Device for spatially resolved temperature measurement
a technology of spatial resolution and temperature measurement, applied in the direction of measuring devices, thermometers, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the temperature resolution of dts devices, changing the polarization along the fiber, and affecting the polarization effect of dts measurements, so as to reduce the polarization dependence of thin-film filters and achieve sufficient polarization effects. small
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
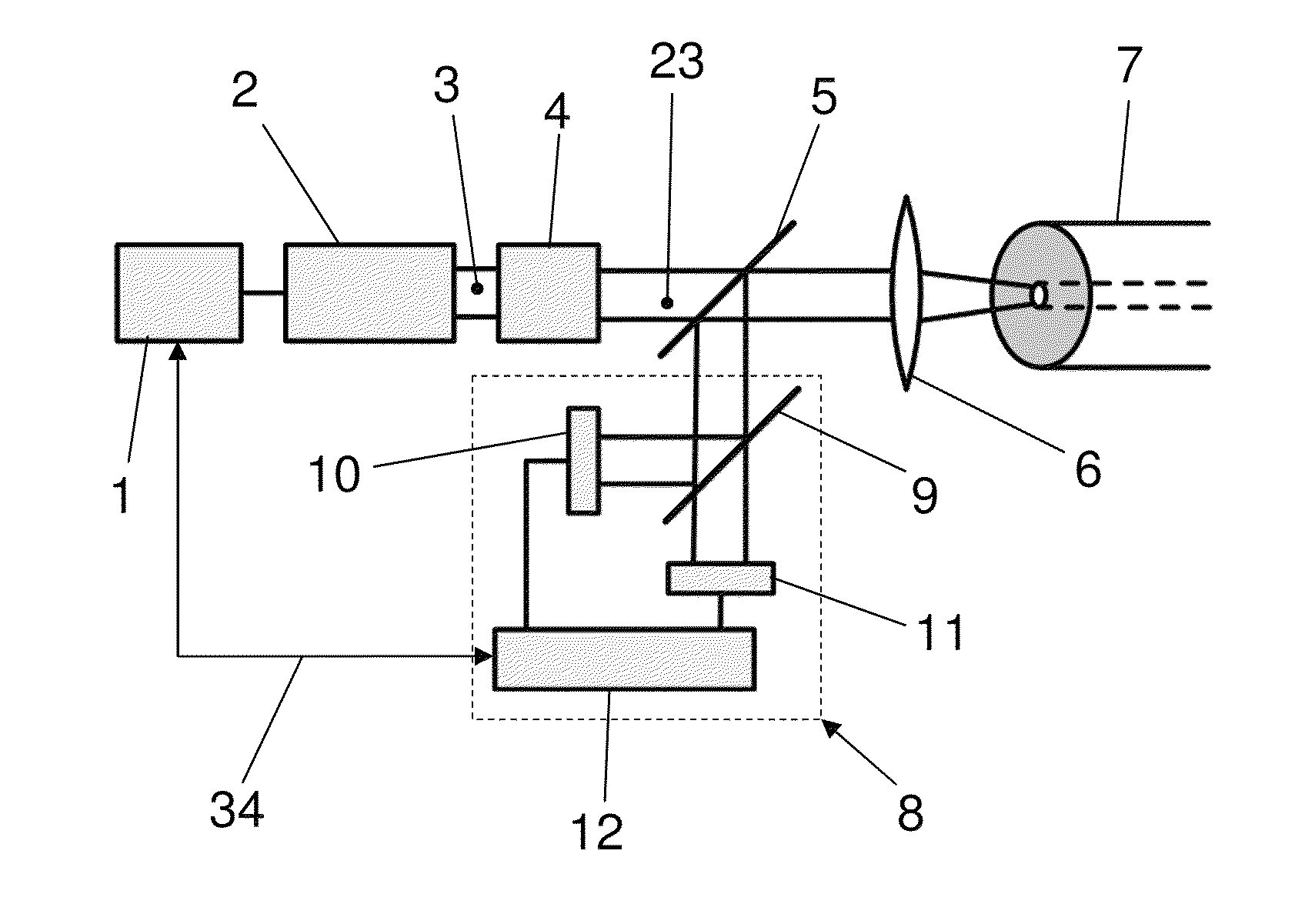
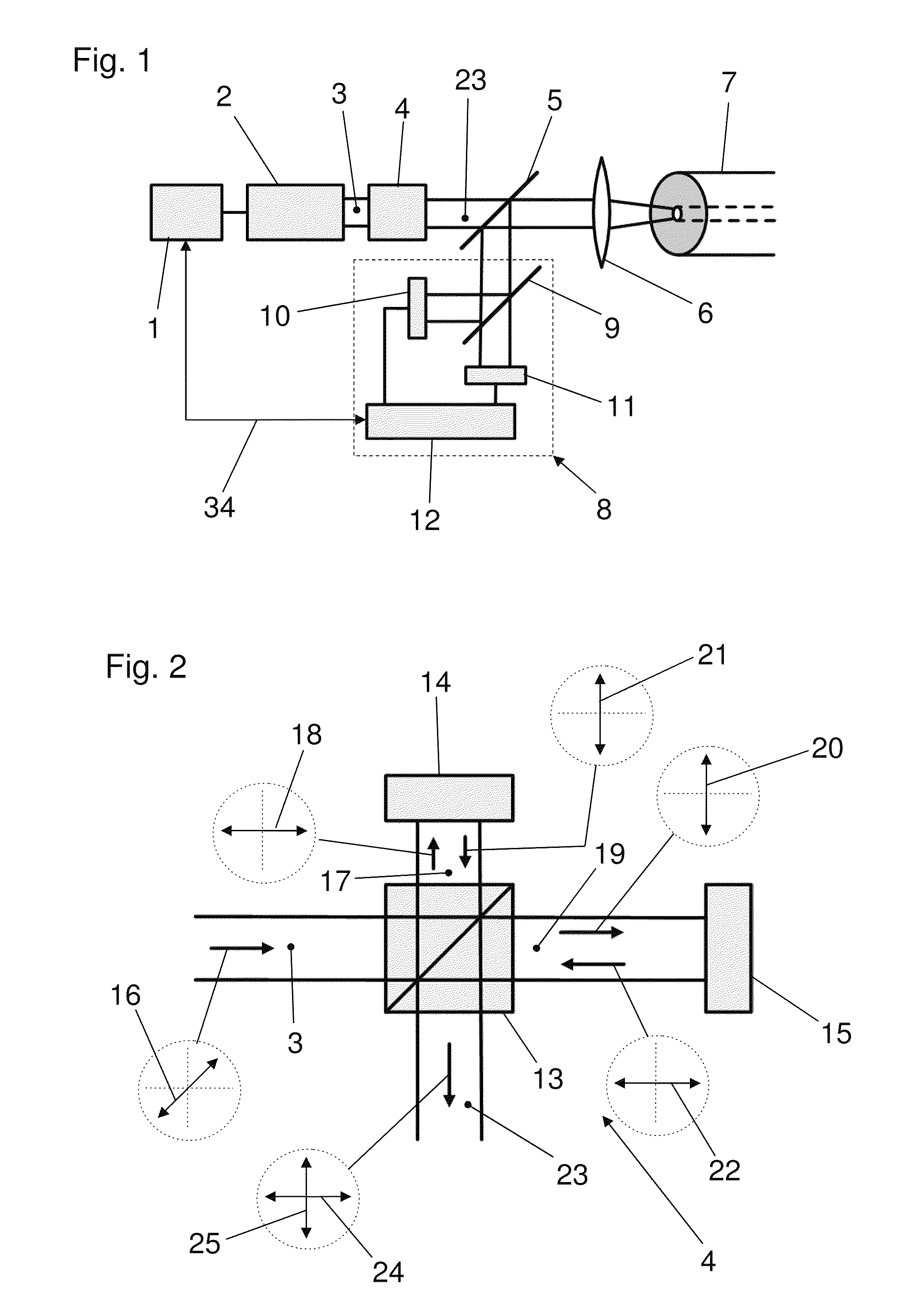
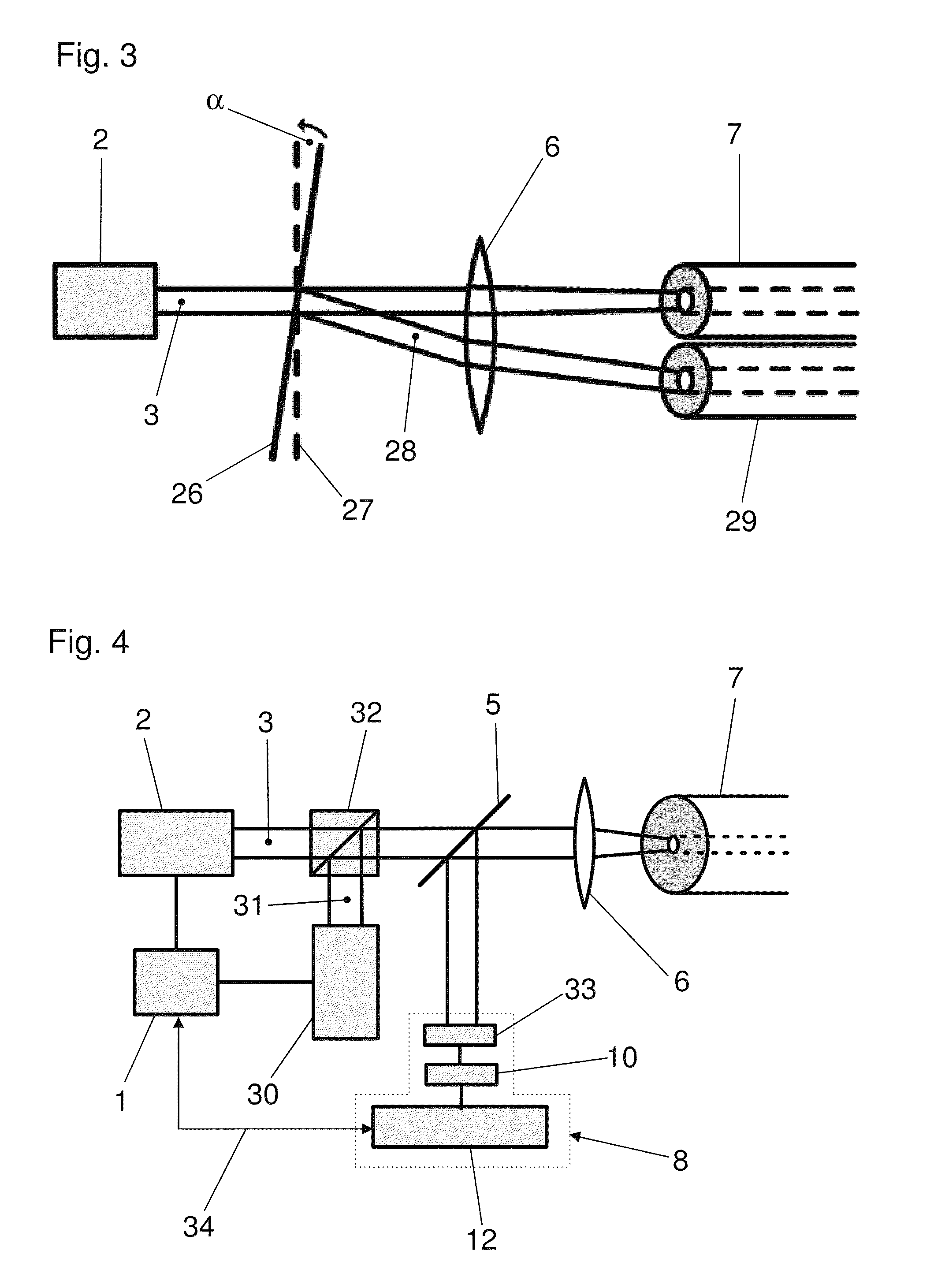
[0038]Identical elements or elements performing the same function are indicated in the figures with identical references symbols.
[0039]FIG. 1 illustrates an embodiment of an apparatus according to the invention with a laser light source 2 controlled by control means 1. The light 3 from the laser light source 2 passes through a polarization modifier 4 which can depolarize the light 3 or temporally and / or spatially change the polarization state of the light 3. After passing through the polarization modifier 4, the light 3 is coupled by coupling means, which include a spectral splitter 5 and for example a lens 6, into an optical fiber 7 used for the temperature measurement.
[0040]The lens 6 and the spectral splitter 5 also operate as decoupling means and can transmit the backscattered portions of the light 3 generated by the laser light source 2 to schematically indicated evaluation means 8. The evaluation means 8 include, for example, a spectral splitter 9 for the laser wavelength and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle of incidence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com