Systems and methods for inspecting a wafer with increased sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
Background Atmospheric Scattering with Normal Air and Helium Atmospheres
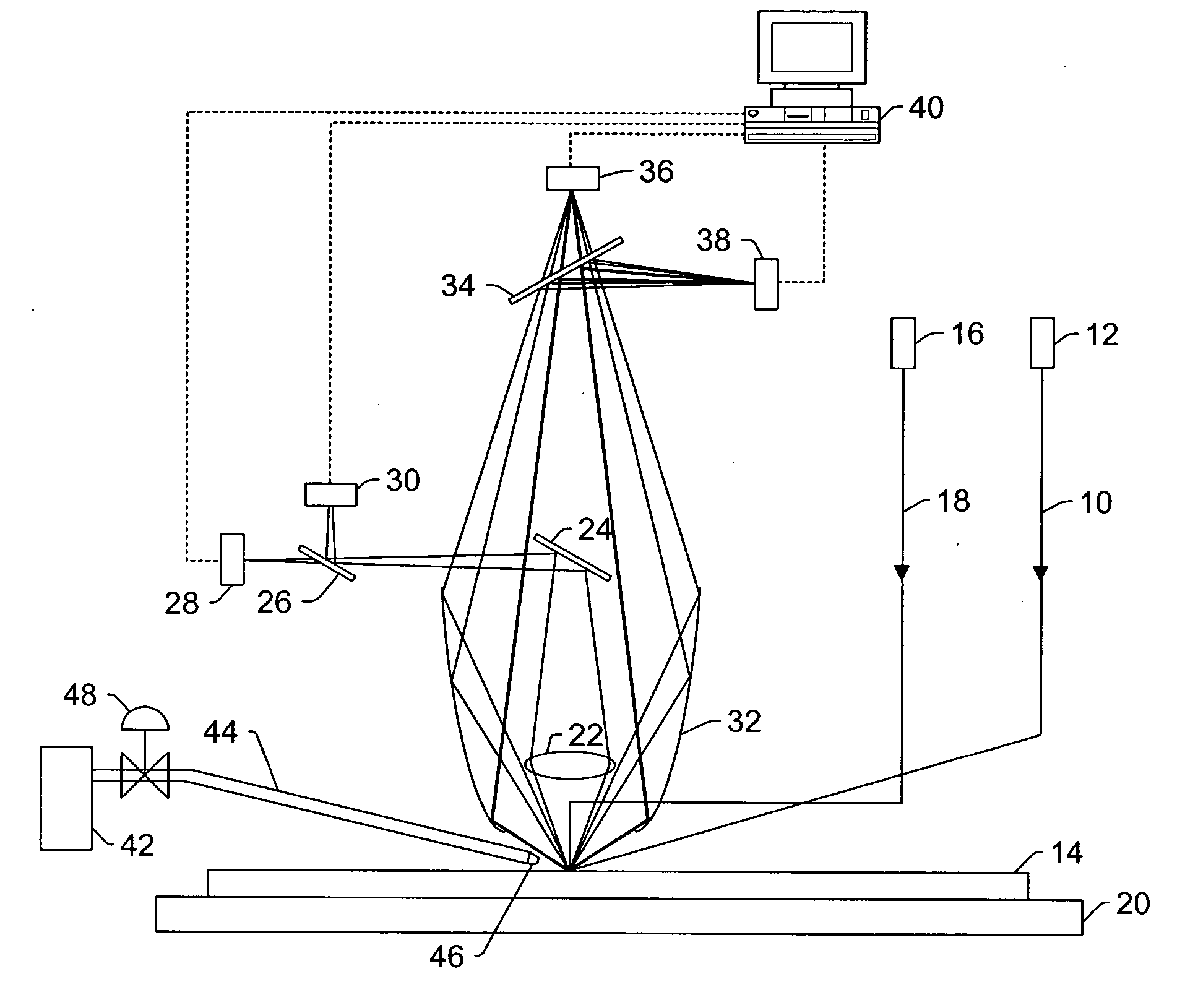
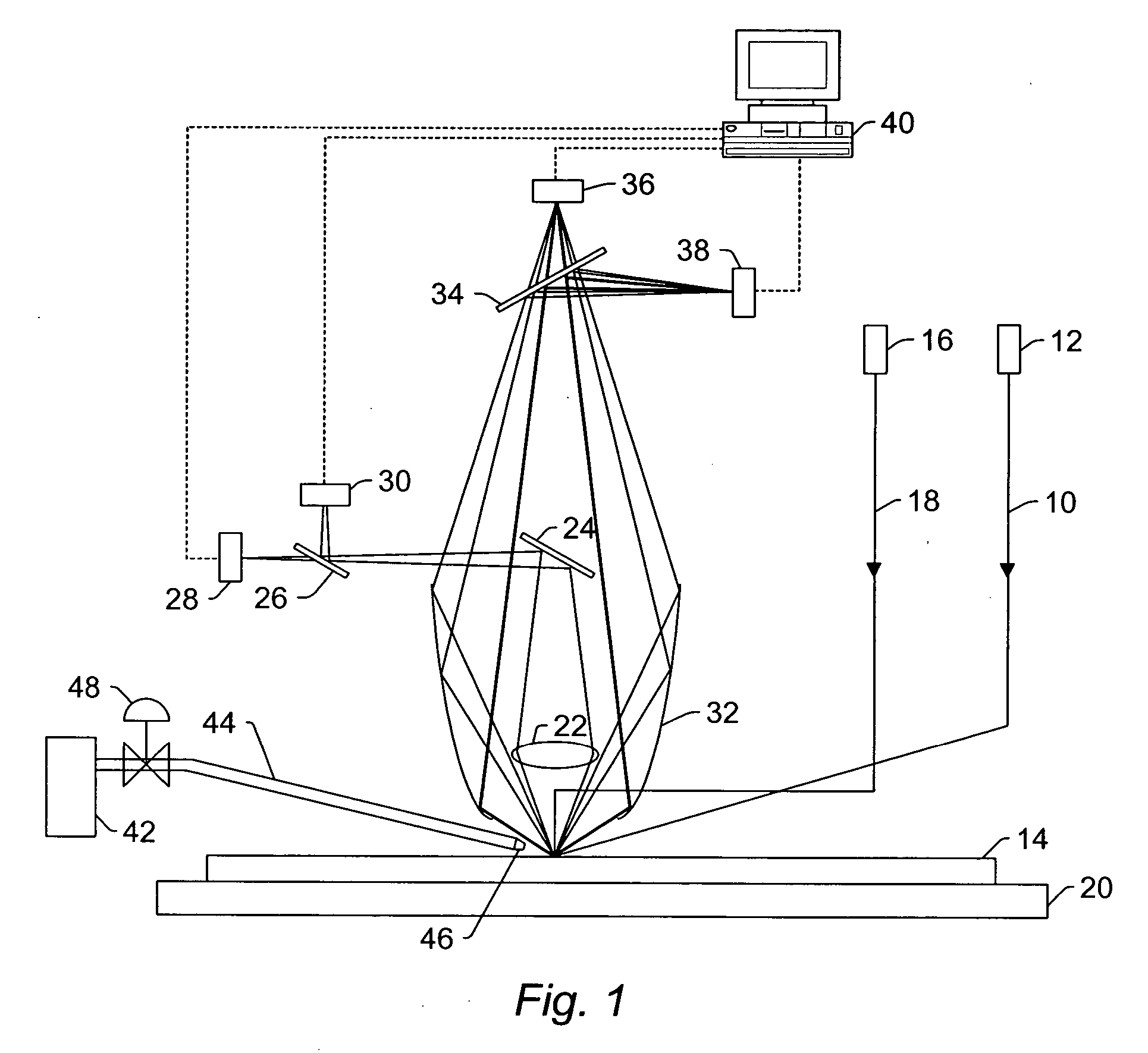
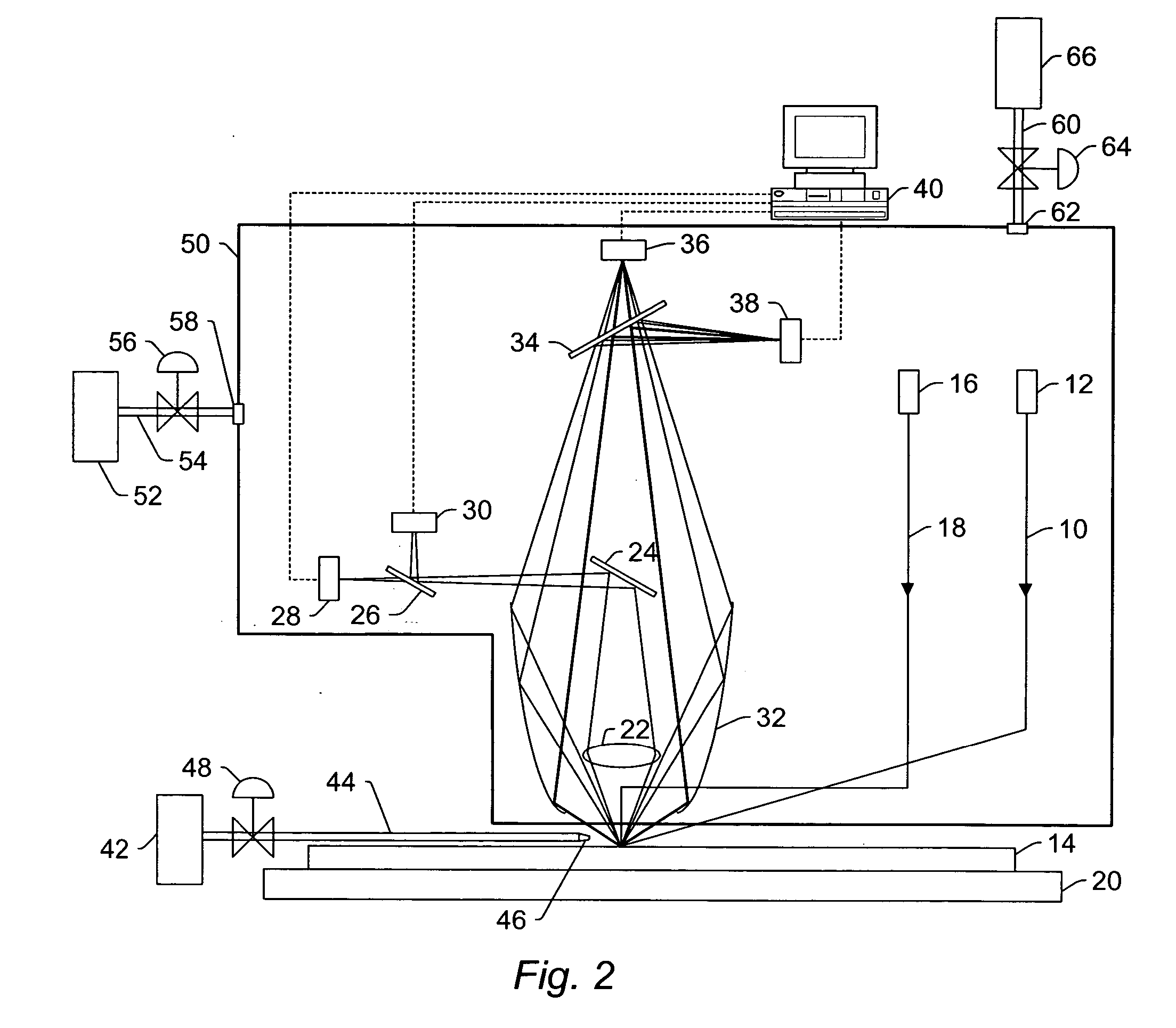
[0088] The background atmospheric scattering of normal air and helium atmospheres was measured using an SP2 tool that included a 350 mW laser operating at a wavelength of 355 nm. The normal air atmosphere in the SP2 tool was replaced with a helium atmosphere by “flooding” the collector of the SP2 tool with high purity helium (>98% purity). The helium was provided to the system using a helium tank and a 400 mm long tube about 50 mm in diameter attached to the bottom of the wide collector (i.e., ellipsoidal mirror 32 described above). The helium was inserted about half way into the tube with an estimated flow rate on the order of 1 L / s. The helium flowed up into the collector thereby replacing some or most of the air in the collector. Openings in the middle section of the collector allowed the helium flow to “push” any residual air out of the collector. The scattering in the two different atmospheres was measured...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com