Method for producing a synthetic material, in particular a synthetic fuel or raw material, an associated device and applications for said method
a synthetic material and method technology, applied in the field of method for producing synthetic materials, can solve the problems of increasing chemical costs, increasing energy and raw material supply, and shortening of these raw materials, so as to improve the overall co2 balance of inventively-created synthetic materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
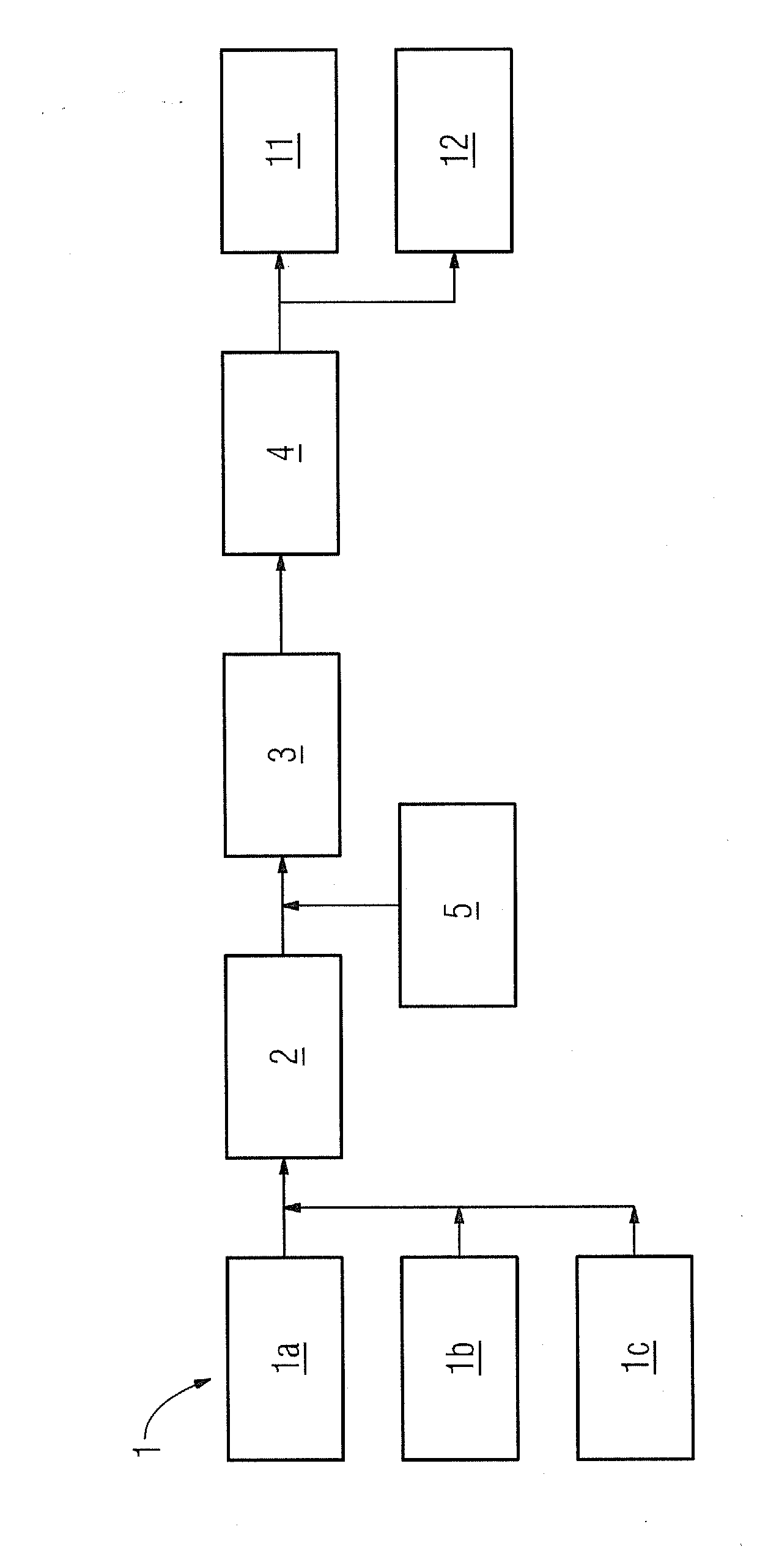
[0021]Labeled 1 in the FIGURE is a unit for generating electrical energy. This electrical energy is provided especially in accordance with unit 1a by wind energy converters. It can however also be provided in the form of solar energy in accordance with unit 1b, or in accordance with unit 1c also in another form, generally purchased on an electricity exchange for example.
[0022]The electrical energy is given to a unit 2 for high-temperature electrolysis (other electrolyzers (PEM / alkali) are also conceivable but not so effective). Connected downstream from the unit 2 are a catalytic reactor 3 and a further unit 4 for conditioning the materials created.
[0023]In the unit 2 for high-temperature electrolysis hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) is created from water (H2O). The CO2 from a CO2-source 5 is now added to the end product. Through the reaction of hydrogen and the added CO2, CH4 and water are produced in accordance with the reaction equations below:
Water electrolysis: .2H2O.2H2+O2
[0024]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com