Die, system, and method for coextruding a plurality of fluid layers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
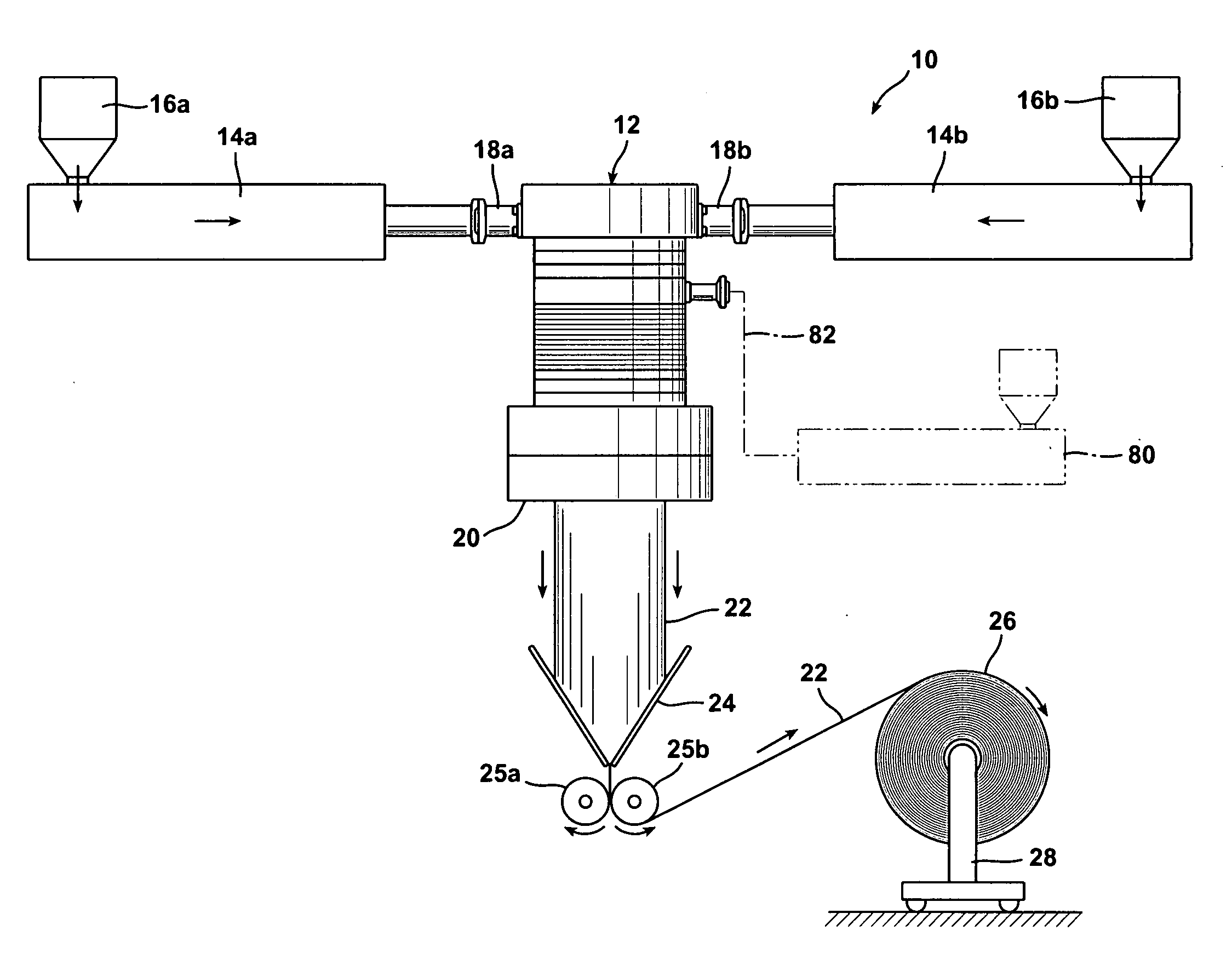
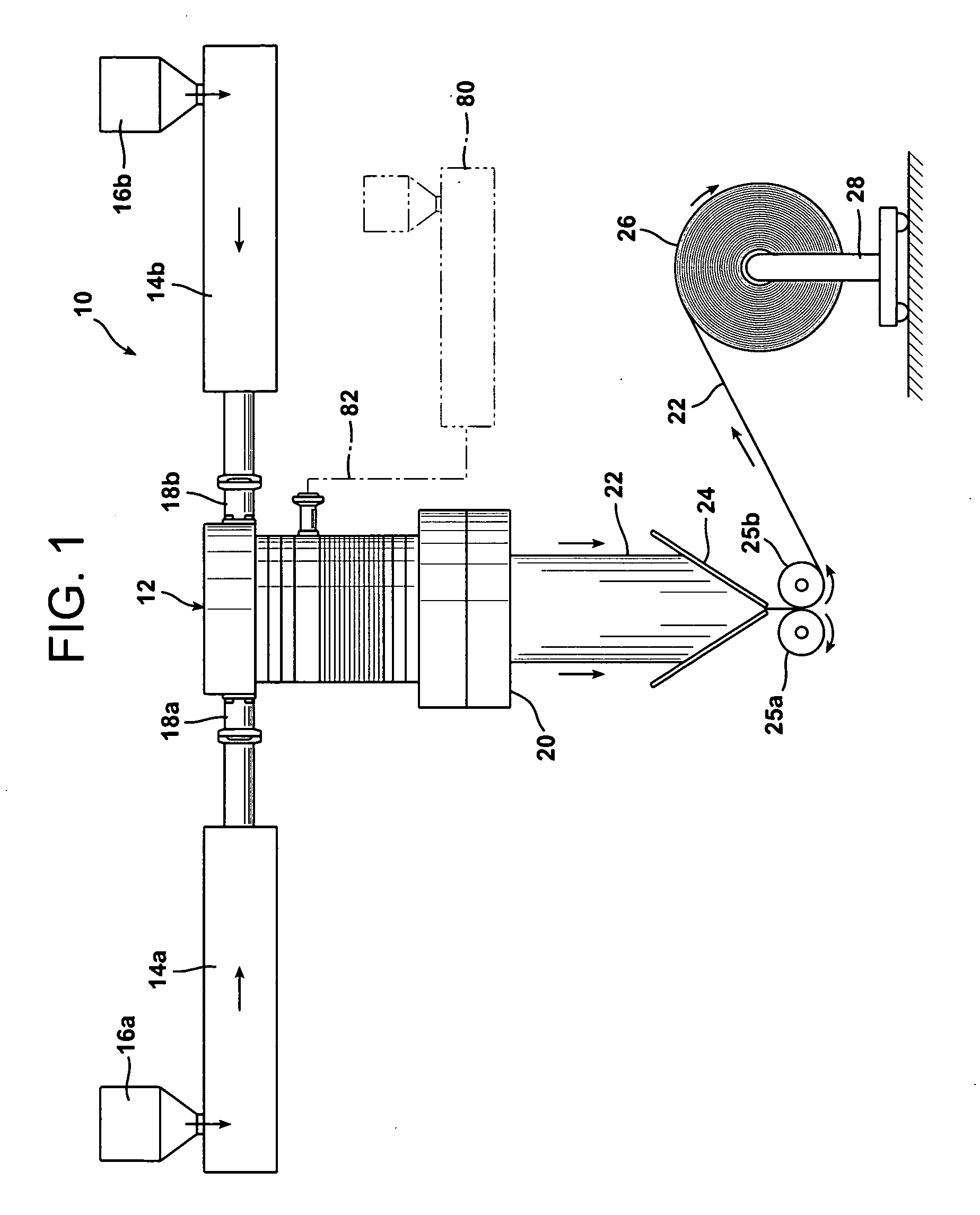
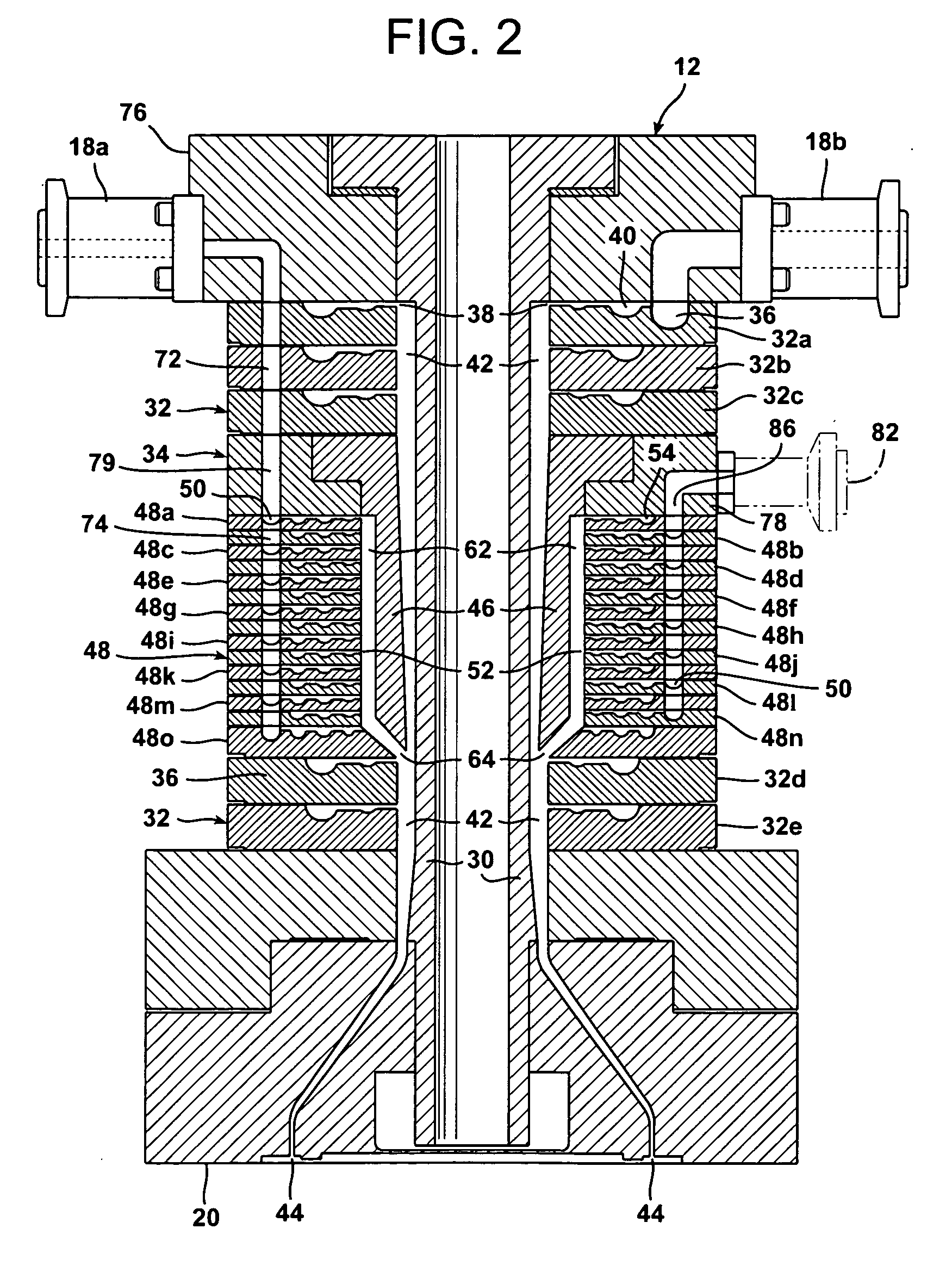
[0026]FIG. 1 schematically illustrates a system 10 in accordance with the present invention for coextruding a plurality of fluid layers. System 10 generally includes a die 12 and one or more extruders 14a and 14b in fluid communication with the die 12 to supply one or more fluids to the die.
[0027]In a typical application, the fluid layers coextruded by die 12 may comprise one or more molten thermoplastic polymers. Examples of such polymers include polyolefins, polyesters (e.g., PET), polystyrenes, polyamide homopolymers and copolymers (e.g. PA6, PA12, PA6 / 12, etc.), polycarbonates, etc. Within the family of polyolefins, various polyethylene homopolymers and copolymers may be used, as well as polypropylene homopolymers and copolymers (e.g., propylene / ethylene copolymer). Polyethylene homopolymers may include low density polyethylene (LDPE) and high density polyethylene (HDPE). Suitable polyethylene copolymers may include a wide variety of polymers, such as, e.g., ionomers, ethylene / v...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com