Method and arrangements relating to satellite-based positioning
a satellite-based positioning and positioning method technology, applied in the field of satellite-based positioning, can solve the problems of significant error in the calculated position of mobile stations, and achieve the effect of increasing robustness, without reducing detection sensitivity, and increasing robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
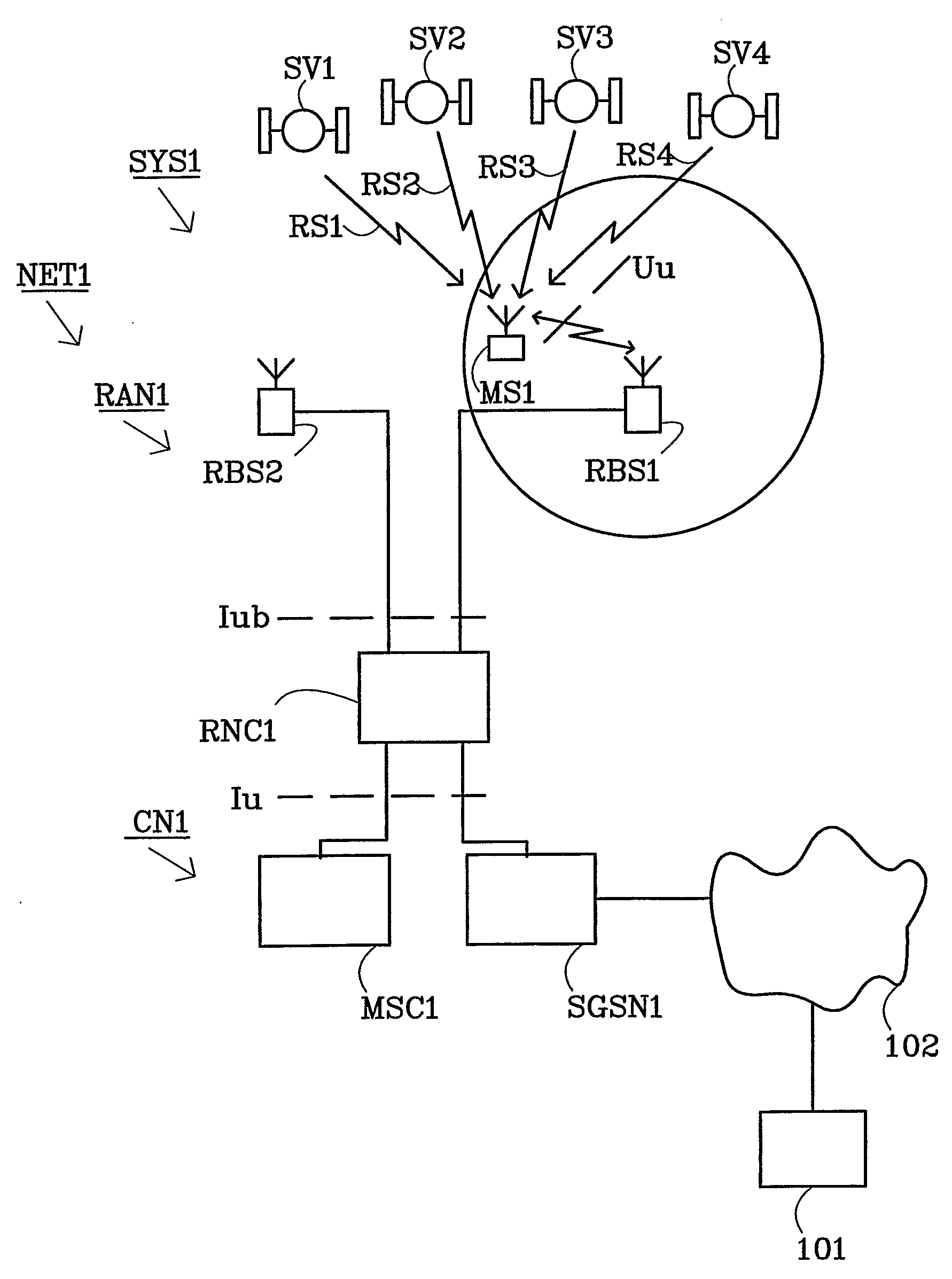
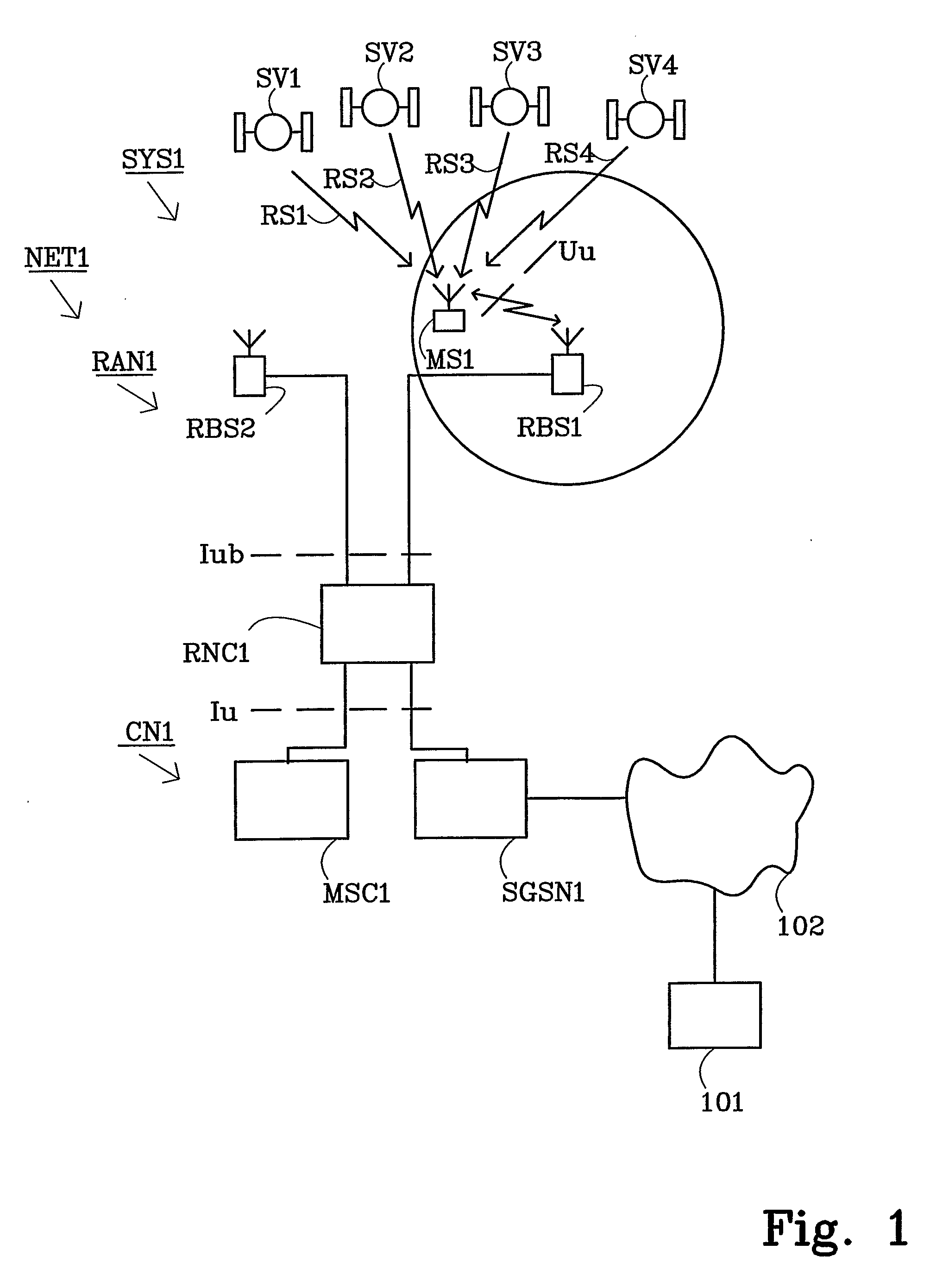
[0024]FIG. 1 illustrates a non-limiting example scenario in which the present invention may be applied. In this example scenario a basic wireless communication system SYS1 together with the Global Positioning System (GPS) is used to provide Mobile Station assisted AGPS. The example wireless communication system SYS1 illustrated in FIG. 1 is a Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS). The communication system SYS1 includes a network part NET1 and User Equipment (UE), alternatively referred to as mobile stations (MS). The network part NET1 comprises a core network CN1 and a UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) RAN1. The core network CN1 includes a Mobile services Switching Center (MSC) node MSC1 that provides circuit-switched services and a General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) node SGSNl, sometimes referred to as a Serving GPRS Support node (SGSN), which is tailored to provide packet-switched type services.
[0025] Each of the core network nodes MSC1 and SGSN1 connects ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com