Symmetric multiprocessor operating system for execution on non-independent lightweight thread contexts
a multi-processor operating system and lightweight technology, applied in multi-programming arrangements, program control, climate sustainability, etc., can solve the problems of low performance improvement that may be achieved through exploitation of instruction-level parallelism, low performance, and low performance of single-threaded microprocessor pipeline stages, etc., to achieve high scalable performance, low cost, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
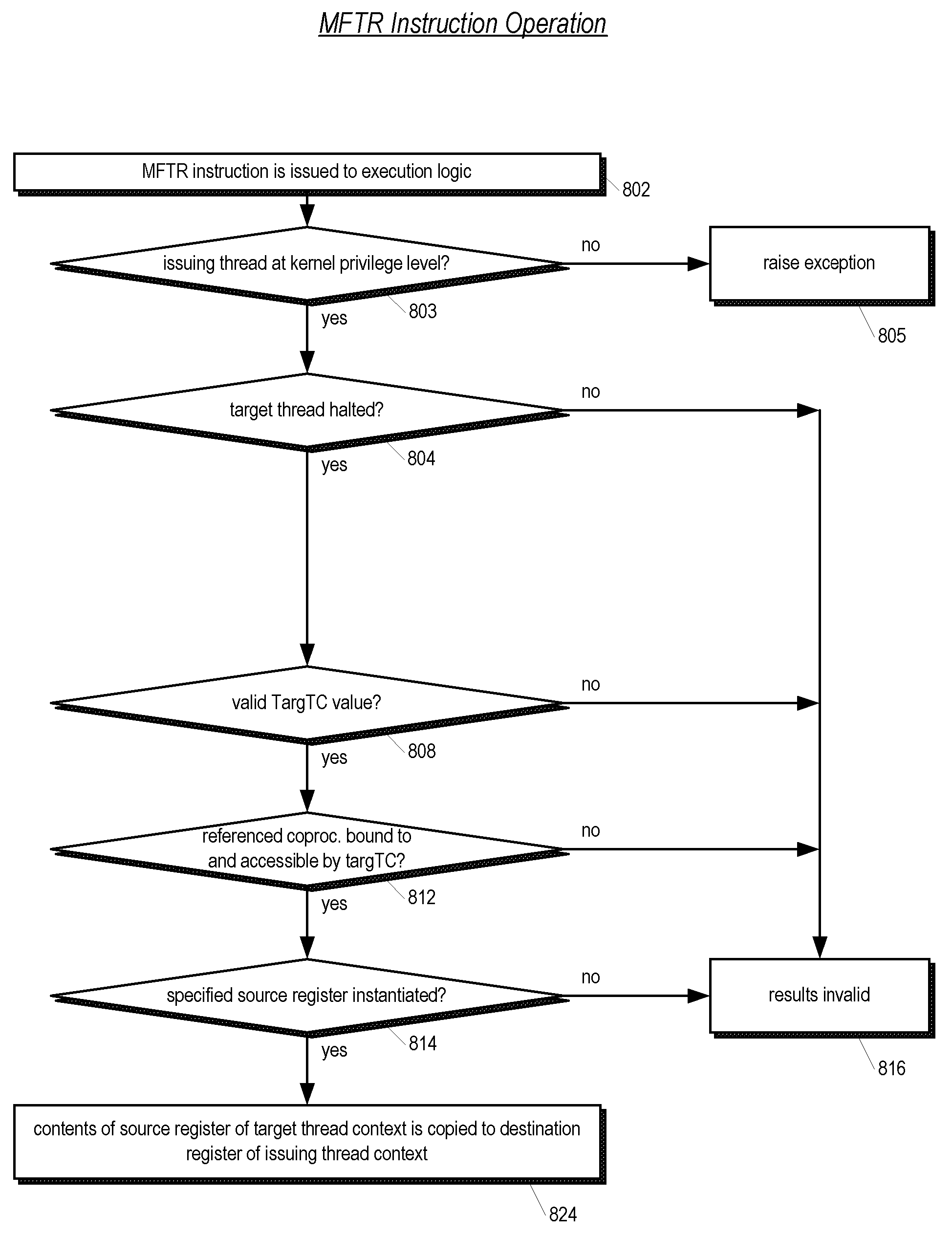
[0051] For a better understanding of exception processing, translation lookaside buffer (TLB) operation, and floating point unit (FPU) coprocessor operation on MIPS architecture processors in general, the reader is referred to MIPS RISC Architecture, by Gerry Kane and Joe Heinrich, published by Prentice Hall, and to See MIPS Run, by Dominic Sweetman, published by Morgan Kaufman Publishers.
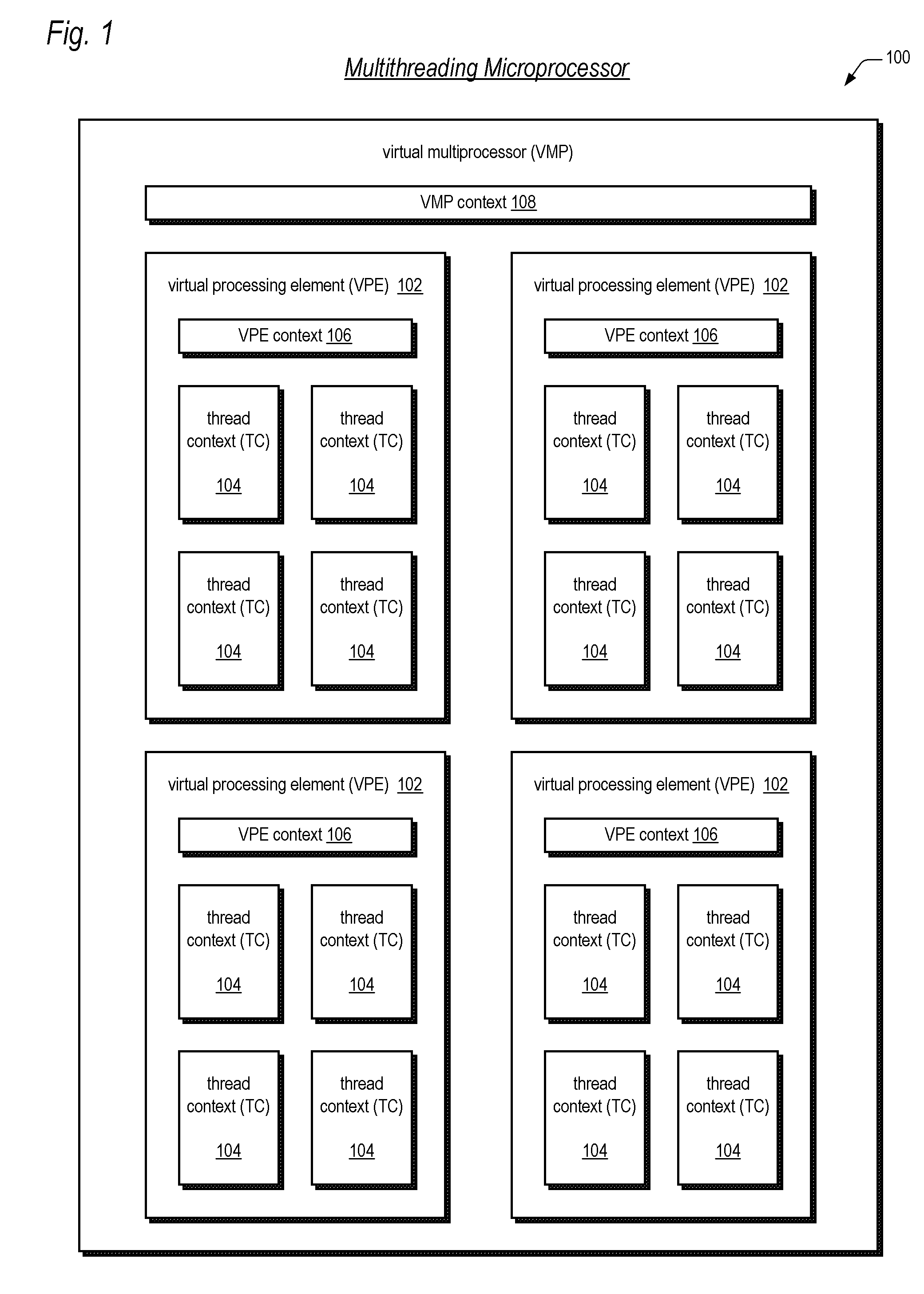
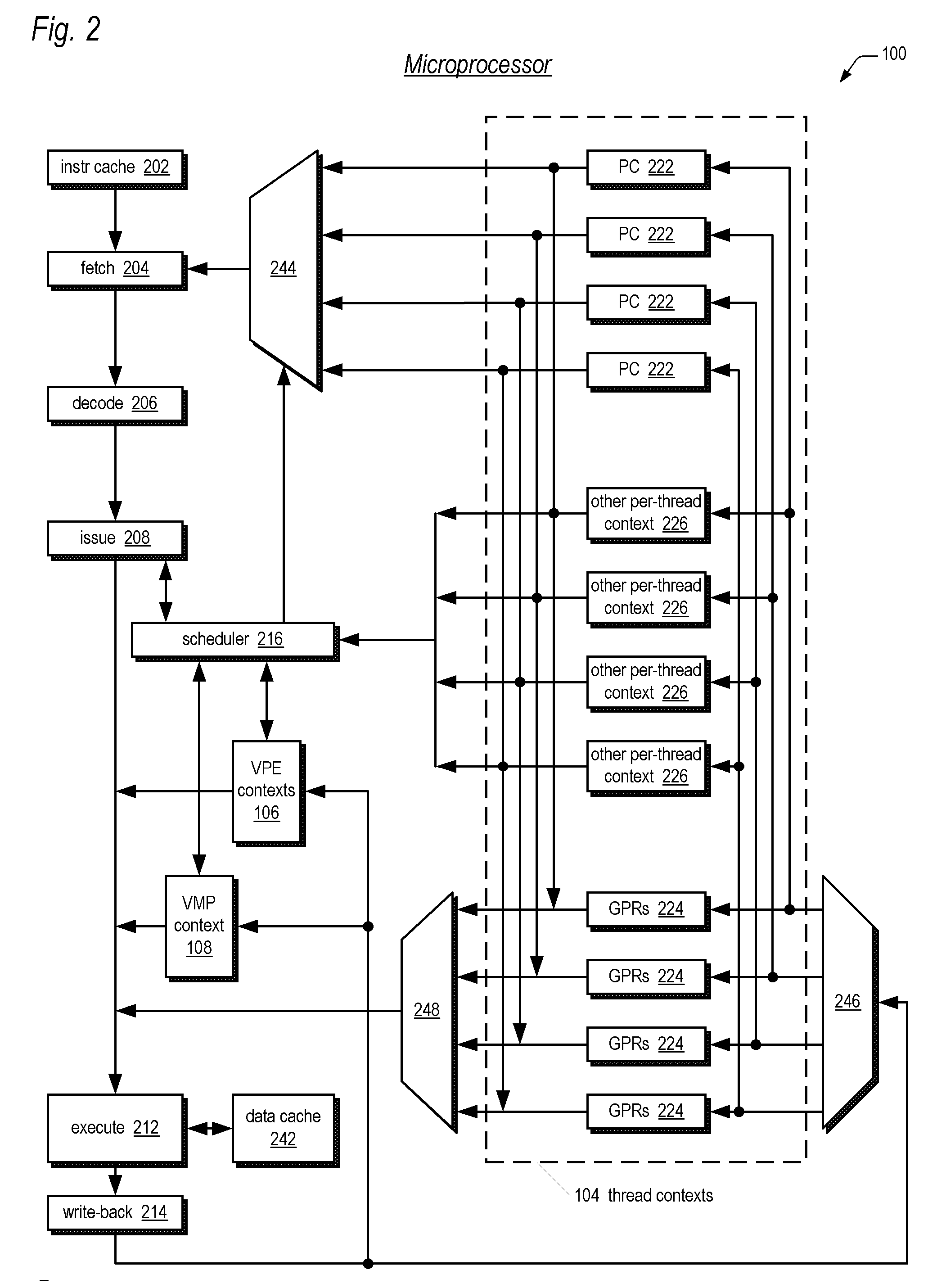
[0052] Embodiments of the present invention are described herein in the context of a processor core that includes the MIPS® MT Application-Specific Extension (ASE) to the MIPS32® Architecture; however, the present invention is not limited to a processor core with said architecture. Rather, the present invention may be implemented in any processor system which includes a plurality of thread contexts for concurrently executing a corresponding plurality of threads, but which does not include an interrupt input for each of the plurality of thread contexts that would allow one thread context to direct ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com