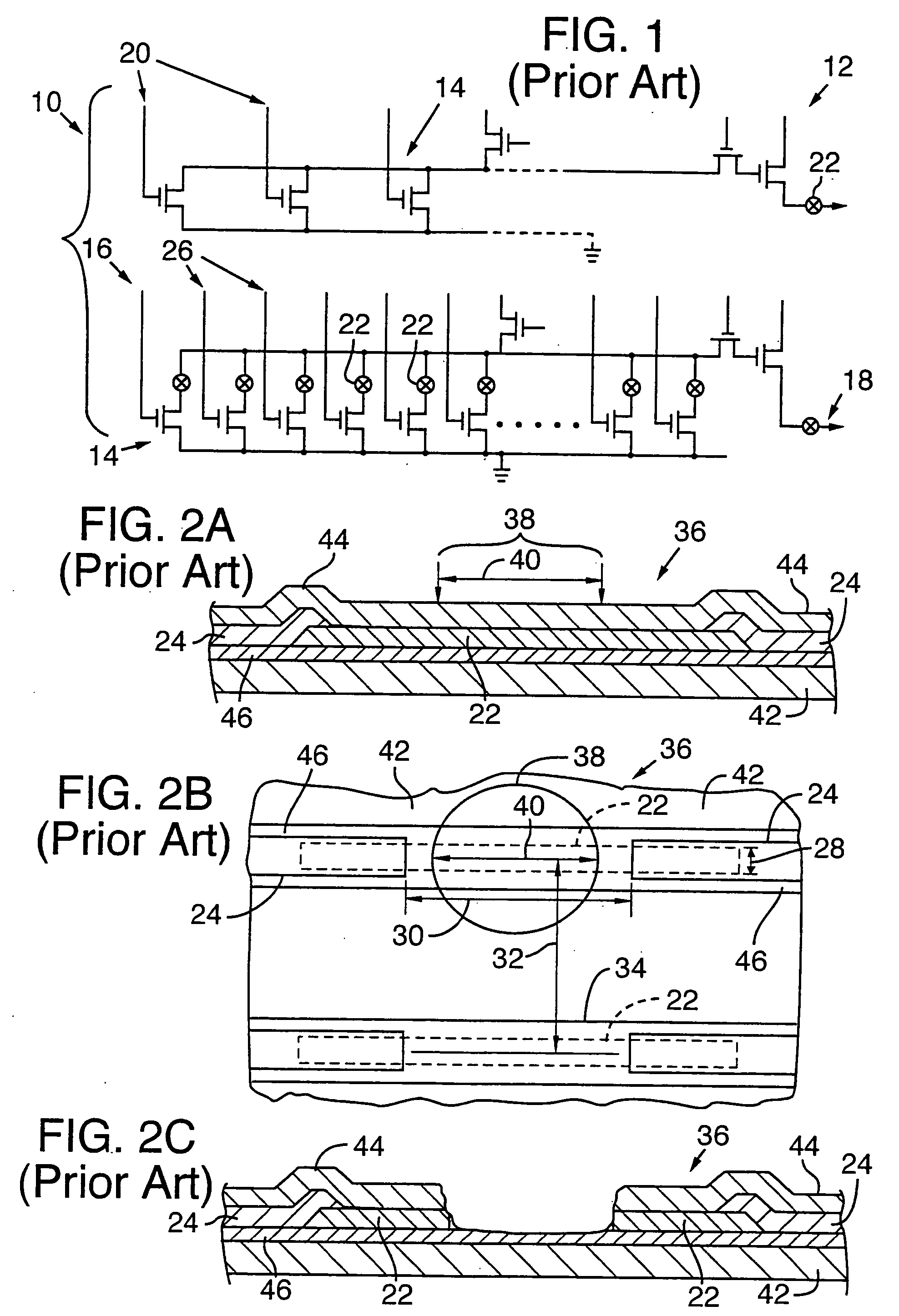
Processing a memory link with a set of at least two laser pulses
a memory link and laser pulse technology, applied in semiconductor lasers, semiconductor/solid-state device details, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete link severing, increased laser pulse energy, and deterioration of the quality of the device that includes the severed link, so as to improve the quality of laser processing of ic links.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
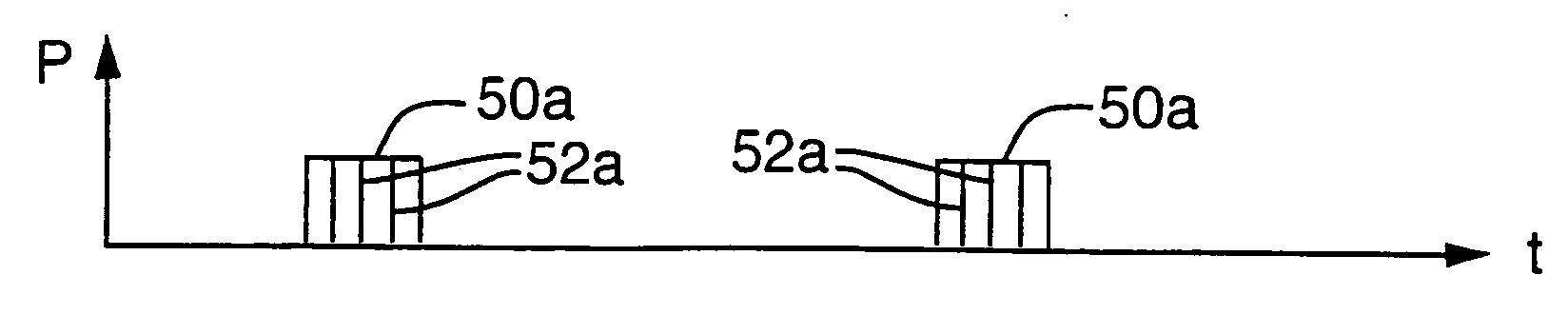
[0039]FIGS. 3-5, 9, 10B, 12, 14D, and 16C show power versus time graphs of exemplary sets 50a, 50b, 50c,50d, 50e, 50f, and 50g (generically sets 50) of laser pulses 52a, 52b1-52b8, 52c1-52c5, 52d1-52d3, 52e1-52e4, 52f1-52f2, and 52g1-52g2 (generically laser pulses 52) employed to sever links 22 in accordance with the present invention. Preferably, each set 50 severs a single link 22. Preferred sets 50 include 2 to 50 pulses 52. The duration of each set 50 is preferably shorter than about 1000 ns, more preferably shorter than 500 ns, and most preferably in the range of about 5 ns to 300 ns. Sets 50 are time-displaced by a programmable delay interval that is typically shorter than 0.1 millisecond and may be a function of the speed of the positioning system 62 and the distance between the links 22 to be processed. The pulse width of each laser pulse 52 within set 50 is in the range of about 100 fs to about 30 ns.
[0040] During a set 50 of laser pulses 52, each laser pulse 52 has insuff...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com