Method for compensating for accessory loading
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
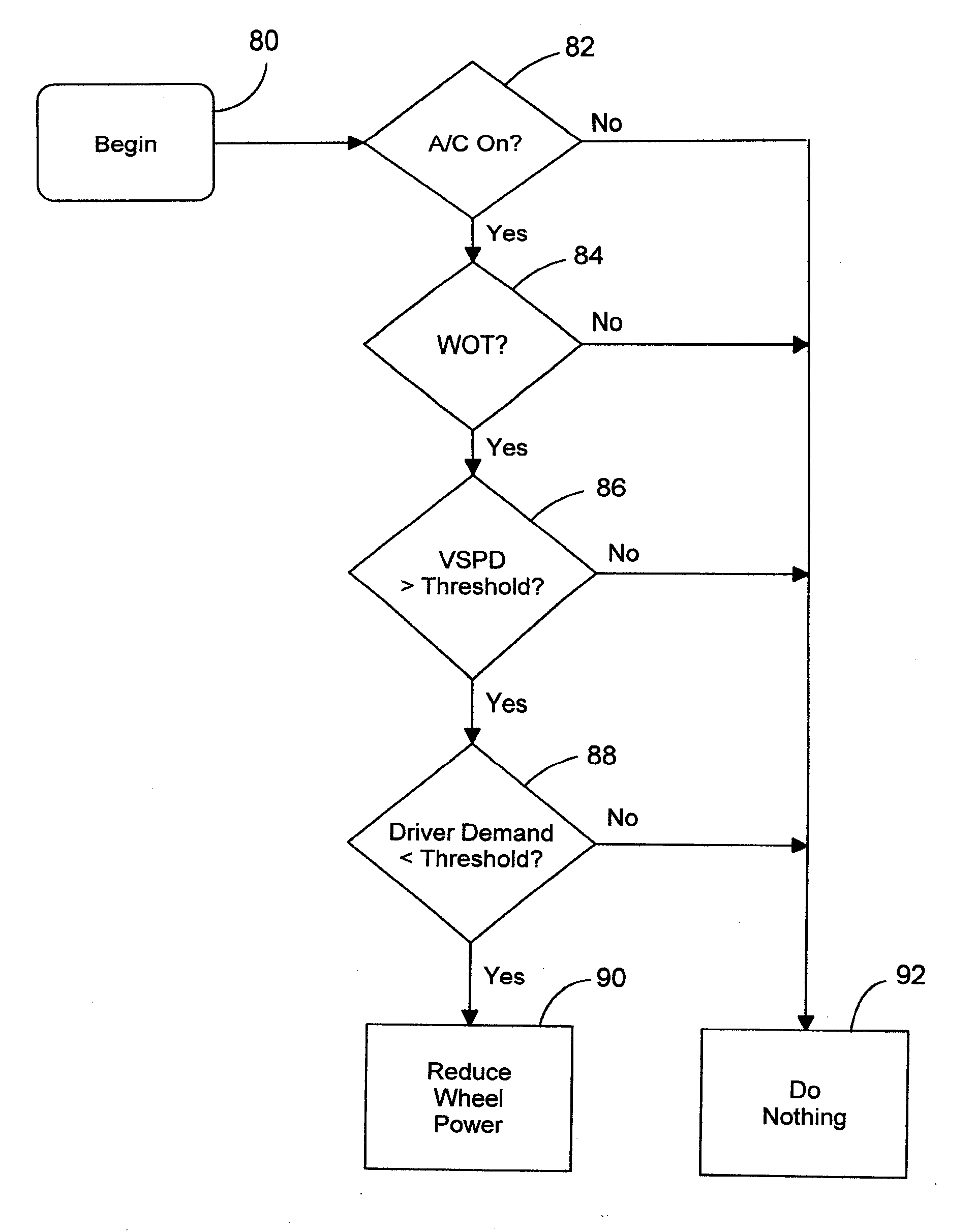
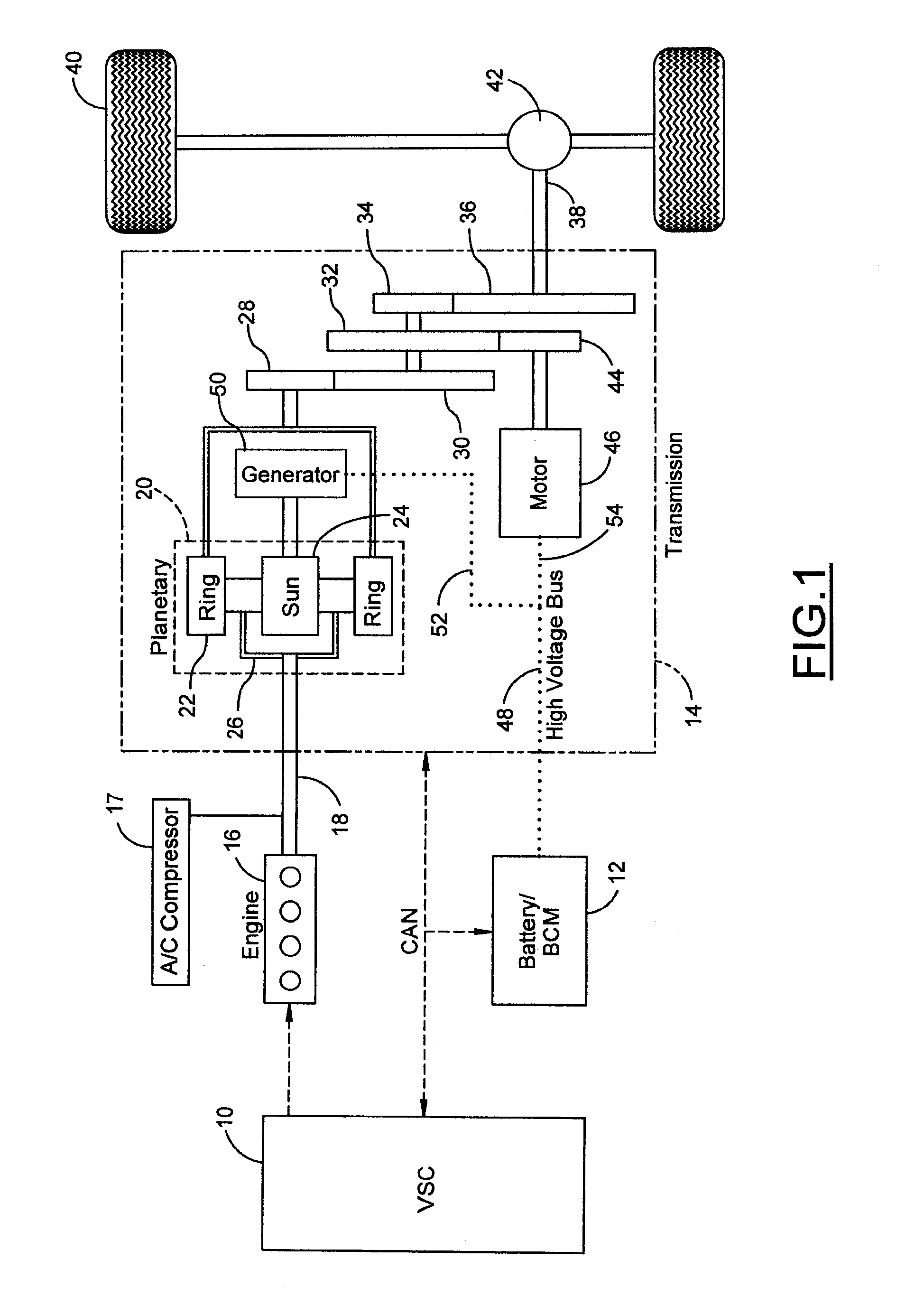
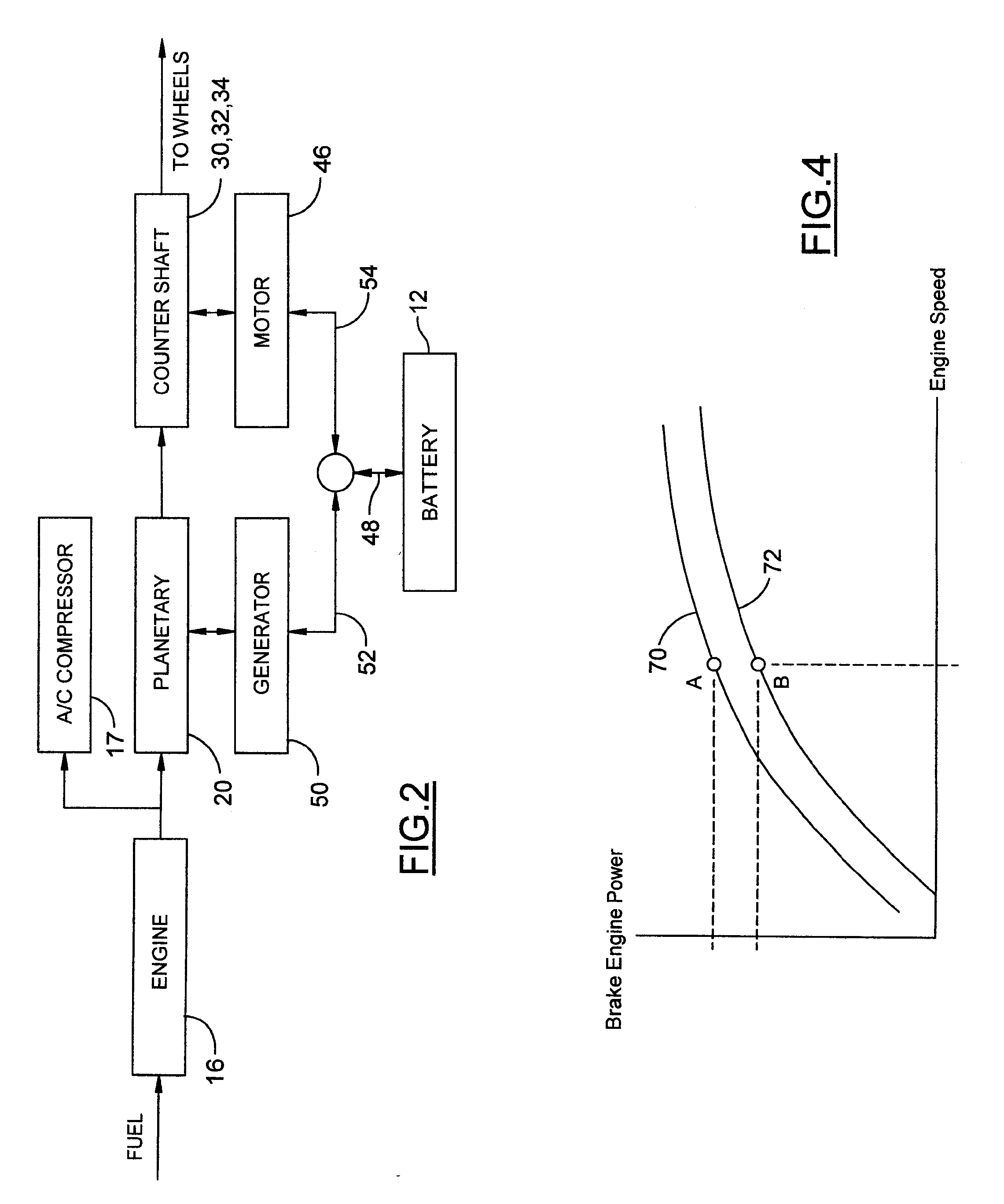
[0019] A hybrid electric vehicle powertrain is shown in FIG. 1. A vehicle system controller (VSC) 10, a battery and battery control module (BCM) 12, and a transmission 14, together with a motor-generator subsystem, comprise a control area network (CAN). An engine 16, controlled by VSC 10, distributes torque through torque input shaft 18 to transmission 14.
[0020] The transmission 14 includes a planetary gear unit 20, which comprises a ring gear 22, a sun gear 24, and a planetary carrier assembly 26. The ring gear 22 distributes torque to step ratio gears comprising meshing gear elements 28, 30, 32, 34, and 36. A torque output shaft 38 for the transmission is drivably connected to vehicle traction wheels 40 through a differential and axle mechanism 42.
[0021] Gears 30, 32, and 34 are mounted on a countershaft, with gear 32 engaging a motor-driven gear 44. Electric motor 46 drives gear 44, which acts as a torque input for the countershaft gearing.
[0022] The battery delivers electric ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com