Flatness monitor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
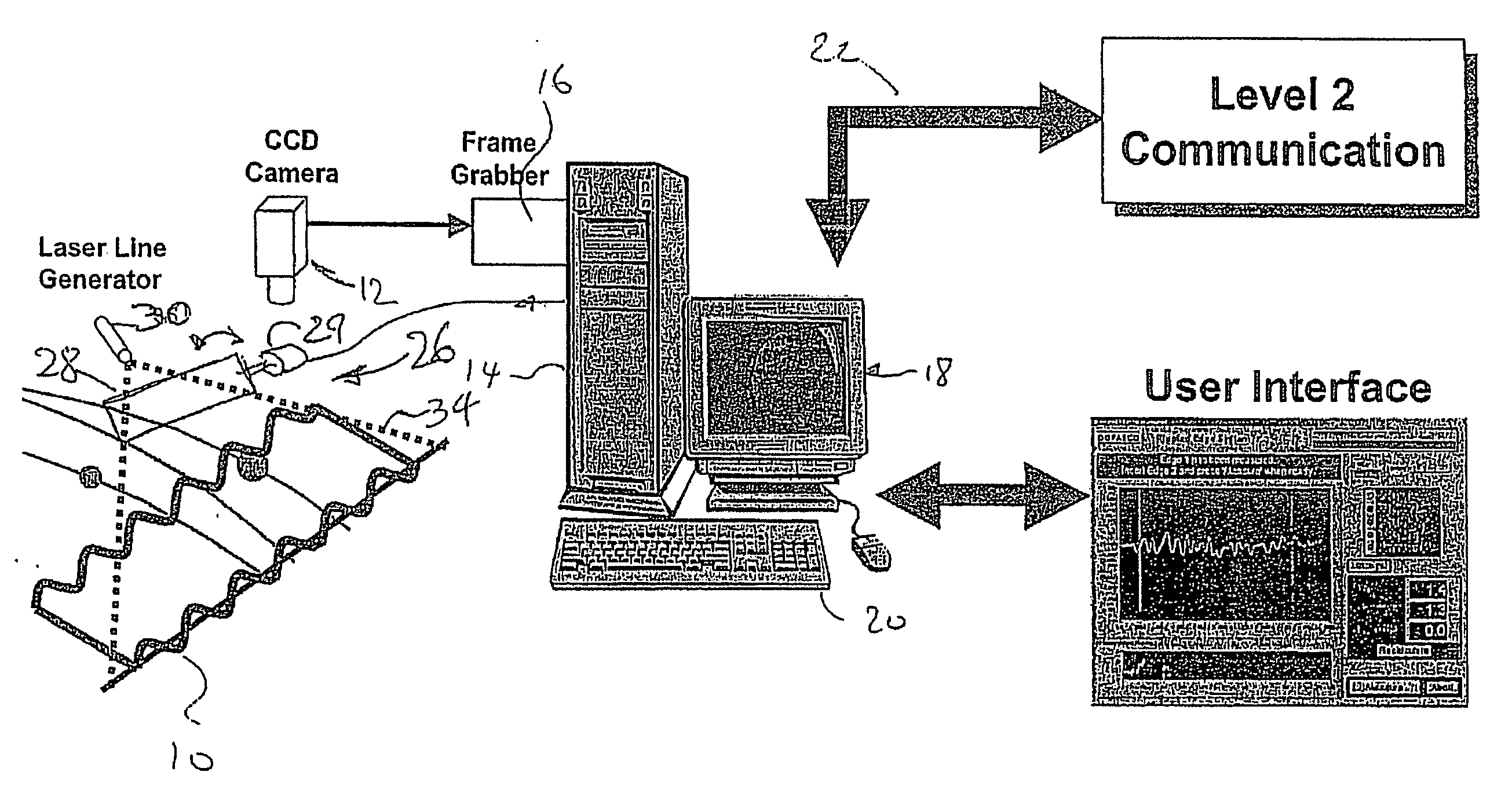
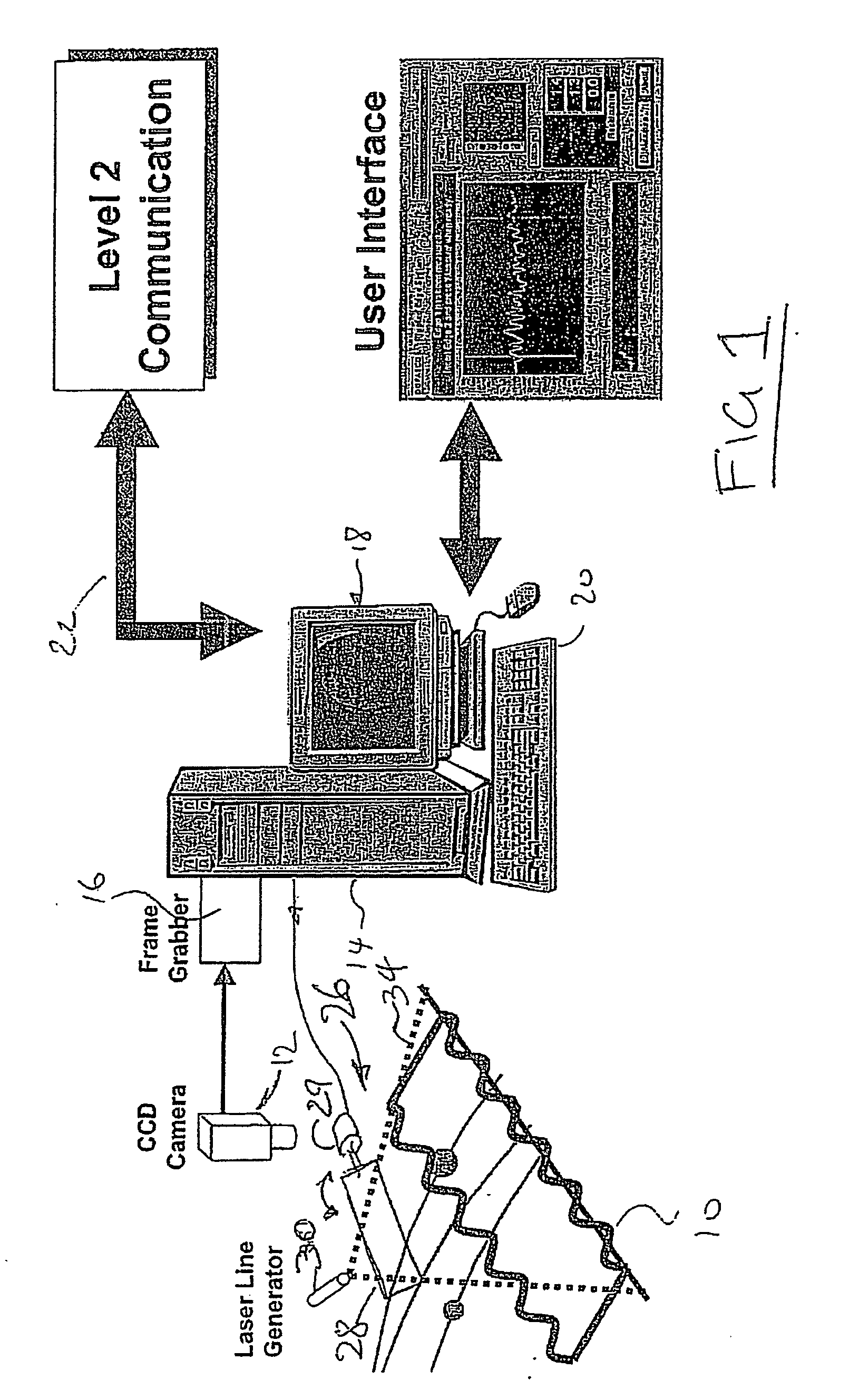
[0019] Referring therefore to FIG. 1, a sample of steel strip 10 whose flatness is to be assessed is supported beneath a camera 12. The camera 12 is connected to a computer 14 having image processing software 16. The computer 14 is connected to a user interface 18 and an input device 20 to control the image produced on the interface 18. The computer 14 may also connect to auxiliary communications related to process control systems as indicated generally at 22.
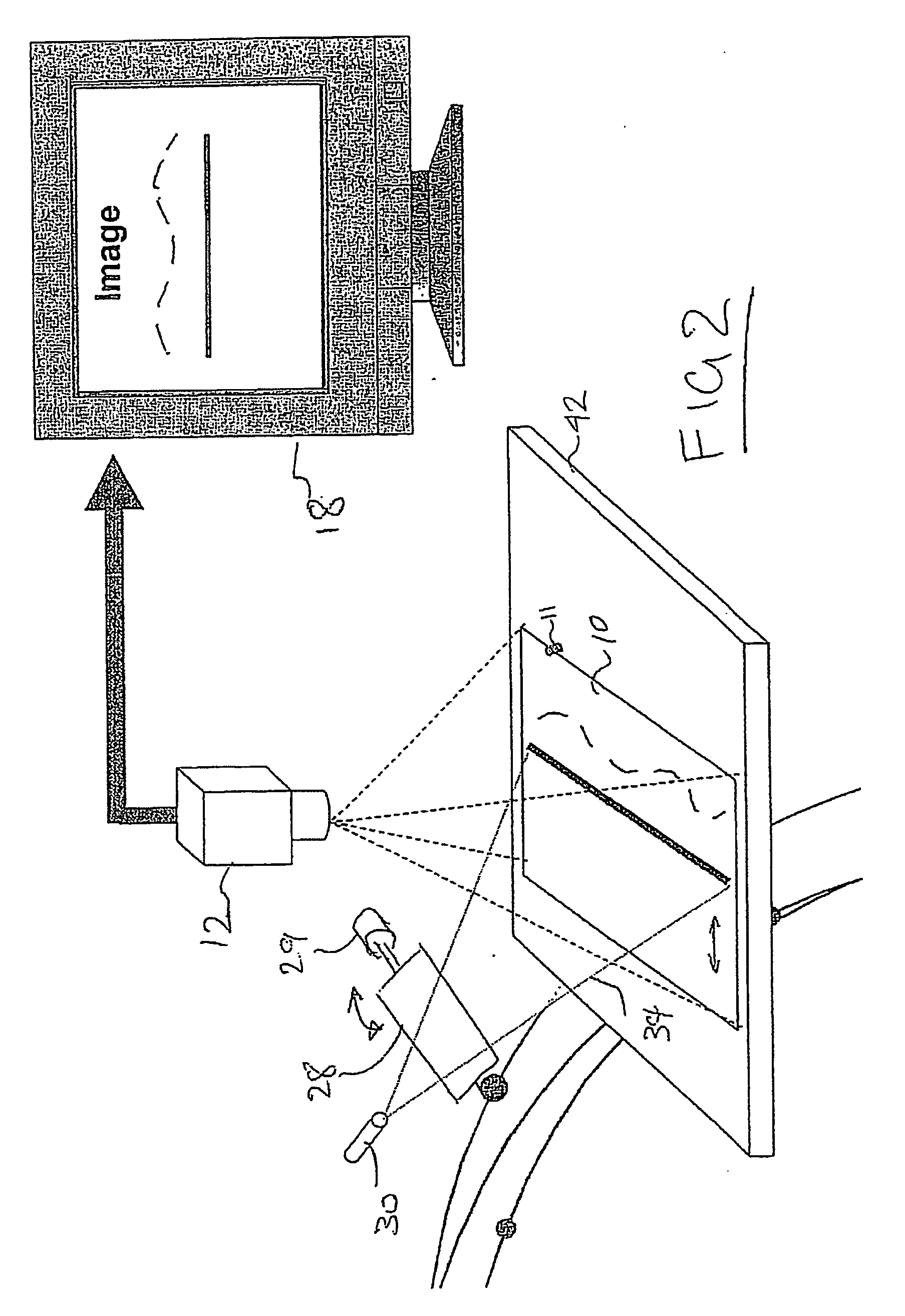
[0020] A scanner assembly 26 includes a scanning mirror 28 driven by a galvonometer 29 controlled by the computer 14. A coherent radiation source, e.g., a laser device 30, includes a lens to produce a fan shaped optical beam 34 that produces a line on a surface. The laser 30 is positioned such that the beam 34 intercepts the surface of the mirror 28 and is reflected on to the sample 10 at an angle to the optical axis of the camera 12. The point of impingement of the beam 34 on the sample 10 is controlled by the orientation of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dimension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com