Grooved cmp polishing pad
a technology of polishing pad and groove, applied in the field of chemical mechanical polishing of substrates, can solve problems such as affecting the uniformity of polishing rate, and achieve the effect of improving the uniformity of polishing removal ra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0030]This example illustrates the superior removal rate stability and removal uniformity stability obtainable in copper CMP utilizing a polishing pad of the present invention.
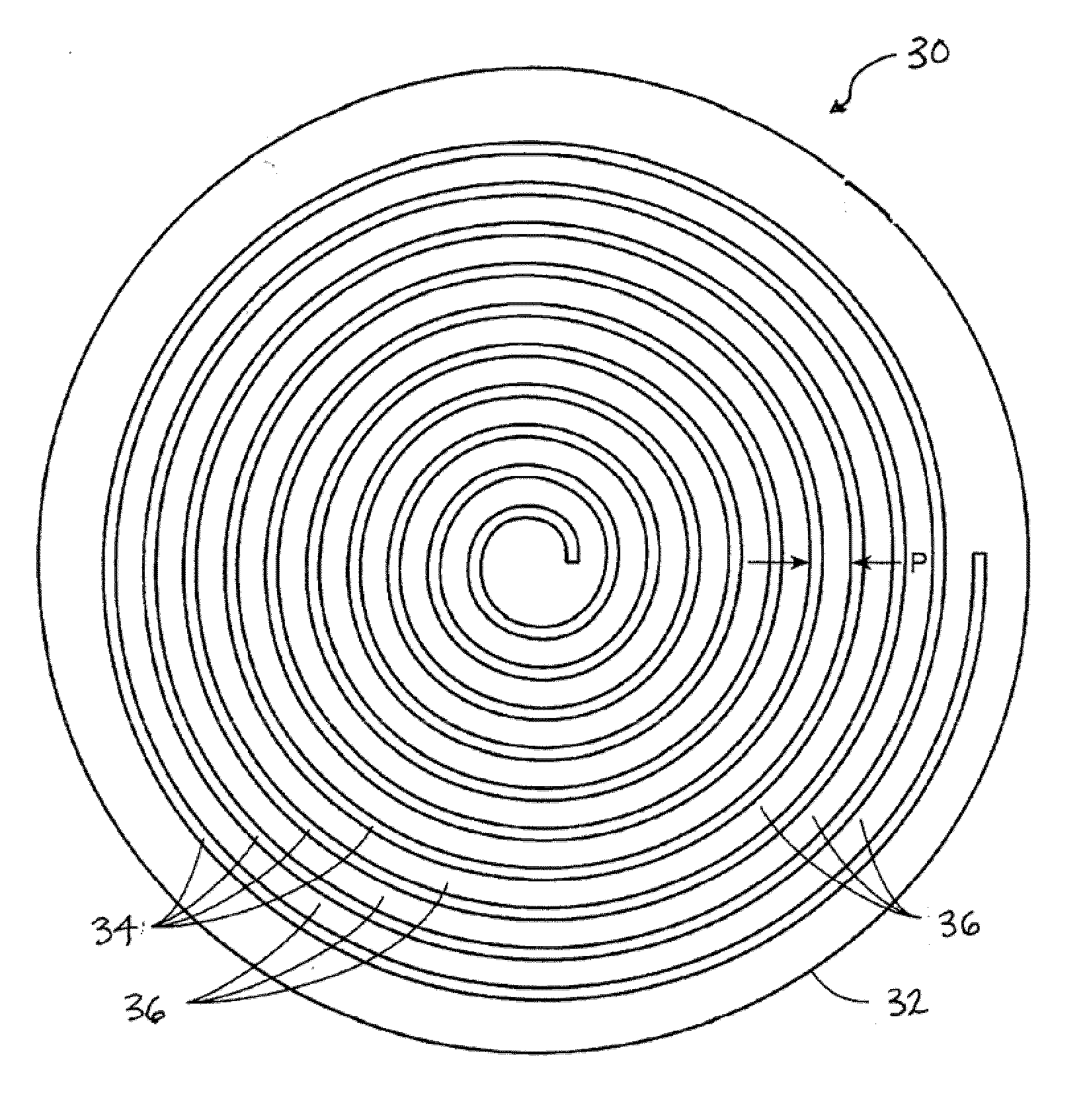
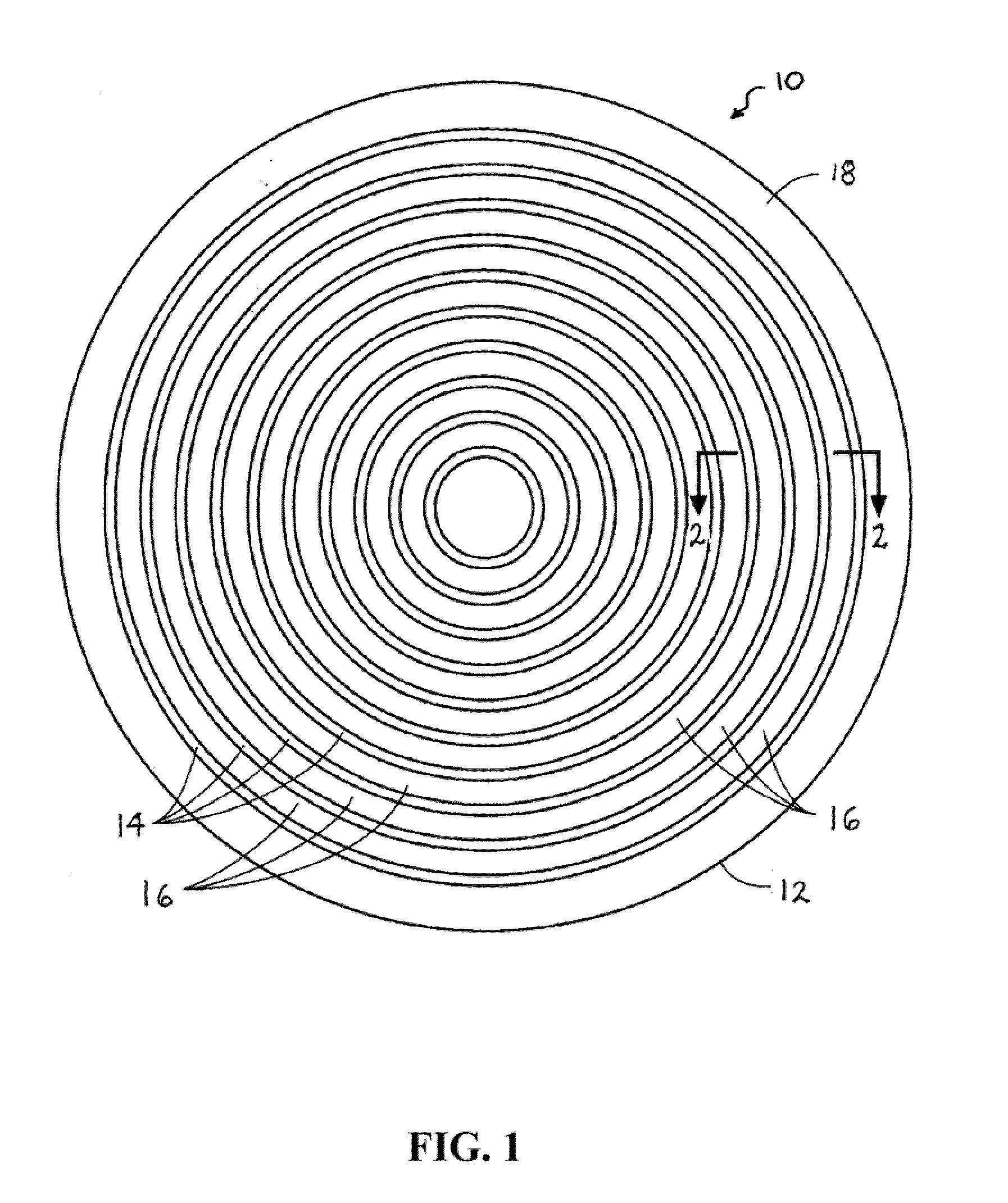
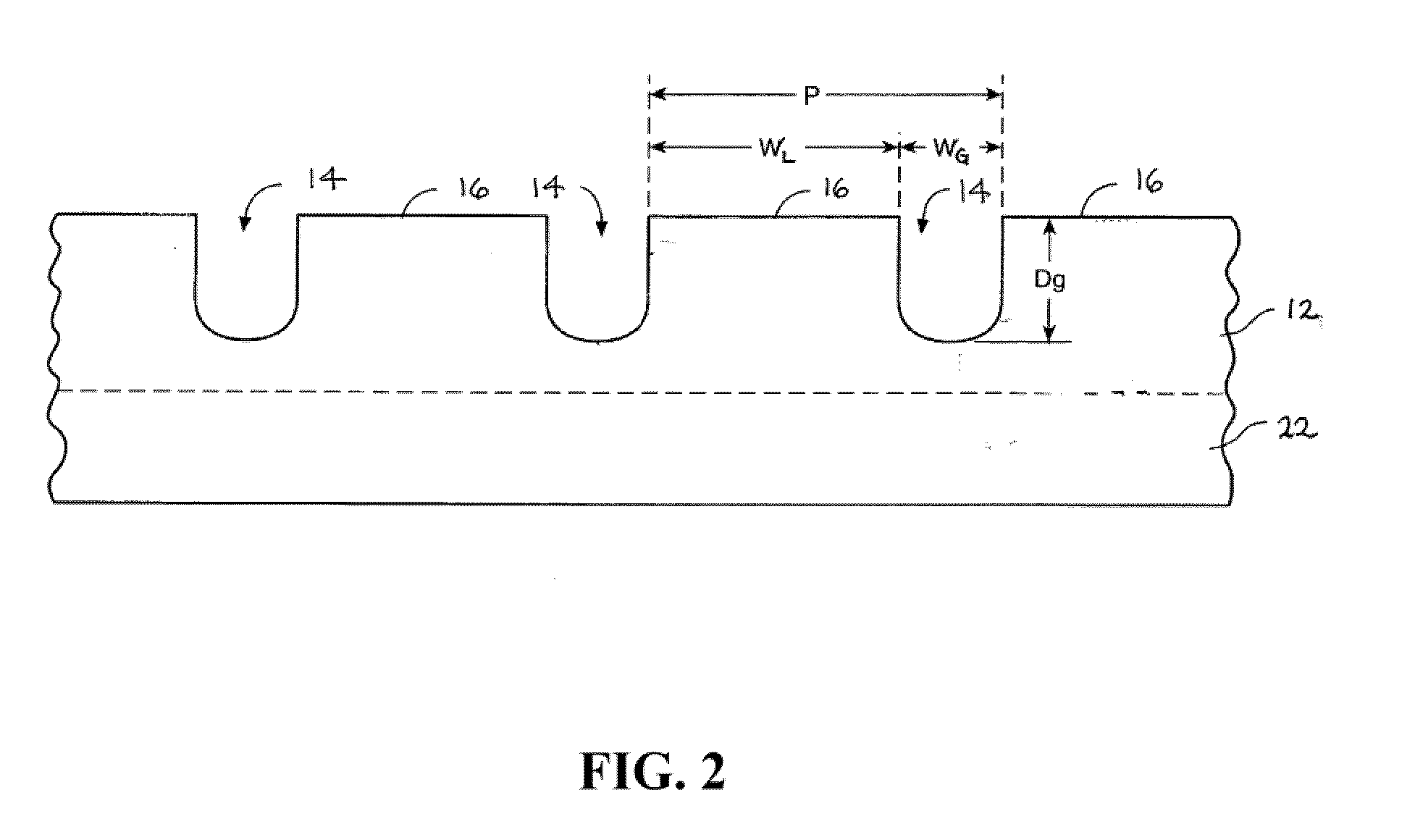
[0031]A polishing pad comprising a thermoplastic polyurethane surface layer including a series of concentric circular grooves each having a width, WG, of about 30 mil, separated by concentric landing surfaces having a width, WL, of 30 mil (pitch of 60 mil), with WL / WG equal to about 1. The polishing was repeatedly performed with the same pad on copper blanket wafers using the commercial polishing slurry C8800 (Cabot Microelectronics Corporation, Aurora, Ill.) on Mirra polisher under the following polishing conditions: down-force of 1 pounds-per-square inch (psi), platen speed of 93 revolutions-per-minute (rpm), carrier speed of 87 rpm, and a slurry feed rate of 100 milliliters-per-minute (mL / min). For comparison, copper blanket wafers were also polished under the same conditions with a similar polyurethane pol...
example 2
[0034]This example illustrates the effect of the grooving configuration on pad wear rate.
[0035]Three polishing pads of the invention comprising a thermoplastic polyurethane surface layer including a series of concentric circular grooves were used for relative pad wear test. The test was performed on an IPEC polisher with 7 ft-lb conditioning down force, 105 rpm platen speed, and 100 rpm conditioner rotational speed. Conditioner was from 3M Co (Model A188). D.I. water was used and the test last for 40 minutes. Wear rate was calculated using data from minute 10 to minute 40, and normalized to mil-per-hour by times 2. The pads had the following dimensions: Pad 60 / 20−WG=20 mil, WL=40 mil, pitch=60 mil, WL / WG=2; Pad 60 / 30−WG=30 mil, WL=30 mil, pitch=60 mil, WL / WG=1; and Pad 40 / 20−WG=20 mil, WL=20 mil, pitch=40 mil, WL / WG=1. For comparison, a similar polyurethane polishing pad having concentric annular grooves separated by concentric annular landing surfaces, but having WL of about 70 mil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com