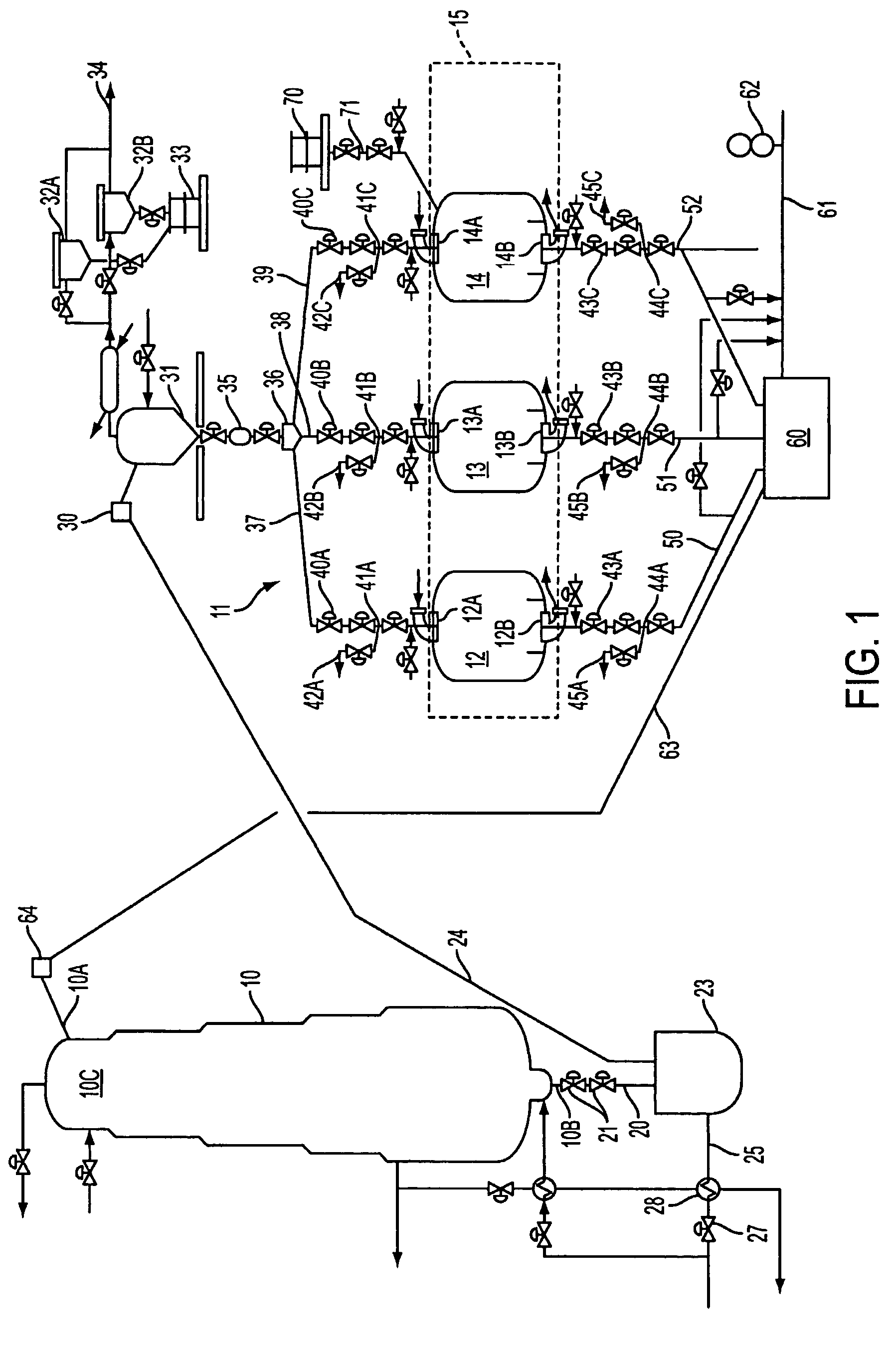
[0015] The present invention provides a substantially lower cost option for refiners to make significant improvements to the performance and service factor of existing fixed-bed reformer units. Non-continuous (or fixed-bed) catalytic reformers which can be subjected to the present conversion scheme could be semi-regenerative catalytic reformers or swing-reactor (also referred to as cyclic regeneration) reformers or hybrid systems (with both fixed and moving bed sections), all of which are known.
[0016] The present conversion scheme is best adapted to the conversion of cyclic reformer units because the required catalyst regeneration equipment will already be in place and can be applied directly to the new service: the compressors, furnace, chemical injection facilities as well as piping, valving and manifolding can be used without substantial modification to the mode of cyclic regeneration used in the converted unit. Cyclic, fixed-bed reformers have been well-known. In units of this ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| swing time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| acid functionality | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com