Thin-type heat pipe structure
a heat pipe and thin-type technology, applied in the field of thin-type heat pipes, can solve the problems of small space provided by heat pipes and rapid drying of heat receiving areas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
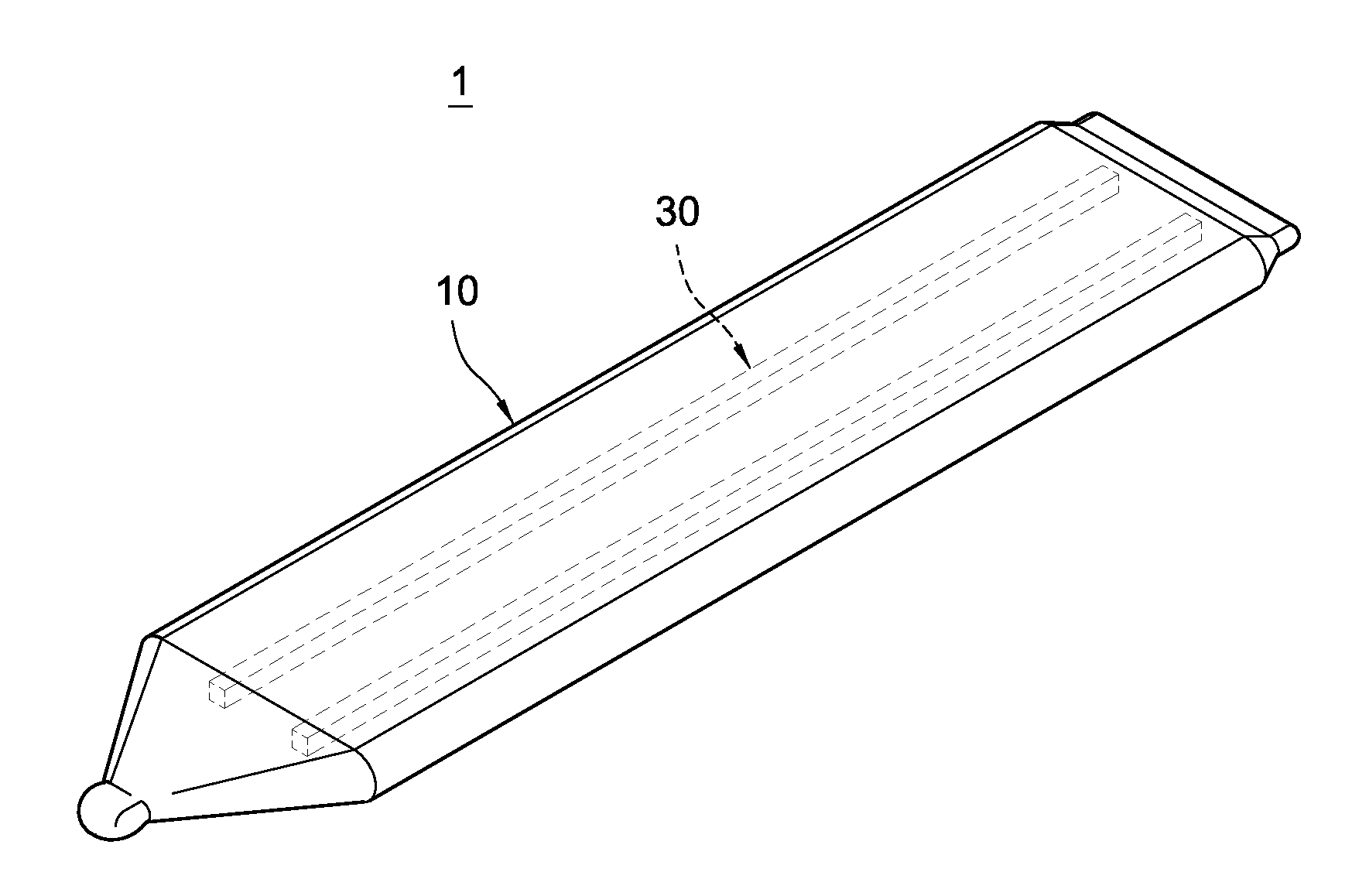
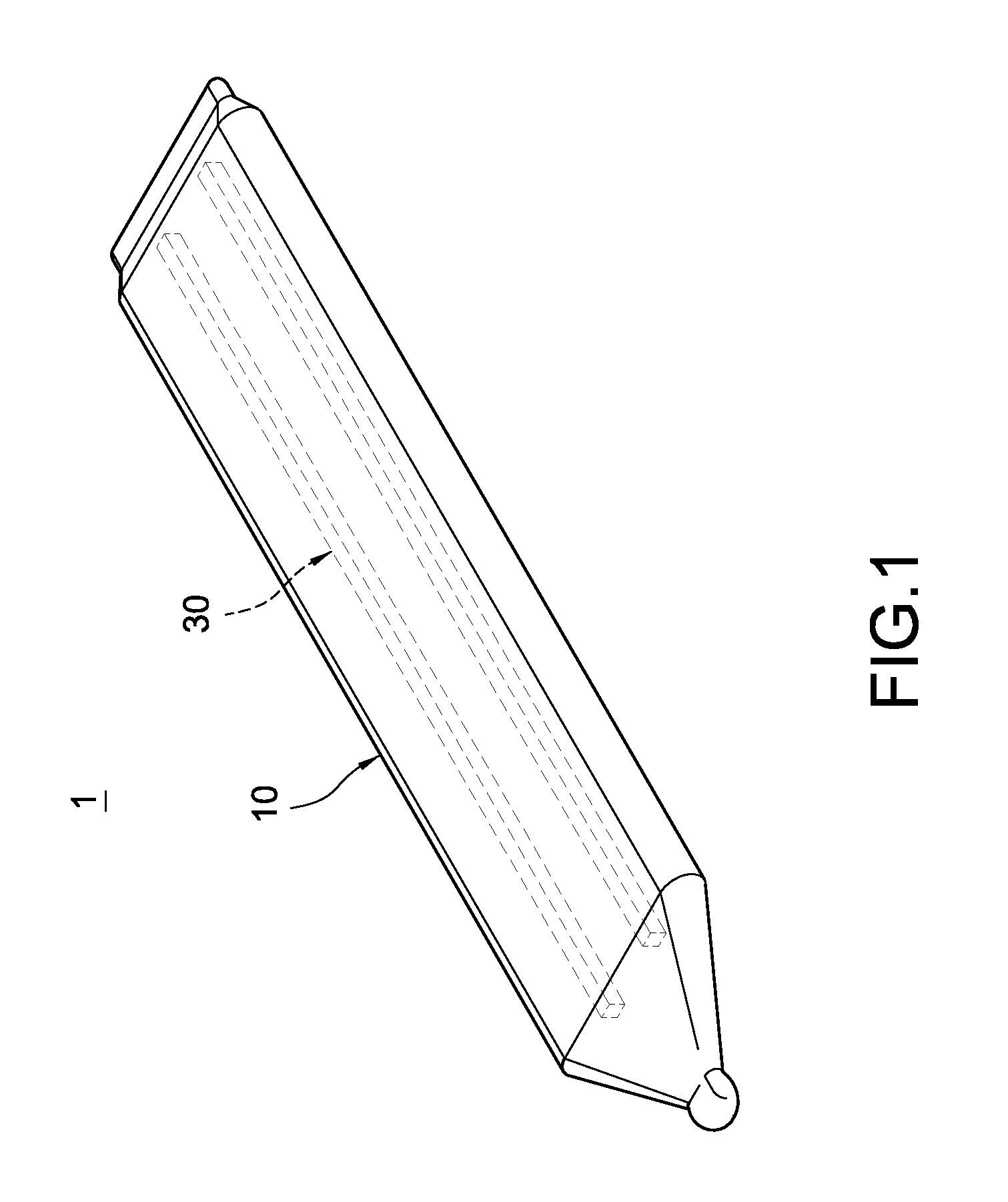
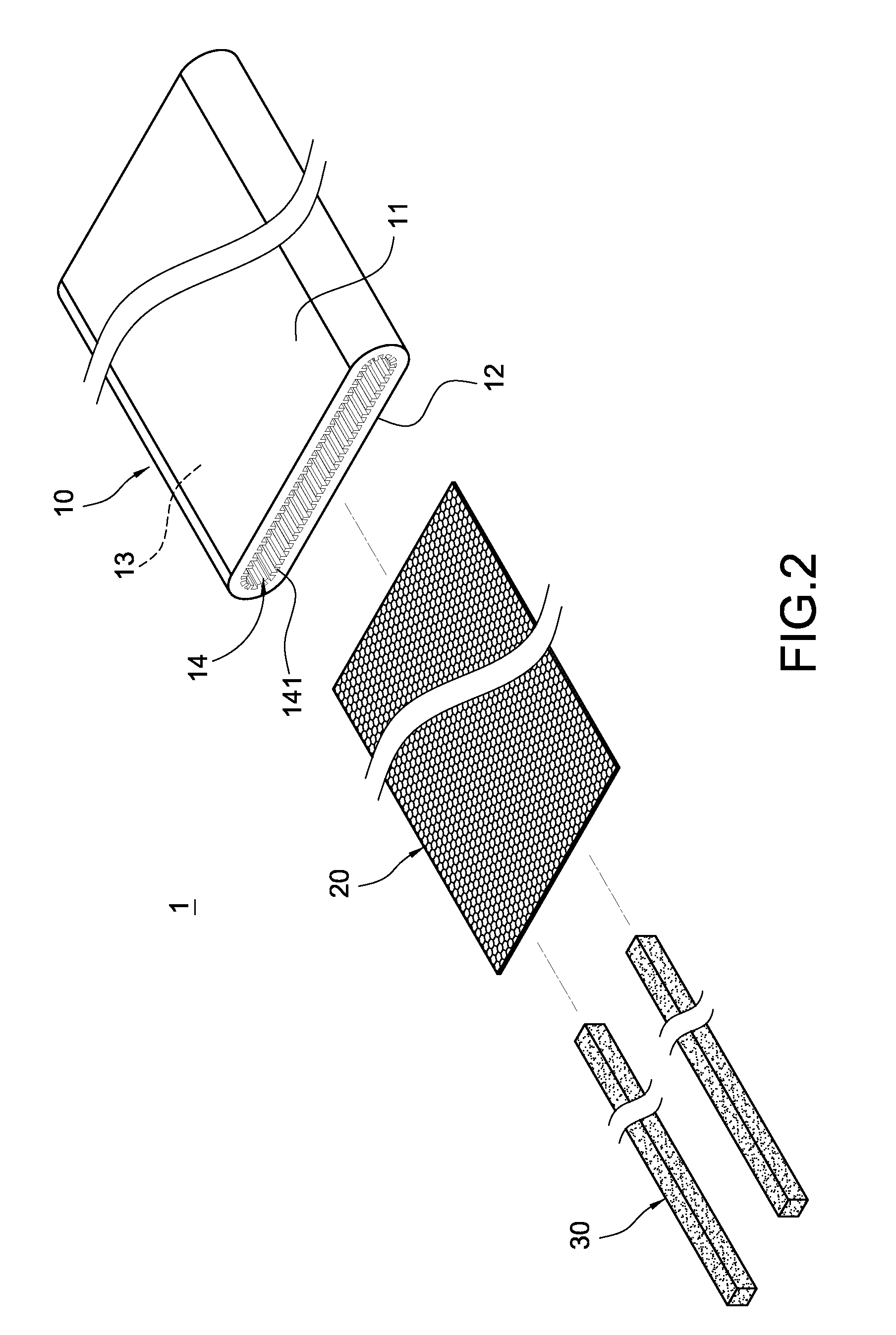
[0016]Please refer to FIG. 1 to FIG. 4. The present invention provides a thin-type heat pipe structure. The thin-type heat pipe 1 mainly includes a flat pipe 10, a second capillary structure 20, a third capillary structure 30, and a working fluid 40.
[0017]The flat pipe 10 is made up of materials with good heat conductivity and good ductility, such as copper or copper alloy. It is formed by pressing a round pipe and hence has a flat shape. In this embodiment, the pipe 10 is a stripe formed by an upper board 11 and a lower board 12 that correspond to each other. Each of the upper and lower boards 11 and 12 is formed by a lateral flat section and a longitudinal curved section that extends from the lateral flat section. As shown in FIG. 2, the lateral flat section and the longitudinal curved section form a shape that is similar to the letter ‘J,’ and are sealed up on an end of the pipe 10 through soldering. A hollow containing chamber 13 exists in between the upper and lower boards 11 a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com