Patents
Literature
254 results about "Synthetic fuel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes gaseous fuel, obtained from syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, in which the syngas was derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by reforming of natural gas.
Synthetic genomes
ActiveUS20070264688A1Complement and facilitate abilitySugar derivativesTissue cultureChemical synthesisHydrogen
Methods are provided for constructing a synthetic genome, comprising generating and assembling nucleic acid cassettes comprising portions of the genome, wherein at least one of the nucleic acid cassettes is constructed from nucleic acid components that have been chemically synthesized, or from copies of the chemically synthesized nucleic acid components. In one embodiment, the entire synthetic genome is constructed from nucleic acid components that have been chemically synthesized, or from copies of the chemically synthesized nucleic acid components. Rational methods may be used to design the synthetic genome (e.g., to establish a minimal genome and / or to optimize the function of genes within a genome, such as by mutating or rearranging the order of the genes). Synthetic genomes of the invention may be introduced into vesicles (e.g., bacterial cells from which part or all of the resident genome has been removed, or synthetic vesicles) to generate synthetic cells. Synthetic genomes or synthetic cells may be used for a variety of purposes, including the generation of synthetic fuels, such as hydrogen or ethanol.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
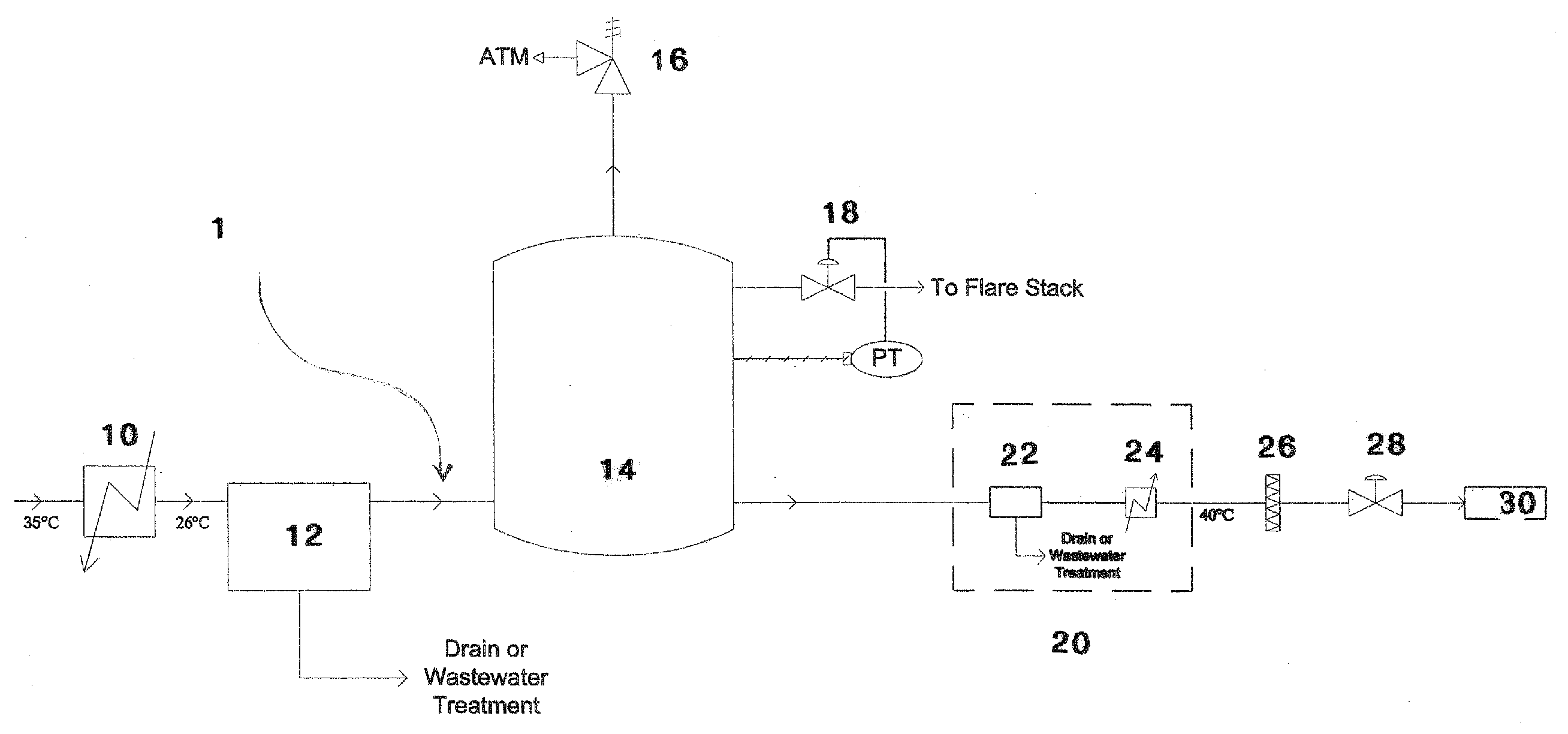
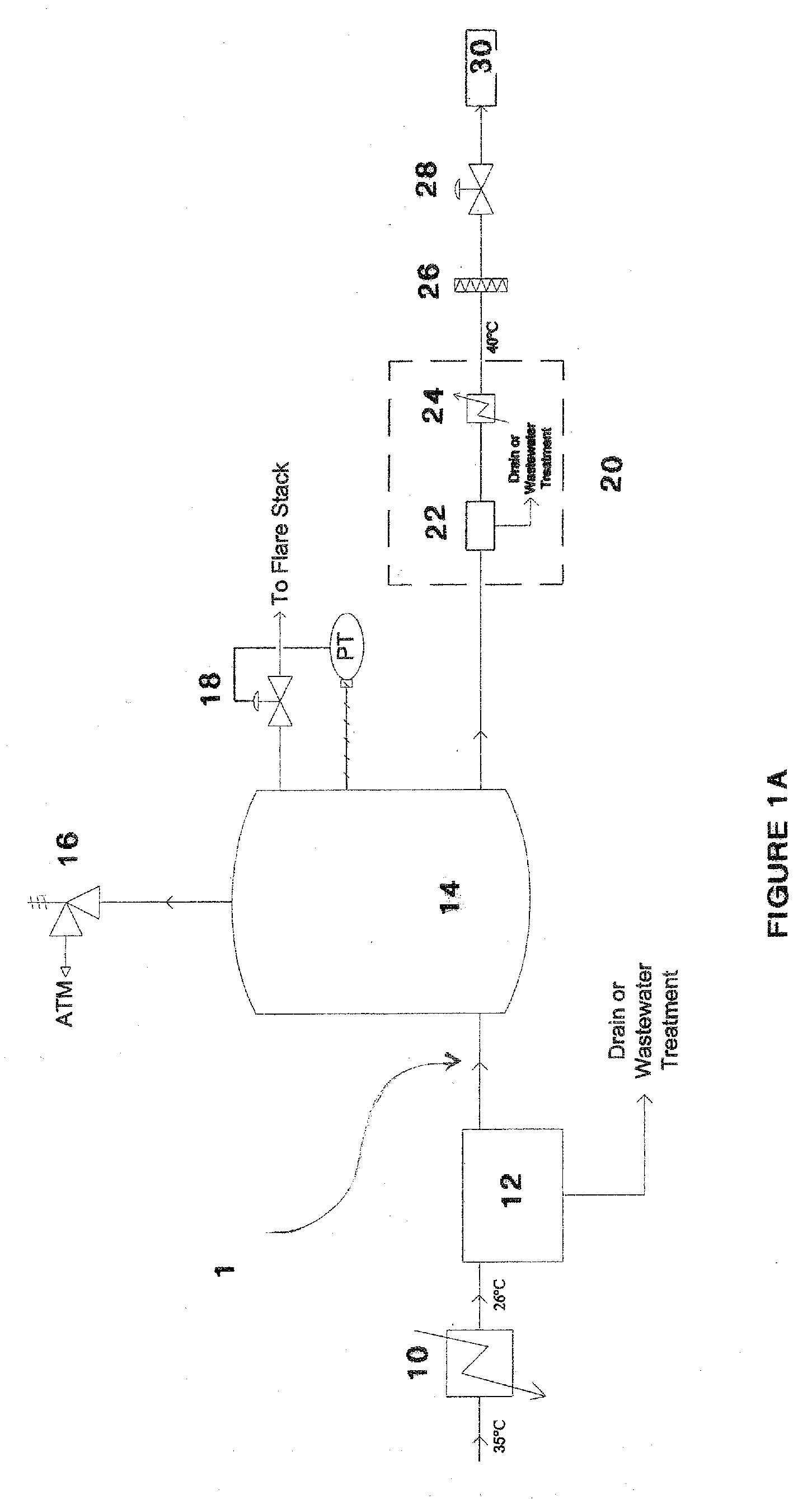
Synthetic fuel production methods and apparatuses
InactiveUS20080098654A1Promote conversionReduce the amount requiredMuffle furnacesRetortsLiquid hydrocarbonsLiquid fuel
Carbon-containing tail gases and pollutants in a coal-to-liquid hydrocarbon production process, or other liquid fuel production process, may be reacted to produce additional synthesis gas which may be used to produce liquid fuels and hydrocarbons or which may be recycled within the liquid fuel production process to improve conversion of carbon to liquid fuels or hydrocarbons.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
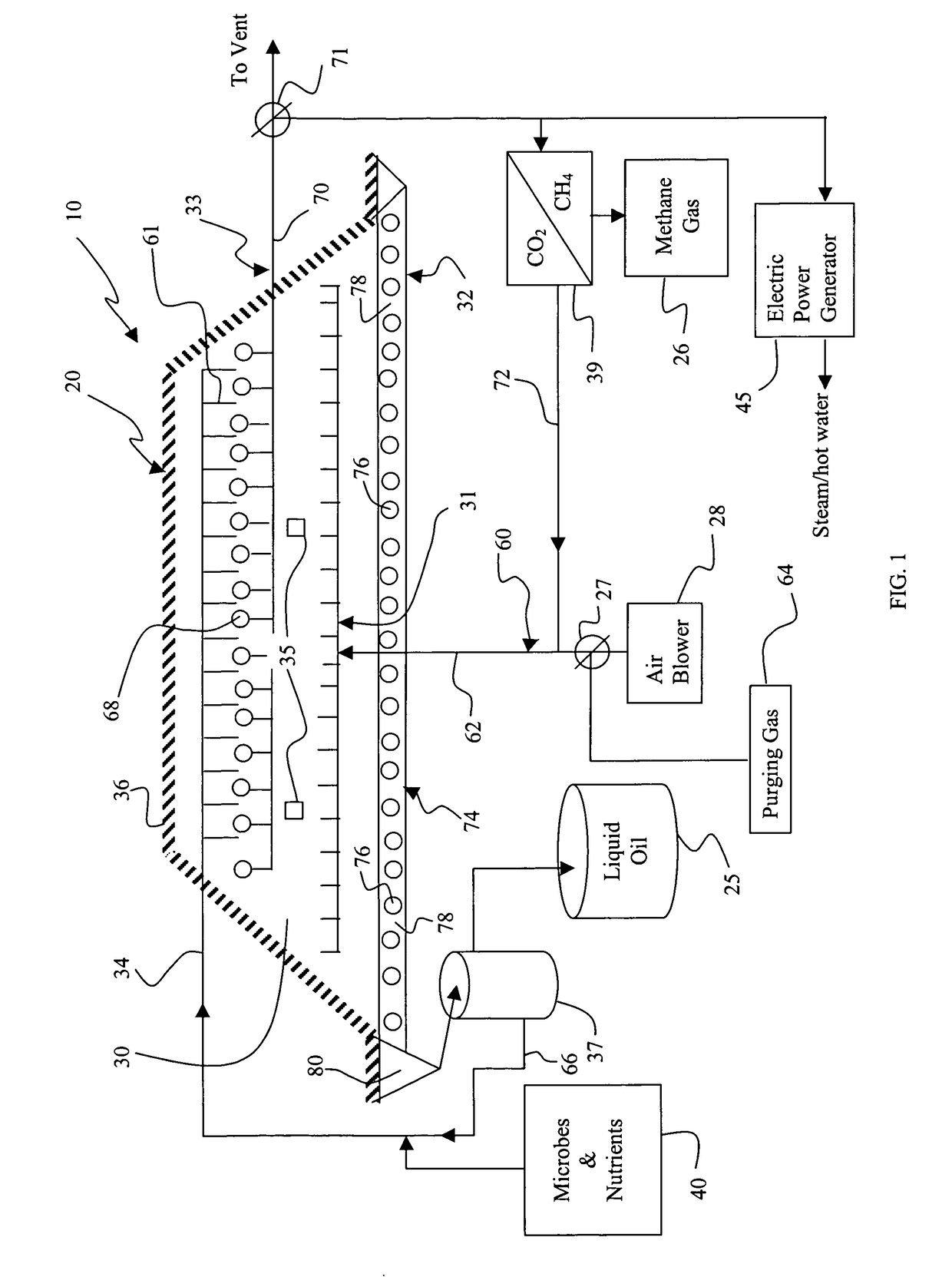
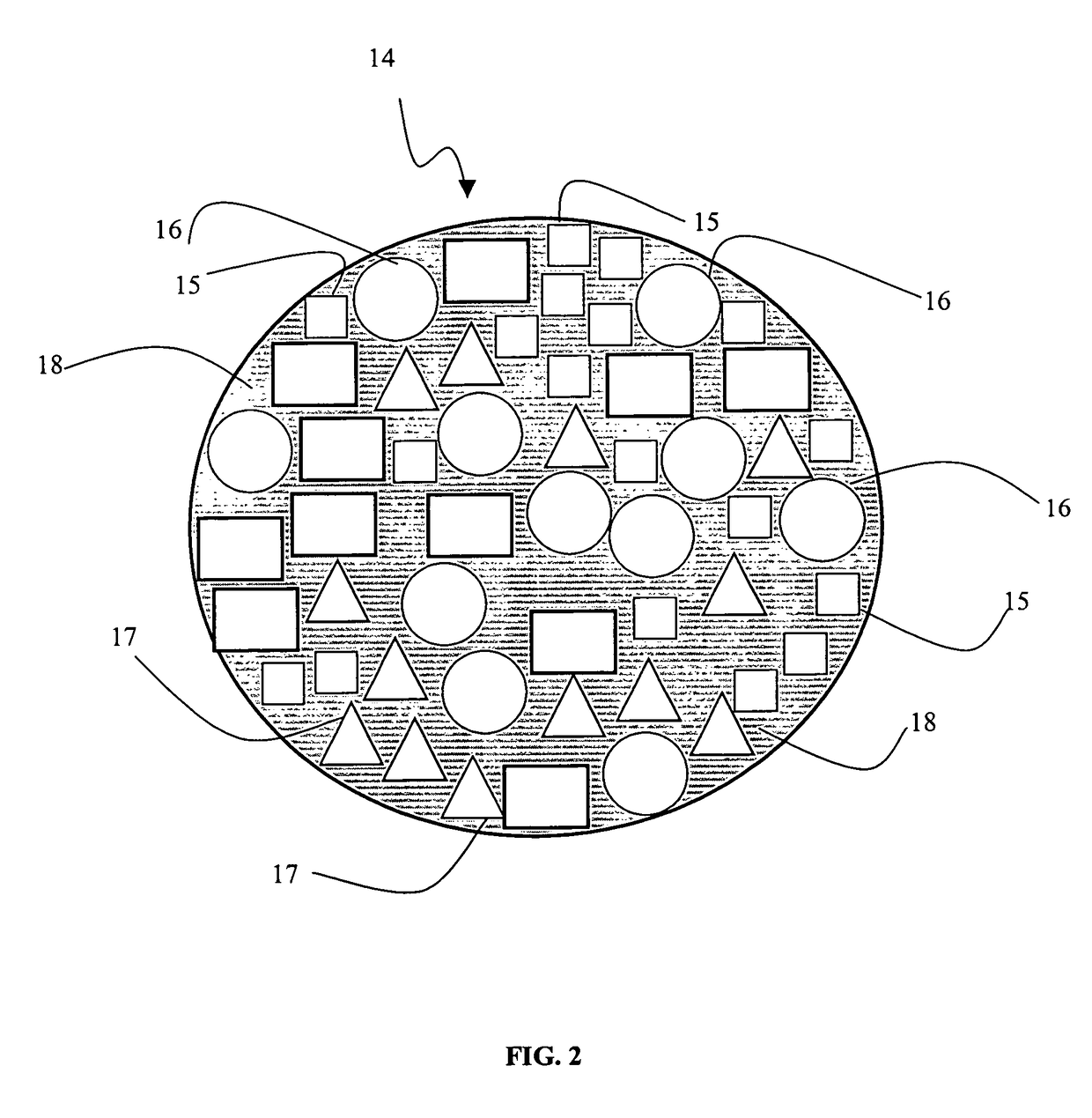
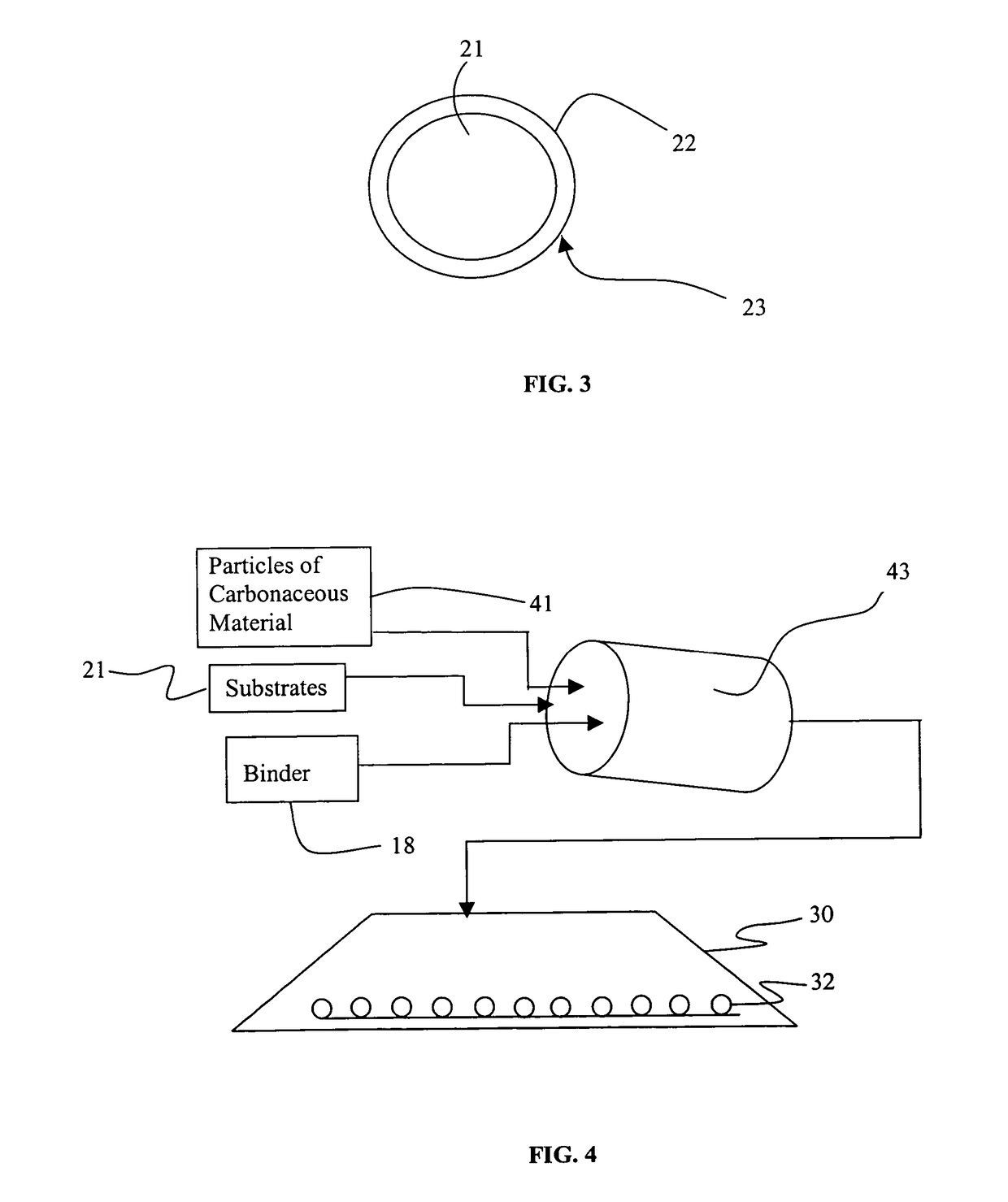
Method and bioreactor for producing synfuel from carbonaceous material
InactiveUS7906304B2Easily biodegradableImprove concentrationGas production bioreactorsWaste based fuelPetroleumBioreactor
A method of producing fuel from biodegradable carbonaceous material using a stacked particle bioreactor is provided. A stacked particle bioreactor is formed from particles including biodegradable carbonaceous material. The biodegradable carbonaceous material in the stacked particle bioreactor is aerobically and / or anaerobically bioconverted into one or more synfuels, which are collected from the reactor. The synfuels produced by the method may include synthetic petroleum, alcohol, and / or a gaseous fuel containing methane. Preferably the method includes an aerobic biotreatment phase followed by an anaerobic bioconversion phase. A stacked particle bioreactor for carrying out the anaerobic, and preferably aerobic, degradation is also described.
Owner:GEOSYNFUELS
Gas Homogenization System
InactiveUS20070266632A1Satisfies requirementCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentChemical synthesisStream flow
A system and process for gas homogenization is disclosed. This has application in the areas of generation of gas and its conversion to electricity in downstream applications. The homogenization system minimizes variance in the gas characteristics (composition, flow, pressure, temperature), thereby rendering a steady stream of gas of consistent quality to the downstream machinery. This homogenization system can be adjusted to optimize the output gas stream for specific end-applications, or to optimize the output gas stream for different input feedstocks. This ensures that overall conversion efficiencies are maximised while keeping the process cost-effective. Such a uniform, steady output gas stream has a wide range of applications in the broad areas of generation of electricity (e.g. using internal combustion engines and combustion turbine engines), chemical synthesis (e.g. of compounds such as ethanol, methanol, hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons), fuel-cell technologies and in polygeneration processes (processes that result in co-production of electricity and synthetic fuels).
Owner:PLASCO ENERGY GROUP INC
Method for synthesizing dimethyl ether by adopting biomass indirect liquification one-step process
InactiveCN1477090ASelf-heating reactionOvercoming the deficiency of hydrogen contentEther preparationSyngasPetroleum
The present invention relates to a method for synthesizing dimethyl ether by high-effectively cleanly utilizing biomass. It utilizes the gasified gas produced by catalytic gasification of biomass air-water vapor, and makes the gasified gas undergo the process of methane reformation to prepare synthetic gas, and utilizes the synthetic gas to directly synthesize clean fuel dimethyl ether.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for converting solar energy into fuel chemical energy
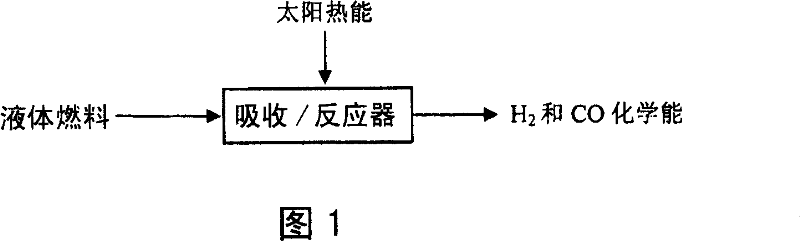
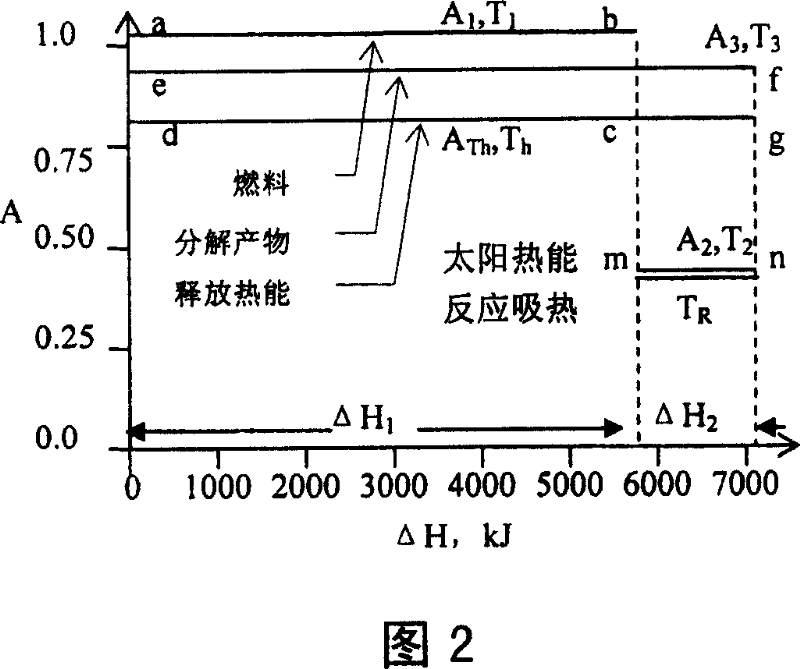
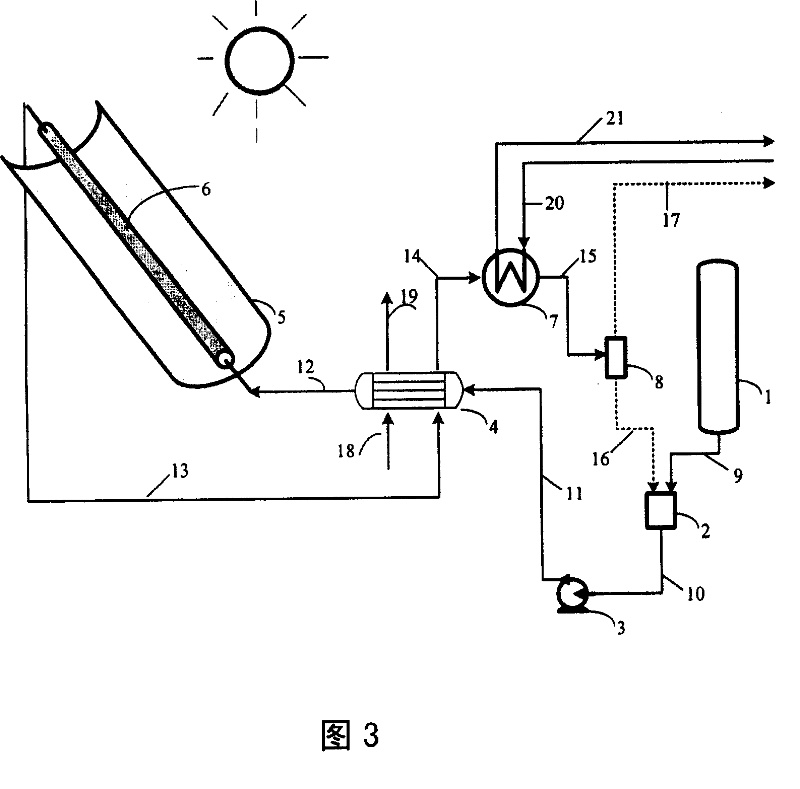
It relates to a method and device of changing solar energy to chemical energy. It accumulates the solar energy and changing it to heat energy ranging from 150deg.C-300deg.C, providing reaction heat for the liquid fuels, allowing the middle and low level solar energy changing and stored into high level chemical energy, with the liquid being carbinol or dimethyl ether synthetic fuel, with the catabolite being hydrogen and monoxide formed gas. It can be used for multi purposes, providing fine synthetic fuel and material for customers.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Alternative fuel and fuel additive compositions
InactiveUS20090013591A1Reduce concentrationReduce severityBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsParticulatesAlternative fuels
Alternative gasoline, diesel fuel, marine diesel fuel, jet fuel, and flexible fuel compositions are disclosed. The compositions include an alcohol and / or a glycerol ether or mixture of glycerol ethers, which can be derived from renewable resources. When combined with gasoline / ethanol blends, the glycerol ethers can reduce the vapor pressure of the ethanol and increasing the fuel economy. When added to diesel fuel / alcohol blends, glycerol ethers improve the cetane value of the blends. All or part of the diesel fuel in the compositions described herein can be biodiesel fuel and / or synthetic fuel derived from a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis process. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis can also use feedstocks derived from sources other than crude oil, such as methane, methanol, ethanol, lignin and glycerol, which can further reduce reliance on foreign sources of crude oil. When used in jet fuel, glycerol ethers can replace all or part of conventional deicing additives, thus lowering skin toxicity, and glycerol ethers ability to reduce particulate emissions can lower the appearance of contrails. When used in marine diesel, the reduction in particulate emissions can be environmentally significant. In another embodiment, the alternative compositions comprise gasoline, ethanol, and n-butanol, and in one aspect, the ethanol and / or n-butanol can be derived from renewable resources. Fuel additive compositions, including glycerol ethers and hydrocarbons and / or alcohols, are also disclosed.
Owner:BRADIN DAVID +2
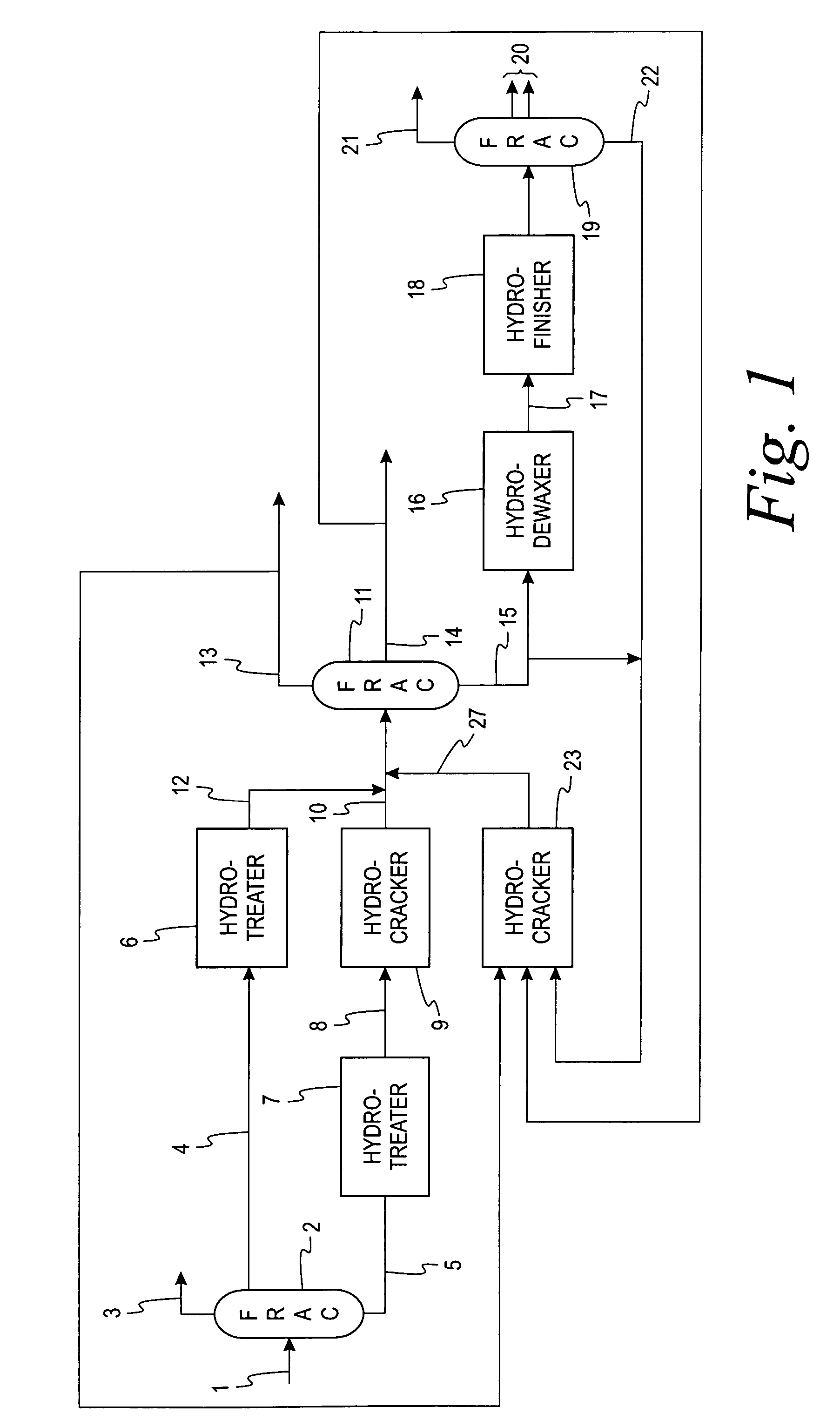
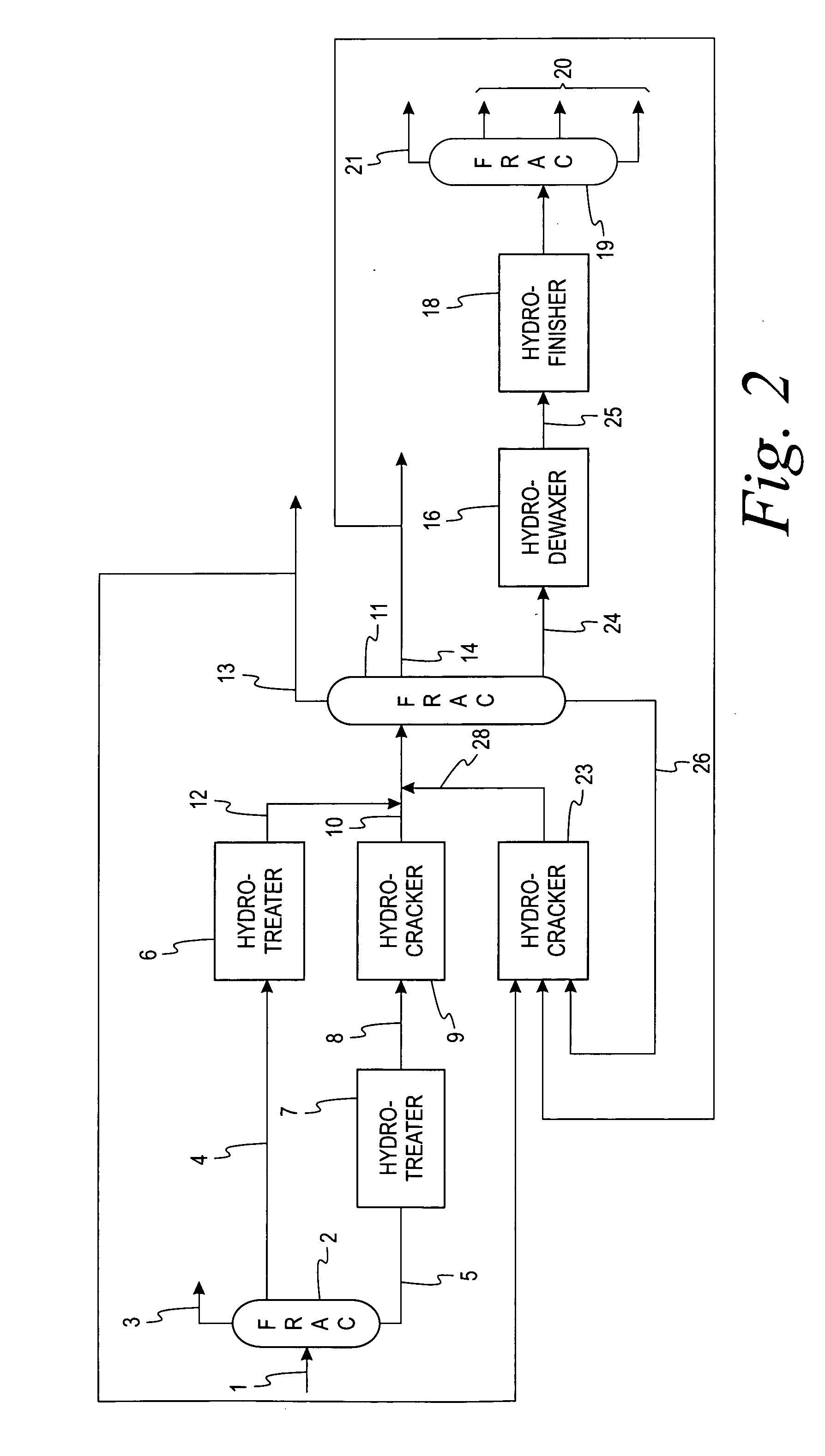
Process to produce synthetic fuels and lubricants
InactiveUS20050183988A1Yield maximizationEquipment cost can be minimizedThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingBase oilPetroleum
A process utilizing a low severity hydrocracker prior to a high severity hydrocracker for the processing of petroleum based and synthetic hydrocarbon feedstocks into distillate fuels and high quality lubricant base oils. The process minimizes the size and conditions required by the high severity hydrocracker by closely matching such configuration with the desired product slate.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
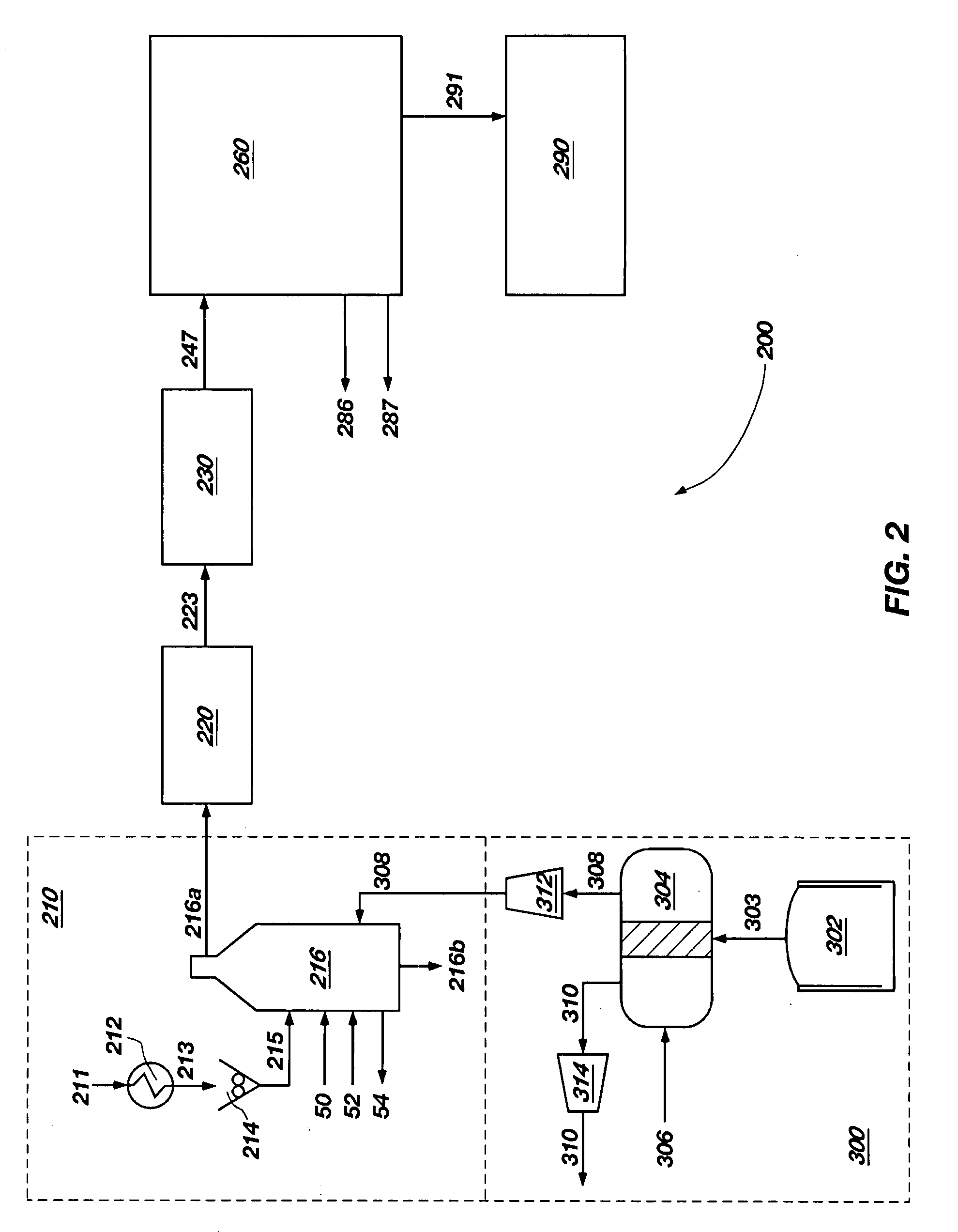
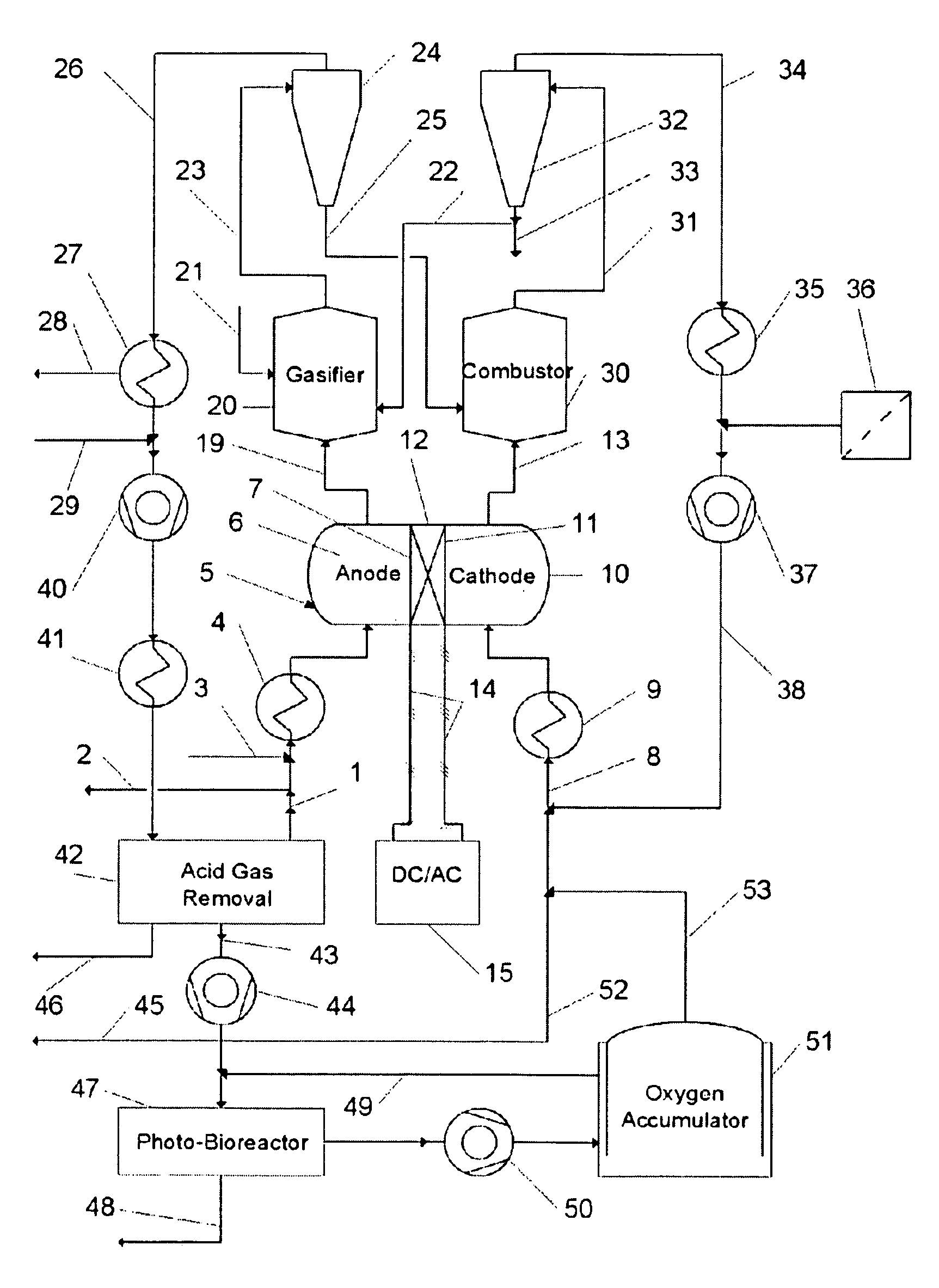
Electricity, heat and fuel generation system using fuel cell, bioreactor and twin-fluid bed steam gasifier
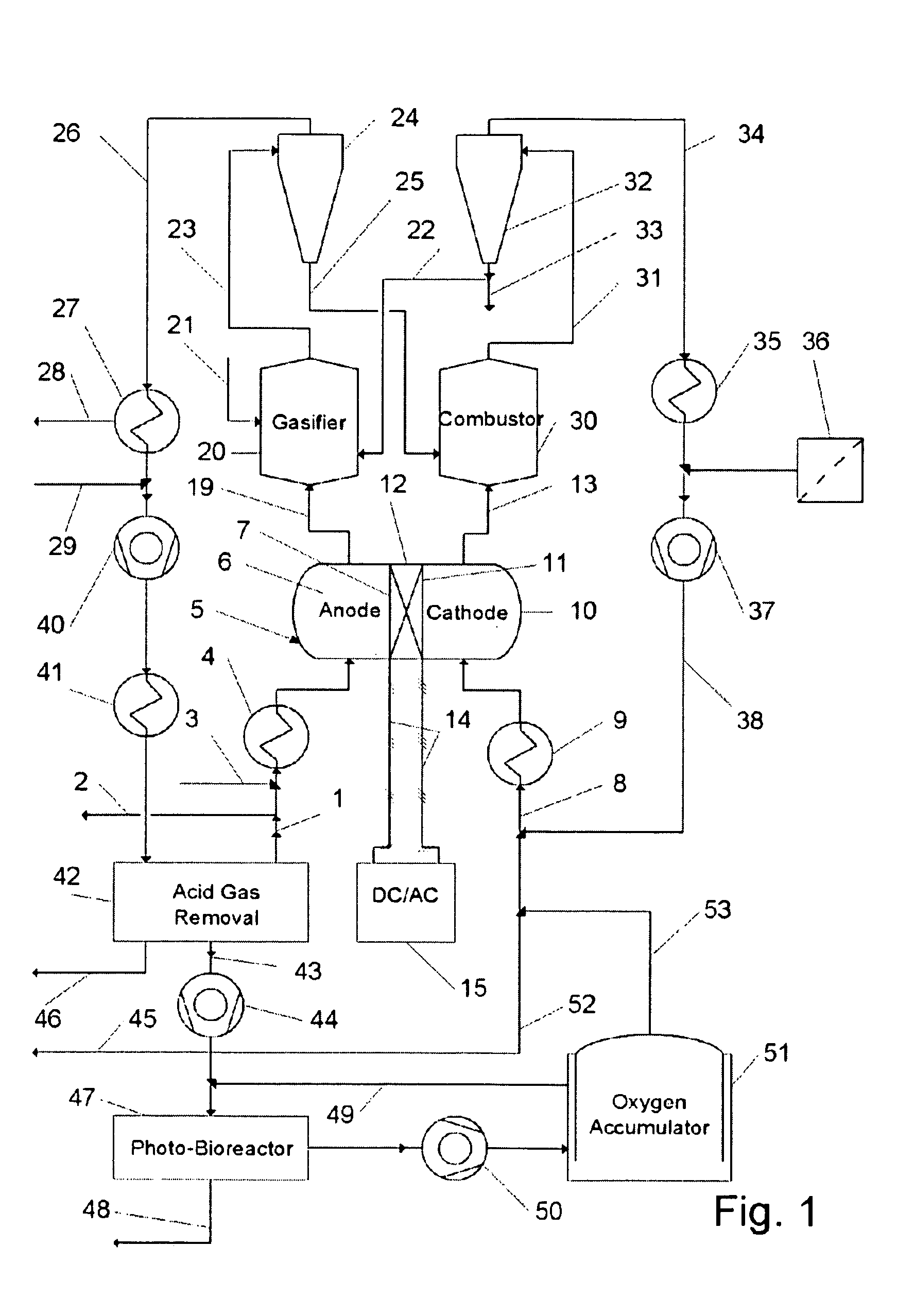
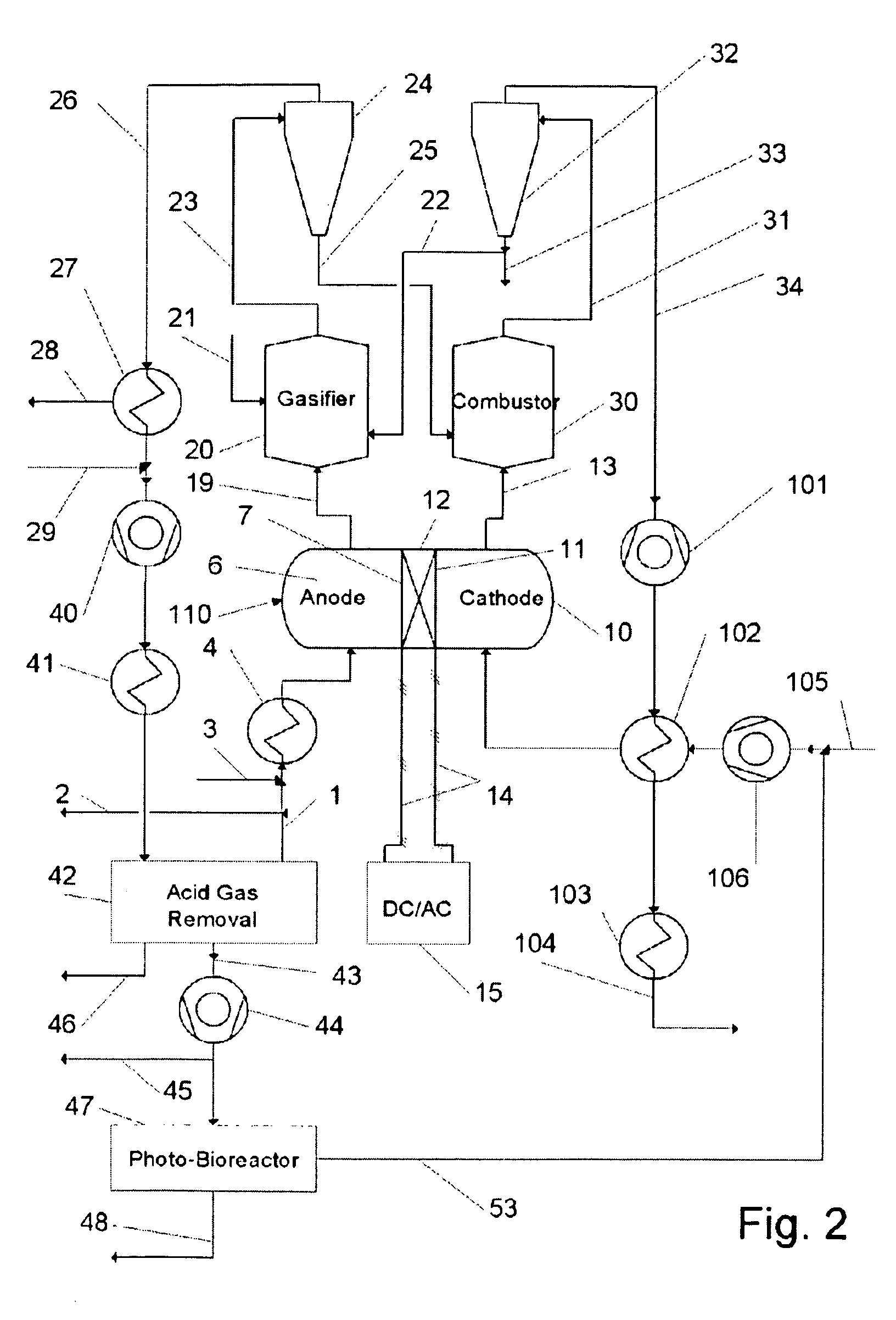
The process and system of the invention converts solid and liquid carbonaceous feedstock into electricity, steam, fuels, and carbon dioxide with minimal air emissions. Oxygen is partially consumed in a fuel cell then exhausted to a combustor of a Twin-Fluid Bed Steam Gasifier Unit (TFBSGU) where it is consumed in burning carbon contained in ash. After particulates are separated, the flue gas is expanded then cooled to recover power before returning to atmosphere or a bio-reactor. Synfuel leaving the TFBGSU is cooled in a heat recovery unit, producing steam and hot water. Carbon monoxide in this stream reacts with steam producing hydrogen and carbon dioxide. The stream is then cooled and compressed. The compressed gas passes through an acid gas removal system removing carbon dioxide and sulfur bearing compounds. Steam is added to the clean gas to prevent coking and the stream enters the anode space of the fuel cell.
Owner:RADOVICH MICHAEL JOHN
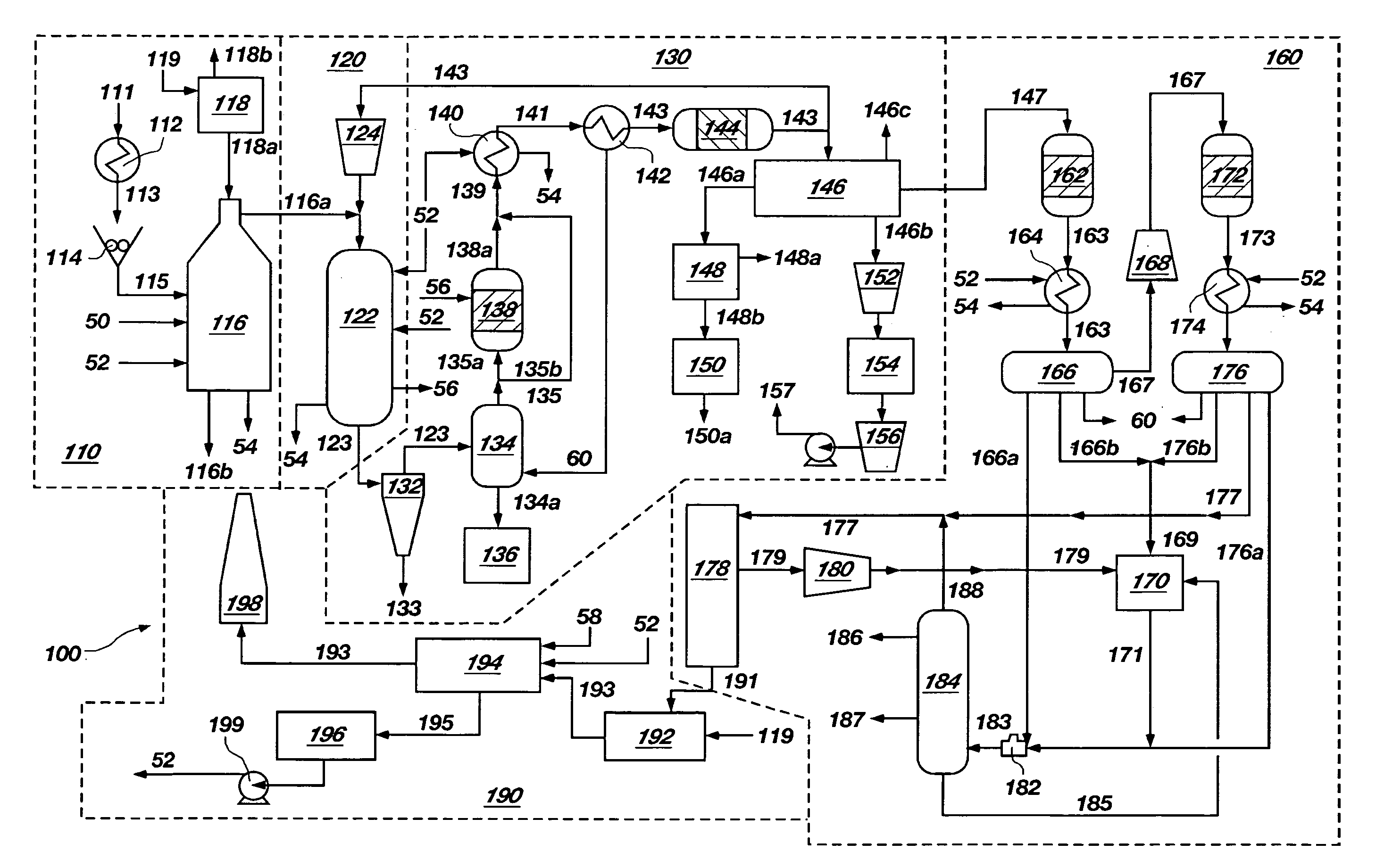
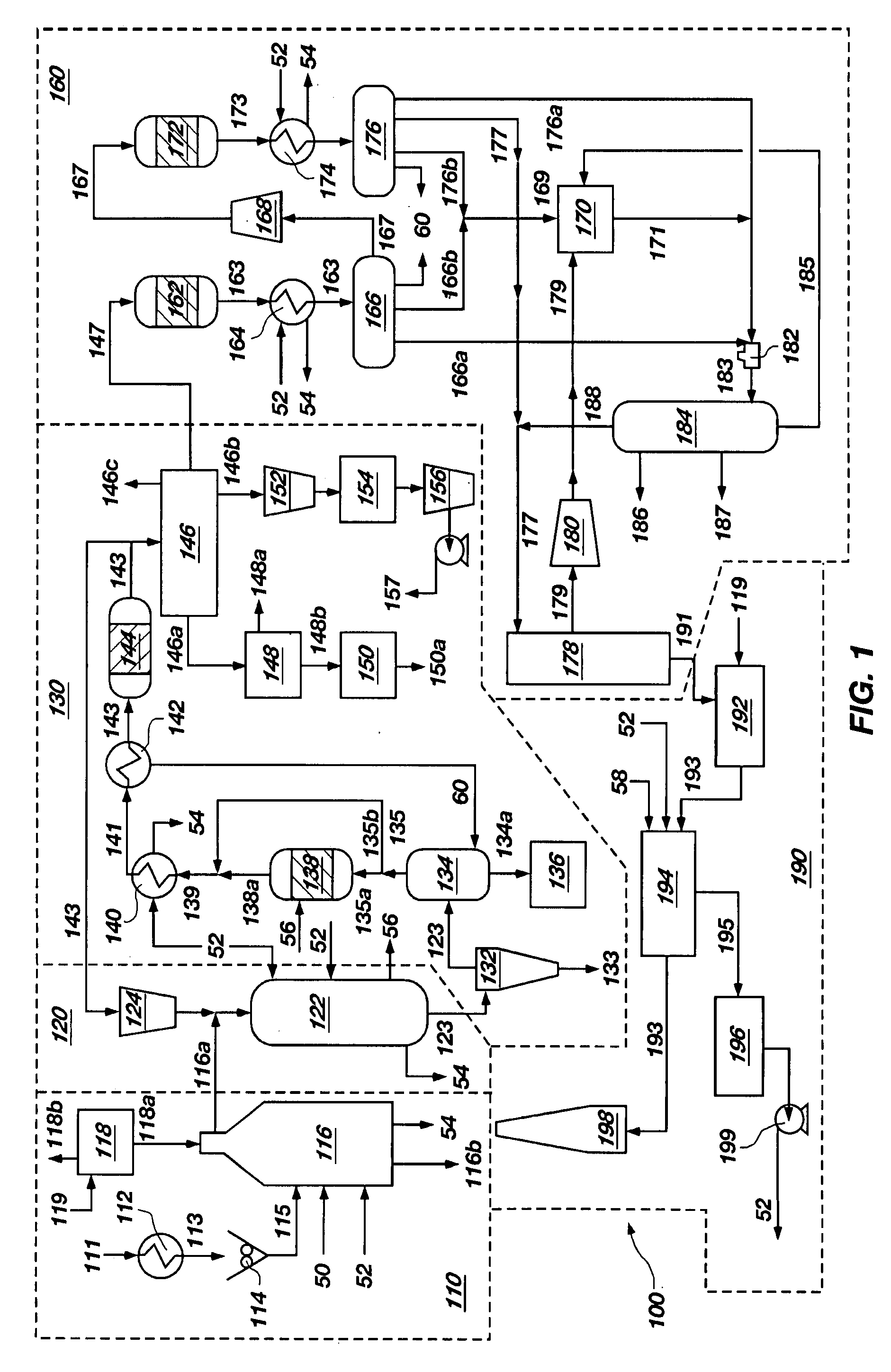
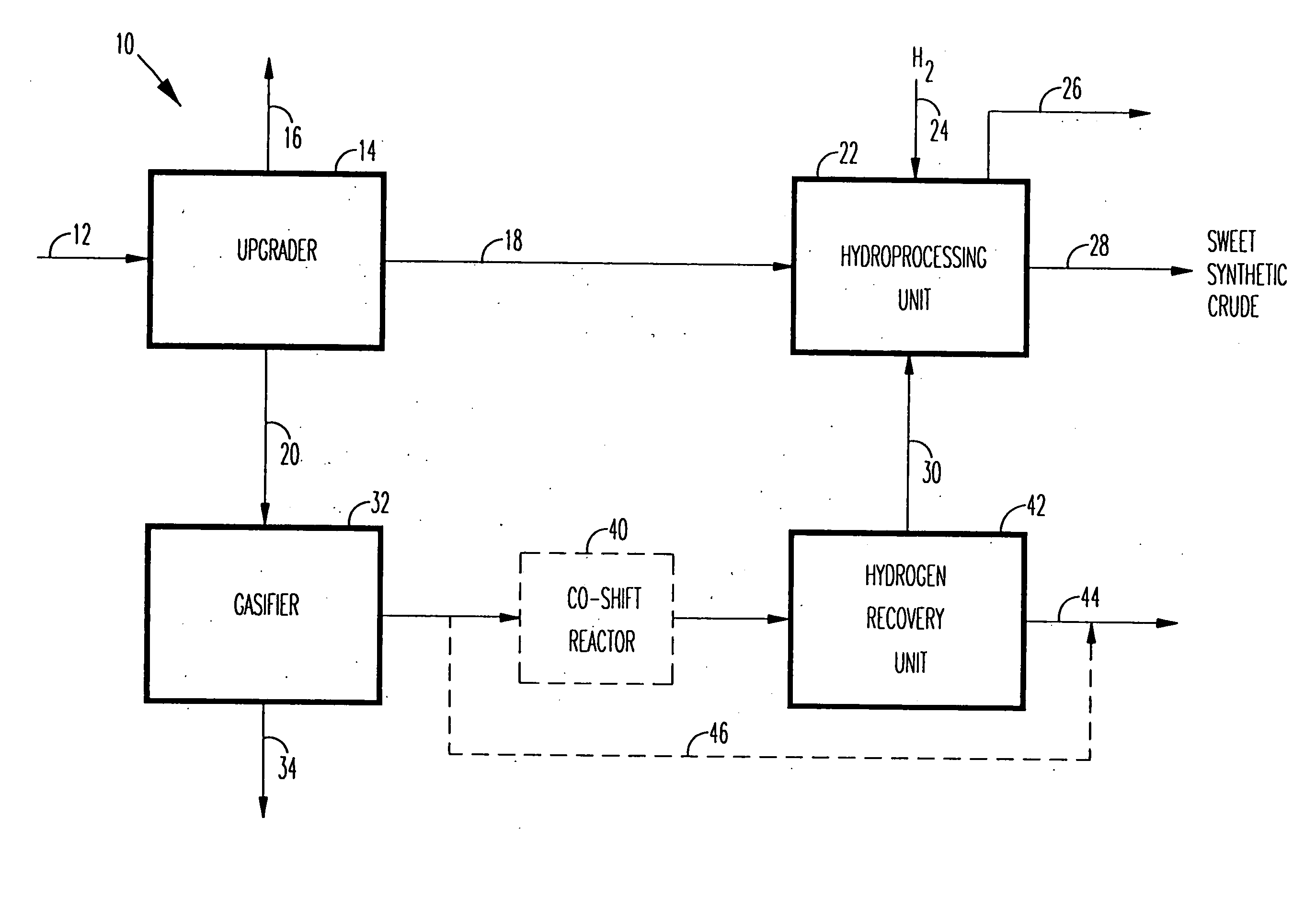
Method of and apparatus for upgrading and gasifying heavy hydrocarbon feeds
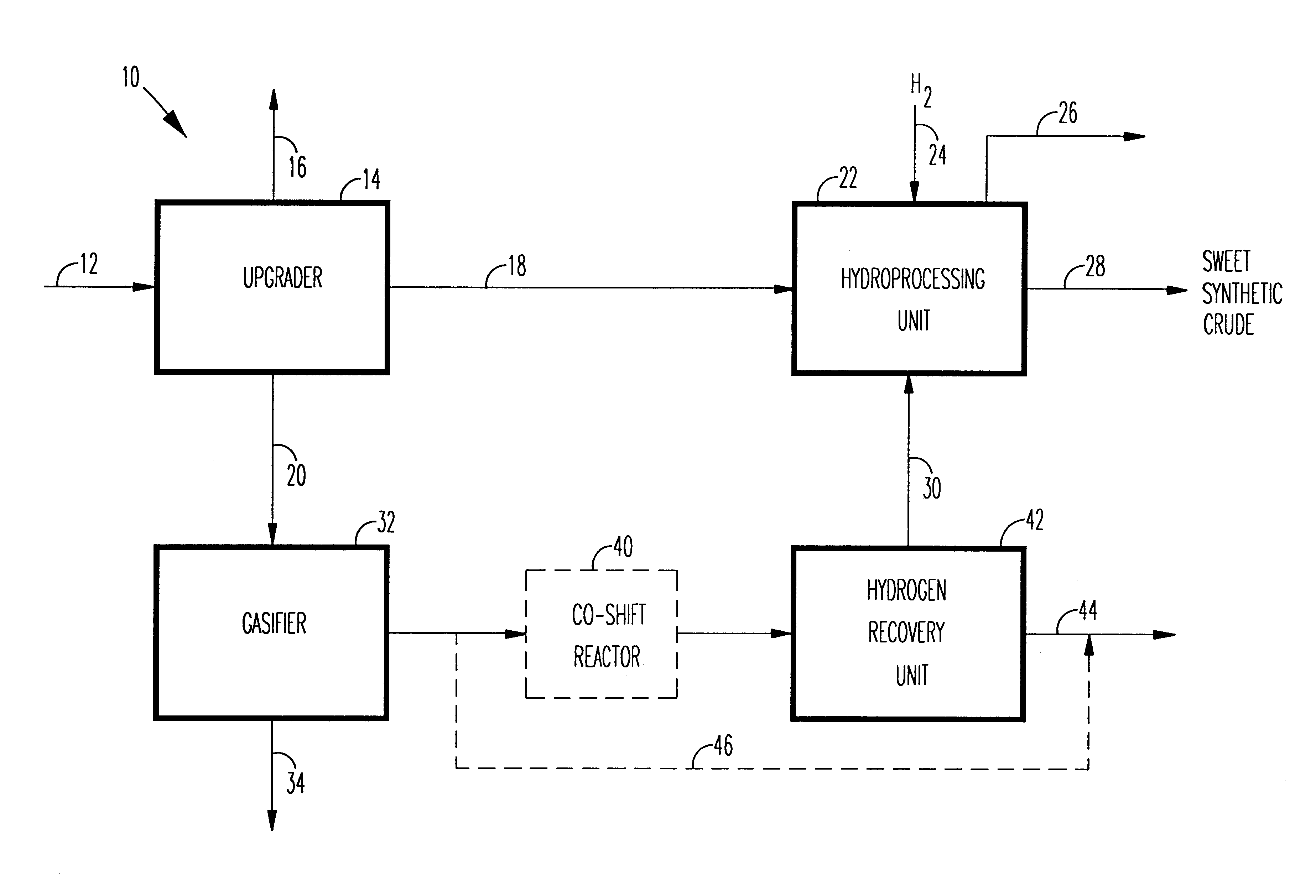
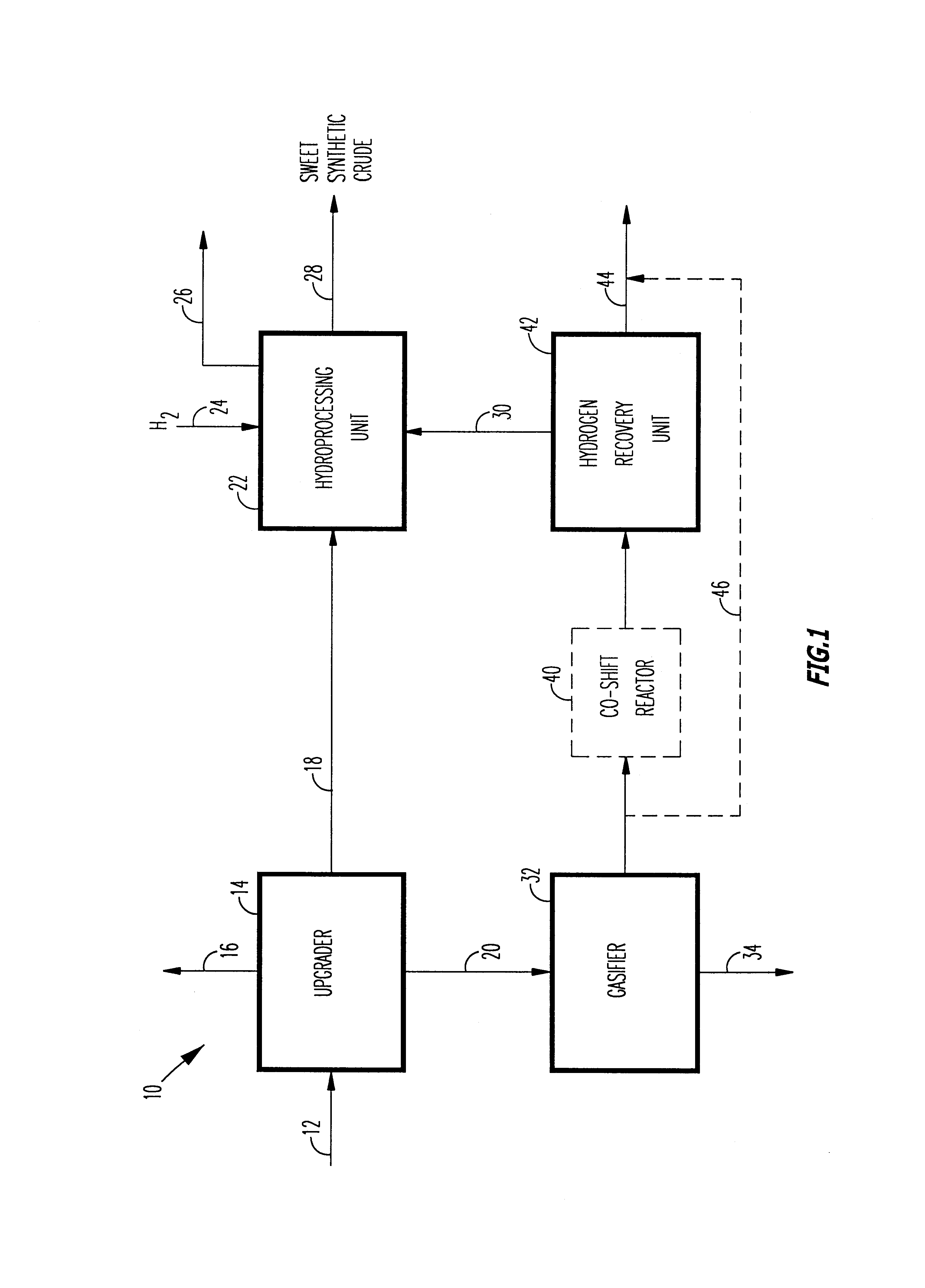
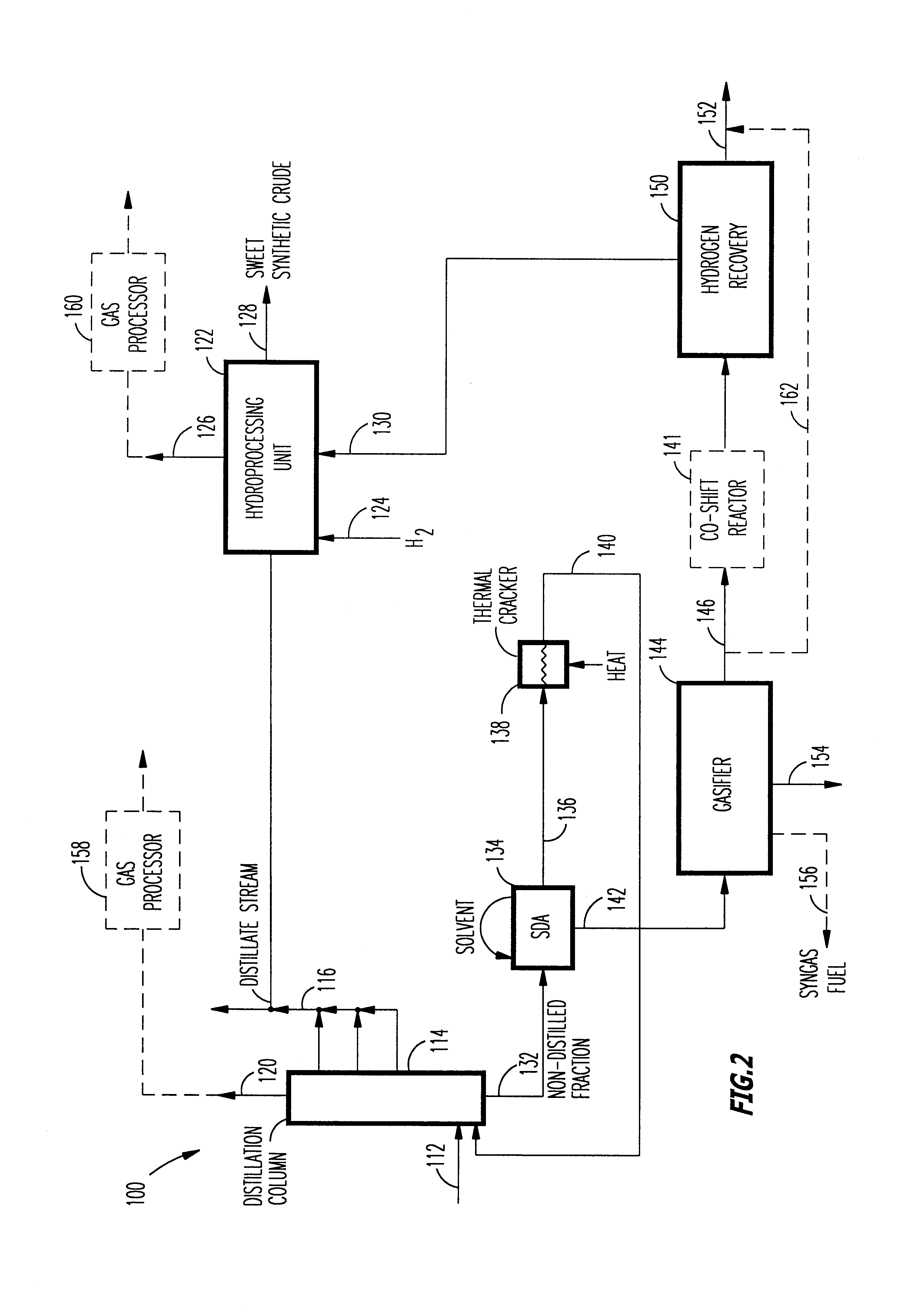
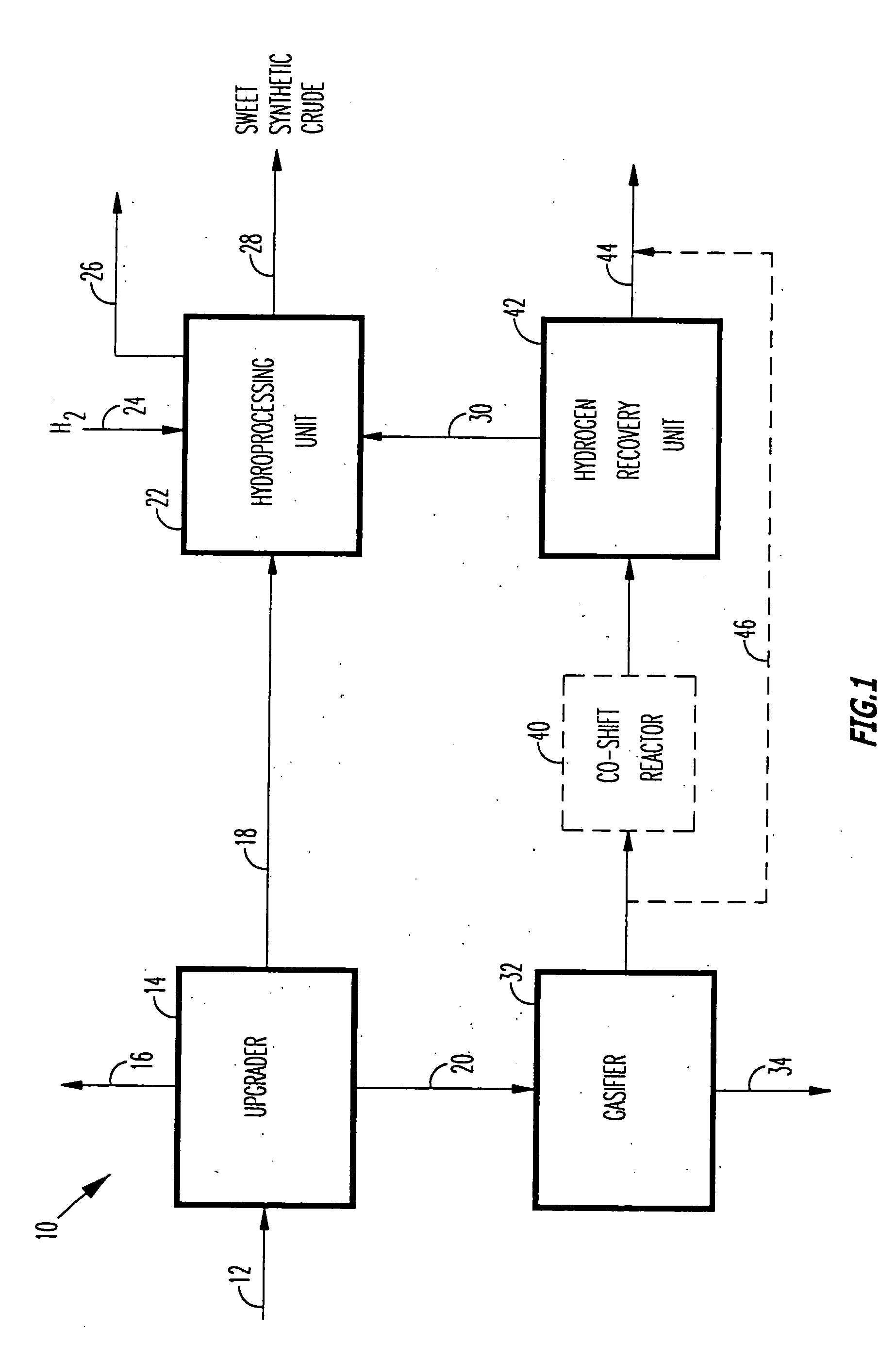
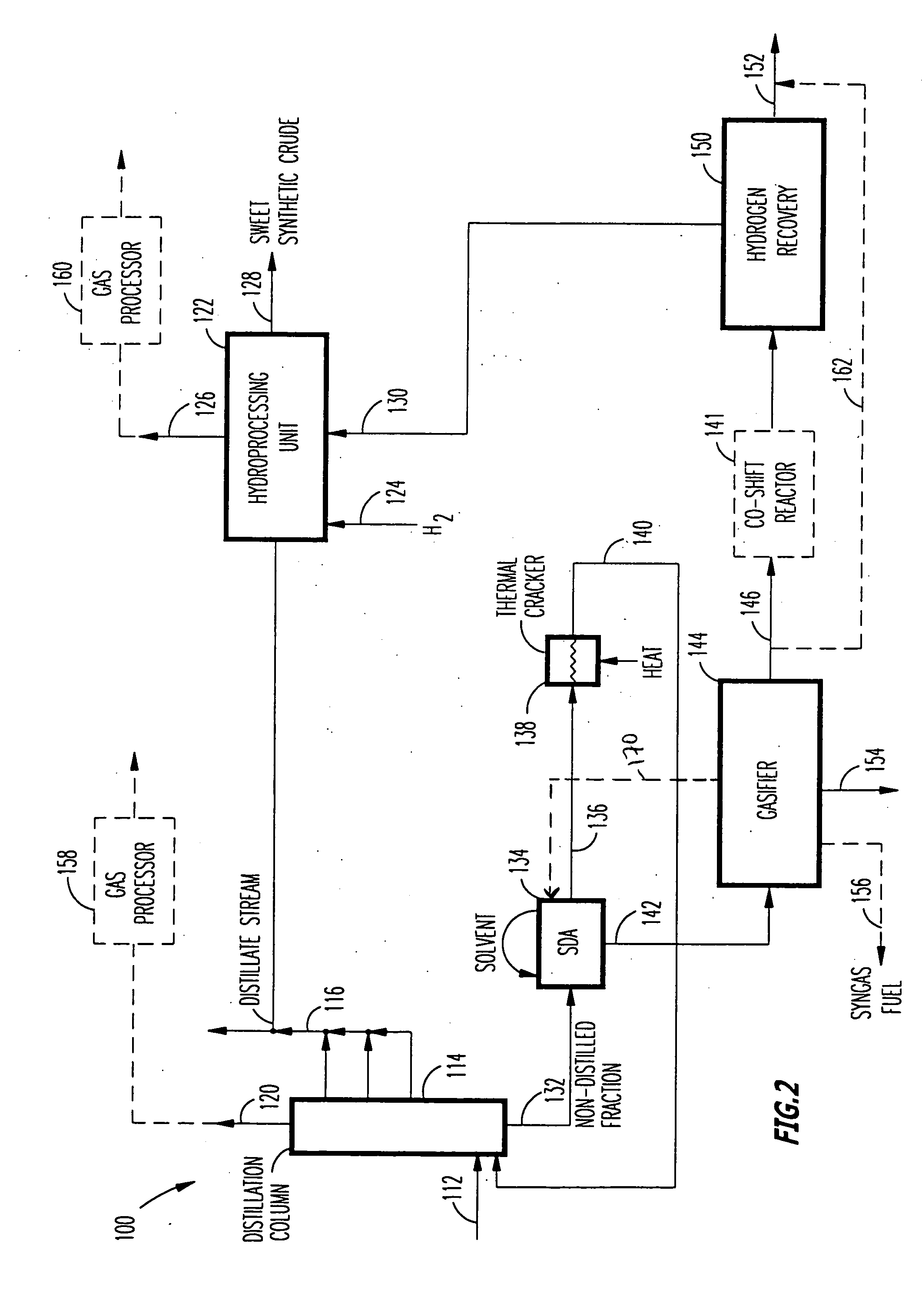
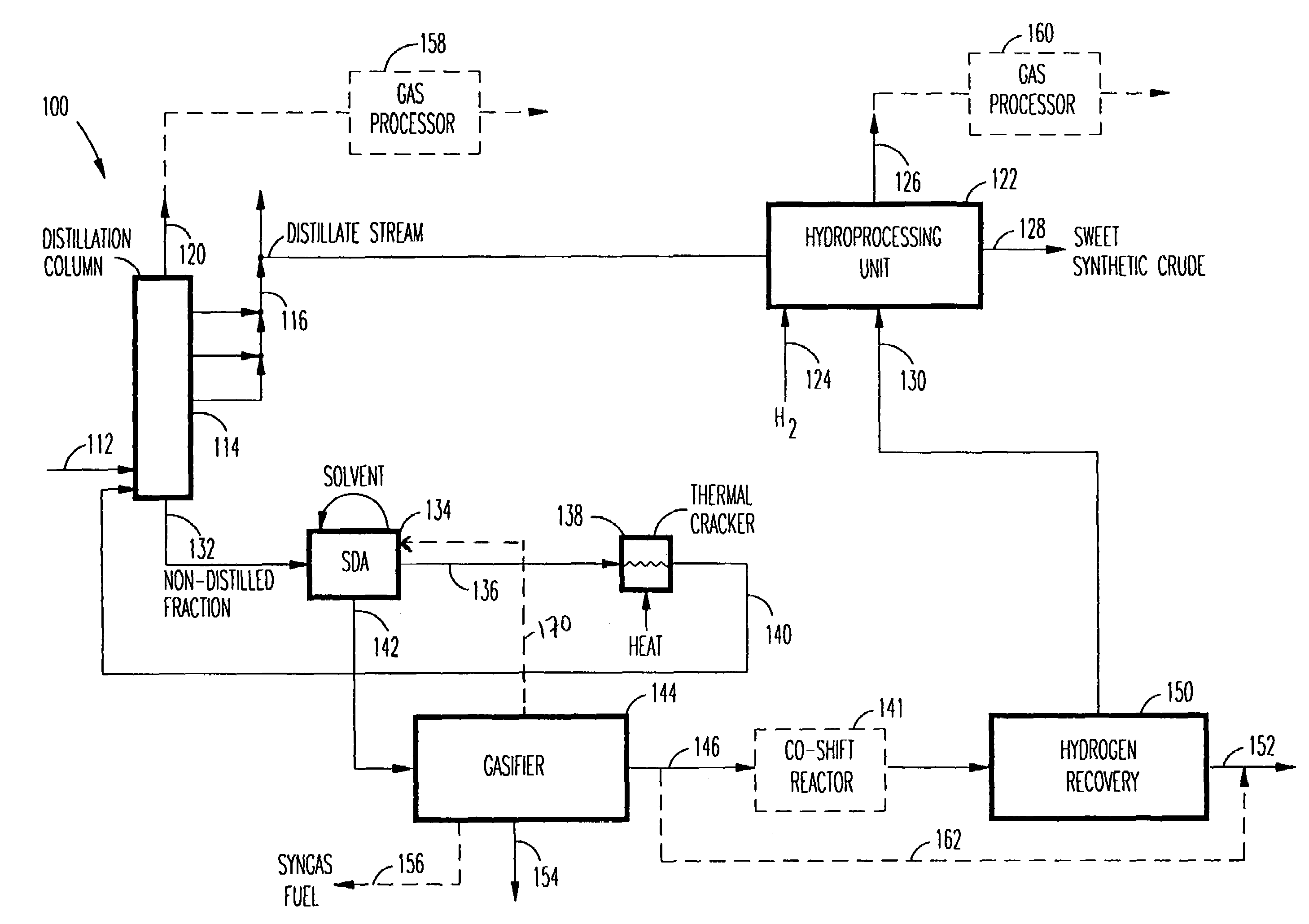
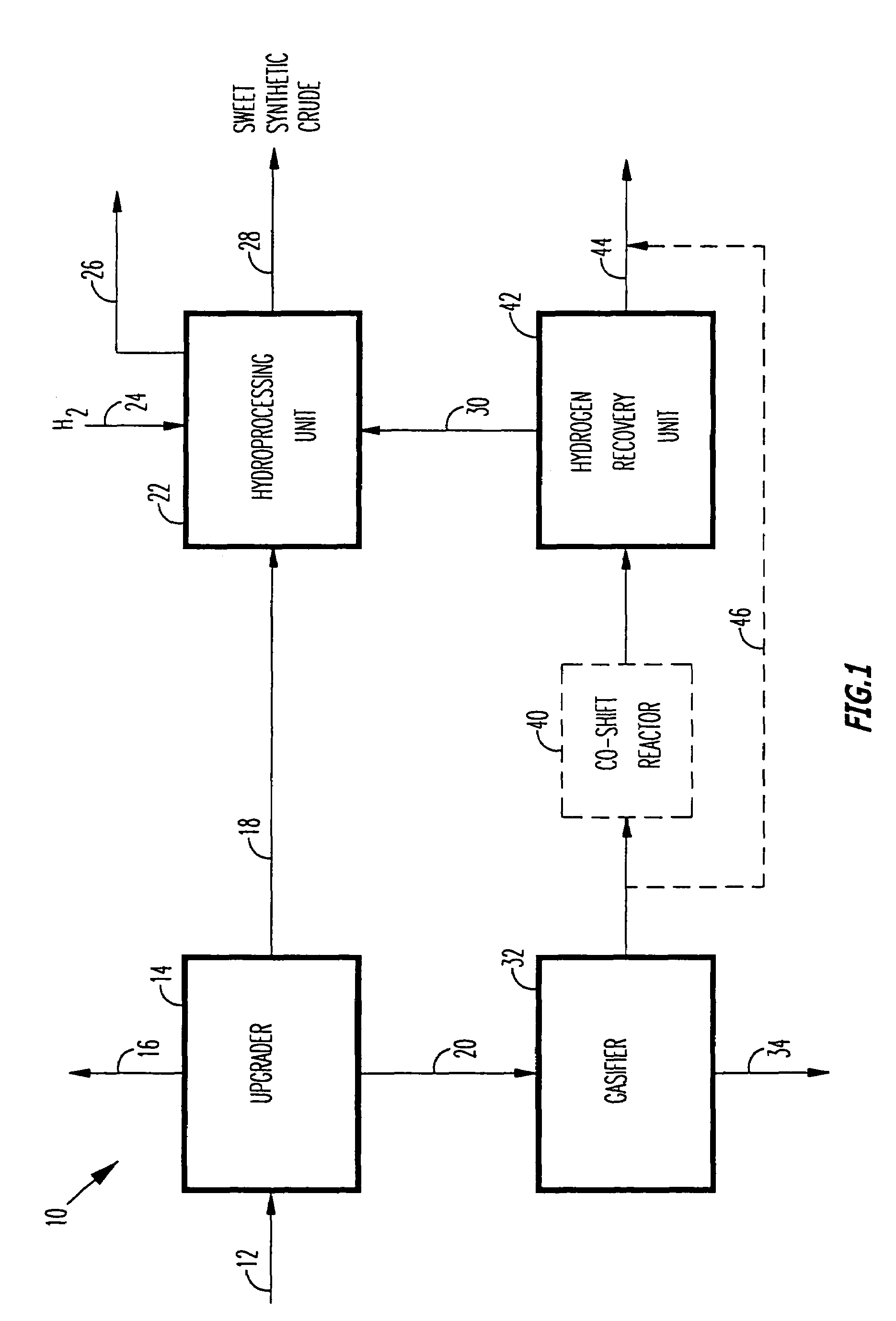
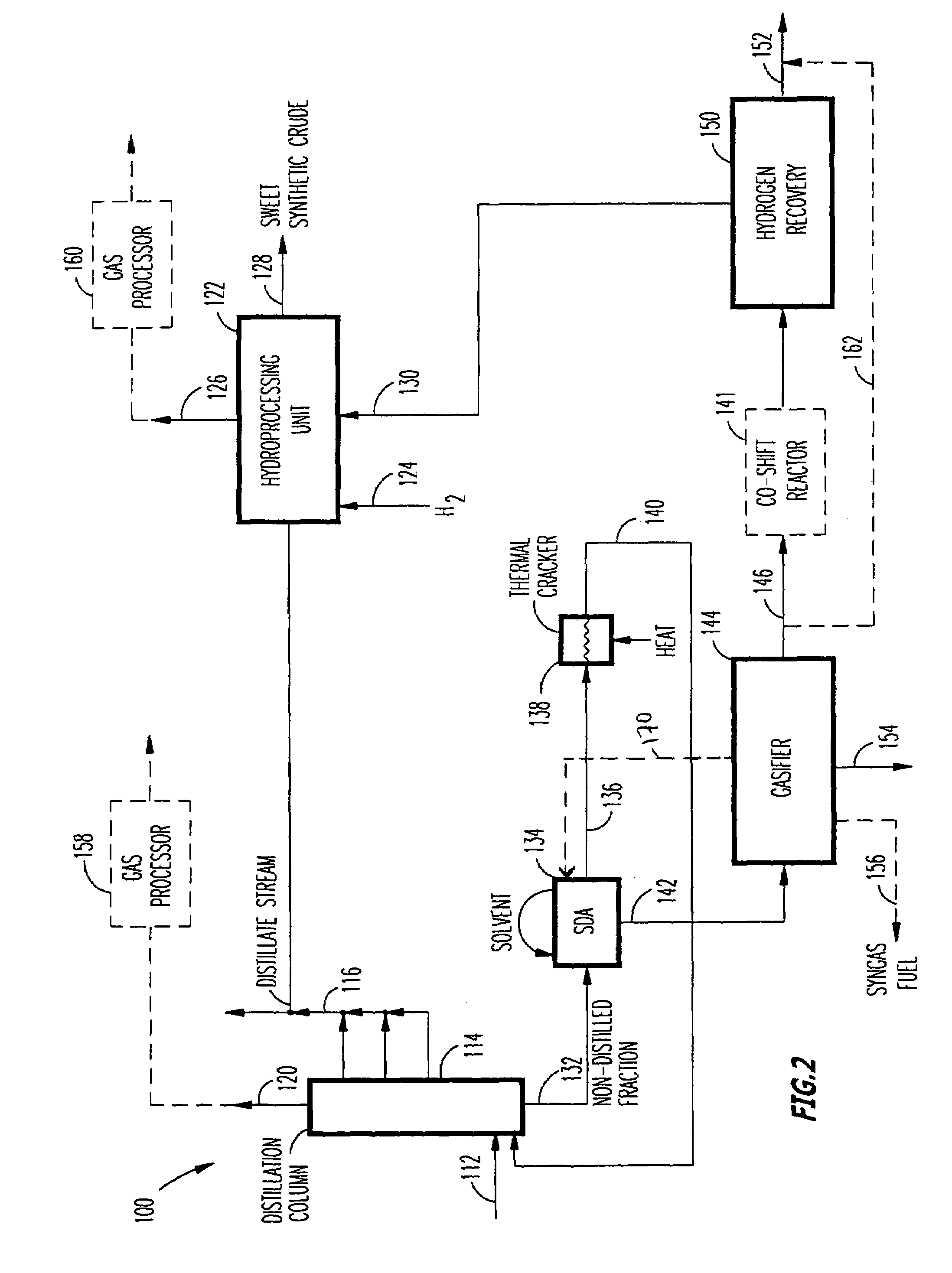
A novel apparatus for producing sweet synthetic crude from a heavy hydrocarbon feed comprising: an upgrader for receiving said heavy hydrocarbon feed and producing a distillate fraction including sour products, and high-carbon content by-products; a gasifier for receiving the high-carbon content by-products and producing synthetic fuel gas and sour by-products; a hydroprocessing unit for receiving the sour by-products and hydrogen gas, thereby producing gas and sweet crude; and a hydrogen recovery unit for receiving said synthetic fuel gas and producing further hydrogen gas and hydrogen-depleted synthetic fuel gas, said further hydrogen gas being supplied to said hydroprocessing unit.
Owner:ORMAT IND LTD
Dual electrolyte membraneless microchannel fuel cells
InactiveUS20060228622A1Maintain structural integrityHigh power deviceElectrolyte holding meansCell electrodesFlow cellEngineering
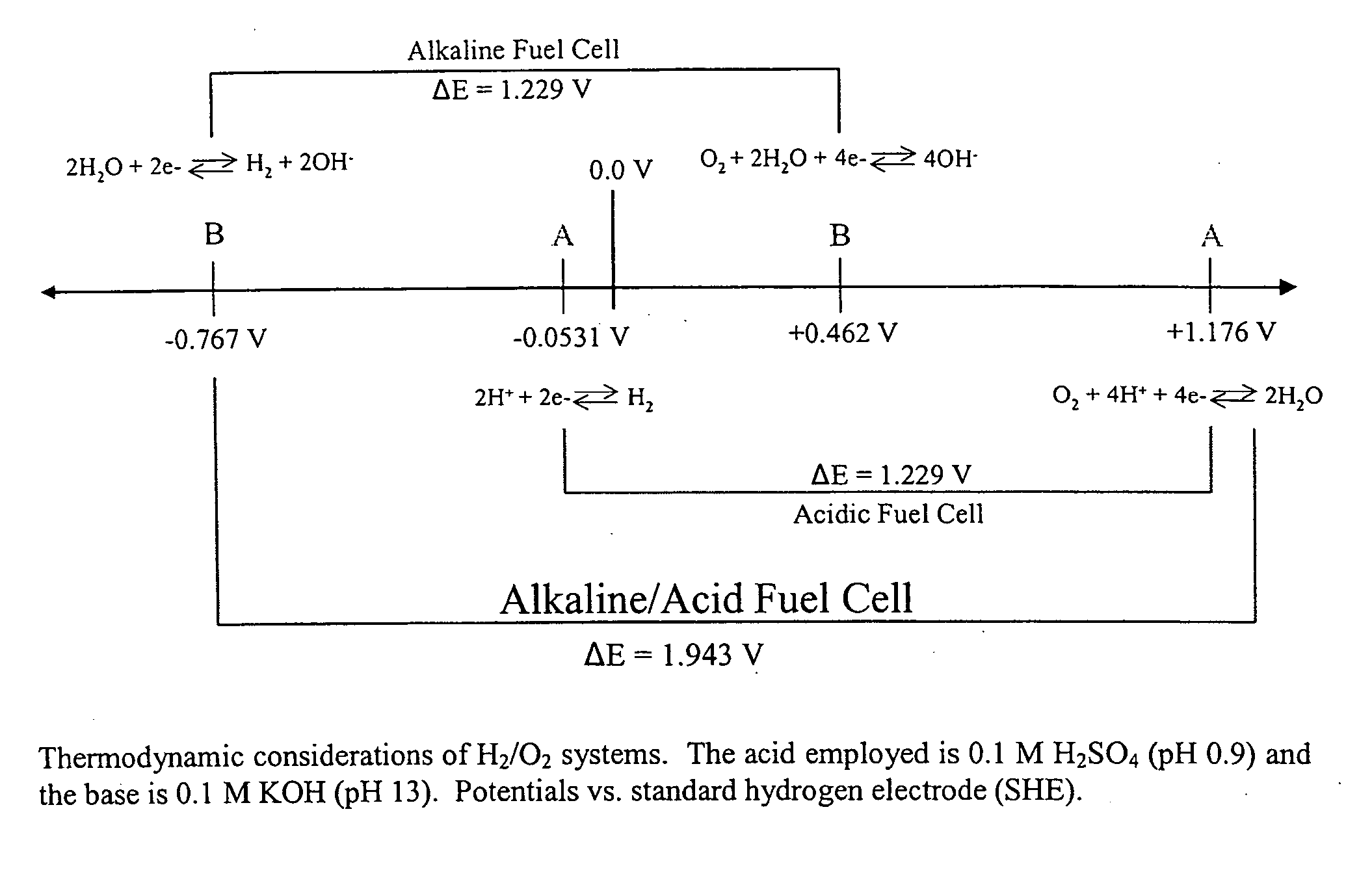
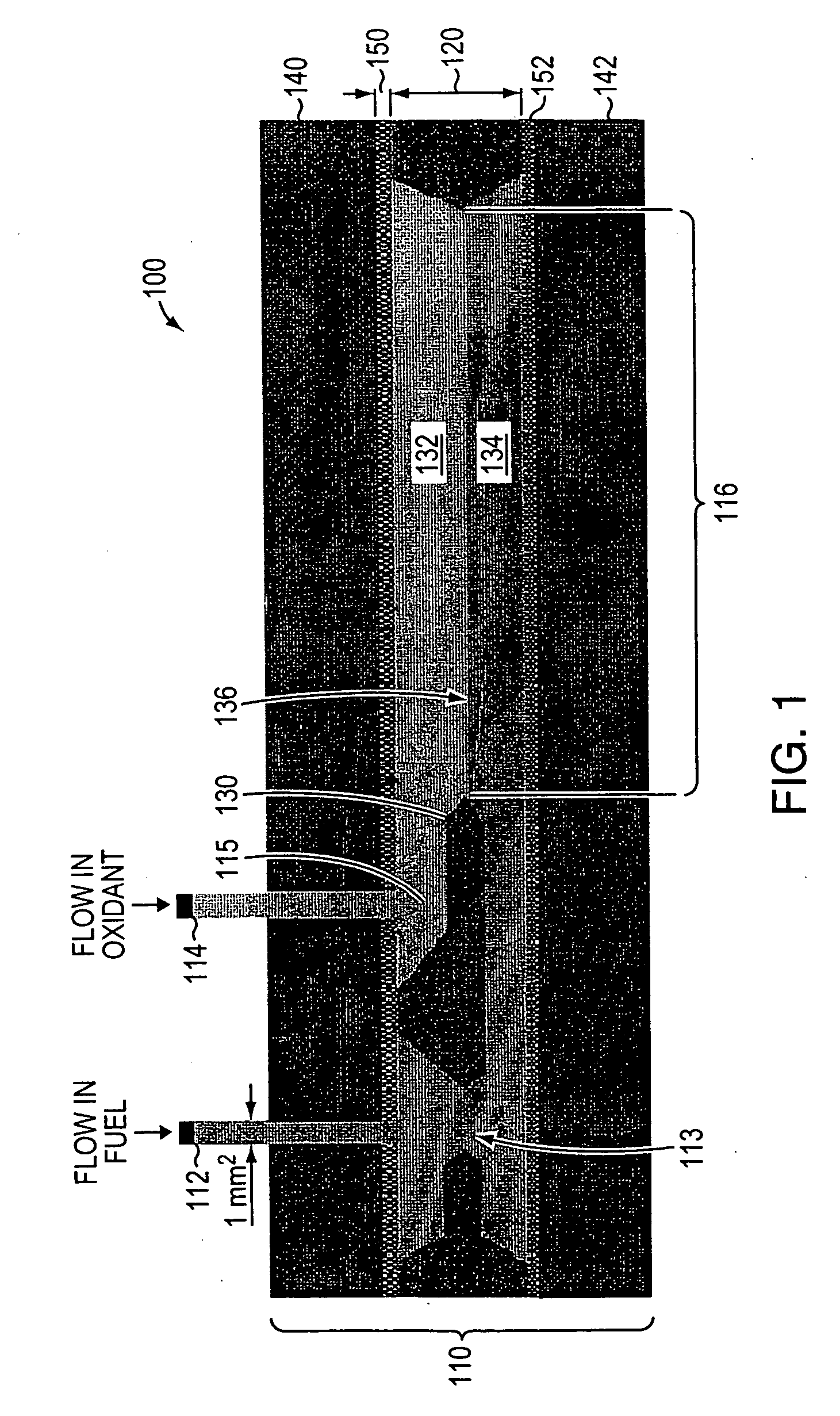
A microfluidic membraneless flow cell formed with multiple acidic / alkaline electrolyte solutions. The flow cell can be adapted to provide a dual electrolyte H2 / O2 fuel cell that generates thermodynamic potentials of up to 1.943 V or possibly greater. The selected fuel can be hydrogen dissolved in 0.1 M KOH, and the selected oxidant can be oxygen dissolved in 0.1 M H2SO4. Individual fuel cells can be combined to form fuel cell stacks to generate increased power output. Furthermore, microchannels of varying dimensions may be selected, including thickness variations, and different flow rates of acid / base electrolyte solutions can be applied to satisfy predetermined power generation needs. Some (micro-) fuel cell embodiments can be formed with silicon microchannels of fixed length and variable width and height, and can be used with hydrogen or formic acid as a fuel and oxygen as an oxidant, each dissolved in different acid / base electrolyte solutions. Micro-fuel cells are also provided which can be designed to generate different power levels for various applications including portable electronic devices such as wireless communication handsets and cellular telephones.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method of producing synthetic fuels and organic chemicals from atmospheric carbon dioxide
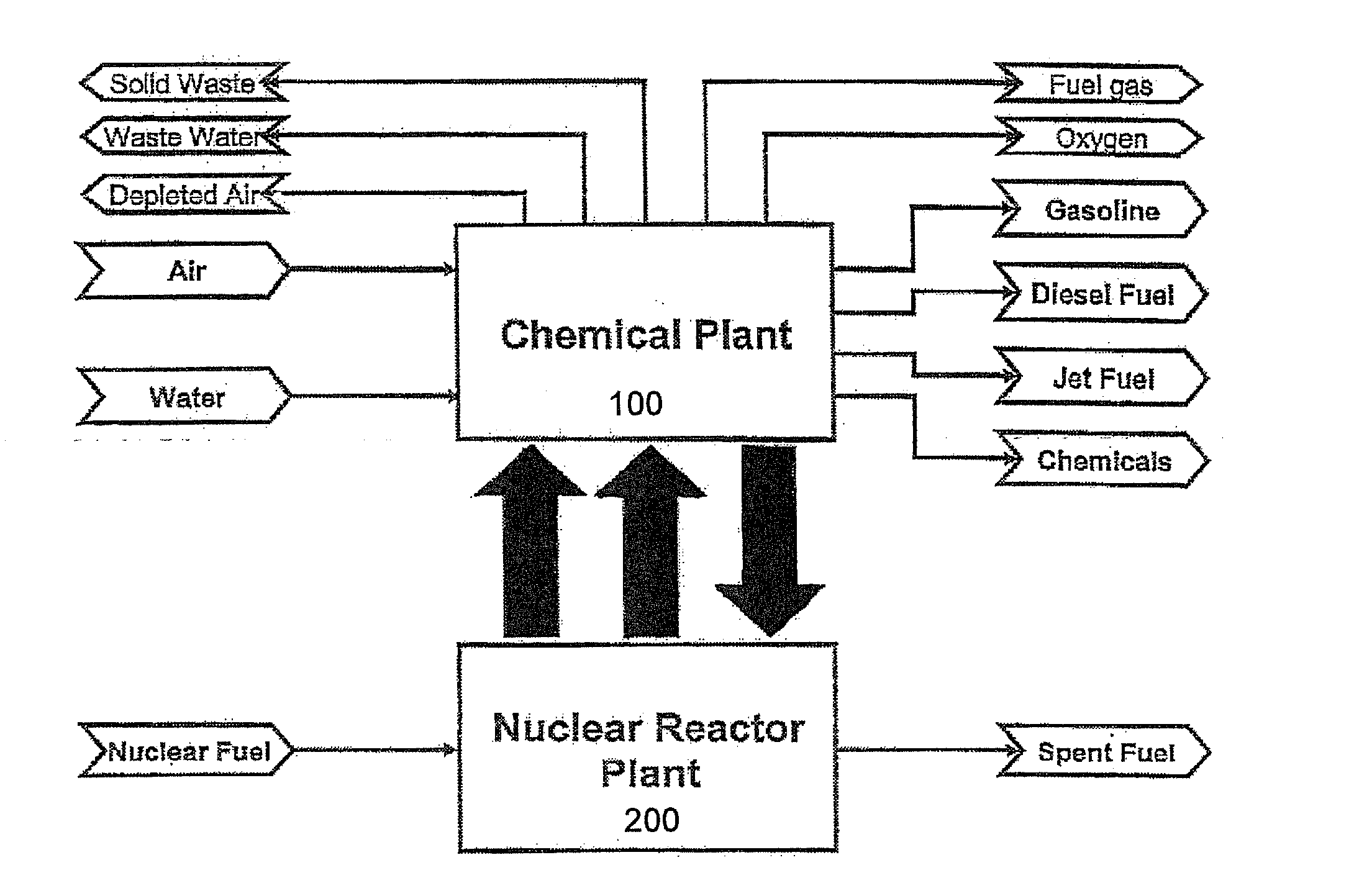
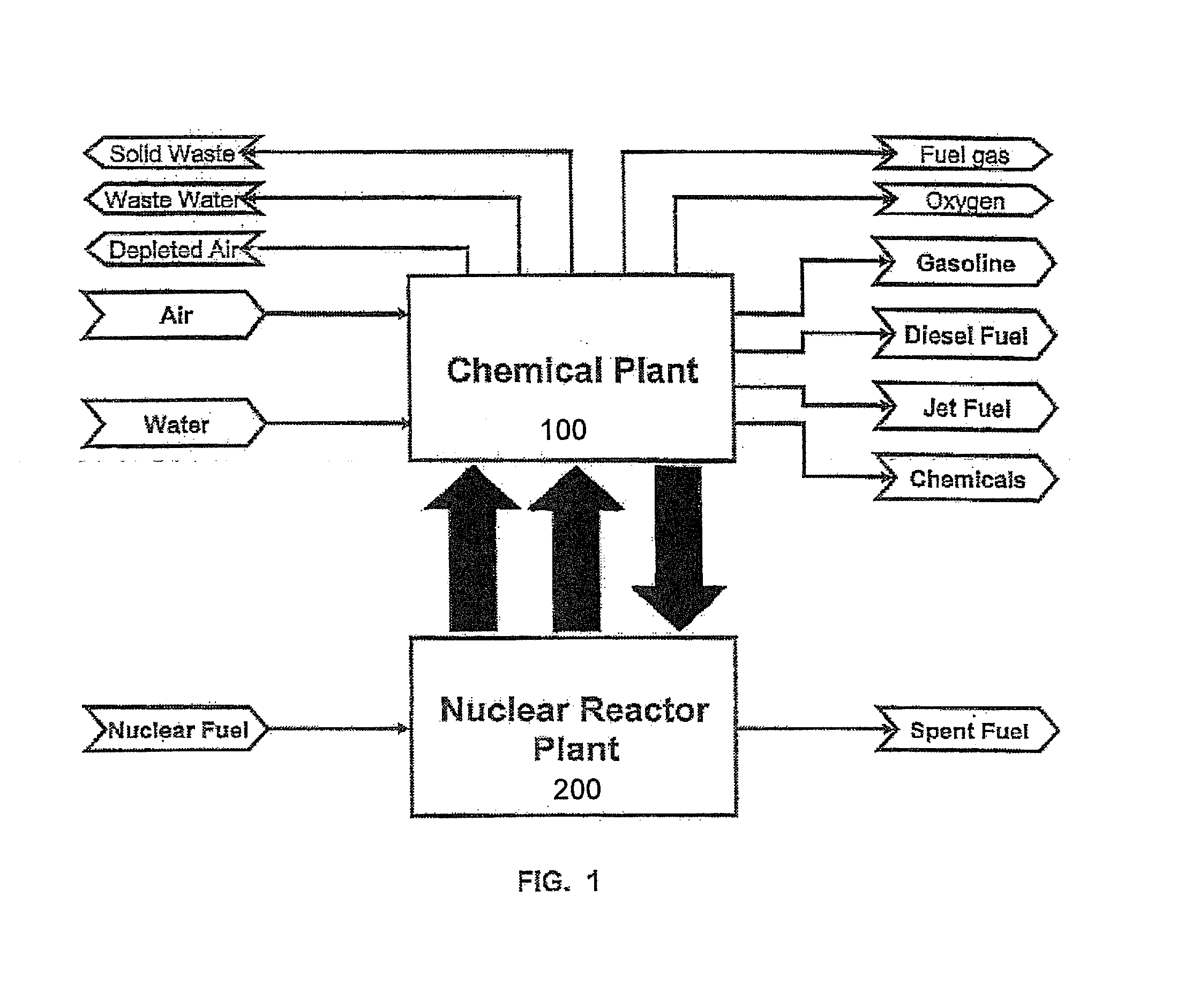
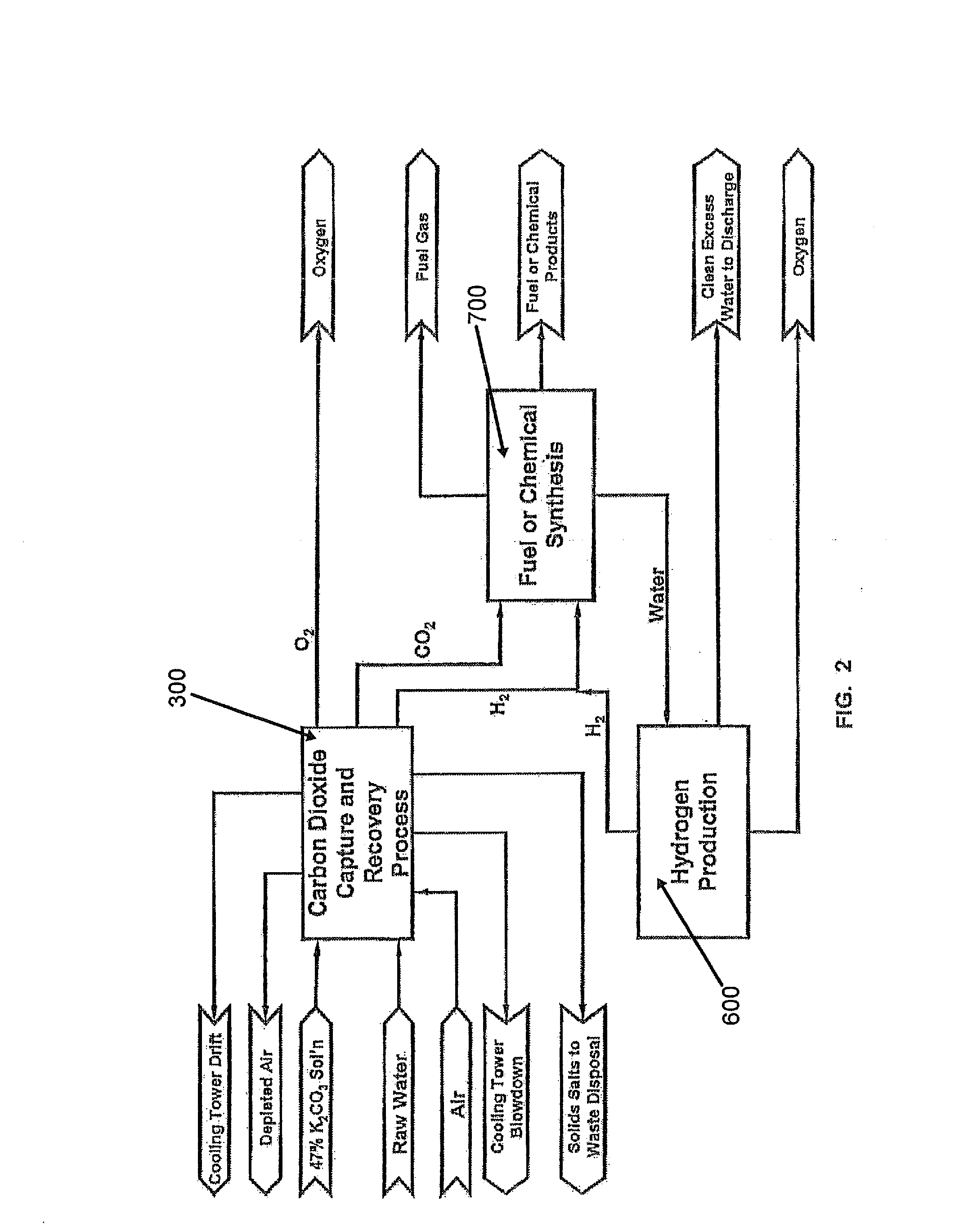
The present invention is directed to providing a method of producing synthetic fuels and organic chemicals from atmospheric carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide gas is extracted from the atmosphere, hydrogen gas is obtained by splitting water, a mixture of the carbon dioxide gas and the hydrogen gas (synthesis gas) is generated, and the synthesis gas is converted into synthetic fuels and / or organic products. The present invention is also directed to utilizing a nuclear power reactor to provide power for the method of the present invention.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Flexible glycerol conversion process
ActiveUS20090054701A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationBiodieselHydrogen
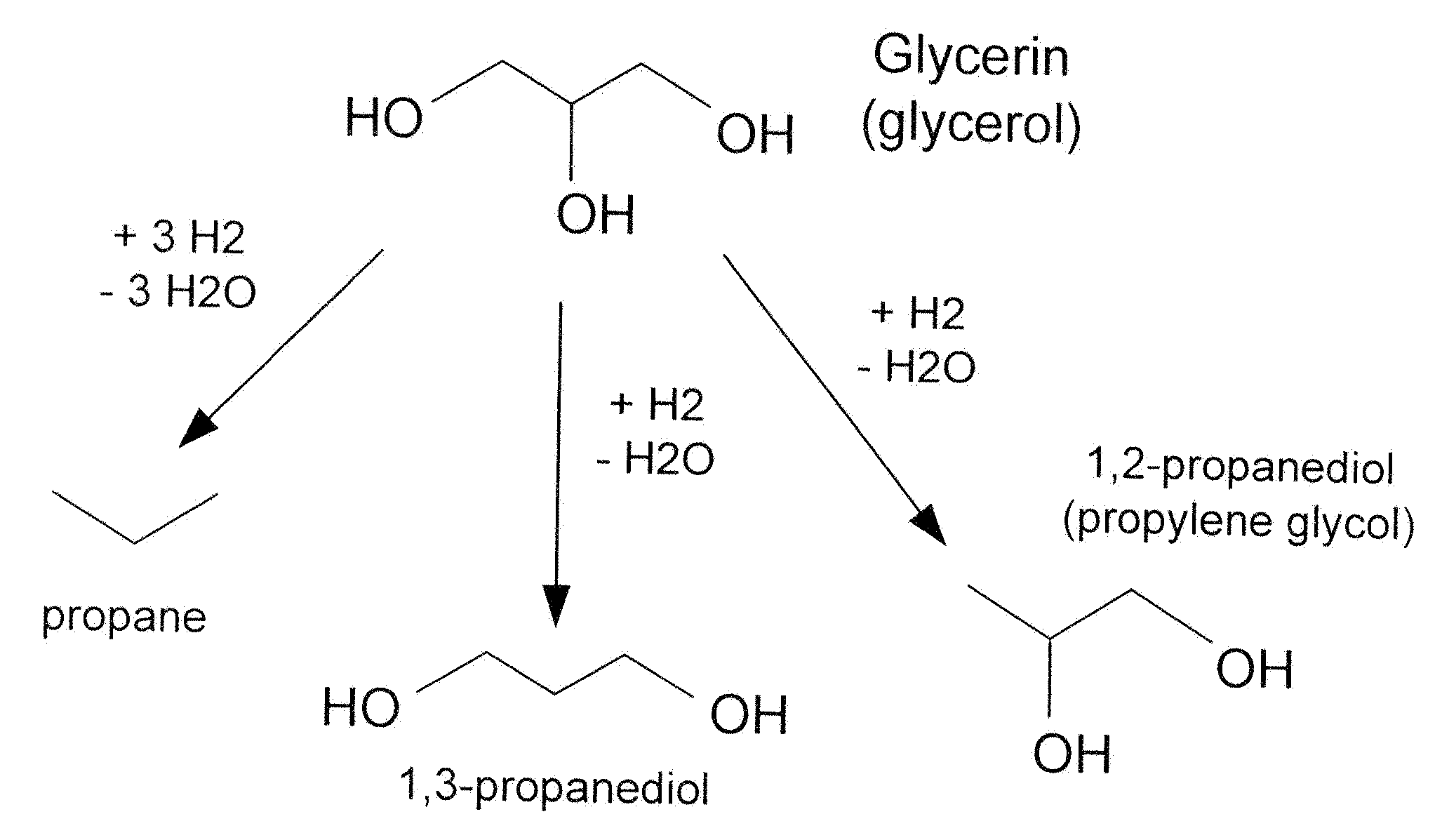
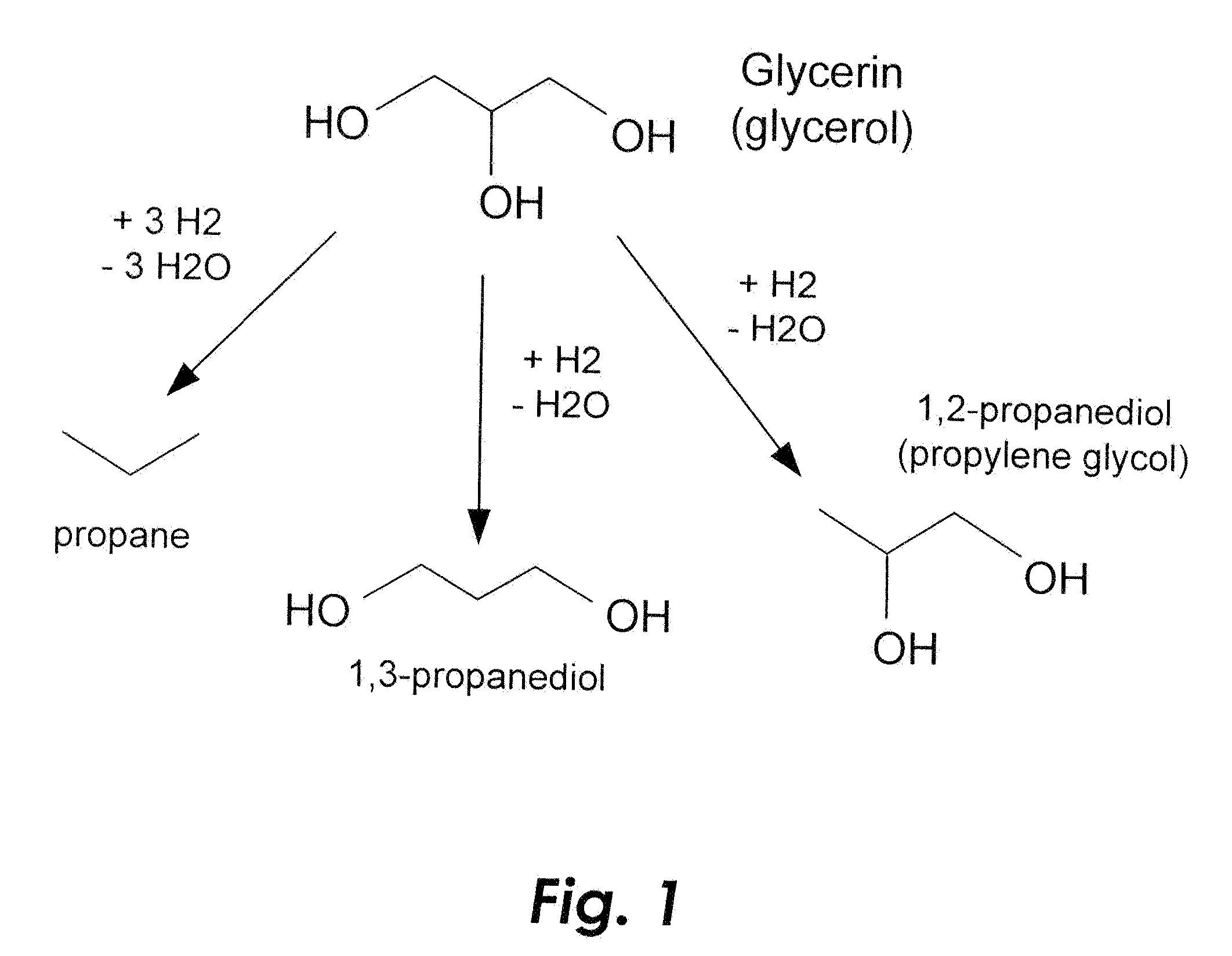
The present invention relates to a process for converting byproducts of the manufacture of biodiesel into industrially useful oxygenated products of greater commercial value. The process includes a trickle bed reactor in which a glycerol-rich feedstock is reacted with hydrogen in the presence of a nickel-tungsten catalyst under typical refining condition of high temperature and pressure, yielding propane synfuel or propanediols.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
Synthetic fuel with reduced particulate matter emissions and a method of operating a compression ignition engine using said fuel in conjunction with oxidation catalysts
InactiveUS20050154240A1Improve conversion efficiencyEmission reductionSolid fuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsParticulatesCarbon number
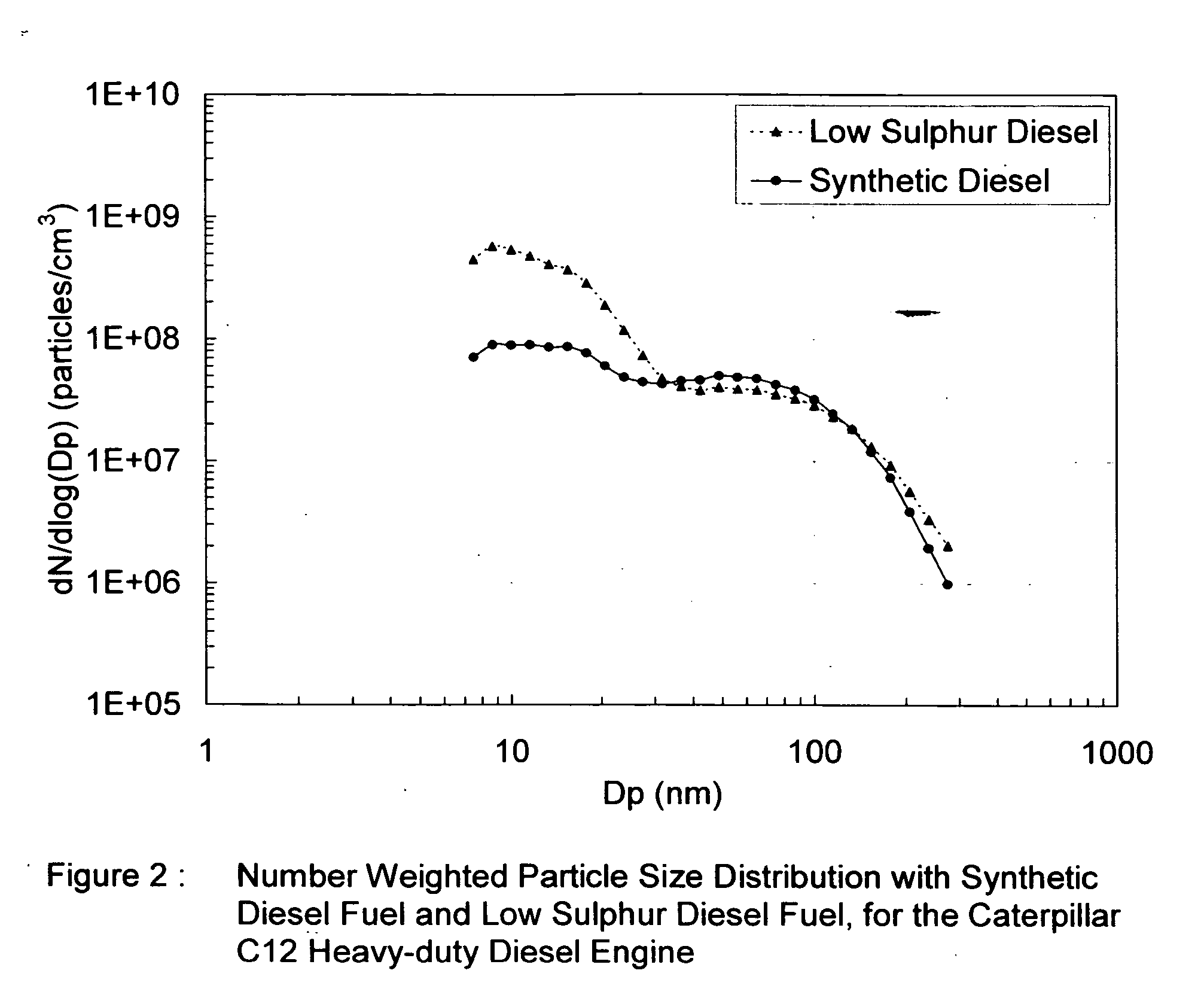
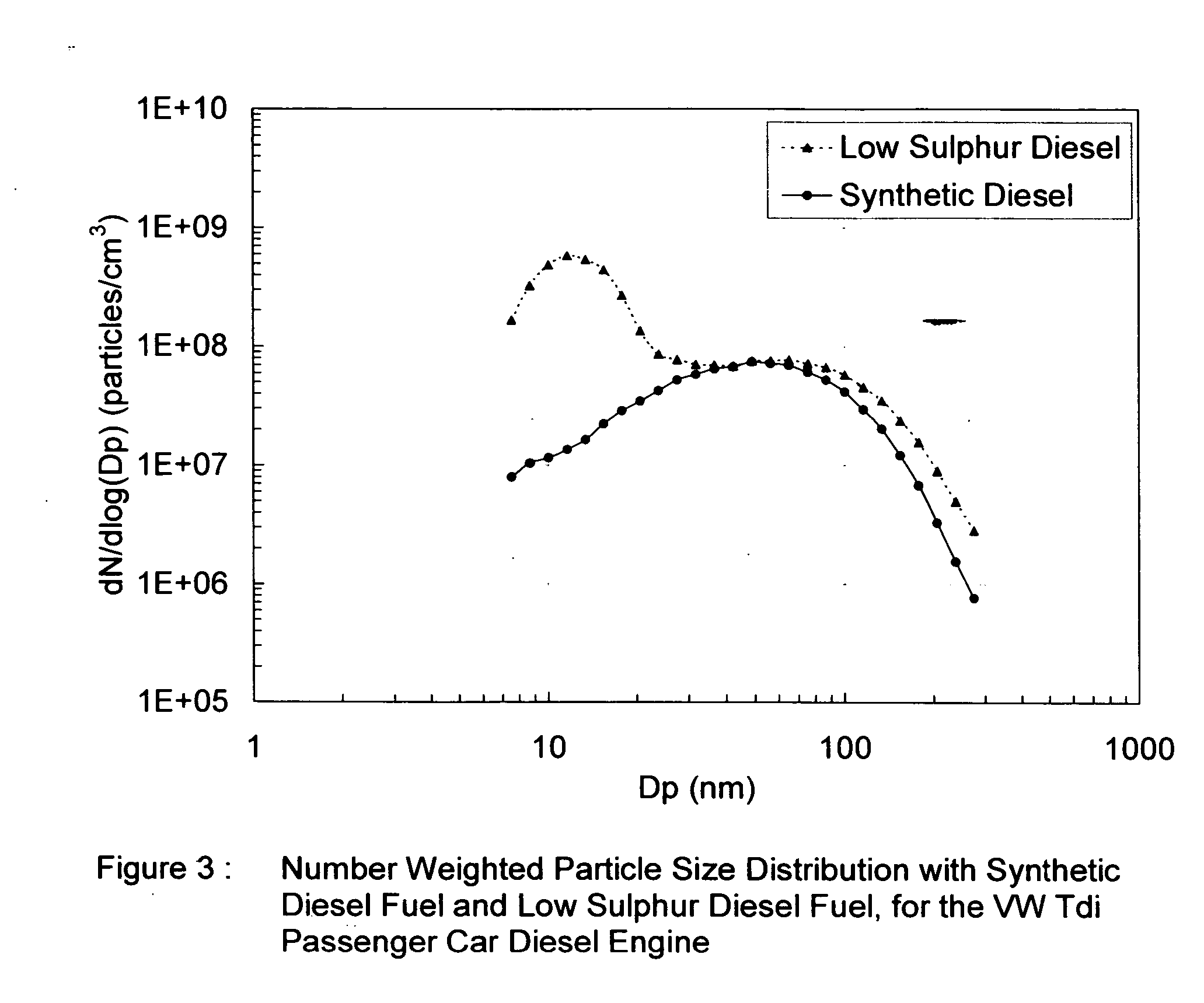
The invention provides a compression ignition engine fuel derived from a Fischer-Tropsch process, which fuel has a generally increasing iso:n paraffins ratio with increasing paraffin carbon number at least between C9 to C18, less than 0.05% m / m sulphur, and less than 10% by mass aromatics. The fuel may have on average more than 0.9 alkyl branches per paraffinic molecule as measured by H+ NMR analysis. The invention also provides a method for operating a compression ignition engine to produce low particulates emissions, which method comprises combusting the fuel with oxygen or an oxygen containing gas in the engine. Yet further the invention provides a method of improving the conversion efficiency of oxidation catalysts used in conjunction with compression ignition engines, said method including combusting the fuel in the compression ignition engine in the presence of said oxidation catalysts and in oxygen or an oxygen containing gas.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD
Synthetic fuel production using coal and nuclear energy
InactiveUS20080103220A1Increase productionReduce productionOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionElectrolysisHydrogen
Oxygen and hydrogen produced in an electrolysis process are used with a carbon-to-liquid hydrocarbon production process to improve the conversion of carbon in coal to synthesis gas products subsequently converted to liquid hydrocarbons. Carbon-containing tail gases and pollutants in a coal-to-liquid hydrocarbon production process may also be recycled to a coal gasification process to improve the conversion of carbon to liquid hydrocarbons and to reduce carbon-based pollutants from the coal-to-liquid hydrocarbon production process.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Devices And Processes For Carbon Dioxide Conversion Into Useful Fuels And Chemicals
ActiveUS20140093799A1Low rateRaise the overpotentialCellsElectrolytic organic productionOrganic acidCompound (substance)
Electrochemical devices for converting carbon dioxide to useful reaction products include a solid or a liquid with a specific pH and / or water content. Chemical processes using the devices are also disclosed, including processes to produce CO, HCO−, H2CO, (HCO2), H2CO2, CH3OH, CH4, C2H4, CH3CH2OH, CH3COO−, CH3COOH, C2H6, (COOH)2, (COO−)2, acrylic acid, diphenyl carbonate, other carbonates, other organic acids and synthetic fuels. The electrochemical device can be a CO2 sensor.
Owner:DIOXIDE MATERIALS
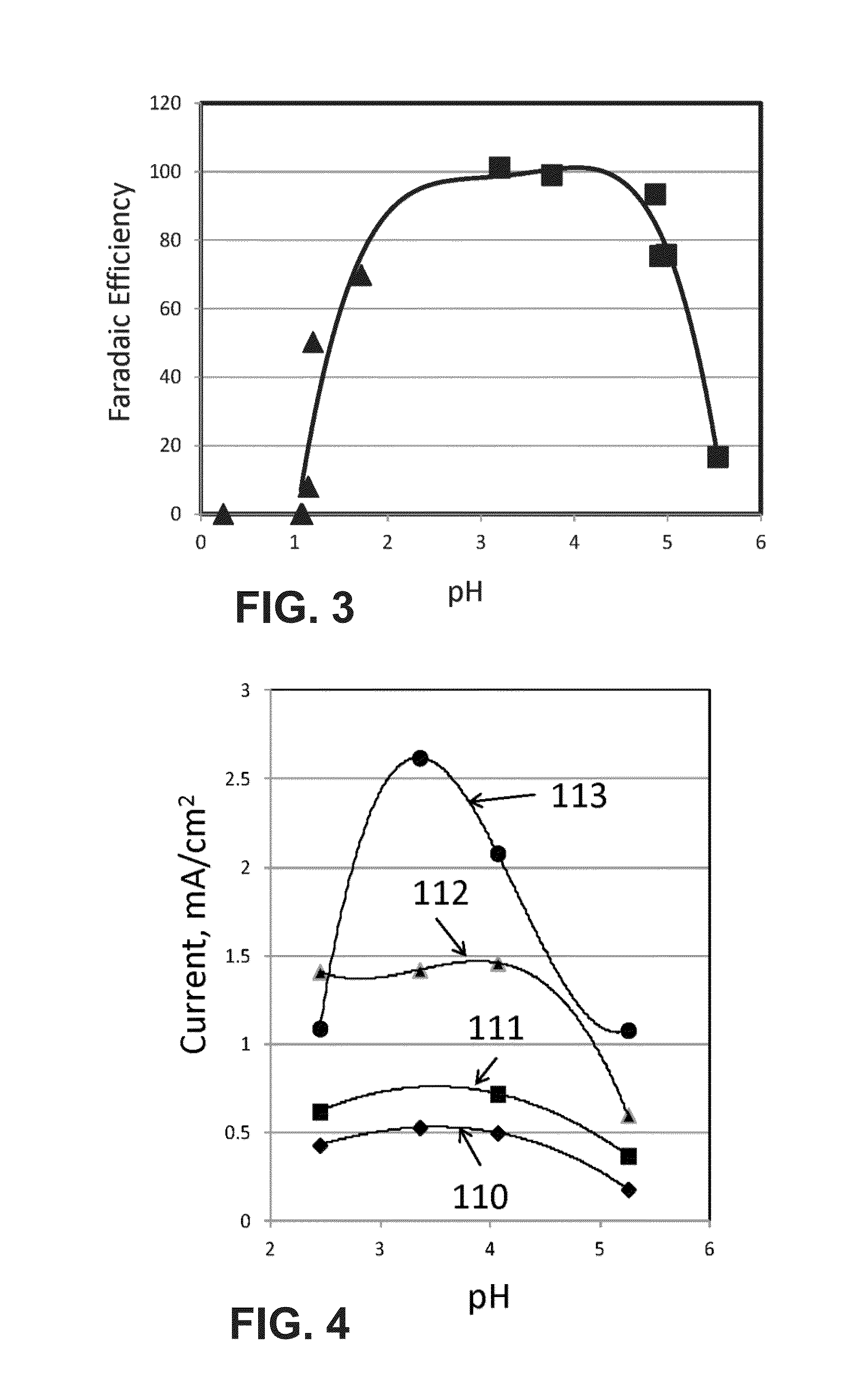
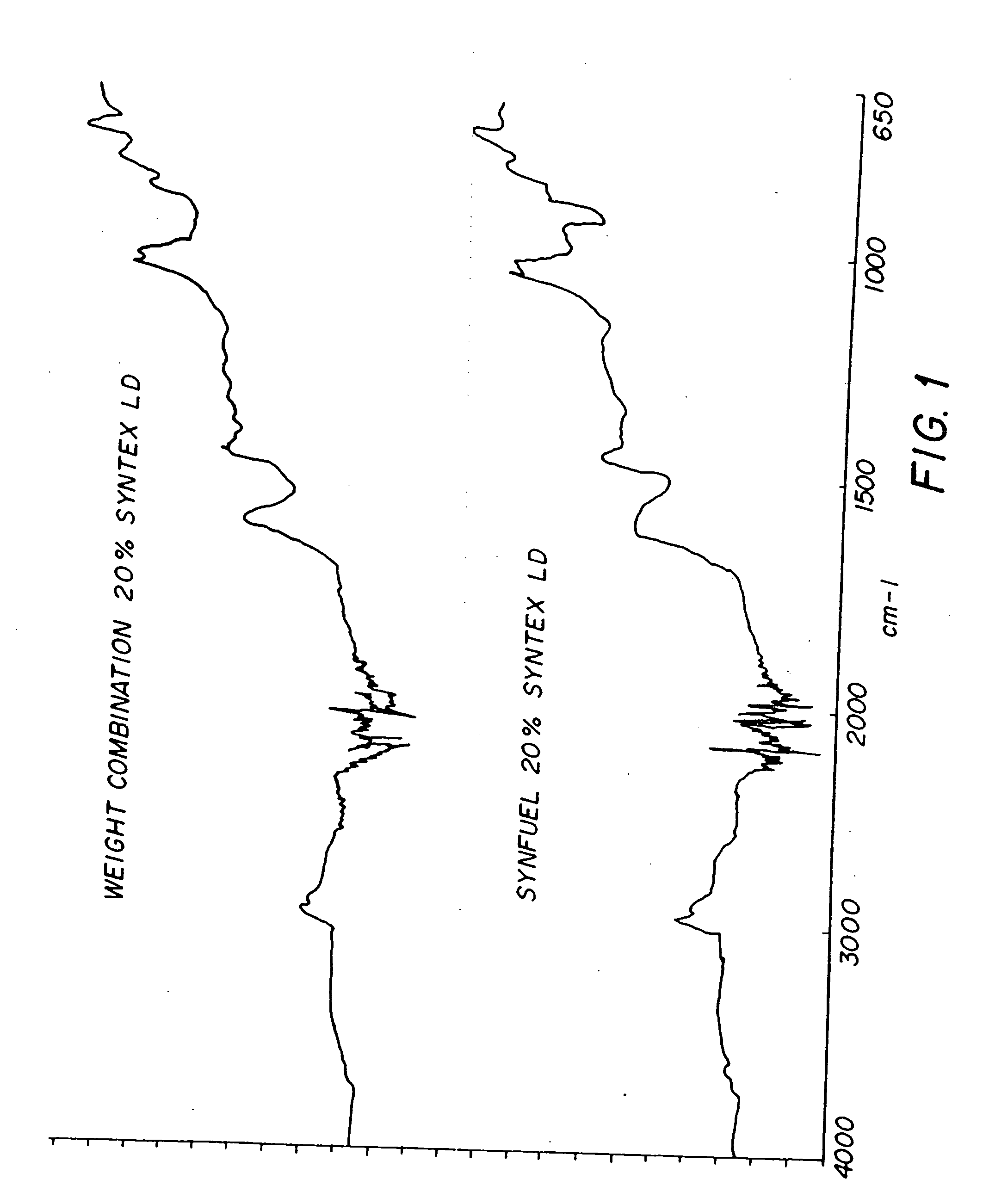
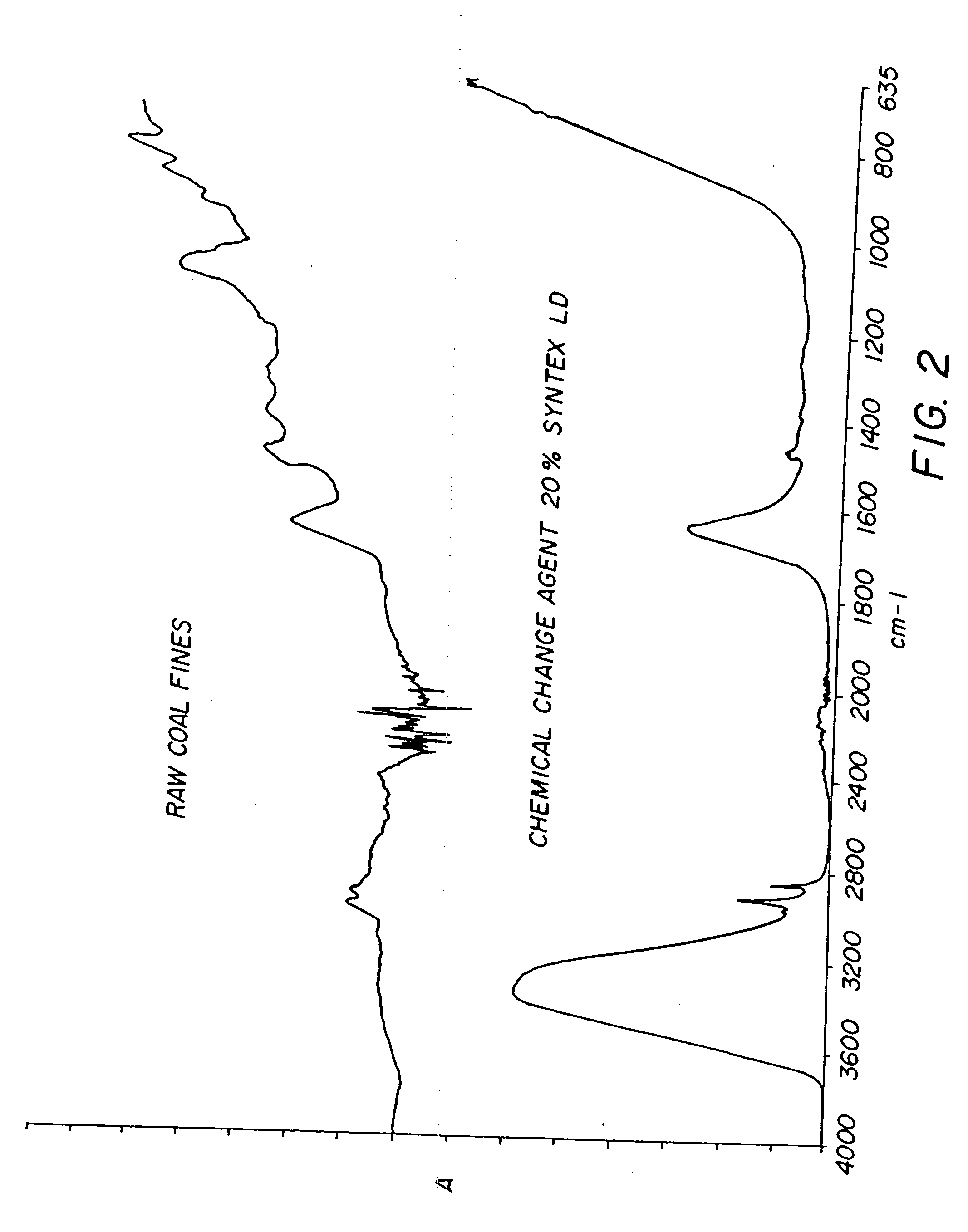
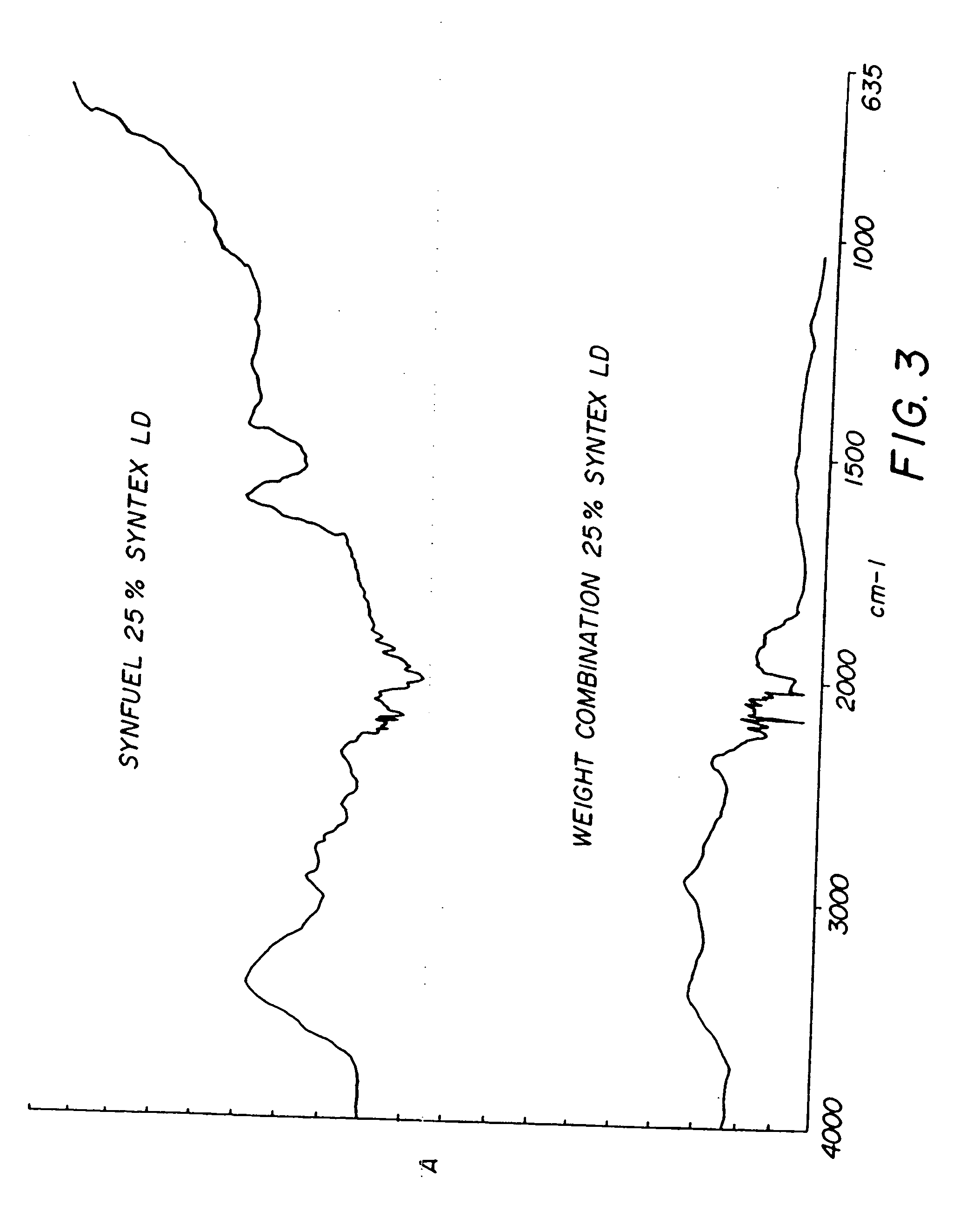
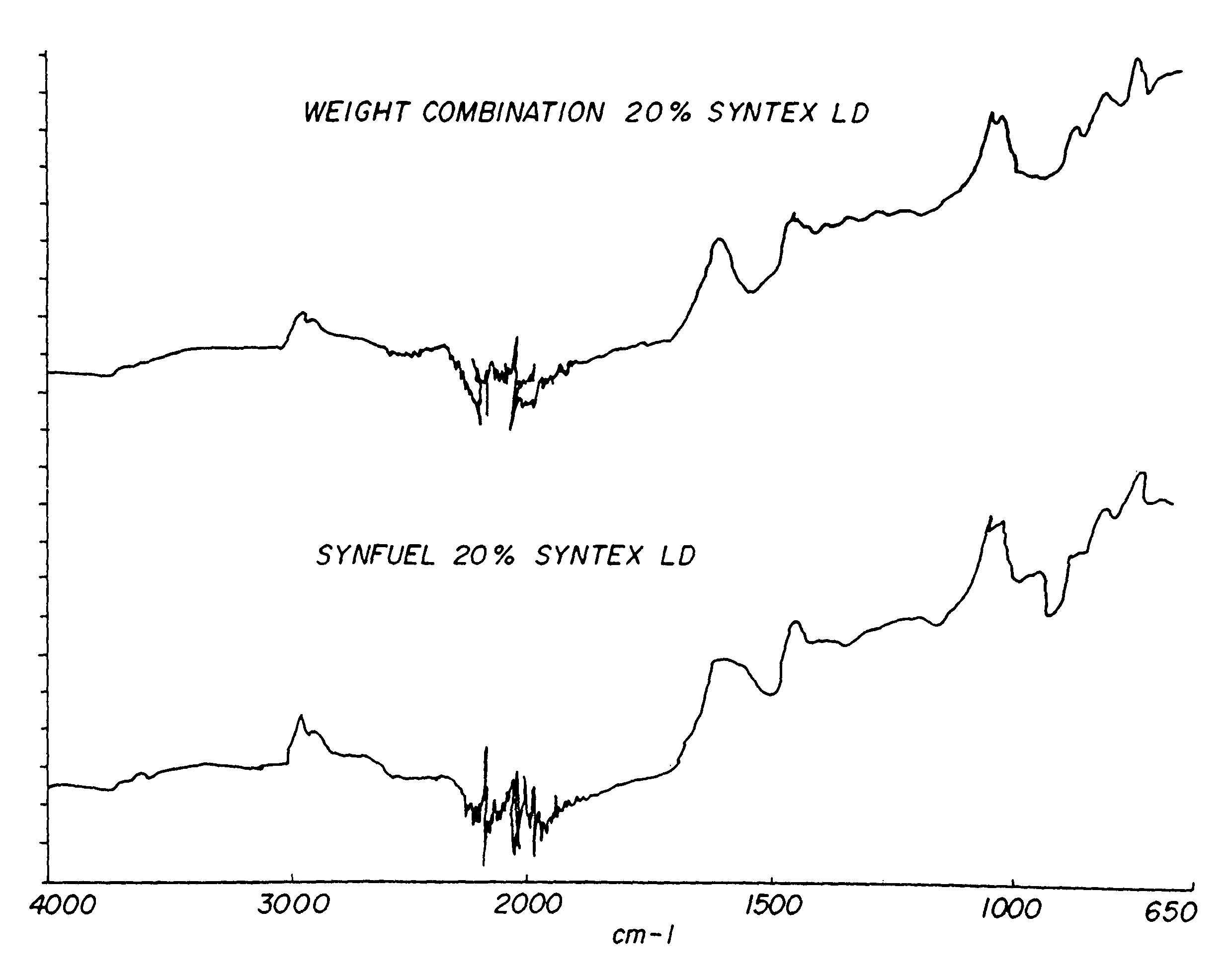
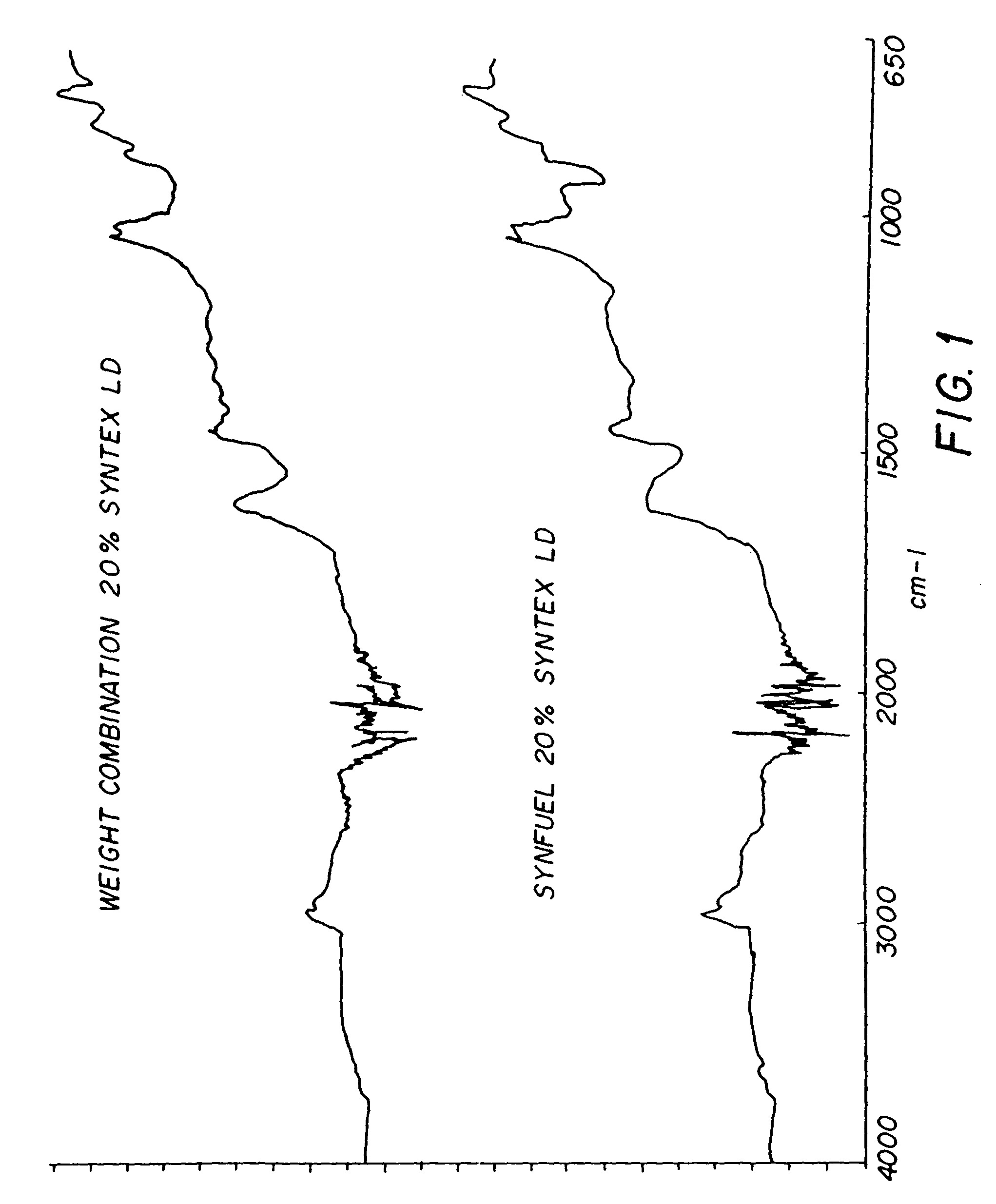
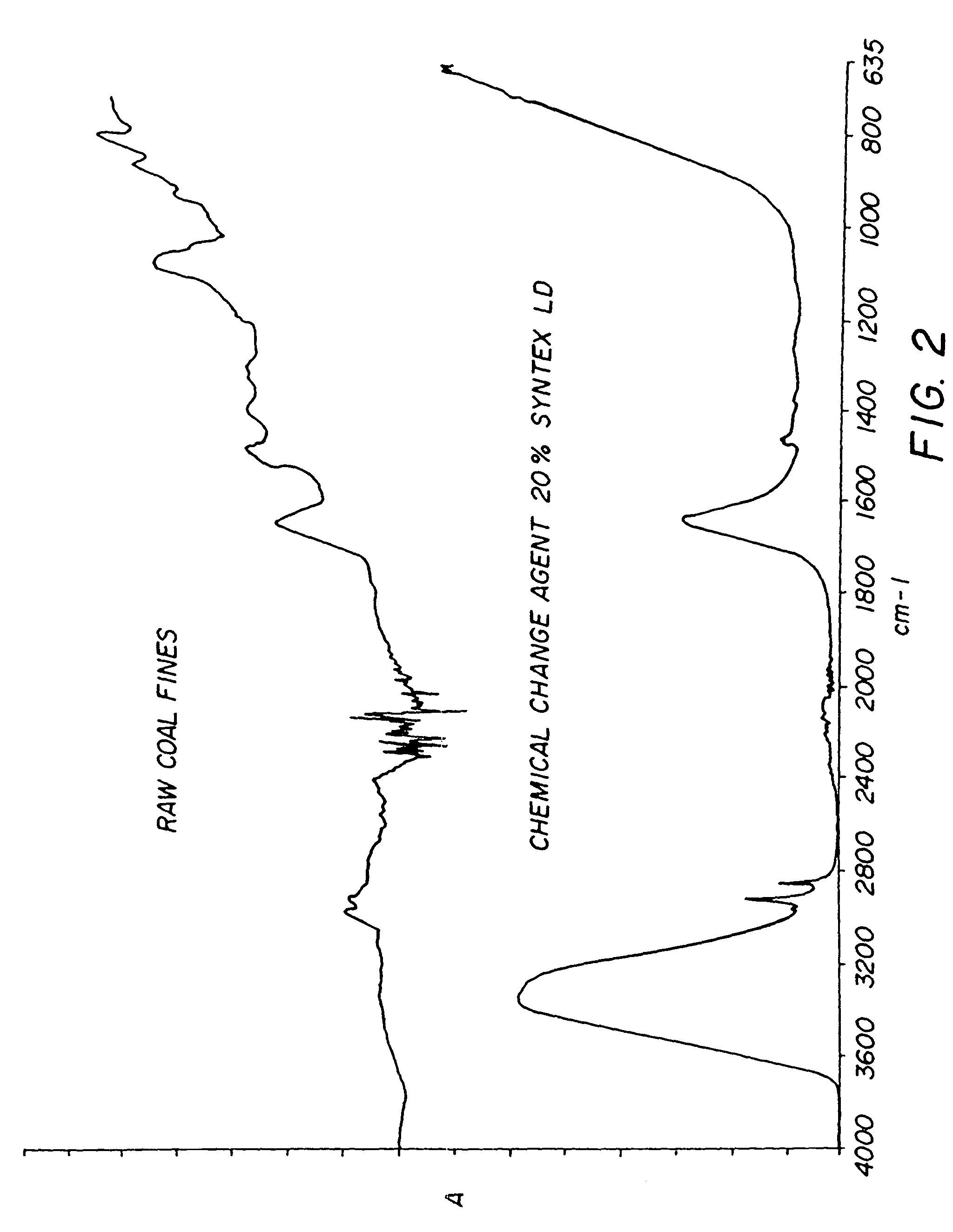
Chemical change agent
InactiveUS20060117651A1Promote combustionEliminate needNitrogen compoundsSolid fuel pretreatmentWaxCombustion
The present invention relates to an improved chemical change reagent which is used as an additive to coal to enhance the complete combustion of the coal after turning it into a synthetic fuel. The composition is a chemical change agent in that it converts the coal / composition mix into a different material which, when burned, results in lower NOx emissions. The composition includes a wax, a base for ph adjustment and water and is mixed with the coal prior to combustion.
Owner:STATE LINE HLDG
Production of Synthesis Gas from Biomass and Any Organic Matter by Reactive Contact with Superheated Steam
ActiveUS20080171899A1Improve efficiencyConsiderable thermal energySolid waste disposalGasifier mechanical detailsLiquid fuelSuperheated steam
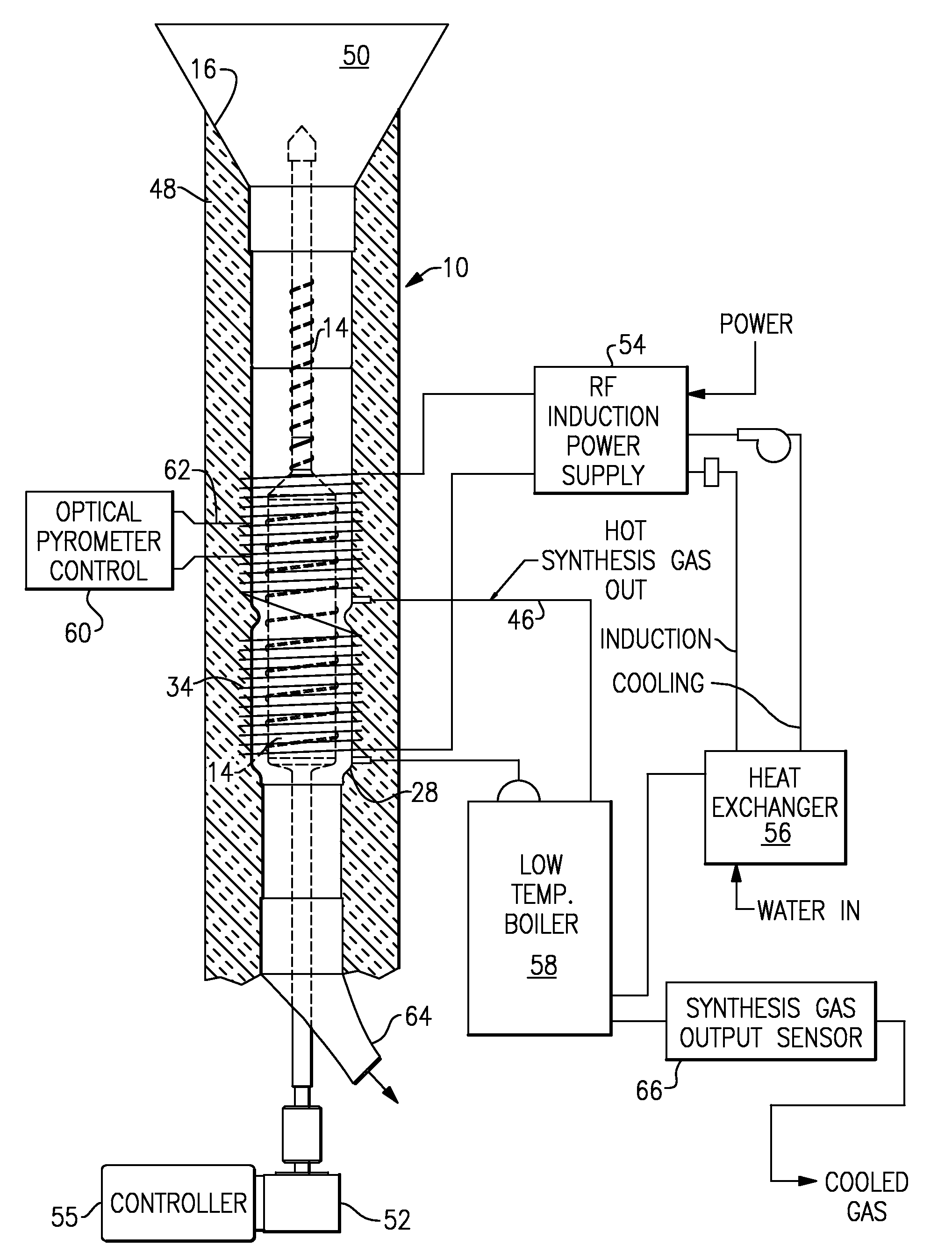
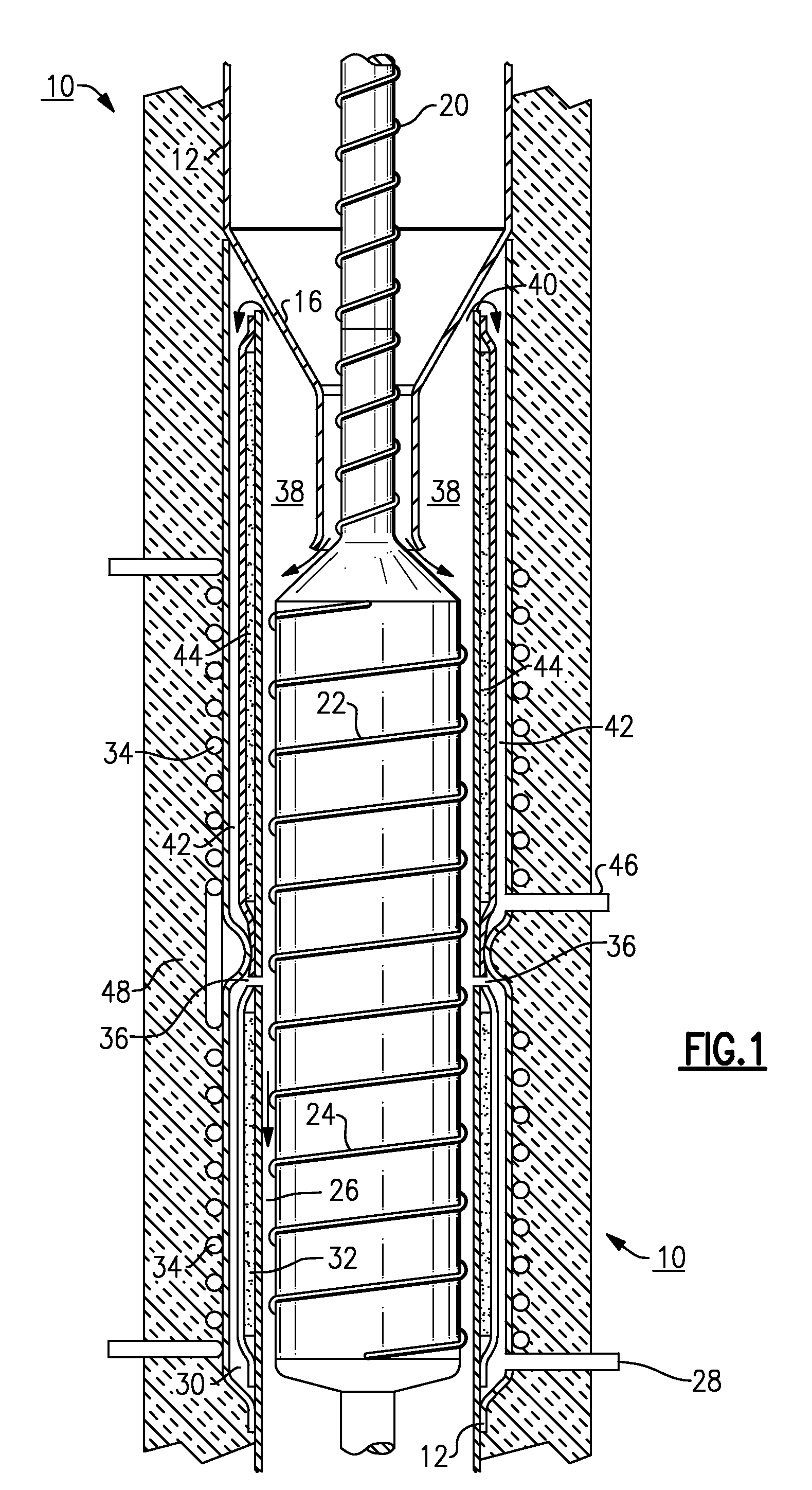
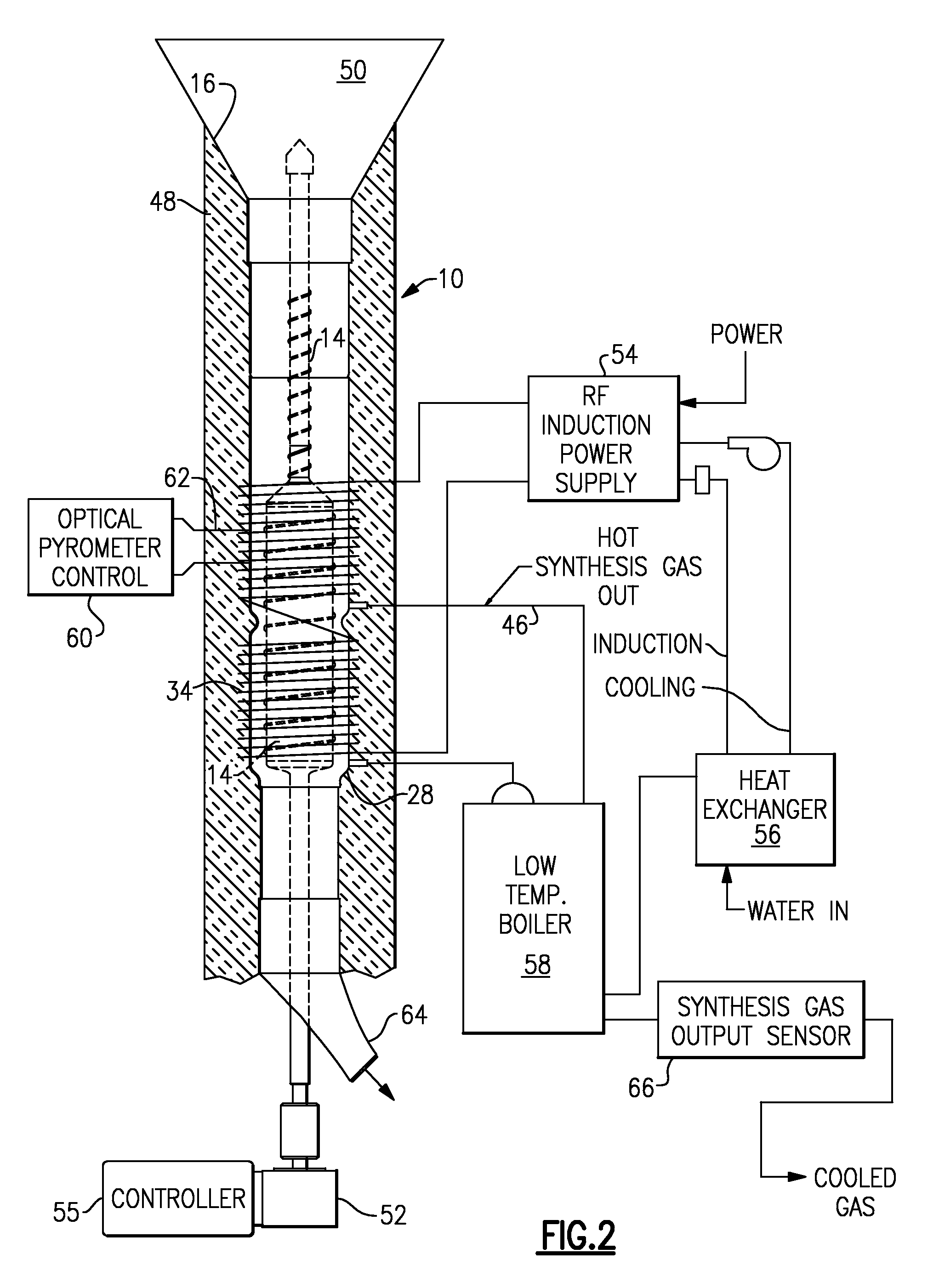
Organic matter, i.e., biomass, fibrous plant matter, organic chemicals or organic waste, or other carbon-based matter is converted to synthesis fuel gas by reactive contact with superheated steam at a temperature of about 200 to 2000 degrees C., typically 500 to 1700 degrees. A reactor has a generally tubular envelope, a rotor within the envelope, and hot reaction spaces disposed annularly within the wall of the tubular envelope. The steam and biomass particles can be heated to the required temperatures by RF induction. The product gases include H2, CO, and CO2 in ratios controlled by a programmable controller. Control of temperature, biomass feed rate and water flow preselects the output synthesis gas mix. The synthesis gas may be processed into portable liquid fuels, or can be used directly in a fuel cell.
Owner:PULKRABEK PETER +1
Gtl-fpso system for conversion of associated gas in oil fields and stranded gas in stranded gas fields, and process for production of synthetic fuel using the same
ActiveUS20110130474A1Improve production yieldLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryFuel cell auxillariesLiquid hydrocarbonsOil field
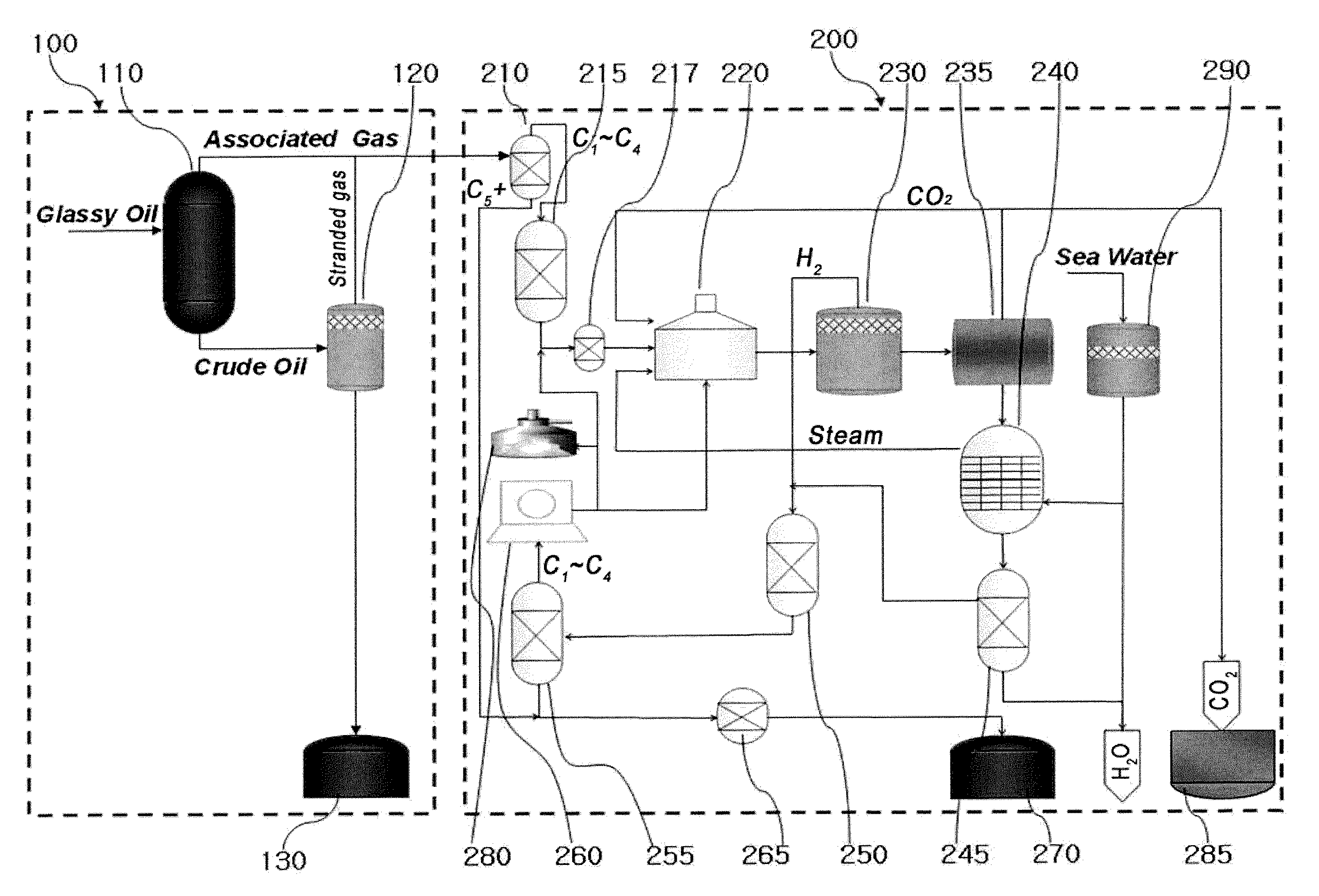
Disclosed are a gas to liquids (GTL)-floating production, storage and offloading (FPSO) system that can be used in offshore oil fields or stranded gas fields and a method for producing synthetic fuel using the same. More particularly, the disclosure relates to a GTL-FPSO system capable of producing liquid synthetic fuel from gas extracted from stranded gas fields or associated gas extracted from oil fields, including a reforming reactor and a liquid hydrocarbon producer, and a method for producing the same.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method For Releasing Organics From Shale And Like Materials To Produce A Liquid Shale Fuel
InactiveUS20100051511A1Reduce the temperatureReduce water consumptionWaste based fuelLiquid carbonaceous fuelsLiquid mediumOrganic solvent
Method for release of organic materials from shale oil and like solid substances, by treating shale oil powder in a liquid medium, with vortical movements, wave movements, acoustic turbulent streams, or combinations thereof. The treatment causes foaming of the liquid medium followed by separation of the foam from the liquid medium, whereby the foam is enriched with organic materials released from the shale oil powder. The foam can be placed in a liquid organic solvent and treated with vortical movements, wave movements, acoustic turbulent streams, or combinations thereof. The treatment causes the extraction of hydrocarbons into the solvent, and the inorganic shale material to precipitate. The remaining inorganic sold material can be utilized in the manufacture of construction materials. The obtained solution of the extracted hydrocarbons into the solvent represents a synthetic fuel, which could be used after slight reforming as motor fuel, jet fuel, or the like.
Owner:OSAT
Electric catalyst with conducing high polymer modification one-dimensional nano carbon as carrier and producing process
InactiveCN1674330AReduce bond strengthSolve the weak combinationCatalyst carriersCell electrodesElectricityPolymer science
An electro - catalyst uses one - dimensional nanocarbon modified by conduction high polymer in large Pi bond structure as carrier. Its preparing process includes preparing one - dimensional nanocarbon modified by conduction high polymer first and then loading Pt or Pt alloy on its surface. The average particle diameter of electro - catalyst is less than or equal to 5 nm and power density of single cell prepared by electro - catalyst is 0.40 - 0.47 W / cm2 under test condition as H2 / Air and Pt loading capacity in 0.20mg / sq cm and 600 mA / sq.cm.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
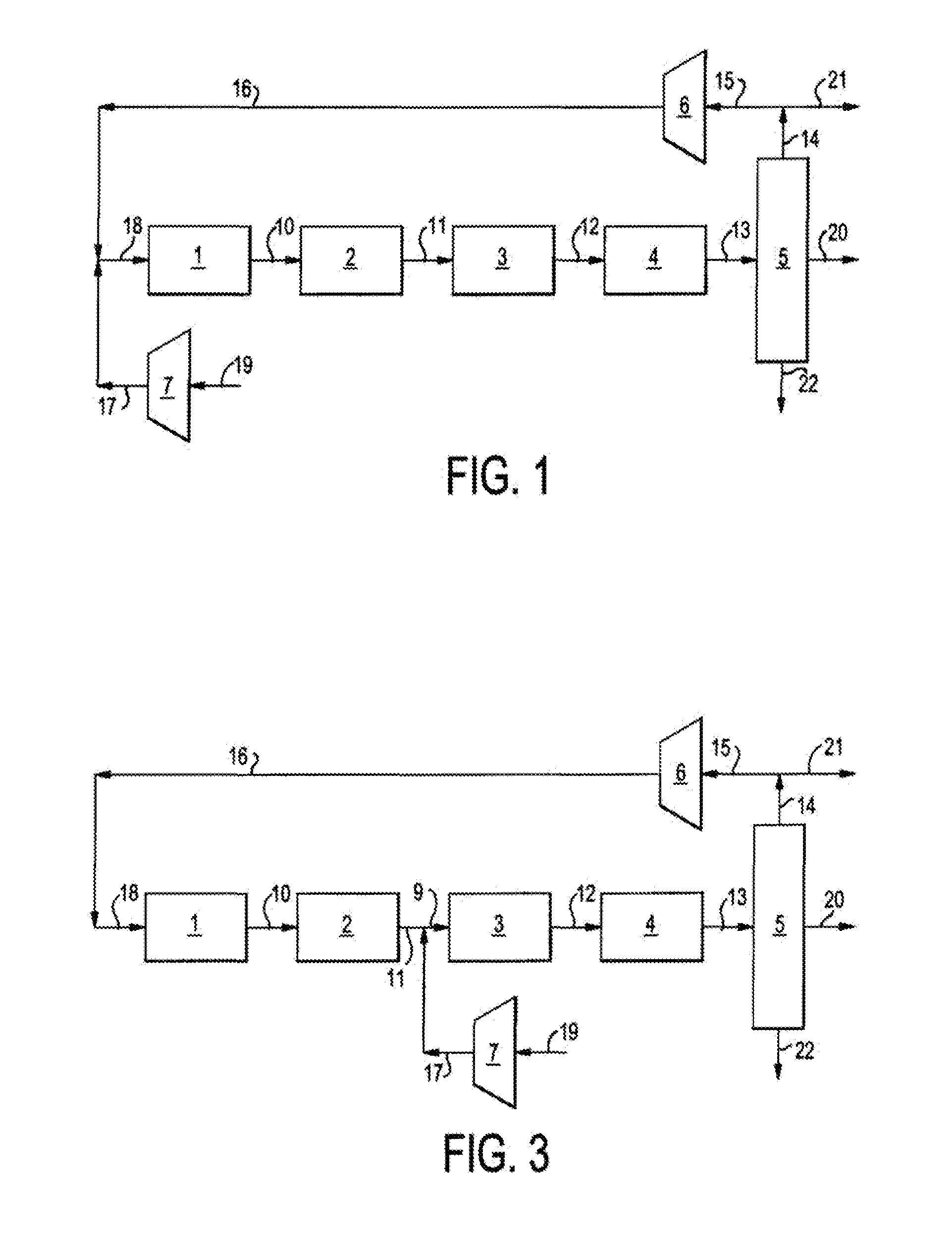
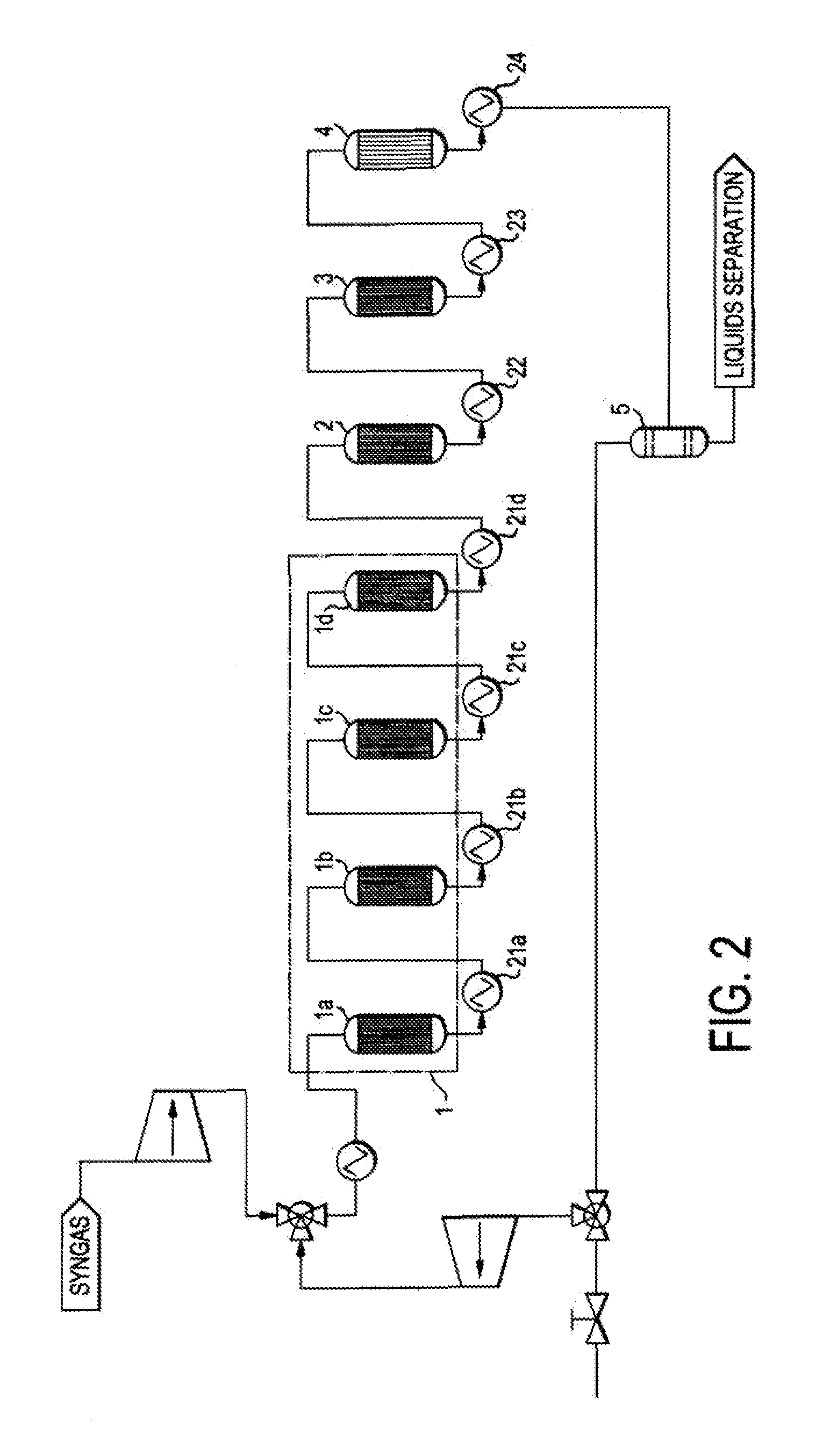
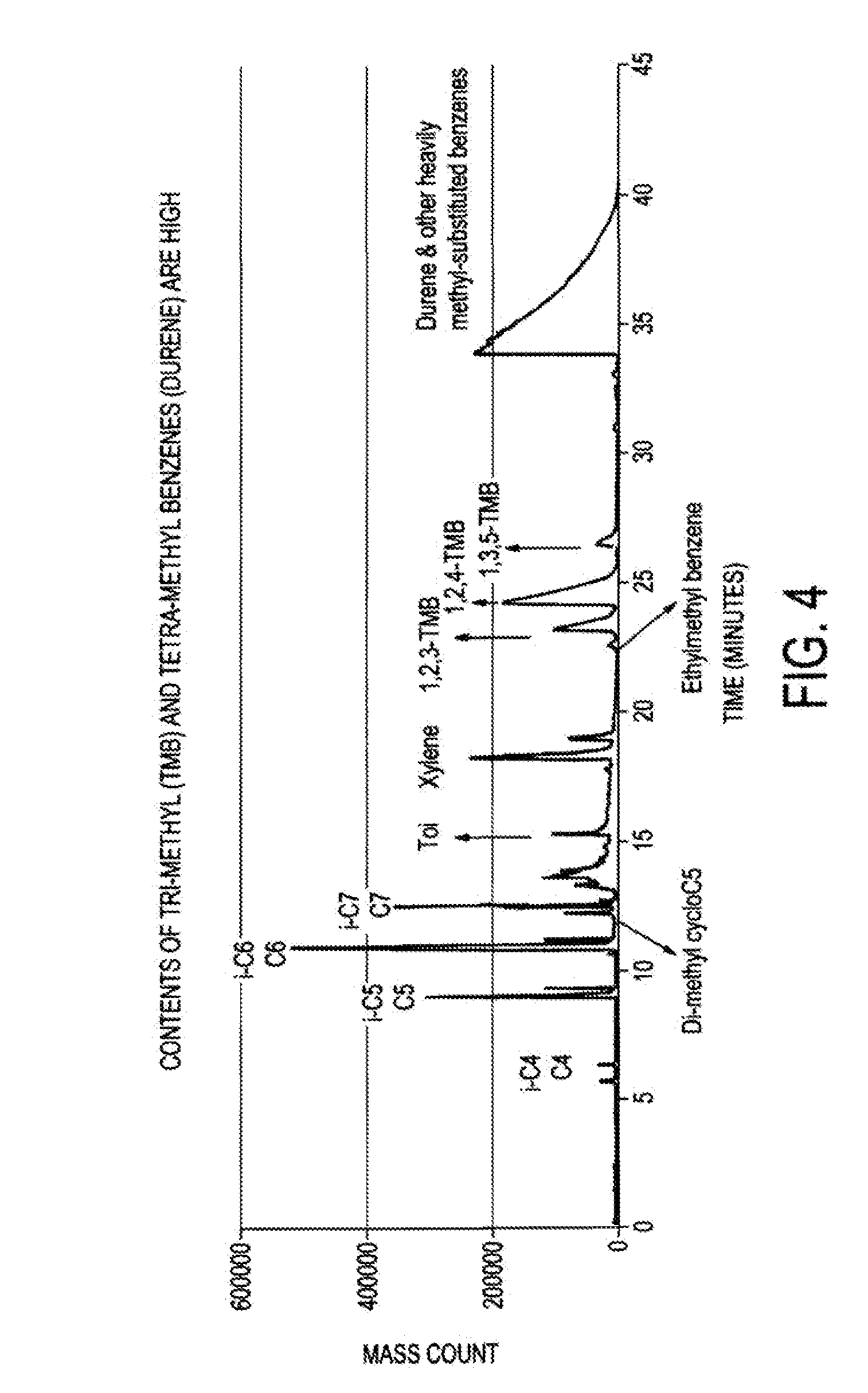
Single loop multistage fuel production
ActiveUS20120116137A1Speed up the conversion processImprove utilization efficiencyRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydroxy compound preparationLiquid fuelHigh pressure
Synthetic fuels are produced from synthesis gas in a four-stage reactor system with a single recycle loop providing the requisite thermal capacity to moderate the high heat release of the reactions and to provide the reactants and reaction environments for the efficient operation of the process. The first stage converts a portion of the synthesis gas to methanol, the second stage converts the methanol to dimethylether, the third stage converts the methanol and dimethylether to fuel and the fourth stage converts the high melting point component, durene, and other low volatility aromatic components such as tri- andtetra-methylbenzenes to high octane branched paraffins. The four-stage catalyst used for hydrotreating is resistant to CO poisoning. The reactions i produce water as a side product that is carried through to a high pressure separator after the fourth stage. The streams from the separator are a liquid fuel stream, a water stream and a gaseous stream that contains light hydrocarbon gases and the unreacted synthesis gas. The larger part of this gas stream is recycled to the inlet of the first stage and mixed with the fresh synthesis gas stream. Alternatively, the fresh synthetic gas stream is mixed with the product of the second stage. The smaller part of the gas stream from the separator is sent to hydrocarbon recovery and to fuel gas used for providing preheat of various streams. The liquid fuel is sent for blending into fuel products, such as gasoline, jet fuel, or diesel, and the water stream can be sent, for example, to the synthesis gas producing plant for steam generation.
Owner:BLUESCAPE CLEAN FUELS LLC
Method of and apparatus for upgrading and gasifying heavy hydrocarbon feeds
InactiveUS20040118745A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingSolvent extractionThermodynamicsProcess engineering
A novel apparatus for producing sweet synthetic crude from a heavy hydrocarbon feed includes: an upgrader for receiving the heavy hydrocarbon feed and producing a distillate fraction including sour products, and high-carbon content by-products; a gasifier for receiving the high-carbon content by-products and producing synthetic fuel gas and sour by-products; a hydroprocessing unit for receiving the sour by-products and hydrogen gas, thereby producing gas and sweet crude; and a hydrogen recovery unit for receiving the synthetic fuel gas and producing further hydrogen gas and hydrogen-depleted synthetic fuel gas, the further hydrogen gas being supplied to the hydroprocessing unit.
Owner:ORMAT IND LTD
Method of and apparatus for upgrading and gasifying heavy hydrocarbon feeds
A novel apparatus for producing sweet synthetic crude from a heavy hydrocarbon feed includes: an upgrader for receiving the heavy hydrocarbon feed and producing a distillate fraction including sour products, and high-carbon content by-products; a gasifier for receiving the high-carbon content by-products and producing synthetic fuel gas and sour by-products; a hydroprocessing unit for receiving the sour by-products and hydrogen gas, thereby producing gas and sweet crude; and a hydrogen recovery unit for receiving the synthetic fuel gas and producing further hydrogen gas and hydrogen-depleted synthetic fuel gas, the further hydrogen gas being supplied to the hydroprocessing unit.
Owner:ORMAT IND LTD
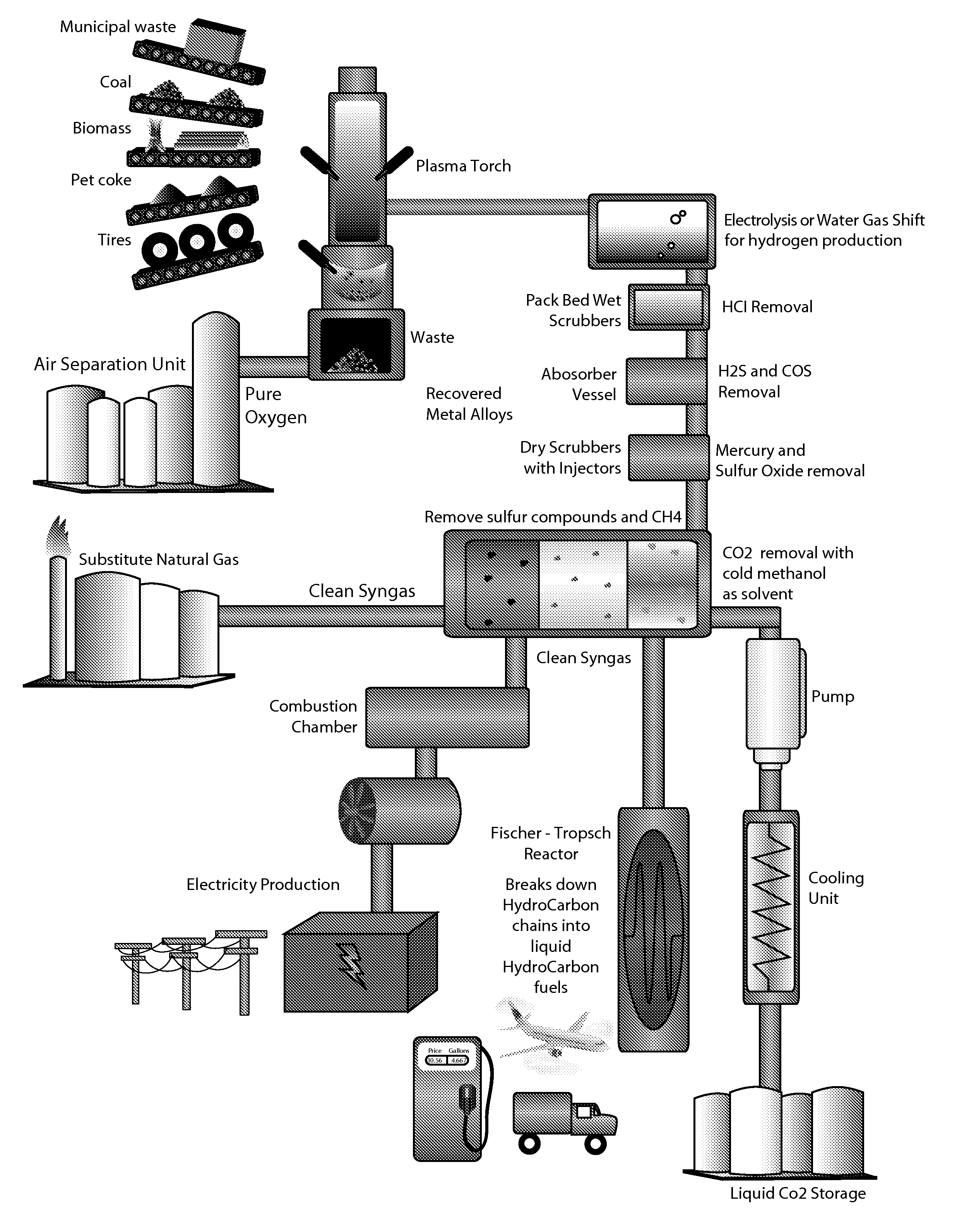
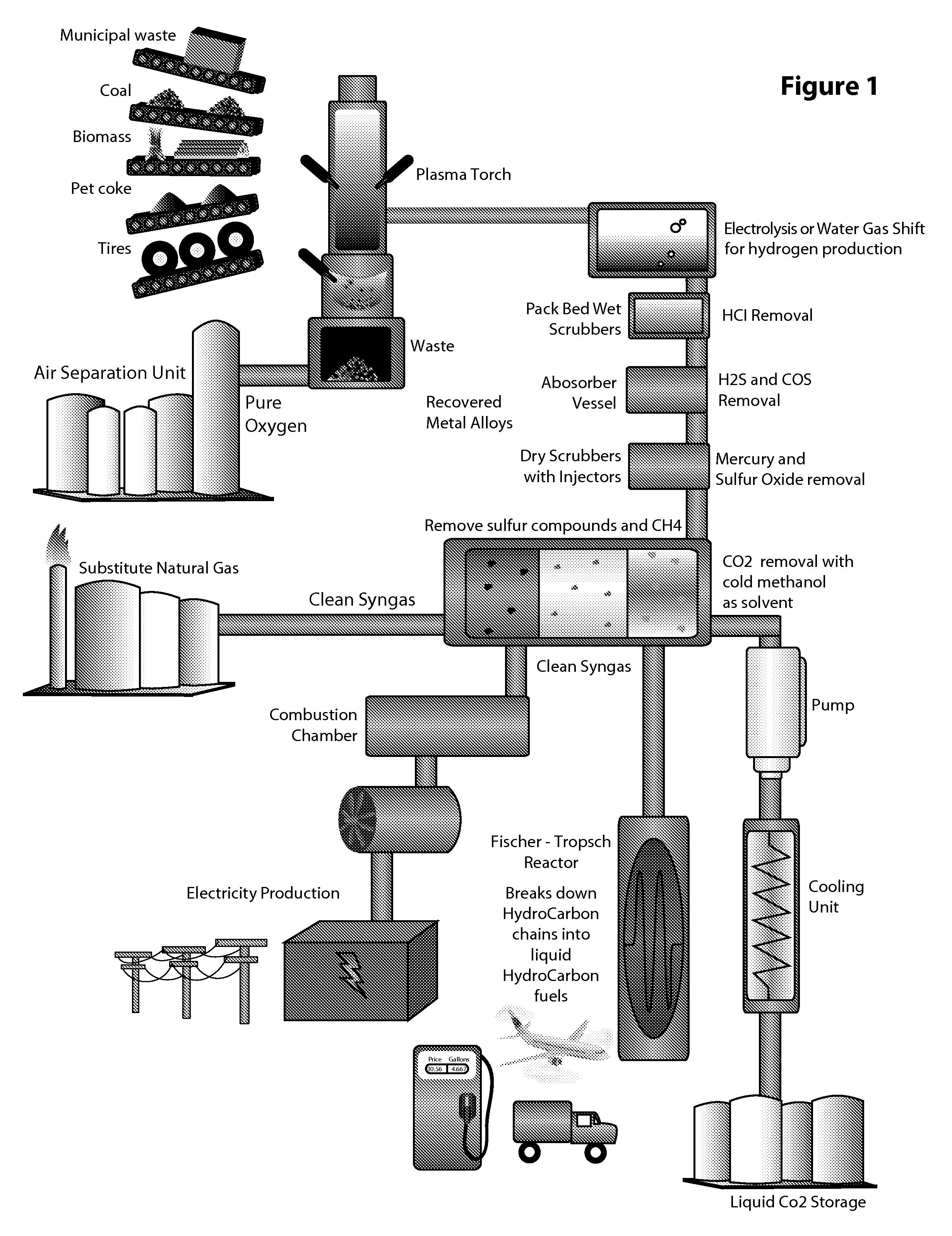
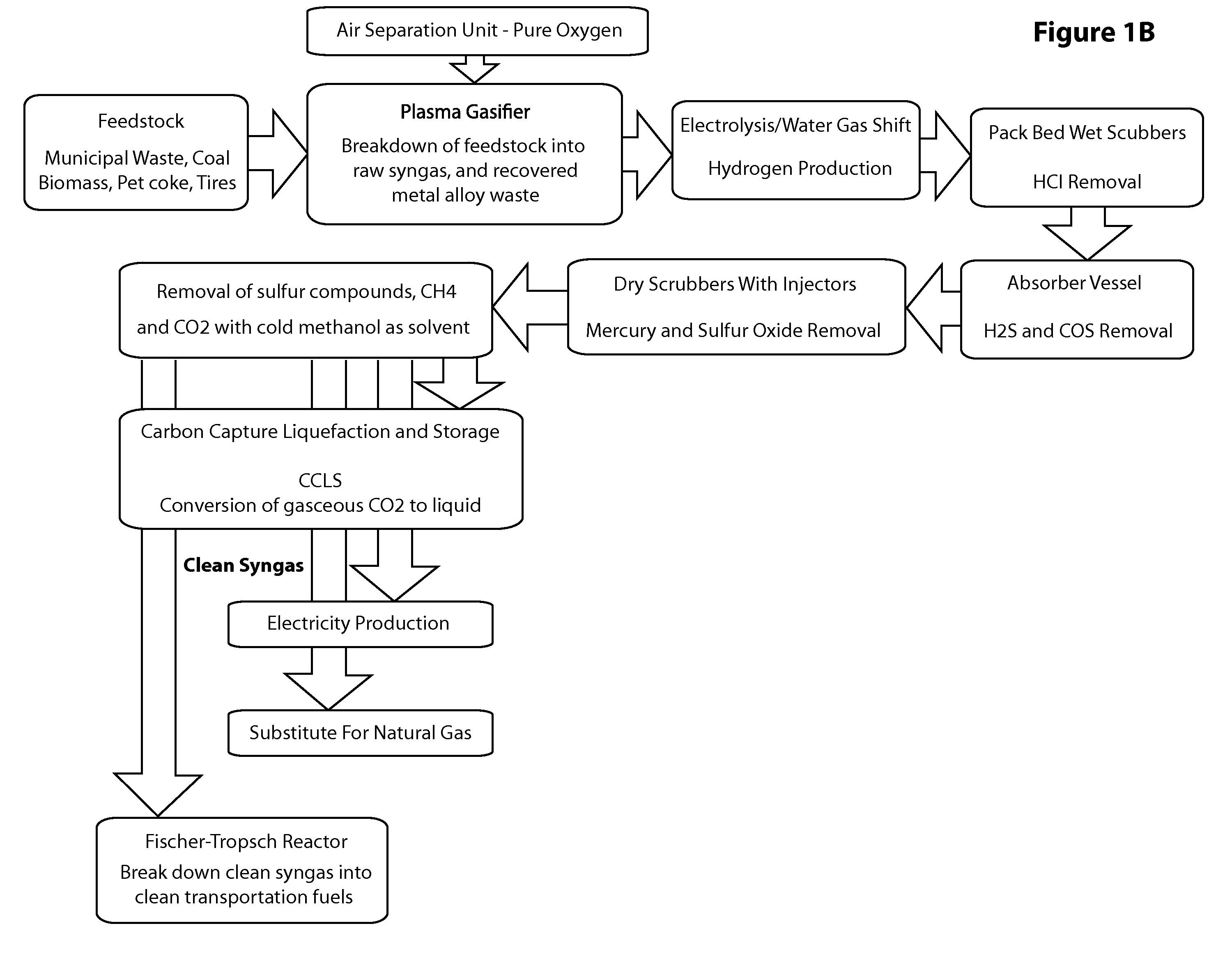
Waste Material, Coal, Used Tires and Biomass Conversion to Alternative Energy and Synthetic Fuels Solutions System with Carbon Capture and Liquefaction
ActiveUS20120032452A1Enhanced overall recoveryImprove powerCombustible gas catalytic treatmentBiofuelsEngineeringOxygen
The system contained within this application for non-provisional patent protection provides the ability to convert municipal solid waste materials, used tires, various biomass including wood chips and other agricultural waste, and the addition of coal into synthesis gas (syngas), with oxygen as plasma gas. The system will accommodate the possibility for variation in feedstock co-gasification of the various materials with plasma torches that will be embedded in a plasma gasification unit. One converted into synthesis gas (syngas), the syngas will be cleaned of acid gases and carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide will be captured and converted for various industrial applications instead of being released into the atmosphere. Clean syngas generated by the system will become the gas fuel for various energy solutions including clean electricity, as substitute for natural gas, and ultra clean FT synthetic fuels.
Owner:KUKU LAI O
Gas homogenization system
InactiveUS8128728B2Combination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentChemical synthesisExternal combustion engine
A system and process for gas homogenization is disclosed. This has application in the areas of generation of gas and its conversion to electricity in downstream applications. The homogenization system minimizes variance in the gas characteristics (composition, flow, pressure, temperature), thereby rendering a steady stream of gas of consistent quality to the downstream machinery. This homogenization system can be adjusted to optimize the output gas stream for specific end-applications, or to optimize the output gas stream for different input feedstocks. This ensures that overall conversion efficiencies are maximized while keeping the process cost-effective. Such a uniform, steady output gas stream has a wide range of applications in the broad areas of generation of electricity (e.g. using internal combustion engines and combustion turbine engines), chemical synthesis (e.g. of compounds such as ethanol, methanol, hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons), fuel-cell technologies and in polygeneration processes (processes that result in co-production of electricity and synthetic fuels).
Owner:PLASCO ENERGY GROUP INC
Novel synthetic fuel and method of preparation thereof
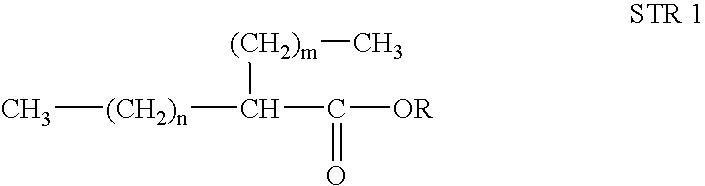
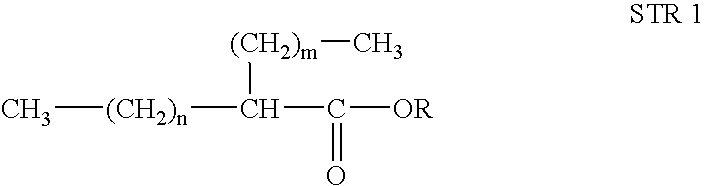
ActiveUS20090038211A1Improved diesel fuel propertyExcellent low temperature propertyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationOxidation stabilityEngineering
Disclosed is a novel synthetic fuel as alternative to diesel, wherein said synthetic fuel comprises branched esters and wherein the fuel having improved fuel properties such as zero aromatic, zero olefin, zero sulphur, low pour, high cetane diesel fuel with improved lubricity and oxidative stability. Further, the present invention provides a method of preparation of said esters.
Owner:INDIAN OIL CORPORATION
Synthetic fuel pellet and methods
InactiveUS20070251143A1Acceptable stabilityReduce the amount requiredSolid fuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFiberCoal
The present invention includes a synthetic fuel pellet, the pellet comprising a compressed agglomeration of: (a) coal fines; (b) a fibrous cellulosic material wherein the fibers of the fibrous cellulosic material have been substantially disintegrated; and (c) at least one binder, the binder adapted to form a pellet of the coal fines and the fibrous cellulosic material.
Owner:SLANE ENERGY
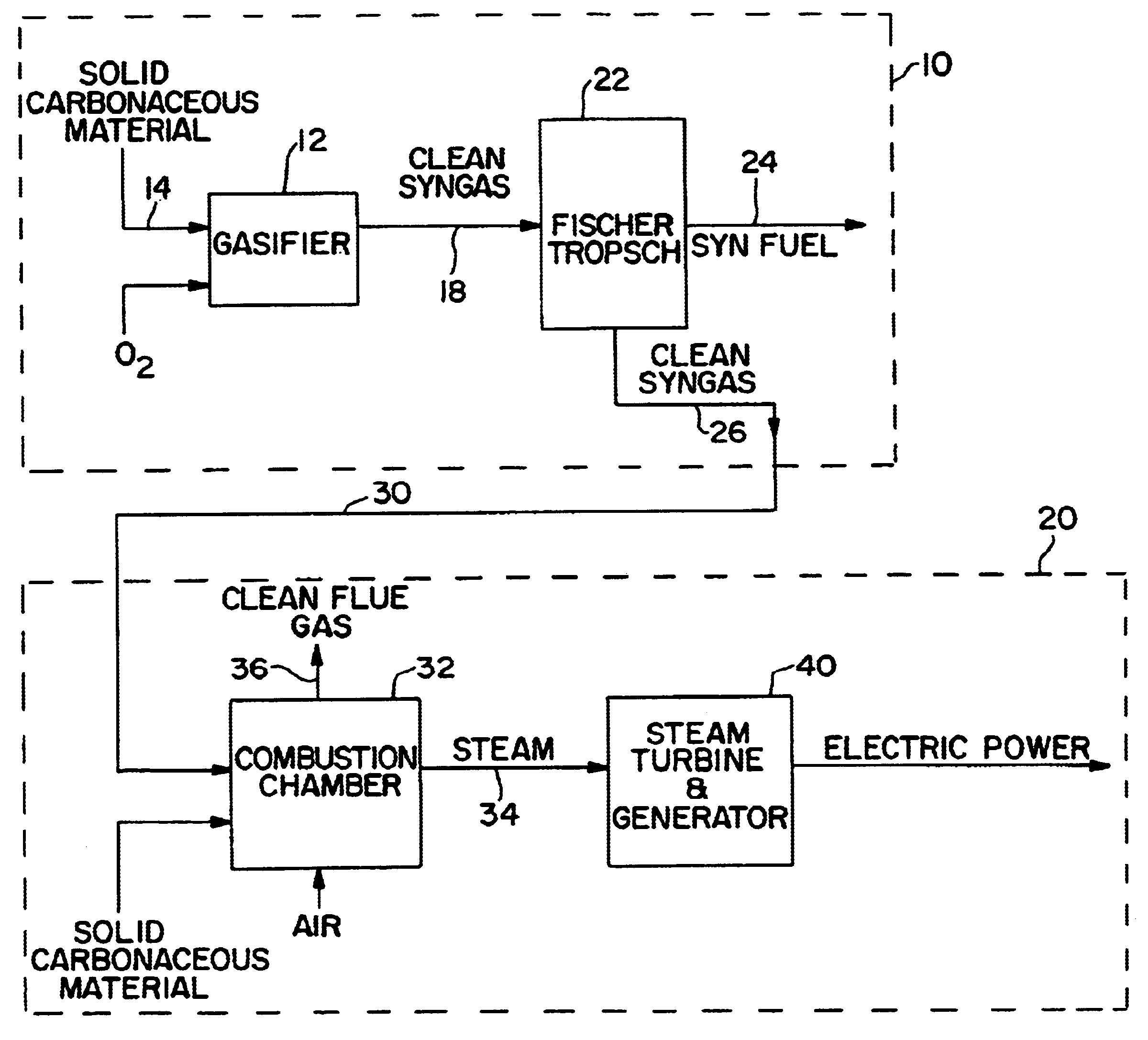
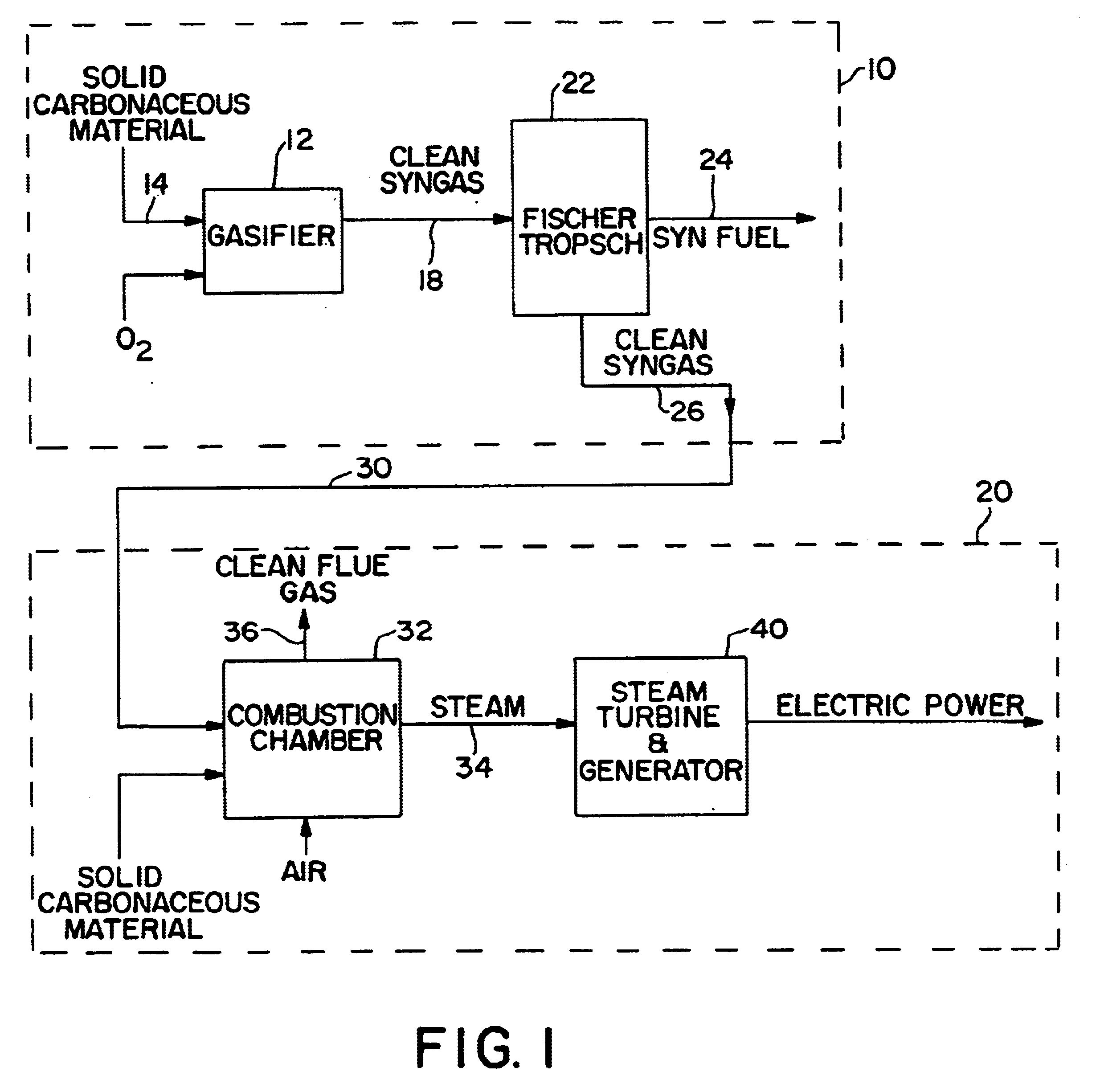
Integrated electric power and synthetic fuel plant
InactiveUS6711903B1Maintain and undesirable componentLiquid degasificationSteam regenerationElectricitySyngas
A power plant generates electricity from carbonaceous material and fuel provided by a syngas plant such that clean electric power is generated and flue gas emissions are minimized. The syngas plant produces liquid fuel and unreacted syngas in a Fischer-Tropsch reactor, and the unreacted syngas is conducted to a combustion chamber of the power plant for use as a clean fuel moiety of the carbonaceous material burned in the combustion chamber. The unreacted syngas enables the electric power plant to operate below acceptable environmental limits in producing steam to generate electricity.
Owner:RICH JR JOHN W
Chemical change agent
InactiveUS7862630B2Easy to identifyHigh strengthNitrogen compoundsSolid fuel pretreatmentCombustionCoal
The present invention relates to an improved chemical change reagent which is used as an additive to coal to enhance the complete combustion of the coal after turning it into a synthetic fuel. The composition is a chemical change agent in that it converts the coal / composition mix into a different material which, when burned, results in lower NOx emissions. The composition includes a wax, a base for ph adjustment and water and is mixed with the coal prior to combustion.
Owner:STATE LINE HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com