Catheter with common guide wire and indicator lumen
a catheter and guide wire technology, applied in the field of blood flow measurement, can solve problems such as reducing the accuracy of measurement, and achieve the effects of convenient operation, improved blood flow measurement accuracy in thermodilution measurement, and reduced measurement accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
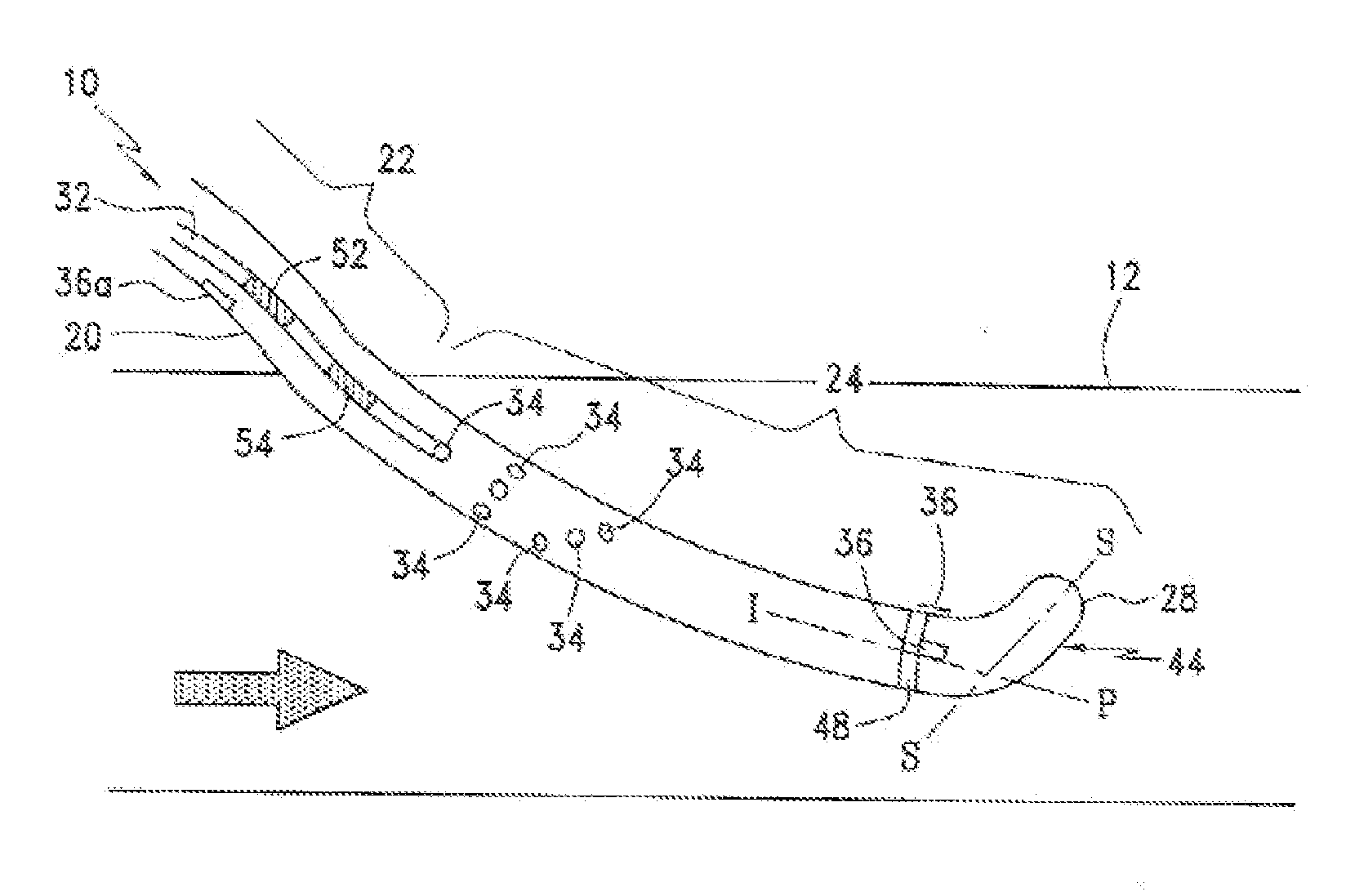
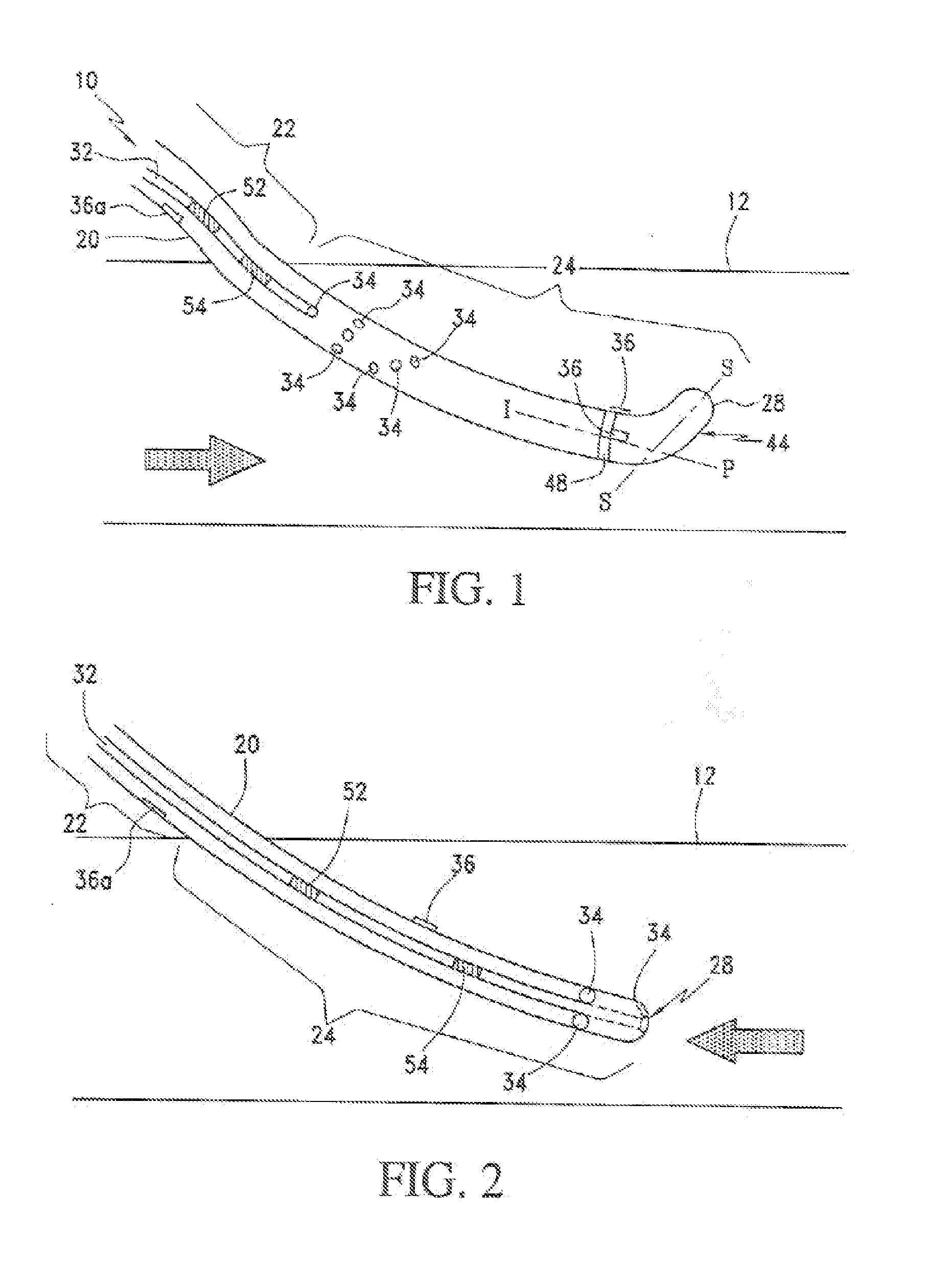
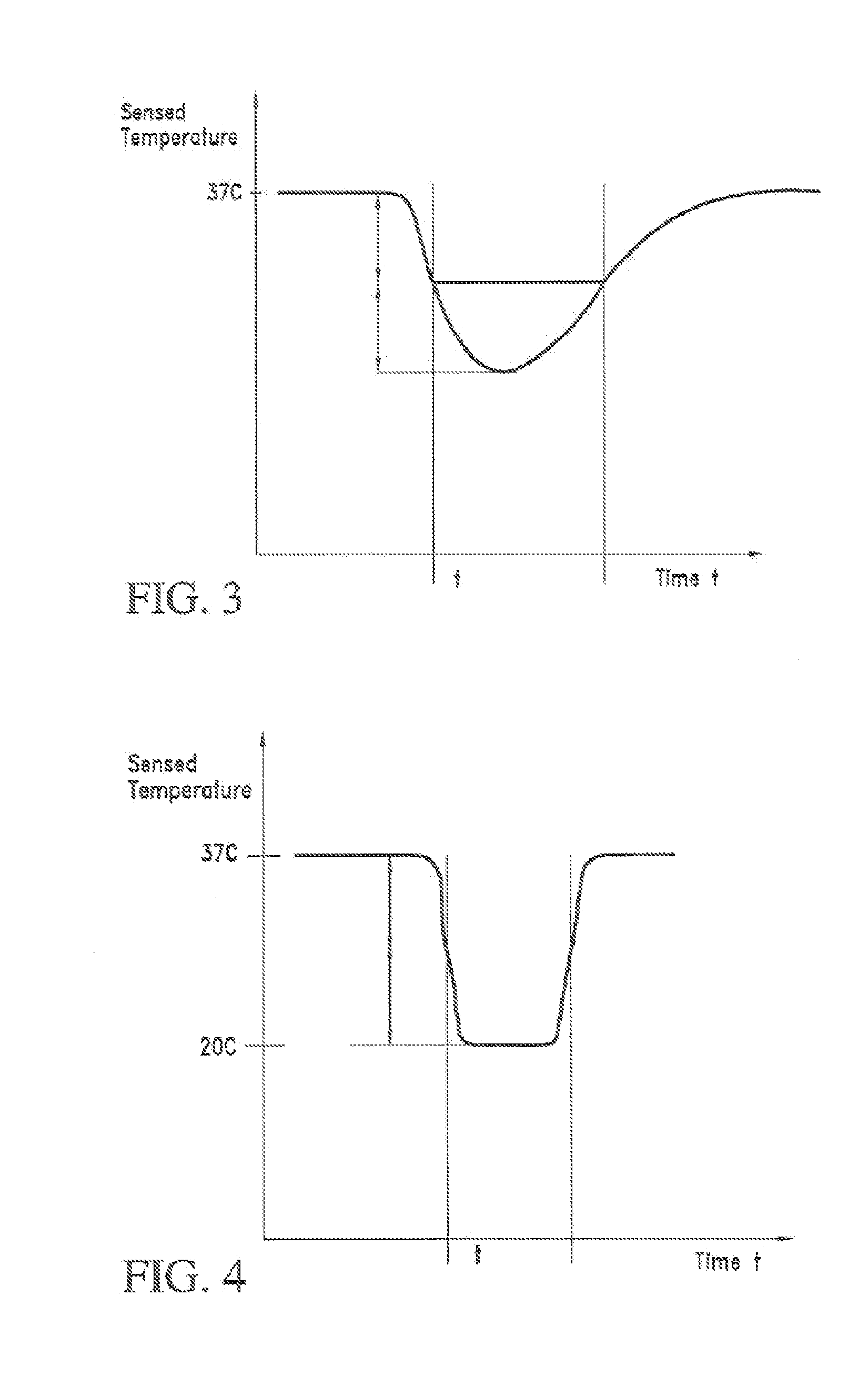
[0040]Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, the present indicator dilution catheter 10 is shown operably located in an arterio-venous (A-V) shunt 12. The A-V shunt 12 has a blood flow shown by the direction of the arrows, the catheter 10 includes an elongate body 20 having an extravascular portion 22 and an intravascular portion 24. The extravascular portion 22 being that portion or length of the body 20 that is not operably located within the A-V shunt 12 to contact the blood flow in the shunt. The intravascular portion 24 is that portion or length of the body 20 that is operably located within the A-V shunt 12 and contacts the blood flow in the shunt. The body 20 includes a proximal end, a distal end 28, an indicator (injectate) lumen 32, an injection port(s) 34 and a dilution sensor 36 for detecting passage of the injected indicator in the blood flow in the A-V shunt 12. That is, the dilution sensor measures a temperature of the diluted blood flow resulting from introduction of the injecta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com