The fluid in such application in many instances is costly in character, and / or deleterious in effect if mis-dispensed.
Mis-dispensing of the fluid additionally may impair, or even render useless, a
semiconductor device that is being manufactured.
Further, many chemical reagents used in
semiconductor manufacturing are very hazardous in character, e.g., being toxic, pyrophoric, corrosive or otherwise harmful in
exposure to persons or
processing equipment.
An intrinsic problem with such coupling of supply vessel and dispensing
assembly is that an incorrect coupling, i.e., connection of a wrong dispensing
assembly to a supply vessel, results in
contamination when the sealing membrane on the
package is punctured by the dip tube of the dispense head, and it then is discovered that a wrong dispensing
assembly has been utilized.
This can occur even if the mis-connection is immediately discovered, e.g., by inability to engage the dispensing assembly with any complementary connection structure on the fluid
package.
Another issue of significance in the use of liner-based fluid storage and dispensing packages of the above-describe type, is the need to dispense as much of the fluid contents of the liner as possible, so that the fluid, which as discussed above may be costly in character, is efficiently utilized, without significant amounts of fluid being left in the liner at the conclusion of the dispensing operation.
Although small in volume, this headspace gas is deleterious to the contained fluid.
A primary
disadvantage of the headspace gas is that when the liner is subjected to
external pressure in the dispensing operation, the resultingly compressed headspace gas solubilizes in the contained fluid to produce dissolved gas therein, in accordance with Henry's Law.
This liberation of dissolved gas causes irregular and variable dispense profiles of the chemical
reagent, e.g., a
photoresist that is being flowed to a
semiconductor manufacturing tool in a semiconductor manufacturing operation, resulting in the formation of potentially severe
wafer defects, bubble formation on surfaces and subsequent popping of such bubbles, etc.
Thus, the presence of significant headspace in the liner entails significant adverse consequences along the entire extent of the fluid delivery path including the final use of the fluid in the process
system.
In the dispensing of liquid from a liner-based
package containing headspace gas, the exhaustion of fluid from the liner causes headspace gas to be drawn into the suction
train of the dispensing flow circuitry, and this entrainment of headspace gas results in the appearance of bubbles in the downstream liquid flow.
The “first bubble” sensing method of empty detection has proven reliable, but is associated with the inherent disadvantages of headspace gas becoming solubilized in the liquid in the liner and subsequently being released from the liquid during the dispensing operation, since such
efflux of gas may give a premature indication of exhaustion of liquid from the liner, thereby preventing maximum utilization of liquid from the liner from being achieved, as well as interfering with the operation of downstream
process equipment.
Users having small hands generally experience difficulty in this disassembly procedure, particularly in pressing in the pivot clamps.
Additionally, it is very difficult to break the static seal of the O-rings.
These factors, taken together, adversely
impact the ease of use of such liner-based fluid storage and dispensing packages.
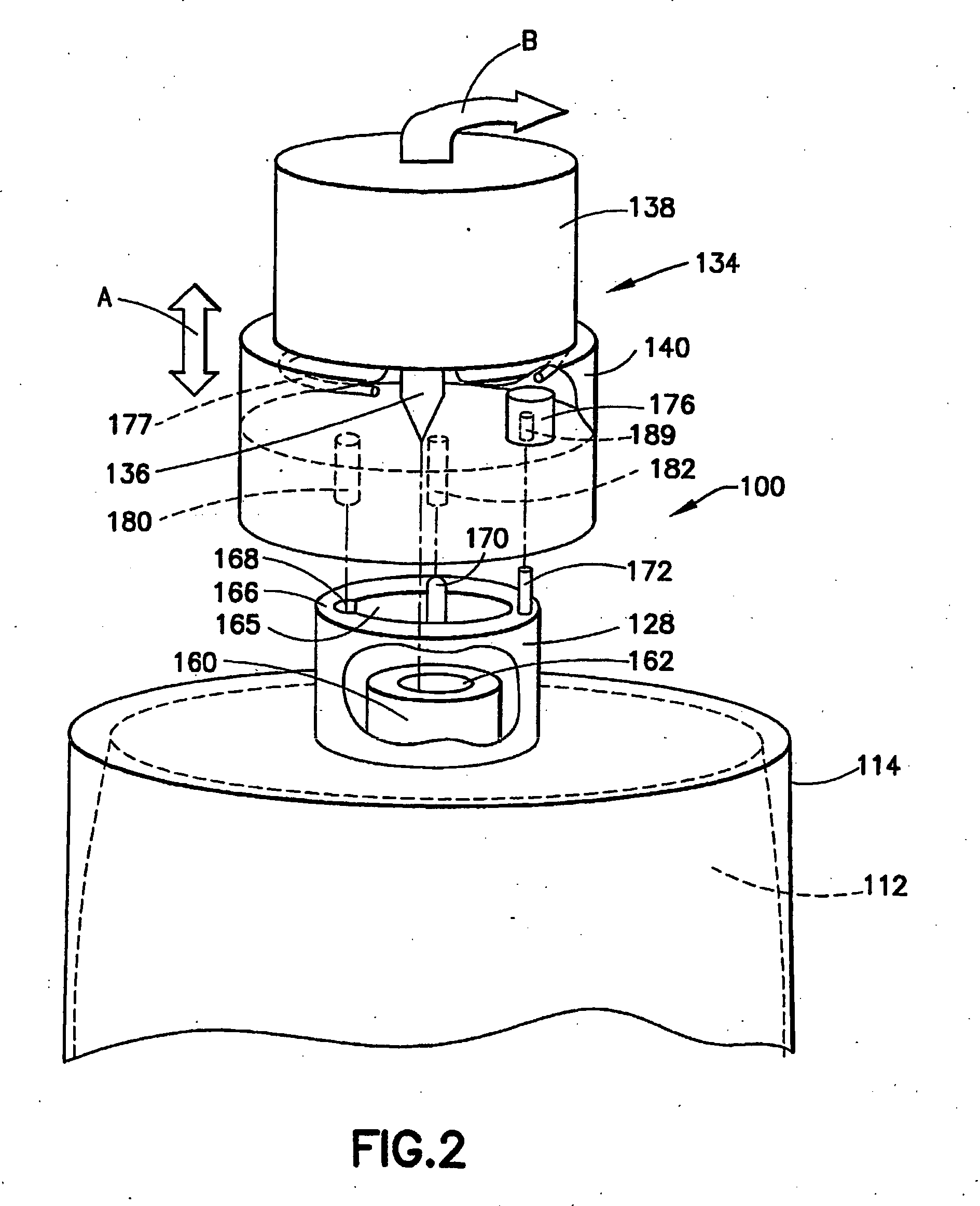
Further, considering the shortcomings involved in prior use of liner-based fluid storage and dispensing packages, various problems are encountered with so-called breakseal or membrane elements that are pierced by the probe of the dispensing assembly when the connector is brought into engagement with the cap of the vessel.
First, breaking through the currently employed breakseal with the dispense probe produces particles that are carried into the contained chemical by the probe, thereby compromising the purity of the contained fluid.
Second, the currently employed breakseal does not allow for material changes to match the needs of the chemical in the liner.
Third, the currently employed breakseal does not allow vessels to be easily resealed for disposal.
Fourth, the currently employed breakseal requires high force to insert the probe connector assembly, since the probe must pierce the membrane seal, which may entail resistance to the engagement of the connector with the vessel.
Fifth, the seal integrity of the currently employed breakseal can be compromised by plastic
creep induced relaxation of the seal clamping force.
In some instances, due to inadequate training or accident, caps are unscrewed from containers with the probe still installed.
This creates difficulties in removing the cap from the probe body and exposes the probe to contaminants, as well as providing the potential for subsequent mis-connection if the probe body and attached cap are then coupled with another container.
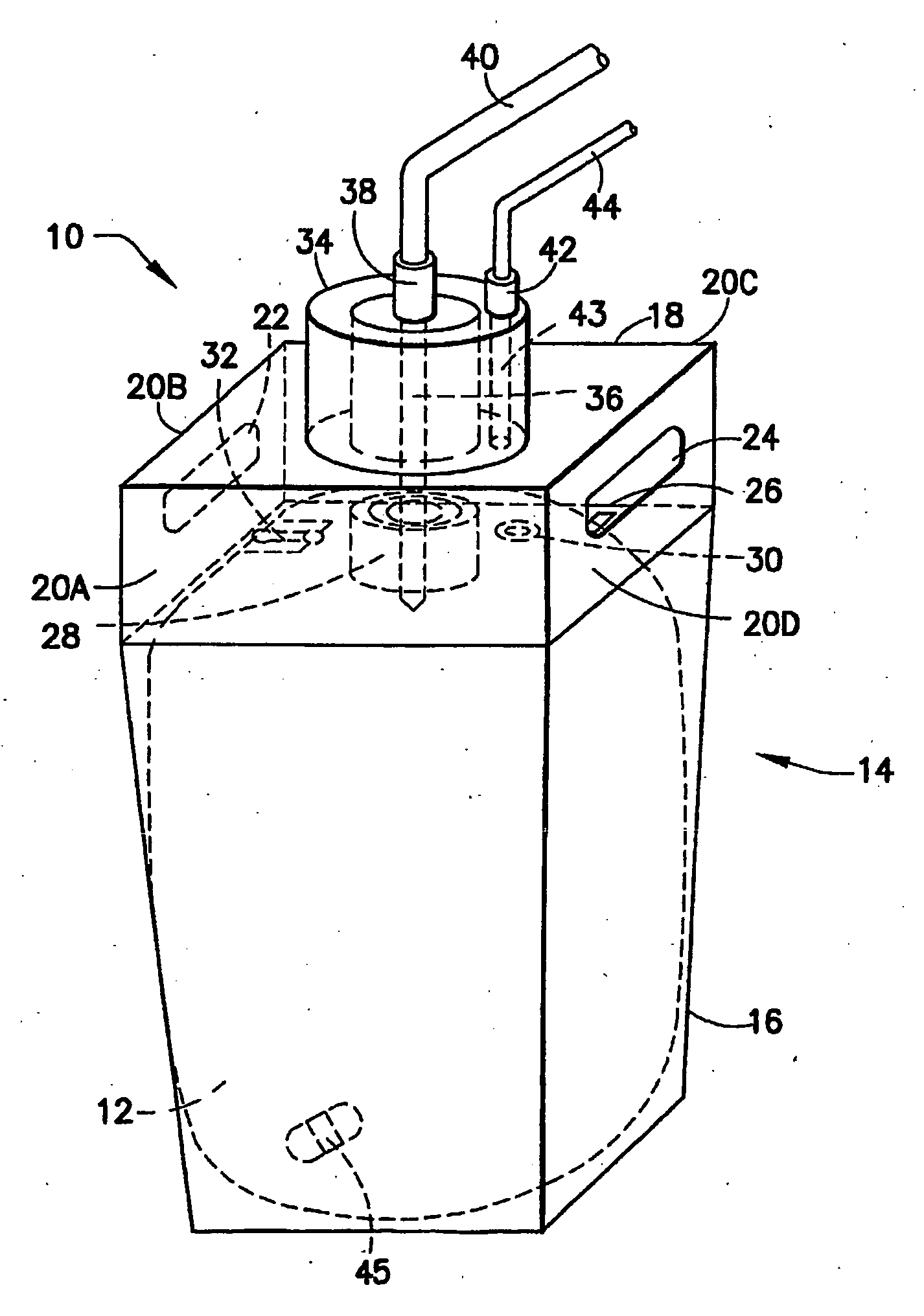
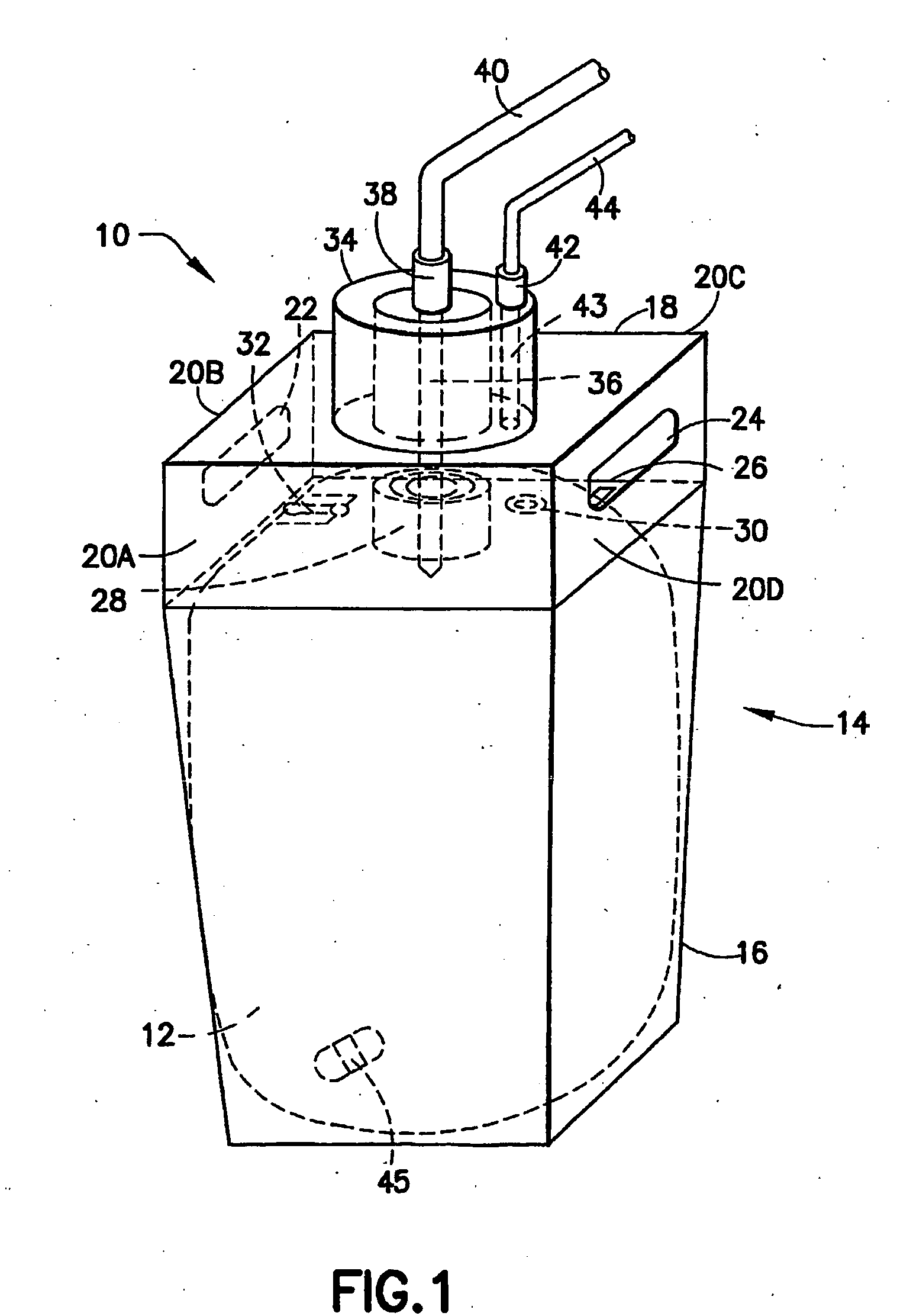
A further deficiency associated with the cap utilized in current liner-based fluid storage and dispensing packages relates to the pressurization opening in the cap, through which pressurizing gas is introduced into the vessel containing the liner, to exert pressure on the exterior surface of the liner, and thereby achieve pressure-mediated dispensing of fluid contained in the liner.
Such pressurization opening in the cap is sealed by a tear tab, and removal of the tear tab to
expose the opening for gas introduction frequently produces rough edges at the pressurization opening, due to the tear tab removal process.
These rough edges in turn cause leaks to the O-ring seal of the dispense
nozzle of the dispensing assembly.
In some instances of use of keycoded caps and probes in liner-based fluid storage and dispensing systems, users have been known to switch caps in order to defeat the keycode
system, and occurrence that could lead to damage or destruction of products manufactured using fluid from such systems.
Such necessity may result from an incorrect keycoding of a fluid
reagent by a chemical supplier, or performance of
specialty chemical and process trials in which keycodes are not assigned, or accidental damage to a cap requiring its replacement.
 Login to View More
Login to View More