In-tube solenoid gas valve
a solenoid gas valve and in-tube technology, applied in the direction of lift valves, valve details, engine components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult design of appropriate valves that meet all difficult to meet the requirements of piping systems, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the maximum flow rate and reducing the size of the electrical coil
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
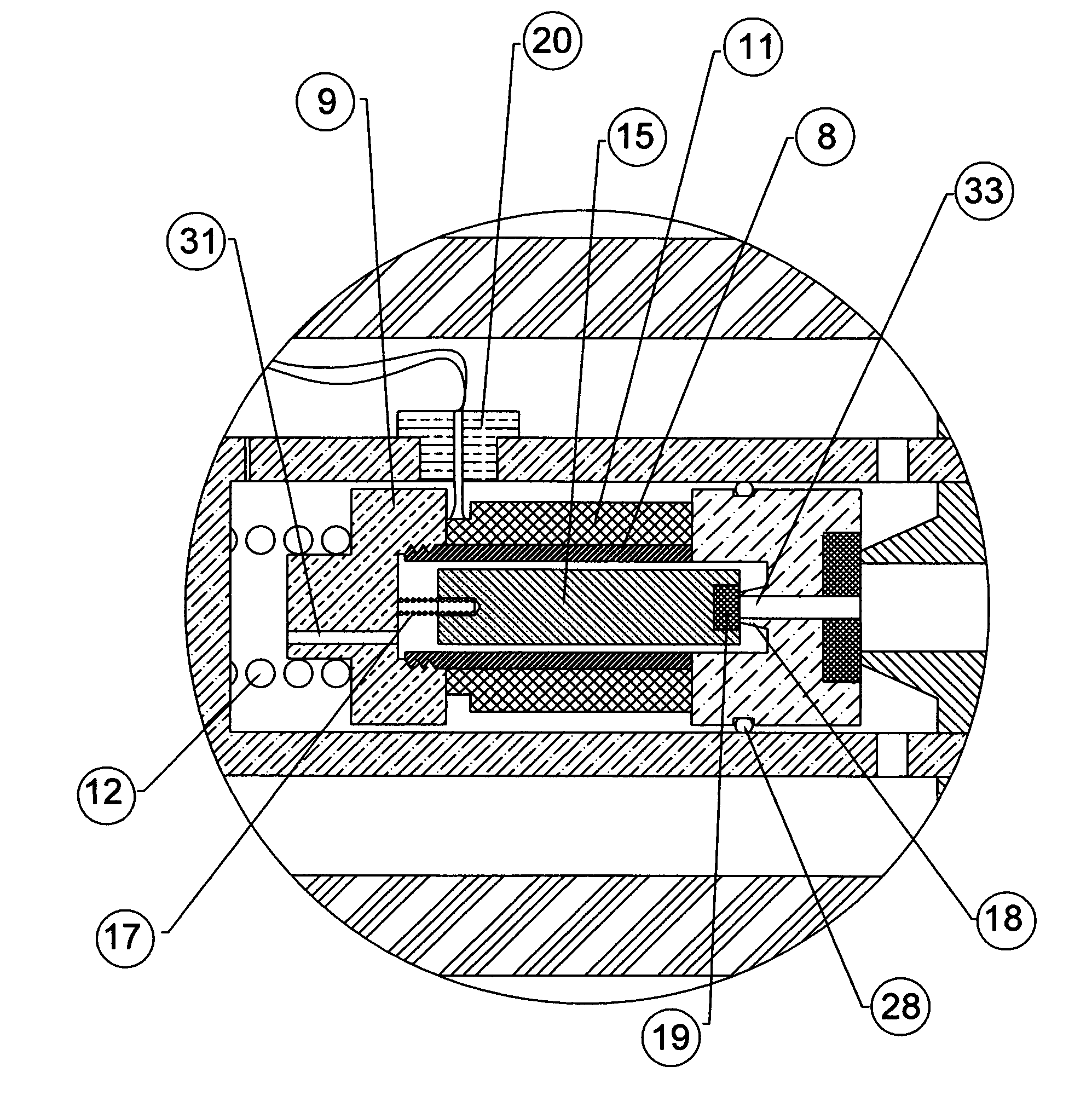
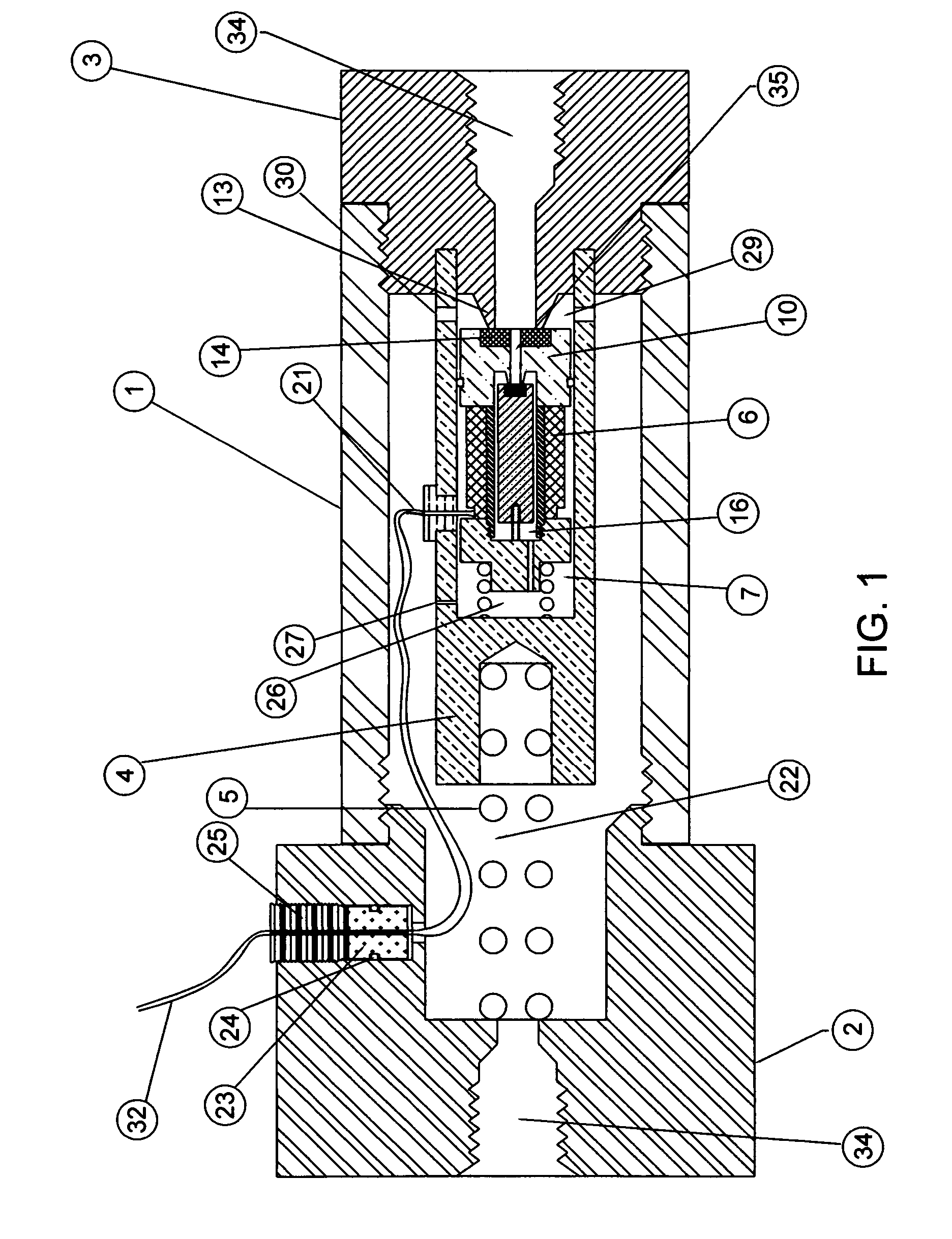
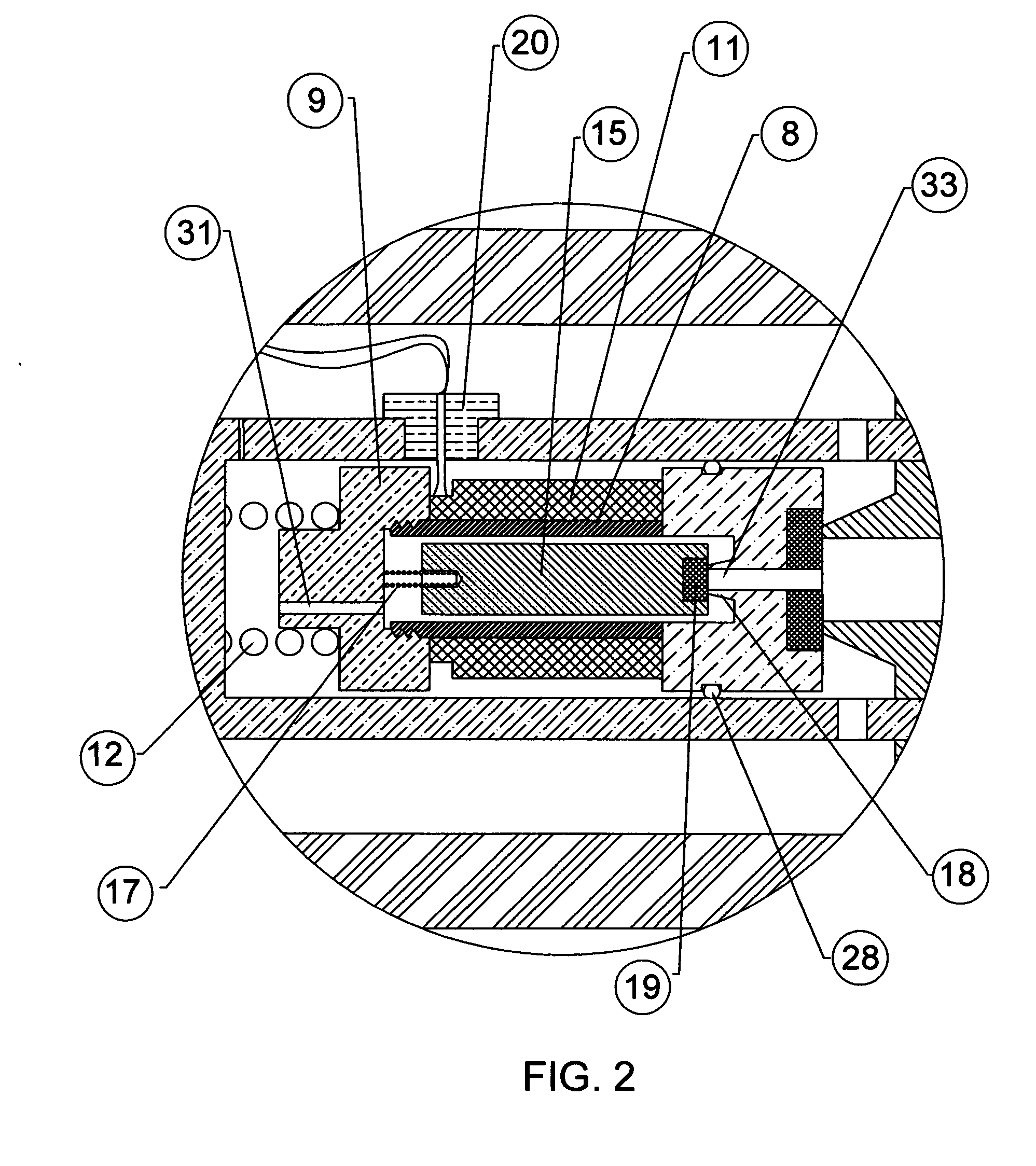
[0021] Attention is first directed to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, which shows an in-tube solenoid gas valve in section view. The valve tube 1 has a hollow hole with internal threads at both ends, to accept both inlet fitting 2 and outlet fitting 3. Both fittings have an axial hole 34 with internal threads for connecting adaptive fittings of piping system. A support cylindrical body 4, pushed by a compression spring 5 against said outlet fitting 3, having a chamber 7, provides the space for movements of the solenoid assembly 6 which comprises of a hollow sleeve 8, a stop 9, a flange 10 and an electrical coil 11.
[0022] A compression spring 12 pushes said solenoid assembly 6 to the seal seat 13 of said outlet fitting 3 at “closed” state. A plastic insert 14 is molded onto said flange 10 to provide seal. A magnetic rod 15 moveable axially in the hollow space 16 of said solenoid assembly 6, while a compression spring 17 pushes said magnetic rod 15 against the small seal seat 18 of said flange 10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com