Semiconductor device
a semiconductor and device technology, applied in the field of semiconductor devices, can solve problems such as the inability to obtain optimal layout systems, and achieve the effect of simplifying the layout structure of semiconductors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
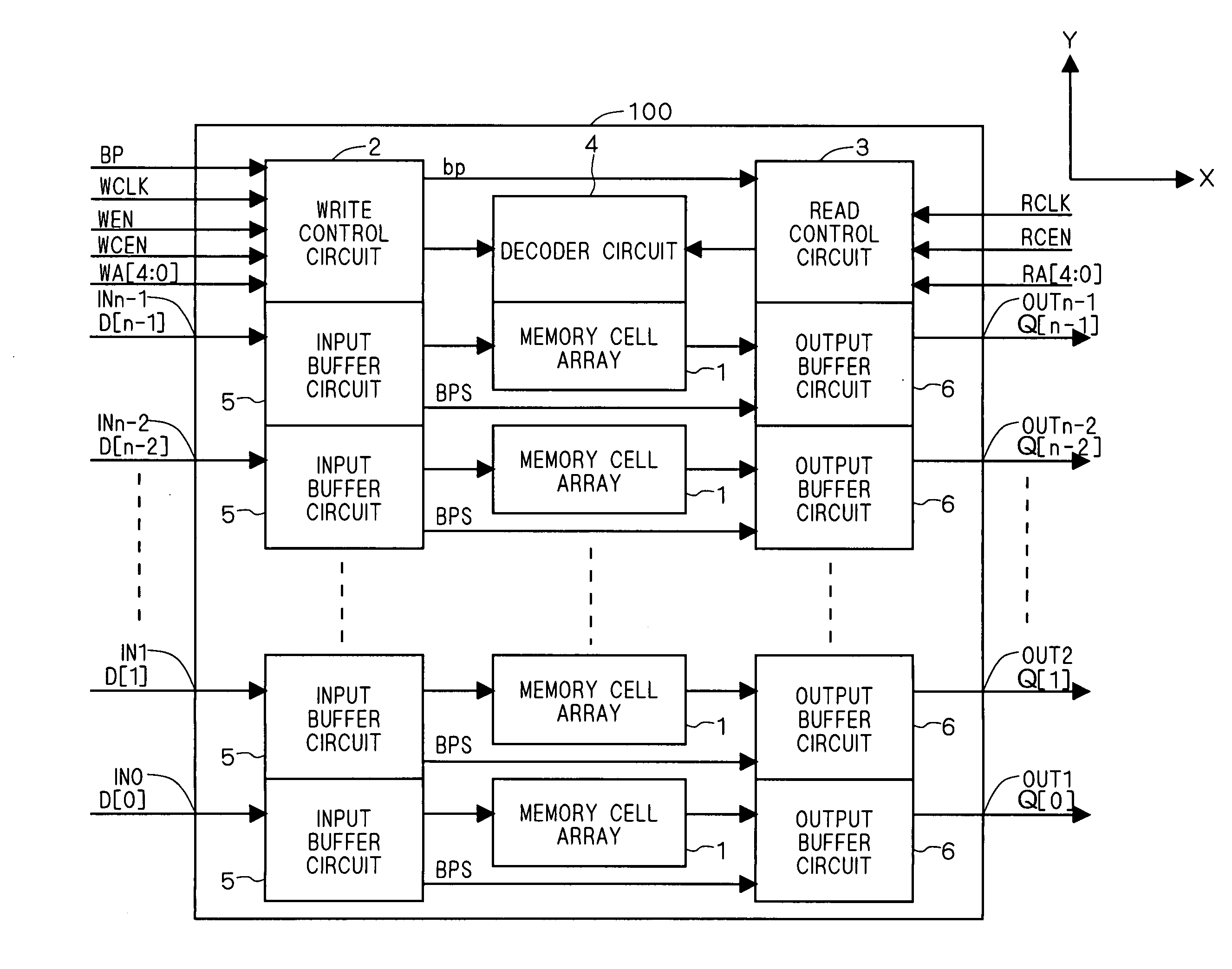
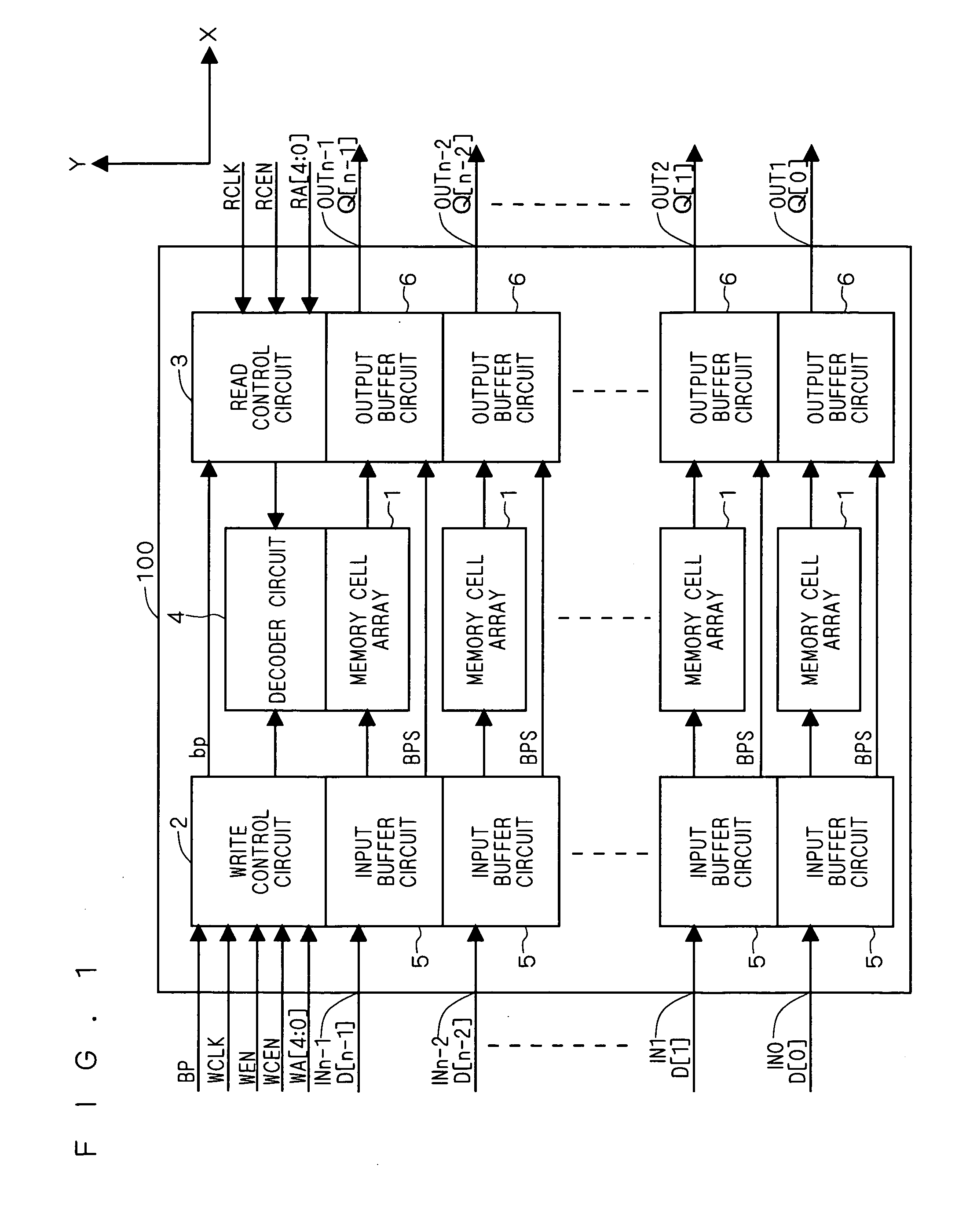
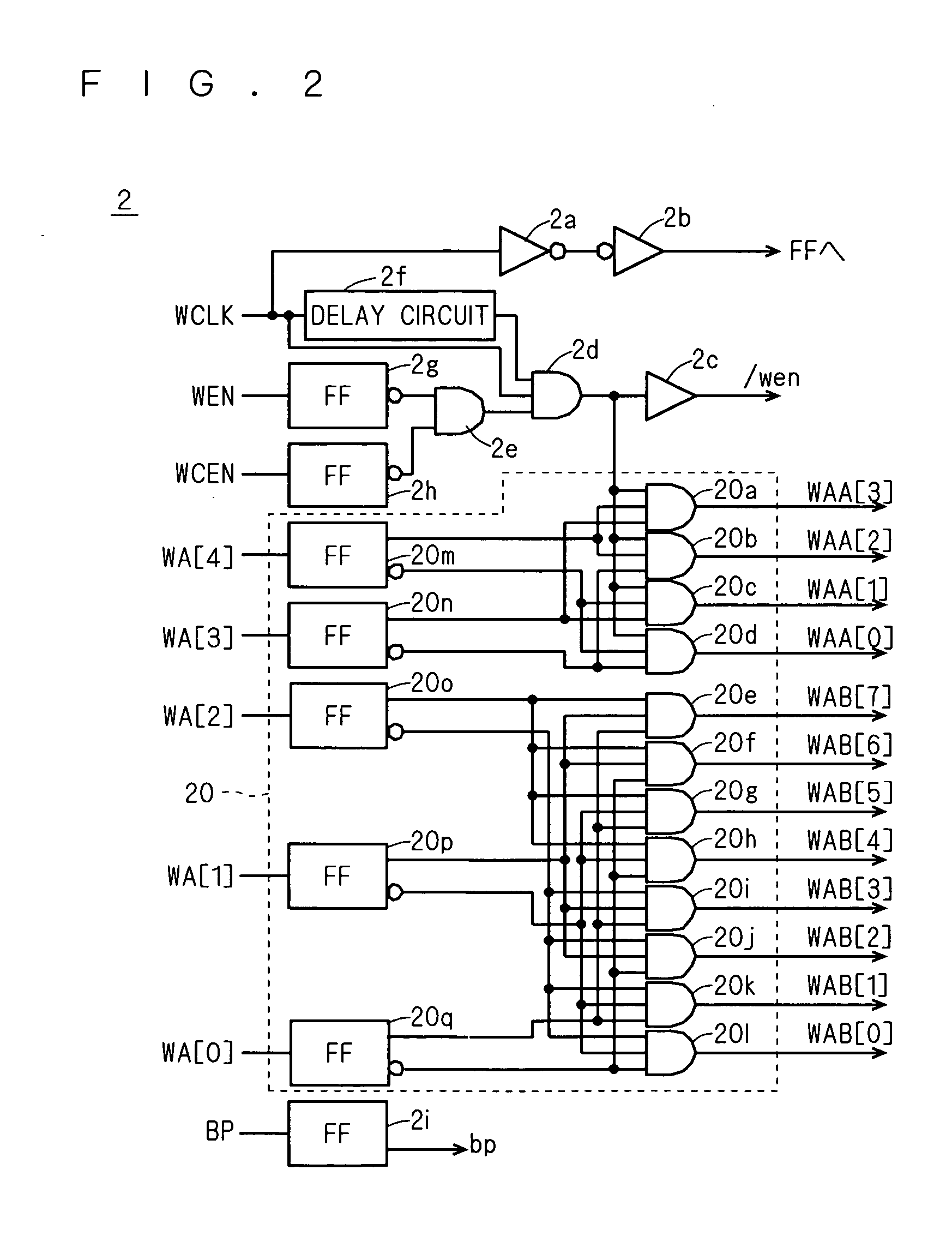
[0037]FIG. 1 is a plan view schematically showing a layout structure of a semiconductor memory device 100 according to a first embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1, the semiconductor memory device 100 according to the first embodiment includes: n input ports (n≧1) IN0 to INn-1; n output ports OUT0 to OUTn-1; a write control circuit 2; a read control circuit 3; and a decoder circuit 4. Further, the semiconductor memory device according to the first embodiment is provided with n groups each consisting of one memory cell array 1, one input buffer circuit 5 and one output buffer circuit 6.
[0038] n-bit input data D[n-1:0] is inputted into the semiconductor memory device 100, and n-bit output data Q[n-1:0] is outputted from the semiconductor memory device 100. Input data D[0] to D[n-1] are respectively inputted into the input ports IN0 to INn-1, and output data Q[0] to Q[n-1] are respectively outputted from the output ports OUT0 to OUTn-1.
[0039] Input data D[i] among ...
second embodiment
[0091]FIG. 10 is a plan view schematically showing a layout structure of the semiconductor memory device 110 according to a second embodiment. The semiconductor memory device 110 according to the second embodiment is a device that can realize the bypass function without arrangement of the bypass line BPL for intended for the purpose by arranging, in the aforesaid semiconductor memory device 100 of the first embodiment, a write control circuit 12 in place of the write control circuit 2, n input buffer circuits 15 in place of the n input buffer circuits 5, and n output buffer circuits 16 in place of the output buffer circuits 6. As in the first embodiment, one input buffer circuit 15, one output buffer circuit 16 and one memory cell array 1 constitute one group. The layout of the write control circuit 12, the input buffer circuit 15 and the output buffer circuit 16 is the same as the layout of the write control circuit 2, the input buffer circuit 5 and the output buffer circuit 6 acco...
third embodiment
[0108] FIGS. 13 to 16 are plan views schematically showing a circuit configuration of a semiconductor memory device according to a third embodiment of the present invention. The semiconductor memory device according to the third embodiment is a device formed by arranging, in the semiconductor memory device 110 according to the second embodiment, n memory cell arrays 21 in place of the n memory cell arrays 1, a write control circuit 22 in place of the write control circuit 12, a read control circuit 33 in place of the read control circuit 3, a decoder circuit 24 in place of the decoder circuit 4, n input buffer circuits 25 in place of the n input buffer circuits 15, and n output buffer circuits 26 in place of the output buffer circuits 16. As in the second embodiment, one input buffer circuit 25, one output buffer circuit 26 and one memory cell array 1 constitute one group. The layout of the memory cell array 21, the write control circuit 22, the read control circuit 23, the decoder ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com