Cosmetic Compositions and Methods Comprising Rhodiola Rosea
a technology of rhodiola rosea and composition, applied in the field of skin care cosmetic compositions and methods, can solve the problems of cosmetically unacceptable opaque formulations, easy to be removed by washing, and relatively short-lived
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
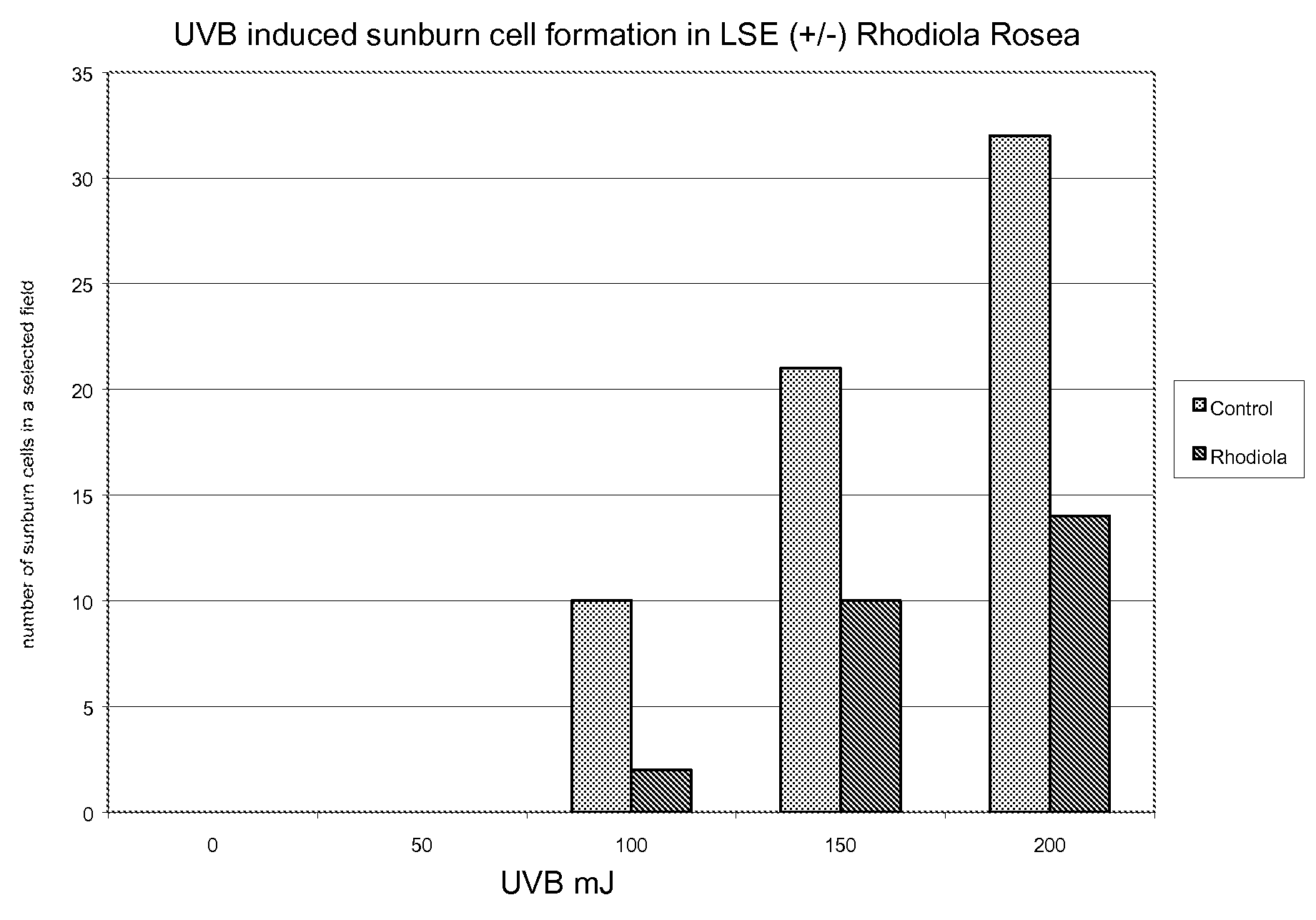
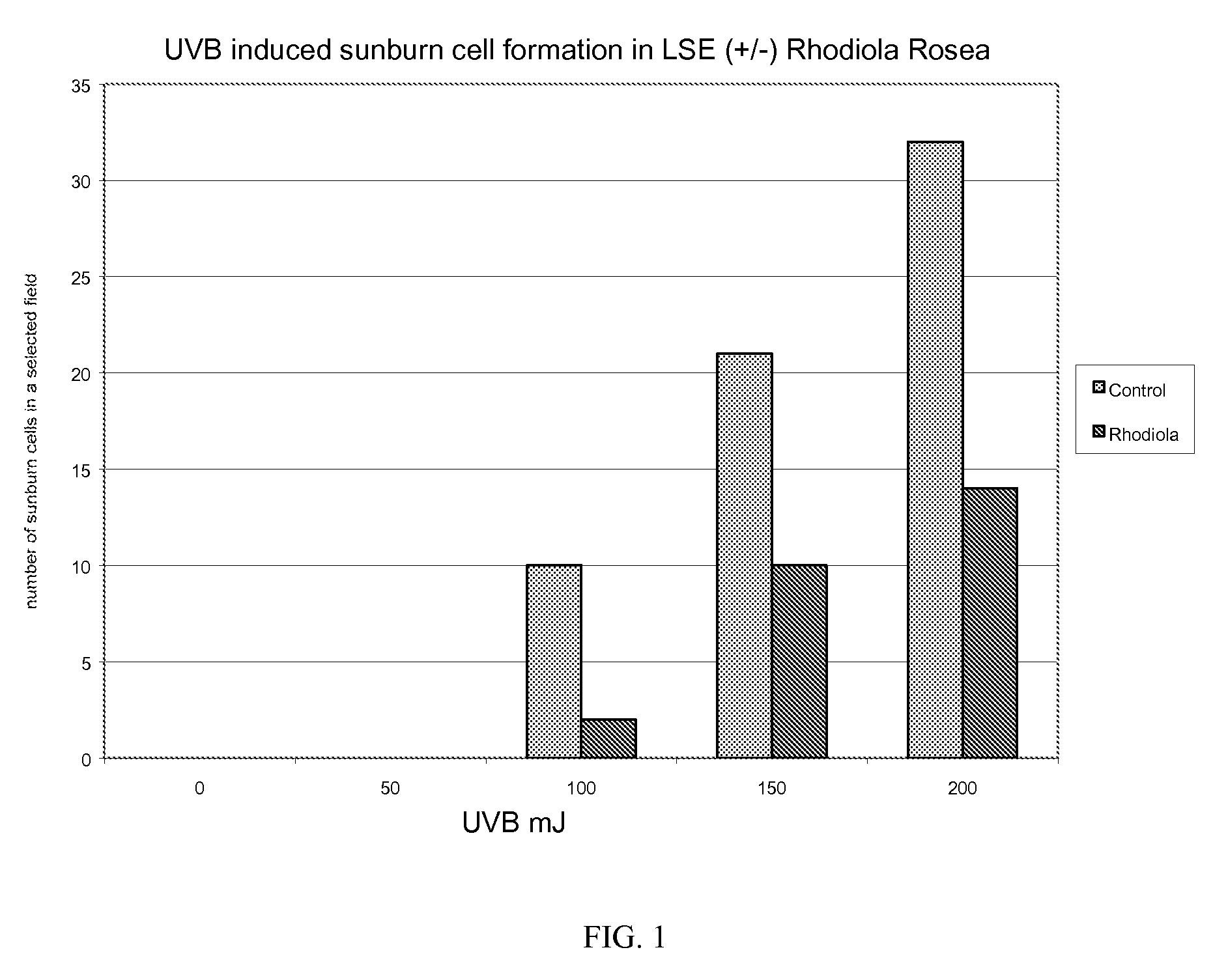
[0037]The effect of Rhodiola rosea on UVB-induced sunburn cell formation in living skin equivalents (LSEs) is tested. Excised portions (8 mm) are taken from living skin equivalents (Organogenesis) and cultured over transwell membrane plates. These excised portions are pre-treated with Rhodiola rosea at 0.1 mg / ml (PBS) for 4 hours. After the post-incubation, these excised portions are UVB-irradiated at 0, 50, 100, 150 and 200 mJ / cm2. Following a 24 hour post-incubation, these skin equivalents are fixed in formalin and stored at −4° C. These samples are then stained using H&E staining. Sections are then evaluated using a microscope at 400× magnification. A section is selected from each sample and counts of sunburn cells were made.
[0038]Results and Discussion: As seen in FIG. 1, UVB induces a dose-dependent increase of sunburn cell formation in living skin equivalents. There are 10, 21 and 32 sunburn cells in a selected field at 100 mJ, 150 mJ, and 200 mJ UVB radiation, respectively (F...
example 2
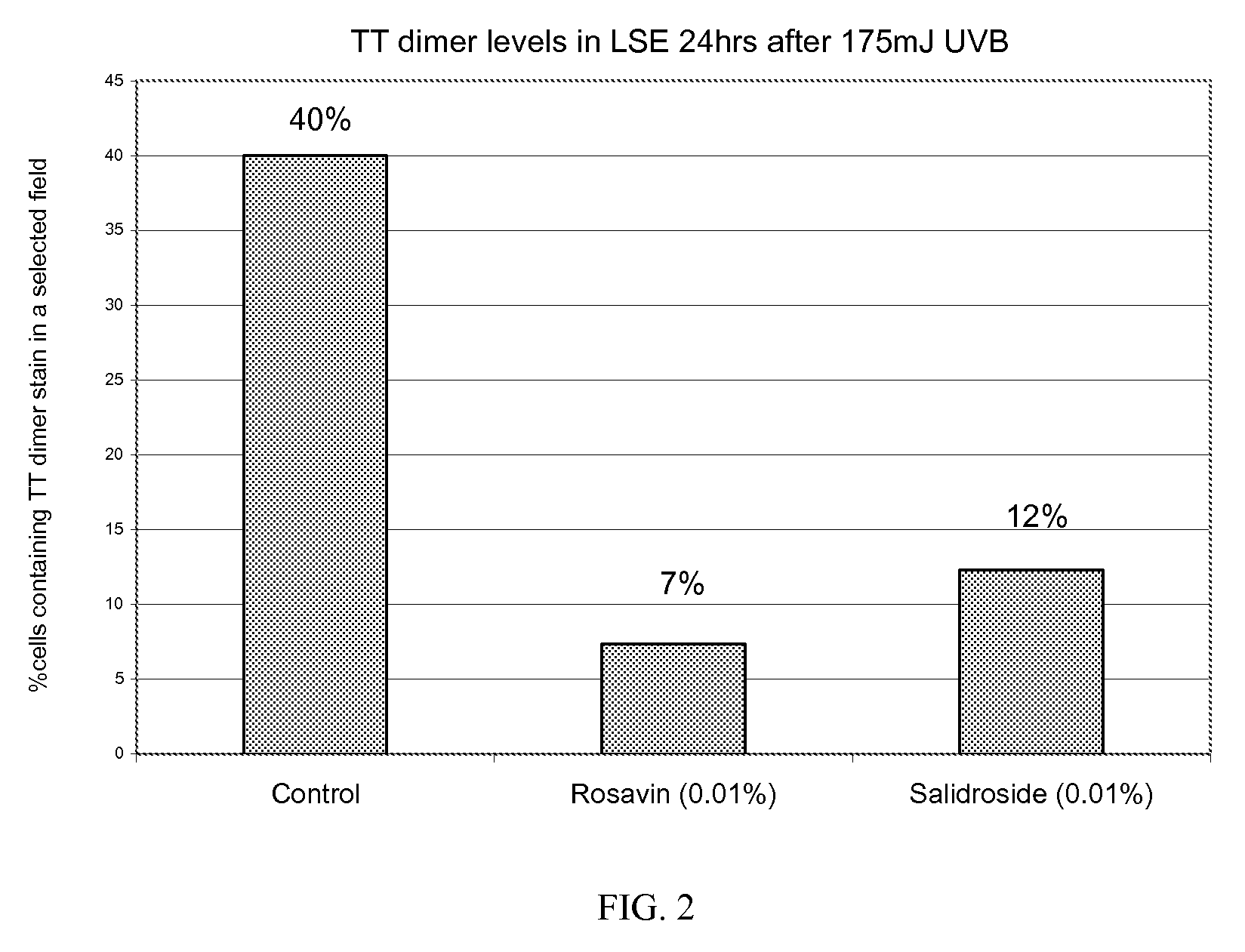
[0039]Excised portions (8 mm) are taken from living skin equivalents (LSE) and cultured over transwell membrane plates. These excised portions are pre-treated with rosavin or salidroside at 0.01% (PBS) for 18 hours. After the post-incubation, these excised portions are UVB-irradiated at 0 and 175 mJ / cm2. One set of LSEs is immediately fixed in formalin to determine TT dimer formation (DNA damage). Following a 24-hour post-incubation, another set of skin equivalents is fixed in formalin. These samples are then prepared for TT dimer immunostaining. Sections are then evaluated using a microscope at 400× magnification. A section is selected from each sample and TT dimer containing cells are evaluated. DNA damage is measured by examining TT dimer stained cells immediately after UVB irradiation. DNA repair (TT dimer removal) in UVB-irradiated LSEs is determined by comparing the levels of TT dimer at 0 hr (immediately after UVB) with the levels of TT dimer at 24 hours (24 hours after UVB)....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com