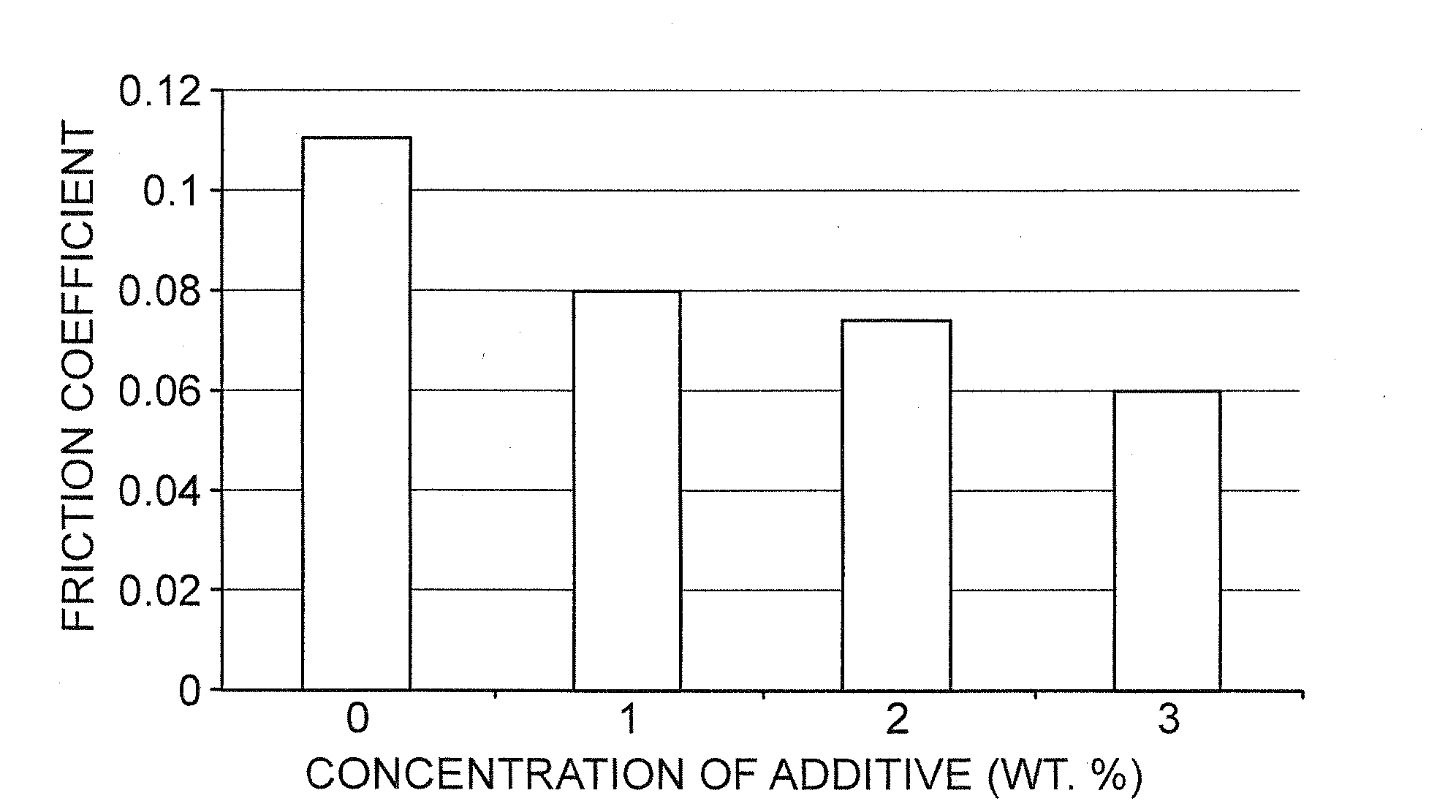
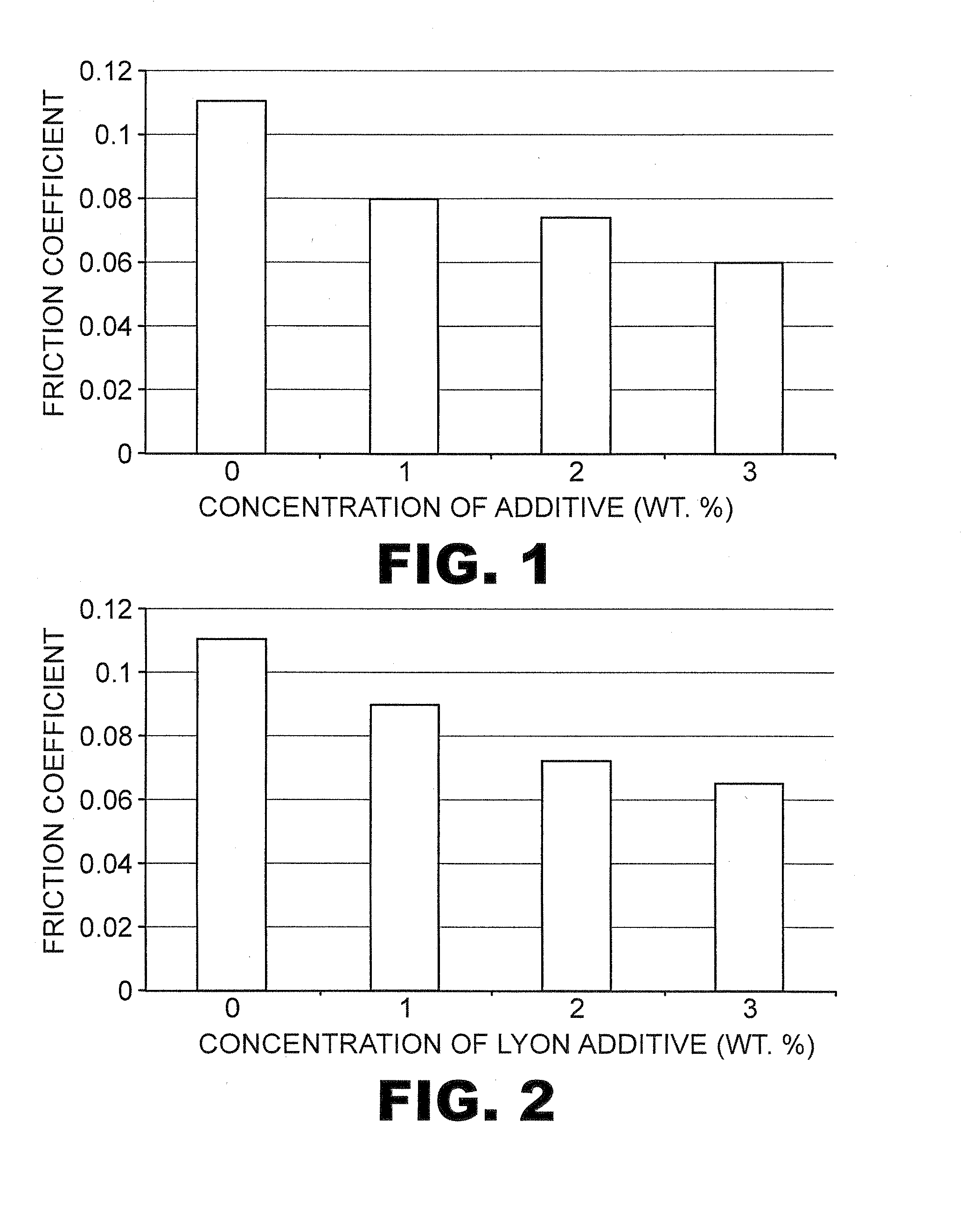
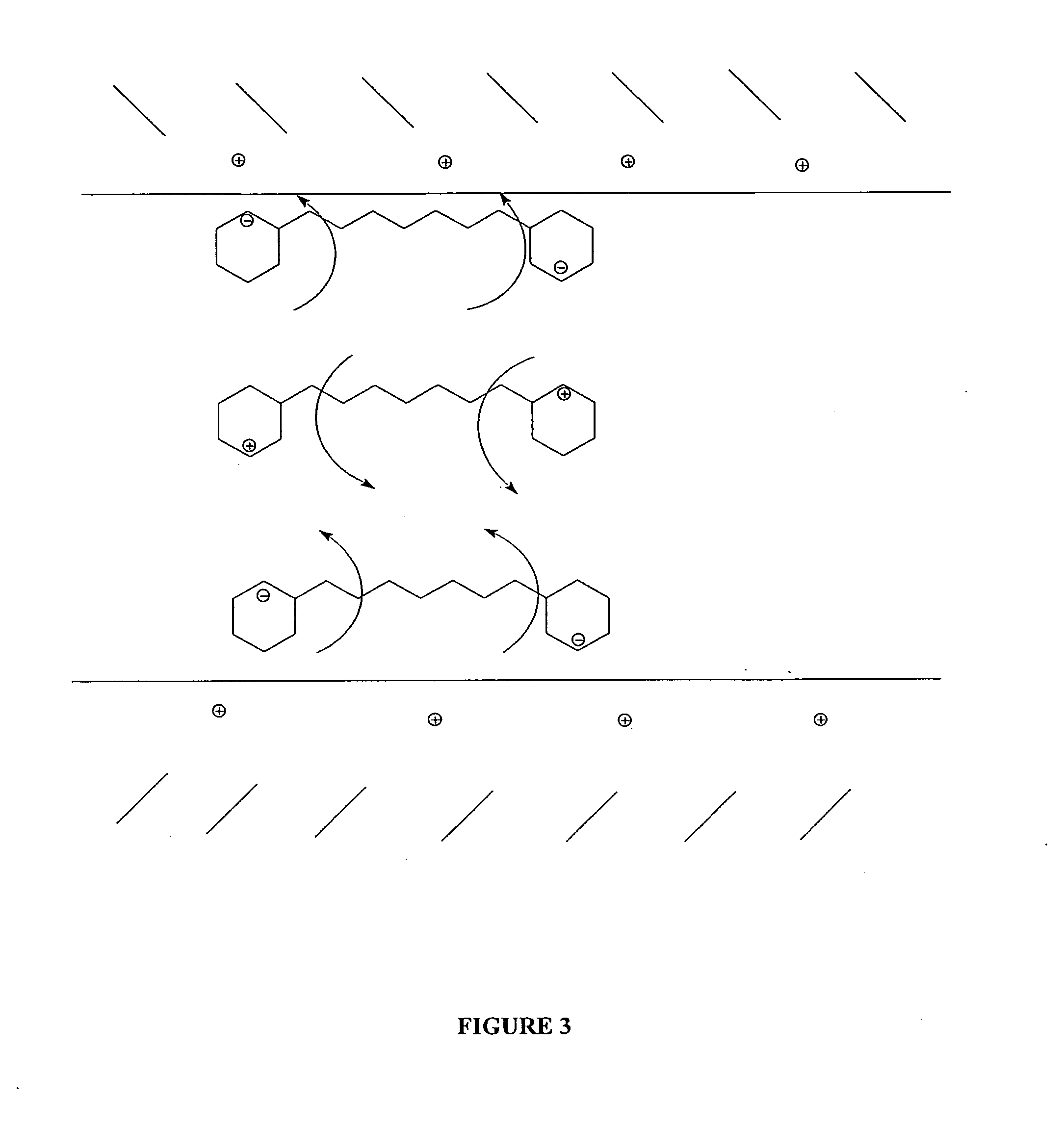
Lubricating formulations for dispersancy and temperature, friction, and wear reduction
a technology of dispersant and temperature, friction, wear reduction, applied in the direction of additives, liquid carbonaceous fuels, base materials, etc., can solve the problems of high corrosiveness of additives and unsuitable for a number of uses, and achieve the effect of reducing the gas consumption of these cars
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment 1
[0185]Initially, a control and a first sample, embodying the technology of the present invention, were subjected to the modified McMillan test. The control included a conventional, petroleum based 5W-30 motor oil (BP); the sample embodying the present invention included the same motor oil and an additive package consisting of a 1.5 percent concentration by weight of the overall composition. Results are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Coef. Of FrictionWear RateControl 10.102.5 × 10−6 mm3 / NmSample 10.0671.0 × 10−8 mm3 / Nm
experiment 2
[0186]Compositions identical to control 1 and sample 1 were subjected to ASTM D 2670 (modified) by Falex Corporation. This data is presented in Table 2.
TABLE 2Final oilBreak-intemperaturetooth lossTest tooth lossFriction factor(° F.)Control 150480.12235Sample 1870.08157
[0187]The Falex test apparatus placed a rotating cylinder between V-blocks in a container filled with the fluid being tested. The test was run in 2 phases, i.e., a break in period of one minute, wherein the cylinder works in uniformly between the V-blocks, followed by a three hour test where the wear, temperature, and torque are monitored. The tooth loss is an indication of the wear and the friction factor is computed from the friction and applied forces.
experiment 3
[0188]A master batch composed of 95 to 100 wt % working fluid (Mobil Super Syn 5W-20) and 0.1 to 5 wt % working fluid additive including: 1 to 100 wt % of an highly polar primary component, 0.4 to 95 wt % of a highly polar secondary material, and 0.02 to 20% organometallic material. The results are presented in Table 3.
TABLE 3Friction factorWear scarControl (neat)0.0940.75Test sample0.0730.60
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com