Cooled Turbine Rotor Blade
a technology of rotor blades and cooling turbines, which is applied in the manufacture of engines, mechanical equipment, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of dead water regions now again occurring, and achieve the effects of reducing pressure losses in coolant, reducing pressure losses, and cooling the terminating wall particularly efficiently
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
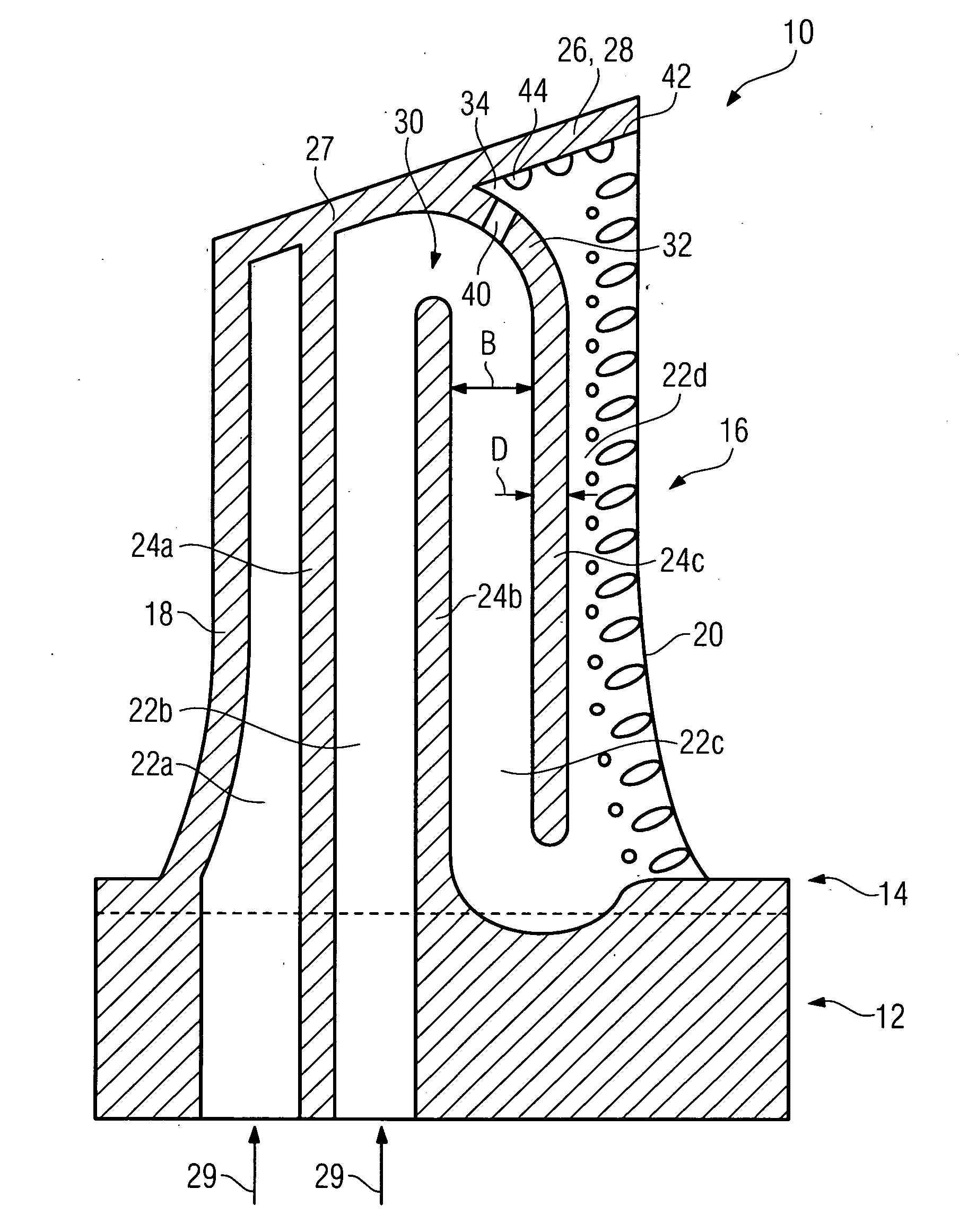
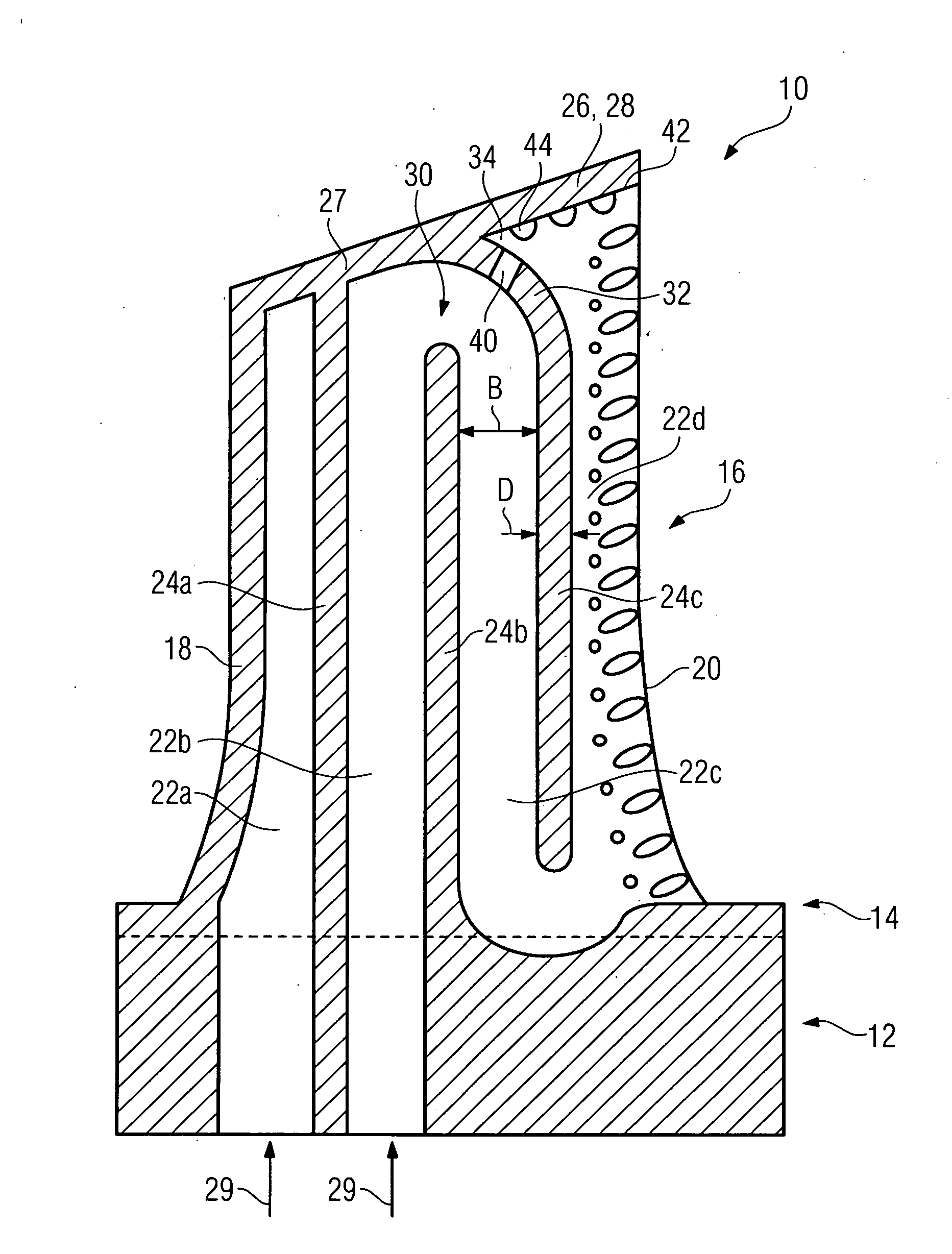
[0015]The FIGURE shows a longitudinal section through a turbine rotor blade 10 which is produced by a casting method. The turbine rotor blade 10, which is therefore integral, has an attachment area 12, with a firtree-shaped cross section, with a platform 14 and an airfoil profile 16 arranged thereon. The airfoil profile 16, which has an aerodynamically profiled cross section, is formed by a suction-side blade wall and a pressure-side blade wall, which each extend from a leading edge 18 to a trailing edge 20 and in this case surround a cavity, which is arranged in the interior of the airfoil profile 16 and in which a plurality of cooling channels 22a, 22b, 22c, 22d are provided. The cooling channels 22 are adjacent to one another and each run approximately parallel to the leading edge 18. The mutually adjacent cooling channels 22 are each separated from one another in places by a rib 24a, 24b, 24c which connects the pressure-side blade wall to the suction-side blade wall. The cooling...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com