Leakage current detection and interruption circuit
a leakage current detection and interruption circuit technology, applied in the direction of emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/current, coupling device connection, switch with electromagnetic release, etc., can solve the problem of short circuit between the ac input terminals of the gfci, disconnection of the protected motor, ground fault on the span
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
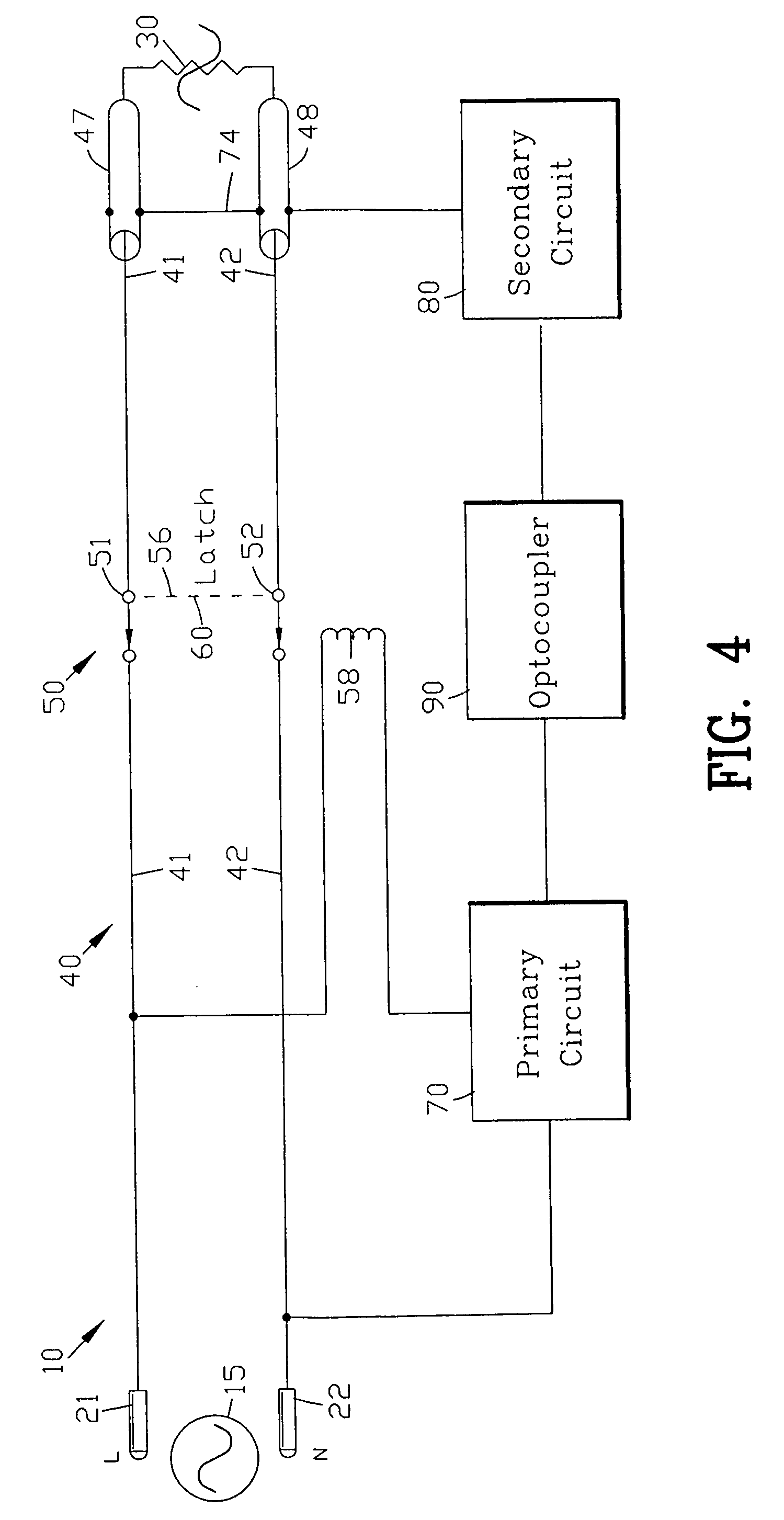
[0092]FIG. 12 is a circuit diagram of the circuit 10 of FIG. 4. The first and second terminals 21 and 22 extending from the housing 20 are connected to the wires 41 and 42 of the wire assembly 40. A surge suppressor shown as a metal oxide varistor 26 is connected across the first and second wires 41 and 42. The function and operation of the metal oxide varistor 26 should be well known to those skilled in the art.
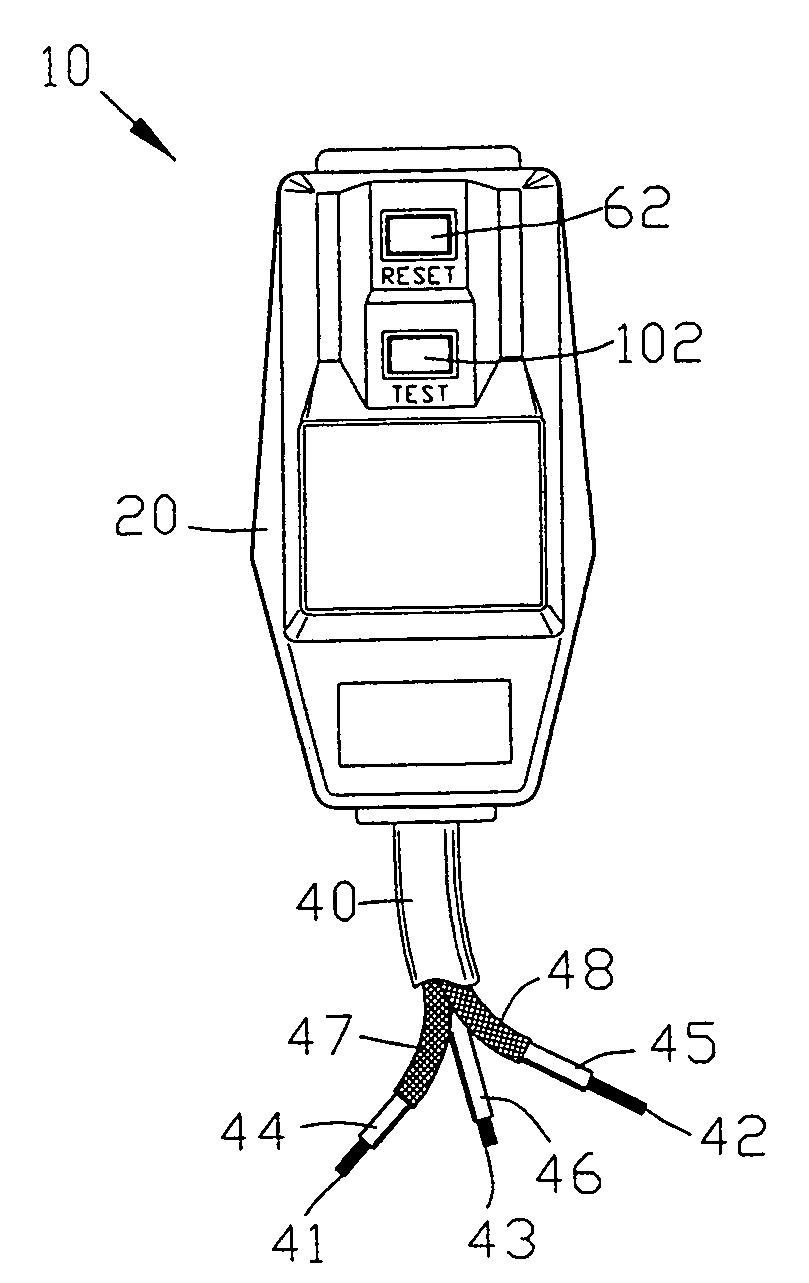
[0093] The disconnect 50 is interposed within the wire assembly 40 with the first and second switches 51 and 52 located within the first and second wires 41 and 42. The disconnect switch 50 is shown in the closed or reset condition.
[0094] The primary circuit 70 is located on a primary side of the disconnect switch 50 for controlling the disconnect switch 50. The primary circuit 70 opens the disconnect switch 50 upon the secondary circuit 80 sensing a leakage current from one of the wire 41 and 42. The disconnect switch 50 is controlled through the solenoid coil 58 by the pr...
second embodiment
[0108]FIG. 17 is a circuit diagram of the circuit 110 of FIGS. 1-4. Similar parts are labeled with similar reference numerals raised by the number 100. In this example, the electrical power source 115 is shown as a conventional 220 volt alternating current (AC) power source. Although the electrical power source 115 has been shown as conventional 220 volt alternating current (AC) power source, it should be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the present invention may be adapted to virtually any type of power source.
[0109] In this example, a voltage dropping resistor 167 is inserted in series between the first wire 141 and diode 168. In this example, the voltage divider network 171 is formed from resistor 172 and zener diode 173. The combination of the voltage dropping resistor 167 and the voltage divider network 171 comprising resistor 172 and zener diode 173 provides a minor conventional current through solenoid coil 158 to supply a collector voltage for the phototransistor...
third embodiment
[0110]FIG. 18 is a circuit diagram of the circuit 210 of FIGS. 1-4. In this embodiment of the invention the disconnect switch 250 is interposed between the source 215 and the load 230. The primary circuit 270 received operating power from a primary side or source side of the disconnect switch 250 by conductors 271 and 272. The secondary circuit 280 received operating power from a secondary side or load side of the disconnect switch 250 by conductors 281 and 282. The secondary circuit 280 is optically connected to the primary circuit 270 by the optocoupler 290.
[0111] In this example a conductor 292 connects a sensor 294 to the secondary circuit 280. The sensor 294 senses any leakage from either the first or the second wires 241 and 242. The sensor 294 may be the ground wire normally included in a conventional 110 volt alternating current power cord.
[0112] When the sensor 294 senses a leakage from either the first or the second wires 241 and 242, the secondary circuit 280 optically a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com