Method of fabricating electronic cards including at least one printed pattern
a technology of electronic cards and printed patterns, which is applied in the association of printed circuit non-printed electric components, instruments, printing, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to use for making patterns in different colours or that completely cover a certain surface of the card, and the method of writing a text or a pattern is limited, etc., to achieve good support, high definition print, and smoke-free
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
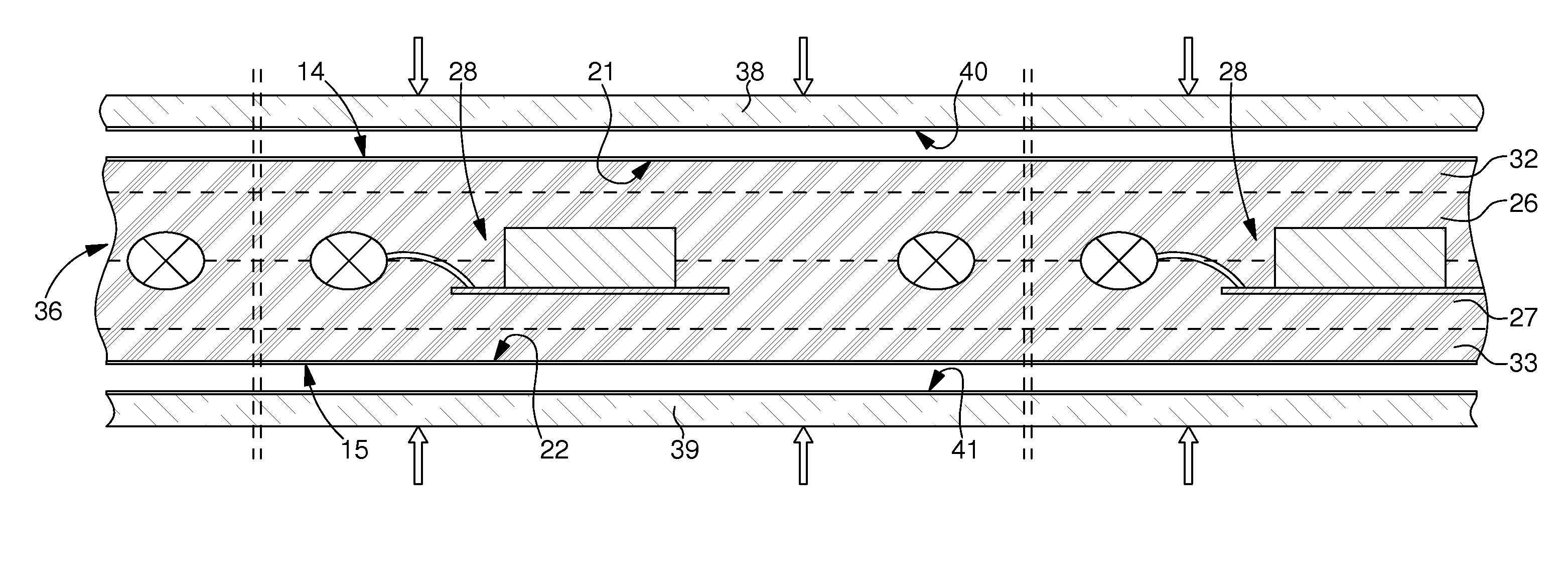
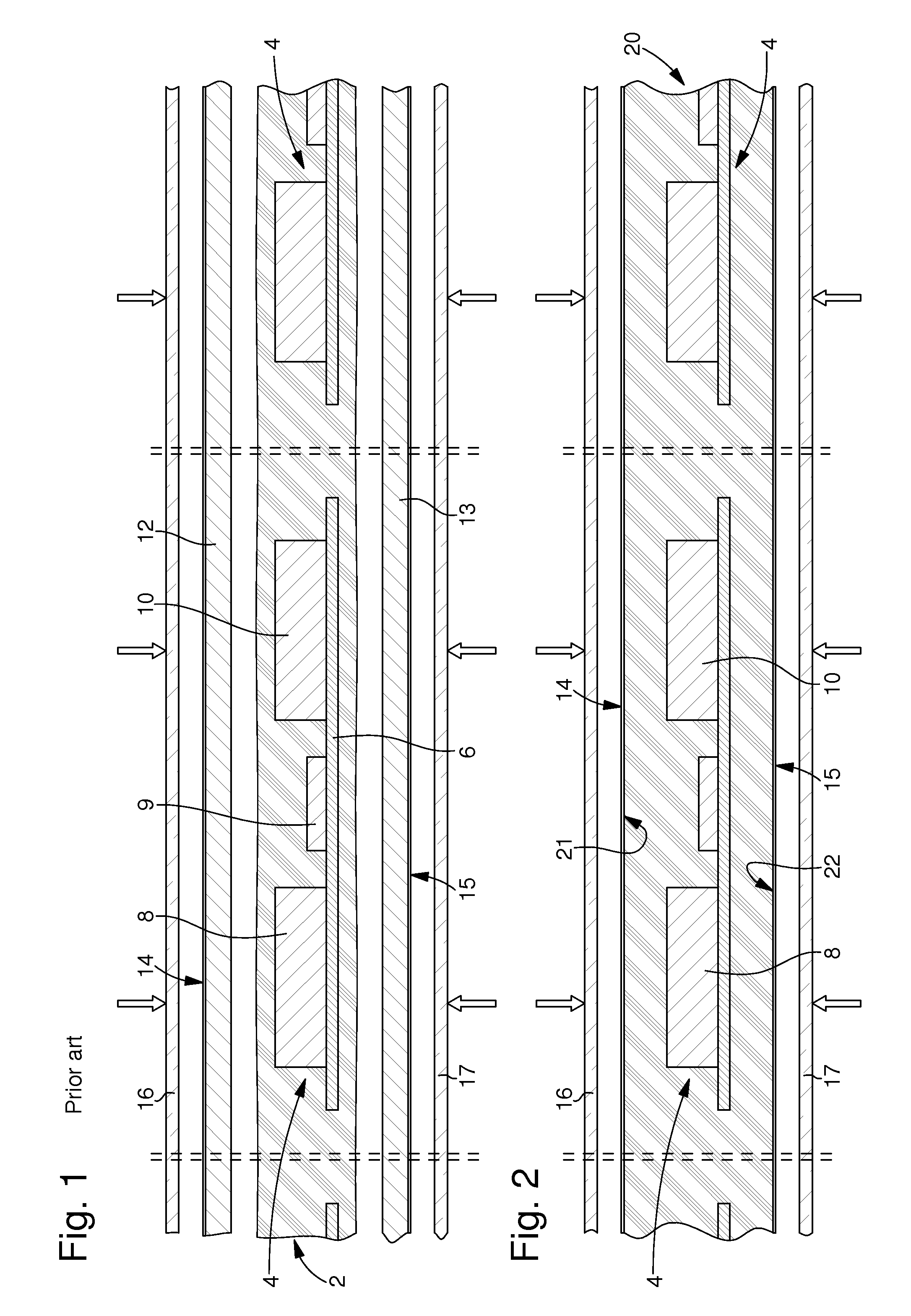
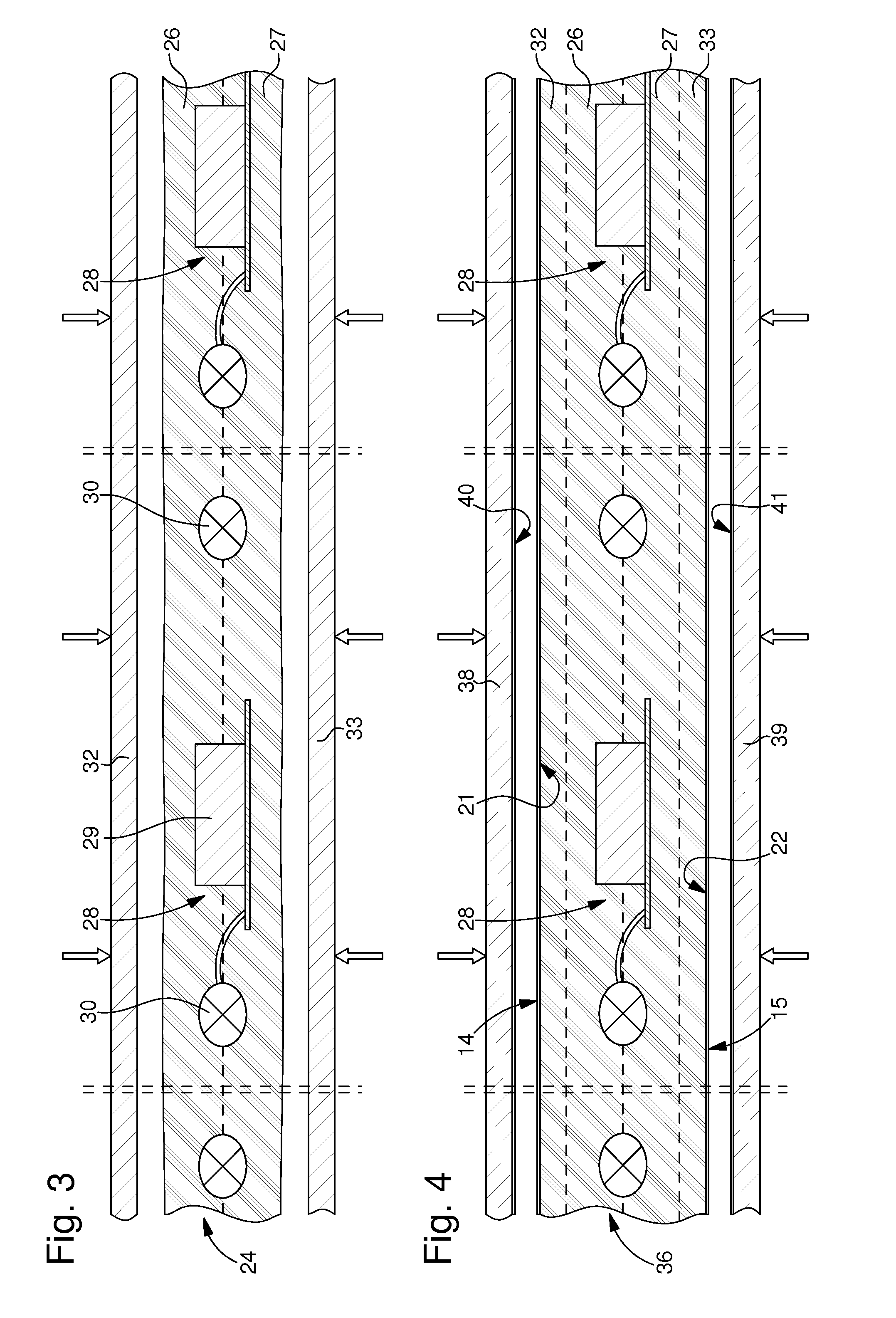
[0071]The first implementation mode of the method according to the invention show in FIG. 2 is characterized in that a thick sheet 20, which incorporates or embeds a plurality of electronic units 4, is first of all formed. This thick sheet 20 defines a plurality of card bodies each including an electronic unit 4.
[0072]The thick sheet 20 can be made by any technique known to those skilled in the art, particularly using several layers laminated or bonded to each other. In a variant, at least one central layer has apertures, which house at least electronic elements 8 and 10. In another variant, electronic unit 4 is incorporated in a press where plastic layers are first of all softened sufficiently and then pressed in a controlled manner so that electronic unit 4 penetrates these layers to form its own housing. Thick sheet 20 can, in another variant, be obtained by pouring or injecting a liquid resin.
[0073]Preferably, flat surfaces 21 and 22 of thick layer 20 are opaque, and in particul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com