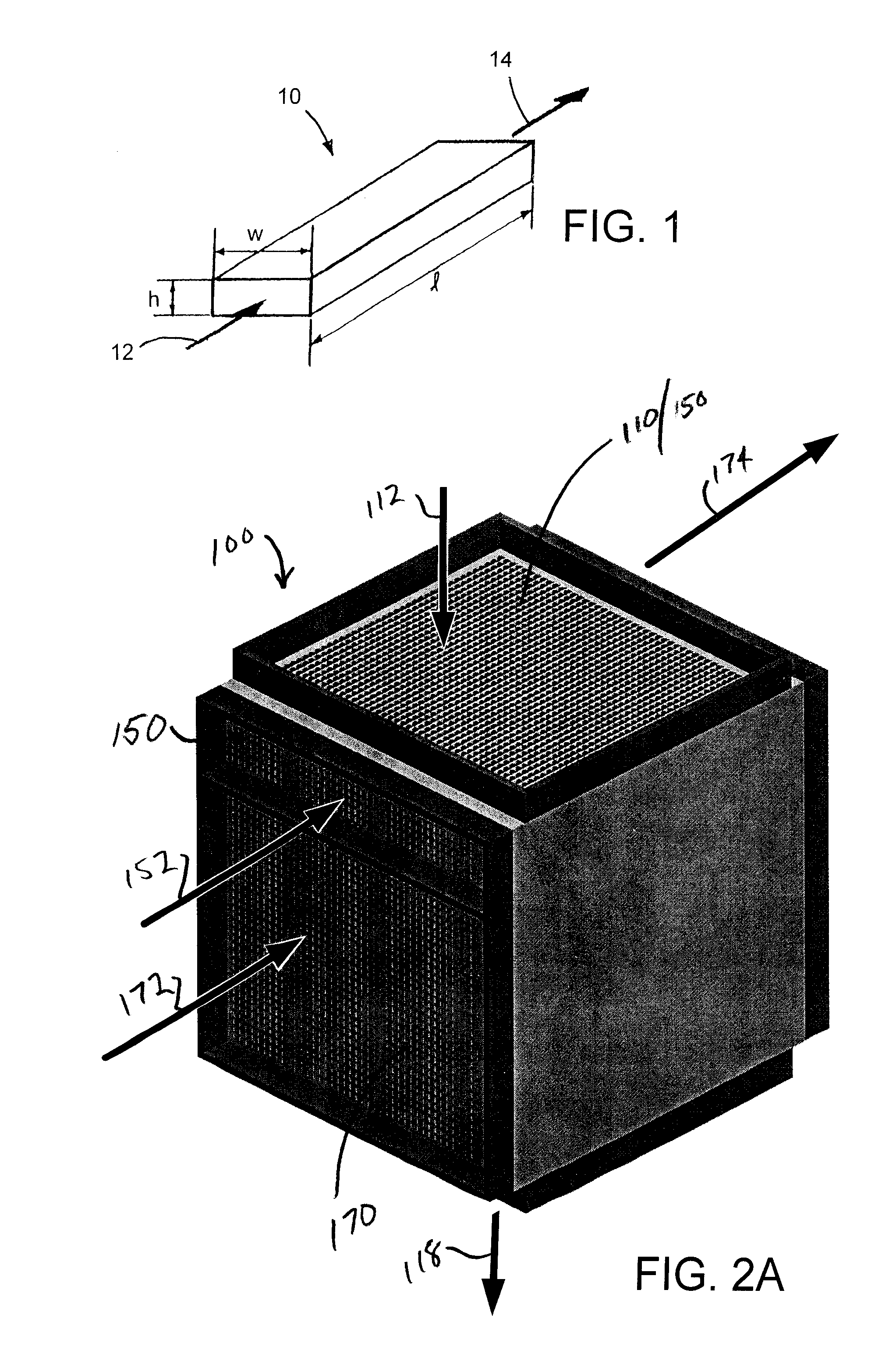
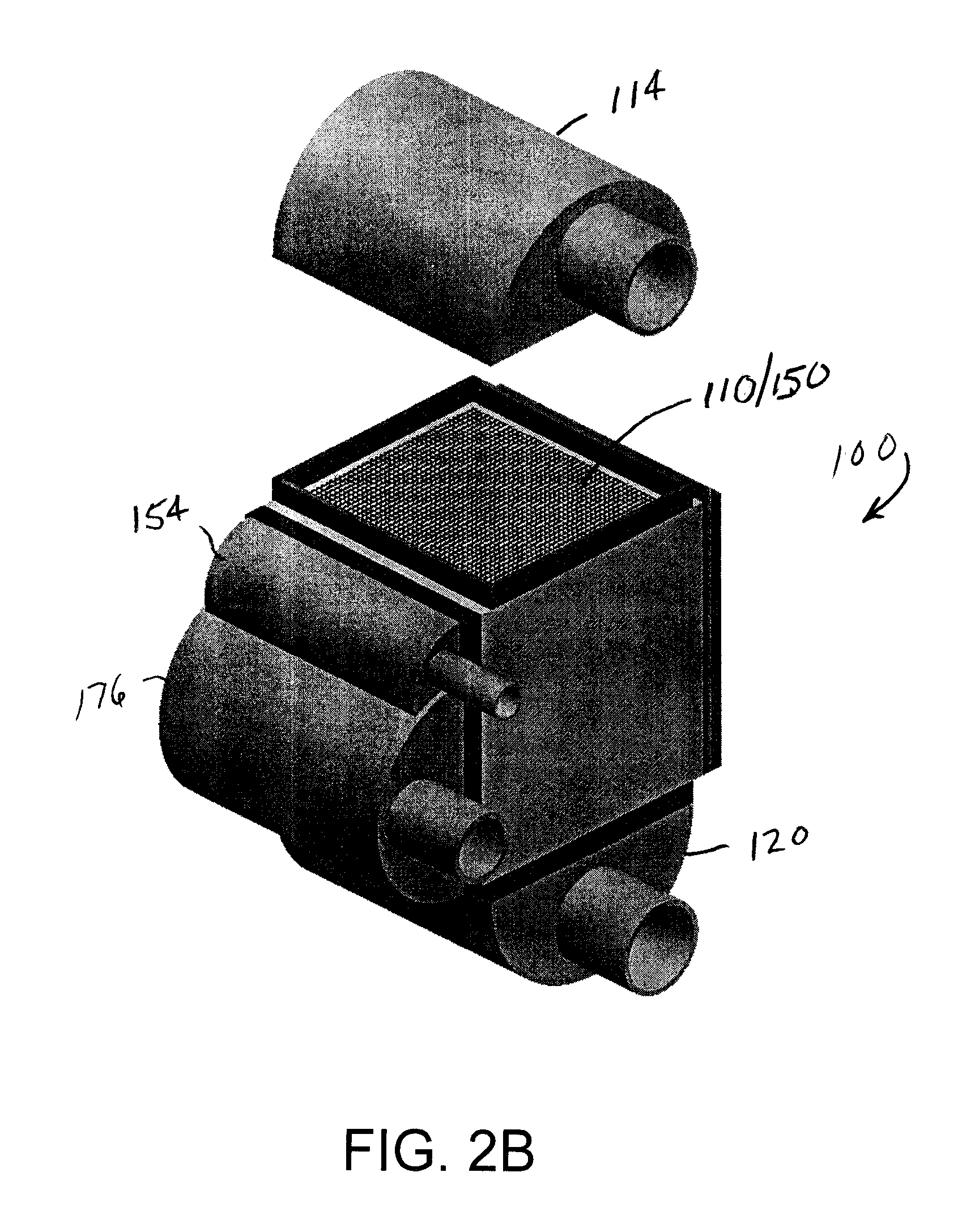
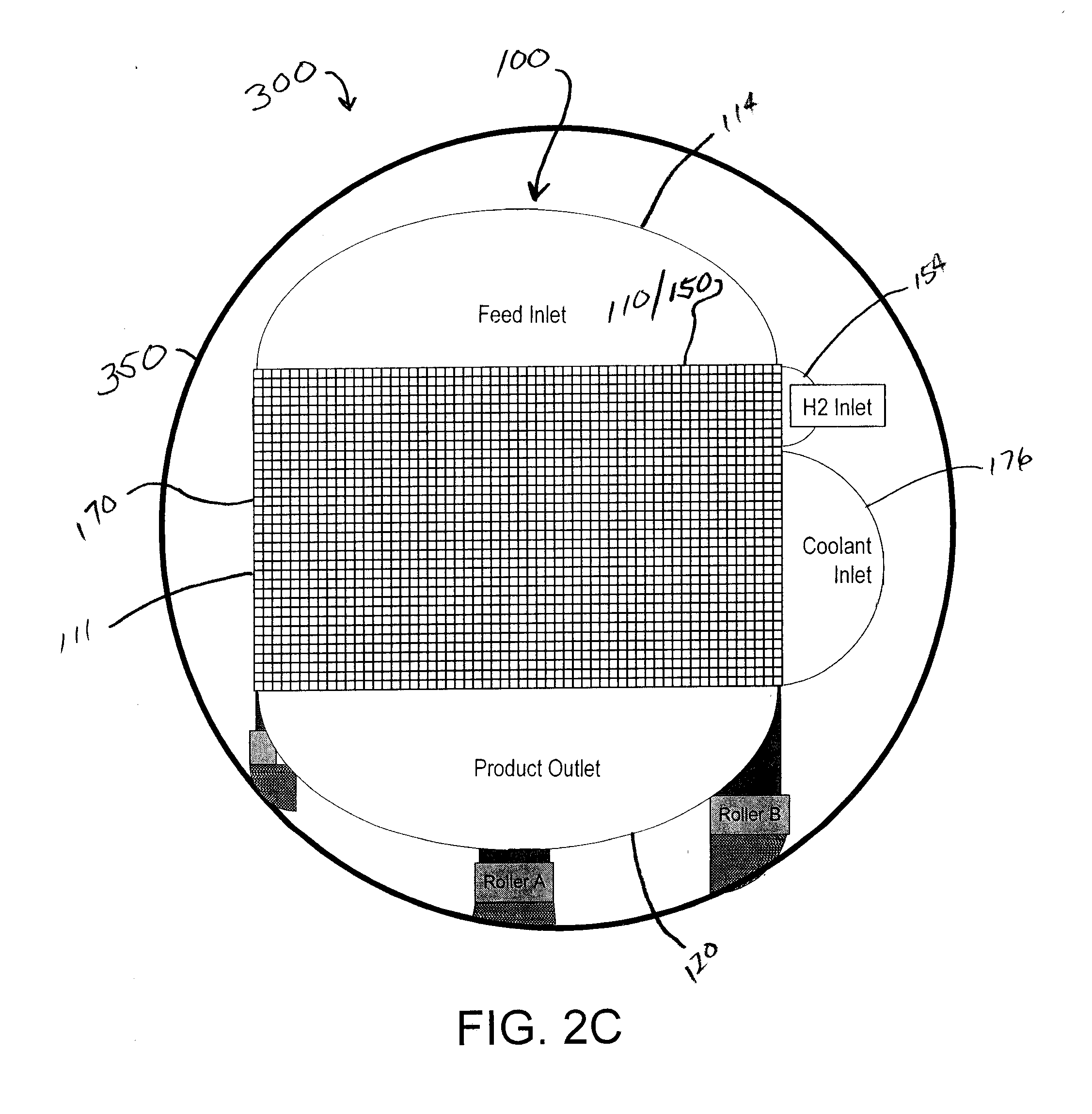
Process for treating heavy oil
a technology for heavy oil and processing, applied in the direction of naphtha treatment, hydrocarbon oil cracking, catalytic naphtha reforming, etc., to achieve the effect of being ready to adapt to the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0067]All ranges and ratio limits disclosed in the specification and claims may be combined in any manner. It is to be understood that unless specifically stated otherwise, references to “a,”“an,” and / or “the” may include one or more than one, and that reference to an item in the singular may also include the item in the plural. All combinations specified in the claims may be combined in any manner.
[0068]The term “heavy oil” refers to C5+ hydrocarbons produced by the gasification, liquefaction or pyrolysis of solid carbonaceous materials (e.g., coal, shale, tar sand, bitumen, biomass, and the like). Heavy oils may also comprise crude oil fractions with an initial boiling point of about 250° C. or above. Heavy oils include vacuum gas oils, atmospheric residiuum, vacuum residiuum, light catalytic cracking oil, heavy catalytic cracking oil, and the like. Heavy oils may have polyaromatic concentrations above about 2% by weight and total aromatic concentrations above about 10% by weight....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com