Turbine Blade
a turbine blade and blade technology, applied in the field of turbine blades, can solve the problems of reducing the protection of the blade base body, reducing the service life of the blade, and endangering the operation safety, so as to reduce the downtime of the gas turbine, reduce the effect of impingement cooling, and increase the service li
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
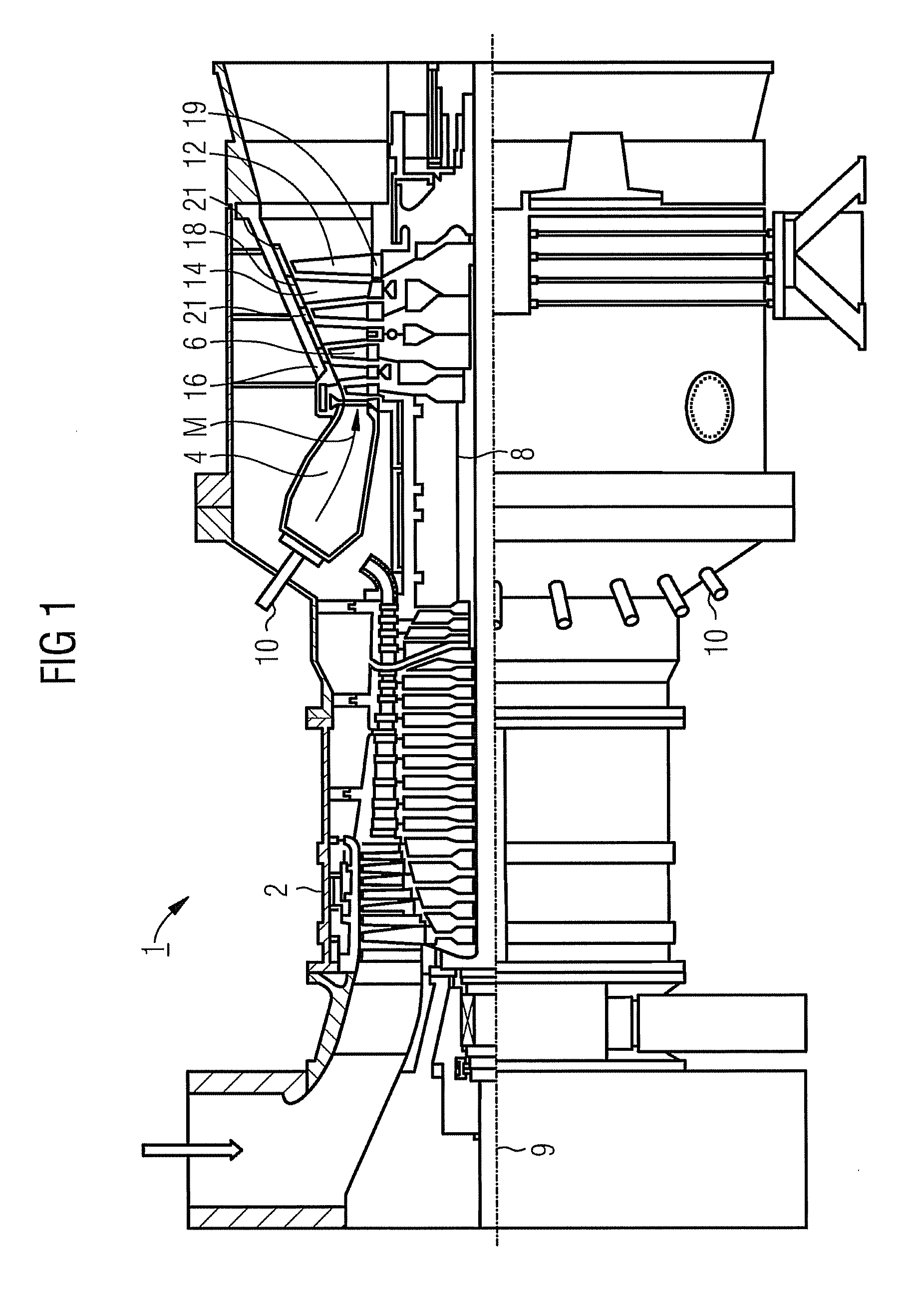
[0036]The gas turbine 1 according to FIG. 1 has a compressor 2 for combustion air, a combustion chamber 4, and also a turbine unit 6 for driving the compressor 2 and for driving a generator, which is not shown, or a driven machine. For this purpose, the turbine unit 6 and the compressor 2 are arranged on a common turbine shaft 8, which is also referred to as a turbine rotor, to which the generator or the driven machine is also connected, and which is rotatably mounted around its center axis 9. The combustion chamber 4, which is designed in the style of an annular combustion chamber, is equipped with a number of burners 10 for combustion of a liquid or gaseous fuel.
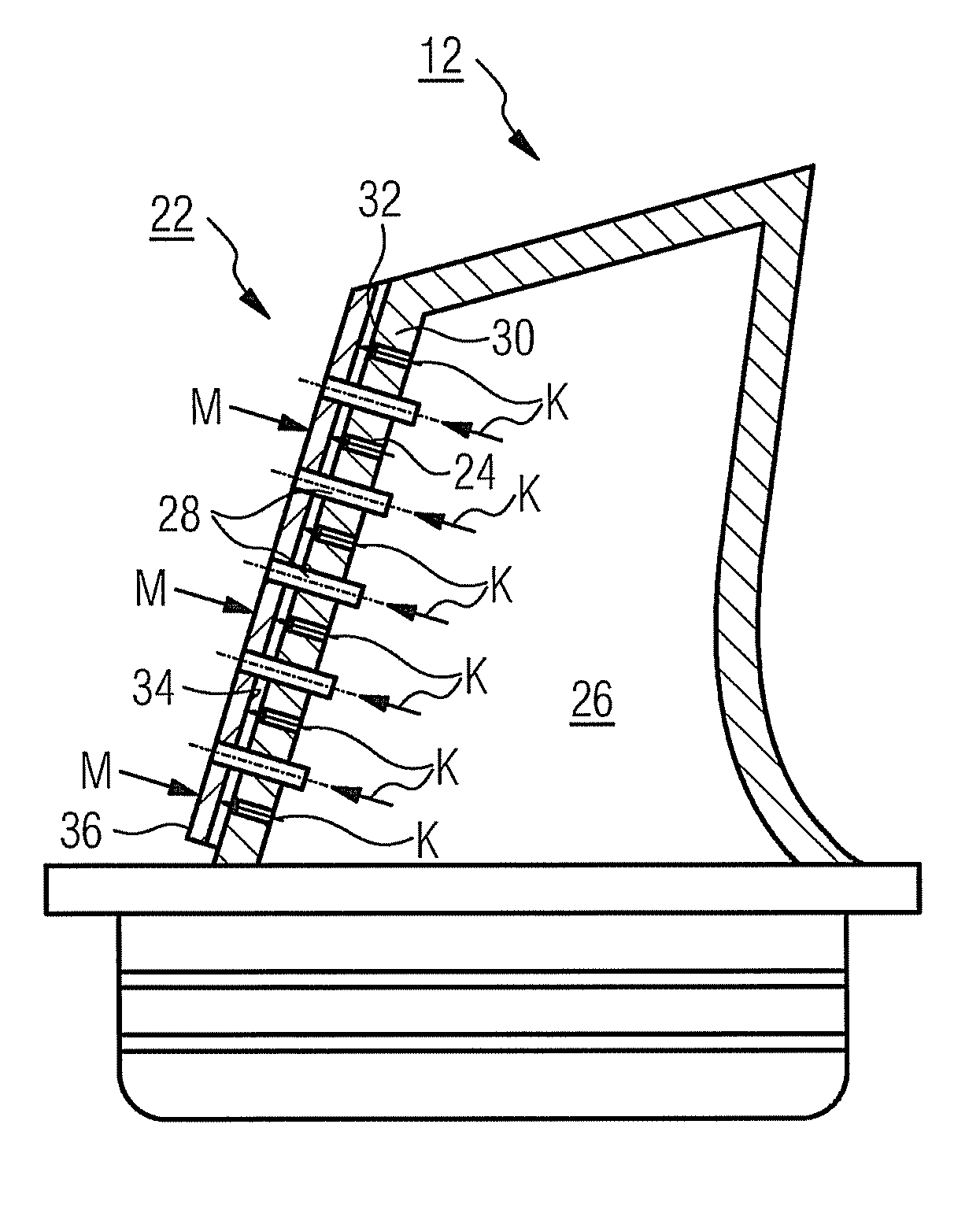
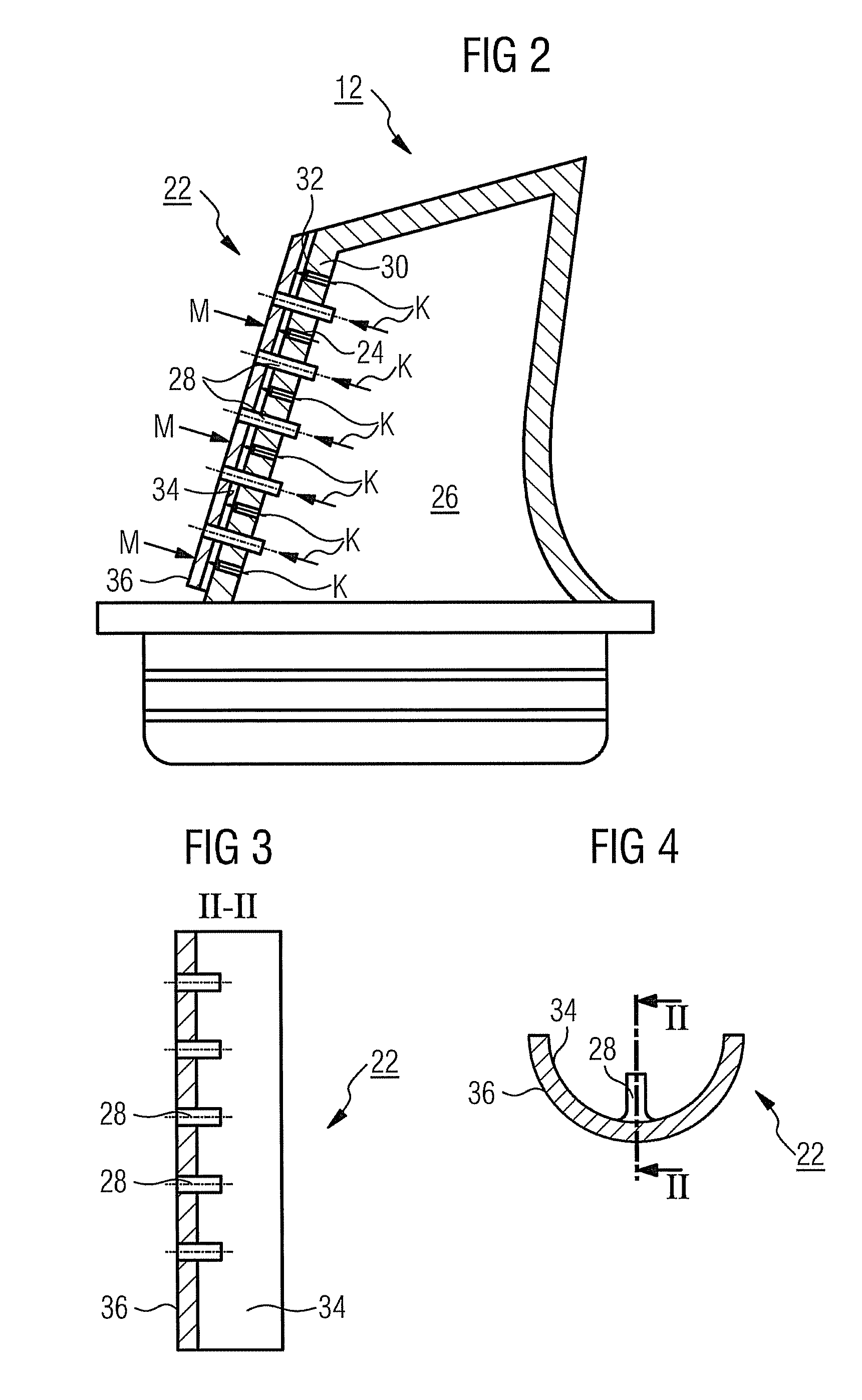
[0037]The turbine unit 6 has a number of rotatable rotor blades 12 which are connected to the turbine shaft 8. The rotor blades 12 are arranged on the turbine shaft 8 in the manner of a ring and so form a number of rotor blade rows. Furthermore, the turbine unit 6 comprises a number of fixed stator blades 14 which are fast...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com